数学物理学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 783-803.
大规模三模网络自回归模型
- 吉林大学数学学院 长春 130012
-
收稿日期:2023-04-28修回日期:2023-11-10出版日期:2024-06-26发布日期:2024-05-17 -
通讯作者:*朱复康,Email:zfk8010@163.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12271206);吉林省教育厅科学研究项目(JJKH20231122KJ)
Autoregressive Model for Large-scale Three-mode Networks
- School of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun 130012
-
Received:2023-04-28Revised:2023-11-10Online:2024-06-26Published:2024-05-17 -
Supported by:NSFC(12271206);Science and Technology Research Planning Project of Jilin Provincial Department of Education(JJKH20231122KJ)
摘要:
