
- Jul. 11, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 313-322.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20202874
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jin-hua XIE1,Le WANG1,*( ),Pan LIU1,Xi-qi SU1,Li-June MING2,3
),Pan LIU1,Xi-qi SU1,Li-June MING2,3
Received:2020-11-19
Online:2021-09-05
Published:2020-12-21
Contact:
Le WANG
E-mail:wangle316@sues.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Jin-hua XIE,Le WANG,Pan LIU,Xi-qi SU,Li-June MING. An NMR Spectroscopy Study on the Exchangeable Protons and Hydrogen Bonds in Tetracycline Hydrochloride[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 313-322.

Fig.2
1H NMR spectra of tetracycline hydrochloride and its derivatives. (a) Metacycline hydrochloride; (b) Oxytetracycline hydrochloride; (c) Tetracycline hydrochloride; (d) Tetracycline hydrochloride (0.02 mmol) in DMSO-d6 after addition of 5.5 mmol D2O; (e) Tetracycline hydrochloride plus one equivalent cobalt ion (CoCl2·6H2O). Some minor signals in Fig. (e) are due to protons hyperfine-coupled with the bound paramagnetic Co2+; The two signals at δH 1.06 and 3.44 in Fig. (a) are ethanol residuals from the manufacturer. S represents the solvent peak, W represents the water peak, and * represents exchangeable hydrogen
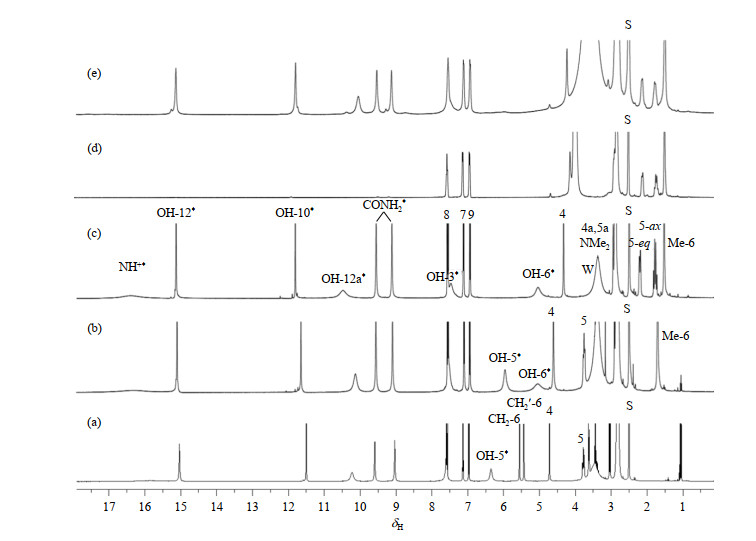
Table 1
NMR signal assignments of tetracycline hydrochloride and its derivatives
| Position | 1A/δH (J/HZ) | 1A/δC | 1B/δH (J/HZ) | 1B/δC | 1C/δH(J/HZ) | 1C/δC |
| 1 | / | 192.7 | / | 193.7 | / | 194.0 |
| 2 | / | 95.4 | / | 96.0 | / | 96.2 |
| 3 | / | 187.8 | / | 187.6 | / | 187.8 |
| 4 | 4.71(s) | 65.8 | 4.58 (s) | 65.4 | 4.34 (s) | 68.7 |
| 4a | 3.02 (d, J=11.4 Hz) | 41.5 | 2.79~2.88 (m) | 42.3 | 2.84~2.90 (m) | 35.5 |
| 5 | 3.76 (dd, J=10.4/9.6 Hz) | 64.5 | 3.72 (dd, J=10.2/9.4 Hz) | 64.9 | 2.21 (dd, J=8.9/3.1 Hz, H-5eq) 1.79 (q, J=13.2 Hz, H-5ax) | 27.5 |
| 5a | 3.60 (d, J=8.9 Hz) | 44.7 | 2.79~2.88 (m) | 50.4 | 2.84~2.90 (m) | 42.2 |
| 6 | / | 141.2 | / | 69.5 | / | 68.5 |
| 6a | / | 143.7 | / | 149.3 | / | 148.5 |
| 7 | 7.12 (d, J=7.2 Hz) | 116.9** | 7.07 (d, J=7.6 Hz) | 115.4** | 7.12 (d, J=7.6 Hz) | 115.7** |
| 8 | 7.57 (dd, J=8.0/8.0 Hz) | 137.6 | 7.52 (dd, J=8.0/8.0 Hz) | 137.0 | 7.56 (dd, J=8.0/8.0 Hz) | 137.1 |
| 9 | 6.95 (d, J=8.4 Hz) | 117.8** | 6.90 (d, J=8.3 Hz) | 117.5** | 6.94 (d, J=8.3 Hz) | 117.5** |
| 10 | / | 161.3 | / | 161.7 | / | 161.9 |
| 10a | / | 114.9 | / | 115.0 | / | 115.0 |
| 11 | / | 194.0 | / | 194.3 | / | 193.5 |
| 11a | / | 105.7 | / | 105.9 | / | 107.4 |
| 12 | / | 174.2 | / | 174.2 | / | 175.6 |
| 12a | / | 74.1 | / | 73.1 | / | 73.7 |
| OH-3 | 7.57* | / | 7.52* | 7.47* | / | |
| OH-10 | 11.48 | / | 11.61 | 11.81 (s) | / | |
| OH-12 | 15.02 | / | 15.06 | 15.13 (s) | / | |
| OH-12a | 10.21* | / | 10.09* | 10.48* | / | |
| CONH2 | 9.57, 9.02 | 172.2 | 9.52, 9.06 | 172.6 | 9.56 (s), 9.12 (s) | 172.6 |
| NH+ | 15.83* | 16.28* | 16.41* | |||
| NMe2 | 2.80 (s) | 42.3 | 2.79~2.88 (m) | 42.7 | 2.84~2.90 (m) | 40.0 |
| R1 | 6.34* | / | 5.92* | / | / | / |
| R2 | 5.54, 5.42 | 114.3 | 1.68 (s) | 25.2 | 1.53 (s) | 23.1 |
| R3 | 5.00* | / | 5.05* | / |
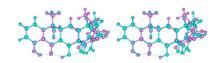
Fig.5
Relaxed-eye stereo view of superimposed tetracycline structures from tetracycline-bound RNA (purple; PDB ID: 1HNW) and elongation factor Tu (cyan; PDB ID: 2HDN). The left and right pictures are for relaxed-eye stereo view[34, 35, 38]. The 2(C)-CONH2 bond in the RNA-bound structure was rotated by 180° to be consistent with that in the Tu-bound structure. The thin green lines are potential H-bonds with proton donors adjusted to proper positions in the H-bond donor/acceptor pairs
| 1 |
FUOCO D . Classification framework and chemical biology of tetracycline-structure-based drugs[J]. Antibiotics, 2012, 1 (1): 1- 3.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics1010001 |
| 2 |
CHOPRA I , ROBERTS M . Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance[J]. Microbiol Mol Biol R, 2001, 65 (2): 232- 260.
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.2.232-260.2001 |
| 3 | PRINGLE M , FELLSTROM C , JOHANSSON K E . Decreased susceptibility to doxycycline associated with a 16S rRNA gene mutation in Brachyspira hyodysenteriae[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2007, 123 (1): 245- 248. |
| 4 |
ONAL A . Overview on liquid chromatographic analysis of tetracycline residues in food matrices[J]. Food Chem, 2011, 127 (1): 197- 203.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.002 |
| 5 |
RAHNAN M S , KOH Y S . Omadacycline, a magic antibiotics for bacterial infections[J]. JBV, 2018, 48 (3): 109- 112.
doi: 10.4167/jbv.2018.48.3.109 |
| 6 |
NELSON M L , LEVY S B . The history of the tetracyclines[J]. Ann Acad Sci, 2011, 1241 (1): 17- 32.
doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06354.x |
| 7 |
CHEN Y , CAI Z , KE Z . Antineuroinflammation of minocycline in stroke[J]. Neurologist, 2017, 22 (4): 120- 126.
doi: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000136 |
| 8 |
CLAUDIA B , GIULIA S , PIETRO L V , et al. Doxycycline counteracts neuroinflammation restoring memory in Alzheimer's disease mouse models[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2018, 70, 128- 139.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.06.002 |
| 9 |
KIM H S , SUH Y H . Minocycline and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2009, 196 (2): 168- 179.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.09.040 |
| 10 |
GARRIDO-MESA N , ZARZUELO A , GALVEZ J . What is behind the non-antibiotic properties of minocycline?[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2013, 67 (1): 18- 30.
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.10.006 |
| 11 | RAVA M , D'ANDREA A , NICOLI P , et al. Therapeutic synergy between tigecycline and venetoclax in a preclinical model of MYC/BCL2 double-hit B cell lymphoma[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2018, 10 (426): 1- 9. |
| 12 |
ZHANG T , NONG J , ALZAHRANI N , et al. Self-assembly of DNA-minocycline complexes by metal ions with controlled drug release[J]. ACS Appl Mater Inter, 2019, 11 (33): 29512- 29521.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b08126 |
| 13 |
PULICHARLA R , HEGDE K , BRAR S K , et al. Tetracyclines metal complexation: Significance and fate of mutual existence in the environment[J]. Environ Pollut, 2017, 221, 1- 14.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.017 |
| 14 |
OU M , ZHANG Z , WEN Y , et al. Cytotoxic study in the treatment of tetracycline by using magnetic Fe3O4-PAMAM-antibody complexes[J]. Environ Chem Lett, 2019, 17 (1): 543- 549.
doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0803-y |
| 15 |
CHEN G , ZHAO L , DONG Y H . Oxidative degradation kinetics and products of chlortetracycline by manganese dioxide[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 193, 128- 138.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.039 |
| 16 |
DAGHRIR R , DROGUI P . Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: a review[J]. Environ Chem Lett, 2013, 11 (3): 209- 227.
doi: 10.1007/s10311-013-0404-8 |
| 17 |
WANG X , RYU D , HOUTKOOPER R H , et al. Antibiotic use and abuse: A threat to mitochondria and chloroplasts with impact on research, health, and environment[J]. Bioessays, 2015, 37 (10): 1045- 1053.
doi: 10.1002/bies.201500071 |
| 18 |
YANG L H , YING G G , SU H C , et al. Growth-inhibiting effects of 12 antibacterial agents and their mixtures on the freshwater microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata[J]. Environ Toxicol Chem, 2008, 27 (5): 1201- 1208.
doi: 10.1897/07-471.1 |
| 19 |
WITTENAU M S V , BLACKWOOD R K . Proton magnetic resonance spectra of tetracyclines[J]. J Org Chem, 1966, 31 (2): 613- 615.
doi: 10.1021/jo01340a519 |
| 20 |
ASELSON G L , STOEL L J , NEWMAN E C , et al. NMR spectra of tetracyclines: Assignment of additional protons[J]. J Pharm Sci-us, 1974, 63 (7): 1144- 1146.
doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630727 |
| 21 |
CASY A F , YASIN A . The identification and stereochemical study of tetracycline antibiotics by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. J Pharmaceut Biomed, 1983, 1 (3): 281- 292.
doi: 10.1016/0731-7085(83)80040-5 |
| 22 |
CASY A F , YASIN A . Stereochemical studies of tetracycline antibiotics and their common impurities by 400 MHz 1H NMR spectroscopy[J]. Magn Reson Chem, 1985, 23 (9): 767- 770.
doi: 10.1002/mrc.1260230917 |
| 23 |
BRODERSEN D E , CLEMONS W M , CARTER A P , et al. The structural basis for the action of the antibiotics tetracycline, pactamycin, and hygromycin B on the 30S ribosomal subunit[J]. Cell, 2000, 103 (7): 1143- 1154.
doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00216-6 |
| 24 |
HEFFRON S E , MUI S , AORORA A , et al. Molecular complementarity between tetracycline and the GTPase active site of elongation factor Tu[J]. Acta Crystallogr Section D Biol Crystallogr, 2006, 62 (11): 1392- 1400.
doi: 10.1107/S0907444906035426 |
| 25 |
ASLESON G L , FRANK C W . Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectral analysis of tetracycline hydrochloride and related antibiotics[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1975, 97 (21): 6246- 6248.
doi: 10.1021/ja00854a051 |
| 26 |
MAZZOLA E P , MELIN J A , WAYLAND L G . 13C-NMR spectroscopy of three tetracycline antibiotics: Minocycline hydrochloride, meclocycline, and rolitetracycline[J]. J Pharm Sci, 1980, 69 (2): 229- 230.
doi: 10.1002/jps.2600690236 |
| 27 |
CASY A F , YASIN A . Application of 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to the analysis and structural investigation of tetracycline antibiotics and their common impurities[J]. J Pharmaceut Biomed, 1984, 2 (1): 19- 36.
doi: 10.1016/0731-7085(84)80086-2 |
| 28 |
MOOIBROEK S , WASYLISHEN R E . A carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study of solid tetracyclines[J]. Can J Chem, 1987, 65 (2): 357- 362.
doi: 10.1139/v87-061 |
| 29 |
TAKEUCHI Y , IMAFUKU Y , NISHIKAWA M . Reassignment of the 13C NMR spectrum of minomycin[J]. ARKIVOC, 2003, 2003 (15): 39- 46.
doi: 10.3998/ark.5550190.0004.f06 |
| 30 |
ORTH P , SCHNAPPINGER D , HILLEN W , et al. Structural basis of gene regulation by the tetracycline inducible Tet repressor-operator system[J]. Nat Struct Biol, 2000, 7 (3): 215- 219.
doi: 10.1038/73324 |
| 31 |
STEZOWSHI J J . Chemical-structural properties of tetracycline derivatives. 1. Molecular structure and conformation of the free base derivatives[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1976, 98 (19): 6012- 6018.
doi: 10.1021/ja00435a039 |
| 32 |
STEZOWSHI J J . Chemical-structural properties of tetracycline antibiotics. 4. Ring A tautomerism involving the protonated amide substituent as observed in the crystal structure of alpha-6-deoxyoxytetracycline hydrohalides[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1977, 99 (4): 1122- 1129.
doi: 10.1021/ja00446a025 |
| 33 | CAIRA MINO R , NASSIMBENI LUIGI R , RUSSELL JILL C . The Crystal and molecular structure of tetracycline hexahydrate[J]. Acta Cryst, 1977, B33, 1171- 1176. |
| 34 |
PALENIK G J , BENTLEY J A . Structural studies of tetracyclines. Crystal and molecular structure of tetracycline methyl betaine pentahydrate[[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1978, 100 (9): 2863- 2867.
doi: 10.1021/ja00477a048 |
| 35 |
HUGHES L J , STEZOWSKI J J , HUGHES R E . Chemical-structural properties of tetracycline derivatives. 7. Evidence for the coexistence of the zwitterionic and nonionized forms of the free base in solution[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1979, 101 (26): 7655- 7657.
doi: 10.1021/ja00520a003 |
| 36 | BORDNER J . Structure of β-6-deoxyoxytetracycline hydrochloride[J]. Acta Cryst, 1979, B35, 219- 222. |
| 37 |
KOZIOL A E , DAVIS J , PALENIK R C , et al. Structural studies of two tetracyclines: 4-dedimethylaminotetracycline hydrate and 6-methylene-5-oxytetracycline hydrochloride[J]. J Cryst Spect Rese, 1992, 22 (4): 493- 501.
doi: 10.1007/BF01195412 |
| 38 | MING L J. Biological and biomedical aspects of metal phenolates[M]. PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. American Cancer Society, 2014. |
| 39 |
HERSCHLAG D , PINNEY M M . Hydrogen bonds: Simple after all?[J]. Biochemistry, 2018, 57 (24): 3338- 3352.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00217 |
| 40 | CLELAND W W , FREY P A , GERLT J A . The low barrier hydrogen bond in enzymatic catalysis[J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 44 (40): 25529- 25532. |
| 41 |
MOCK W L , MORSCH L A . Low barrier hydrogen bonds within salicylate mono-anions[J]. Tetrahedron, 2001, 57 (15): 2957- 2964.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)00158-2 |
| 42 | WALTER DURCKHEIMER . Tetracyclines: chemistry, biochemistry, and structure-activity relations[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 1973, 14 (11): 721- 774. |
| [1] | Xing-xing NIU,Zhi-jie BAI,Yi YANG,Yang-wen GAO,Xue-lu WANG,Ye-feng YAO. A Quantitative Study of Photocatalytic Reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by Operando Low-Field NMR Relaxometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 403-413. |
| [2] | Chong-wu WANG,Xi HUANG,Lei SHI,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Cathepsin B Triggered Hyperpolarization 129Xe MRI Probe for Ultra-Sensitive Lung Cancer Cells Detection [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 336-344. |
| [3] | Jia-min WU,Yu-cheng HE,Zheng XU,Yan-he ZHU,Wen-zheng JIANG. A Wide-Band Matching Method for Radio Frequency Coils Used in Soil Moisture Measurement [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 414-423. |
| [4] | Zi-hao WANG,He XU,Tao WANG,Shan-zhong YANG,Yun-sheng DING,Hai-bing WEI. NMR Spectroscopic Studies on (exo, endo) C-2 Monosubstituted Norbornene Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 323-335. |
| [5] | Shu-huai ZHANG,Hui MA,Zhao-hui GUO,Min-jun MA,Yan QIAO,Ying-xiong WANG. Interactions Between n-Butanol/Propionic Acid and Humic Acid Studied by NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 301-312. |
| [6] | Xiao-li CHEN,Tian-qiao YONG,Cheng CHEN,Juan FU,Jia-mei MO,Qiu-cheng SU. Physical and Chemical Properties of Silicone Electrolyte Materials Evaluated by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 291-300. |
| [7] | Xin-yi ZHAO,Dong HAN,Hong-jun LUO,Wen-bin SHEN,Gong-jun YANG. Spectroscopic Studies of Delafloxacin Meglumine [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 268-276. |
| [8] | Xiao-wen CHEN,Bi-ling HUANG,Shao-hua HUANG,Yu-fen ZHAO. An NMR Study on the clpC Operon Binding Region of Transcription Factor CtsR from Bacillus subtilis [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 155-163. |
| [9] | Song SUI,Guo-liang GAO,Xue-lu WANG,Da-xiu WEI,Ye-feng YAO. An Operando Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study on Solid-Liquid-Gas Heterogeneous Benzene Hydrogenation Reaction [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 194-203. |
| [10] | Yi LI,Jia-xiang XIN,Jia-chen WANG,Da-xiu WEI,Ye-feng YAO. Preparation Efficiency of Nuclear Spin Singlet State: A Comparison Among Three Pulse Sequences [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 227-238. |
| [11] | Lei JIANG,Yang FU,Wen-wen GUO,Guo ZHENG,Qiang WANG. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Assignment and Crystal Structure of 3, 22-Dihydroxyhopane [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 255-267. |
| [12] | Jin-bo YU,Cai ZHANG,Ze-ting ZHANG,Guo-hua XU,Cong-gang LI. Interactions Between α-synuclein and Intact Mitochondria Studied by NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 164-172. |
| [13] | Meng-yu DOU,Qi ZHAO,Xiang-lin HOU,Lei LIU,Ming-xing TANG,Ying-xiong WANG. Structural Elucidation and Quantitative Analysis of Hydrogenation Products of Anthracene by NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 239-248. |
| [14] | Wei ZHANG,Yi-ming WU,Wei-ping CUI,Liang XIAO. Correction for the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Porosity in Heavy Oil-bearing Reservoirs [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 204-214. |
| [15] | Xiao-li CHEN,Wei LV,Qiu-cheng SU,Juan FU,Jia-mei MO,Qi-ying LIU. Conversion of Lignocellulose Studied by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(2): 277-290. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||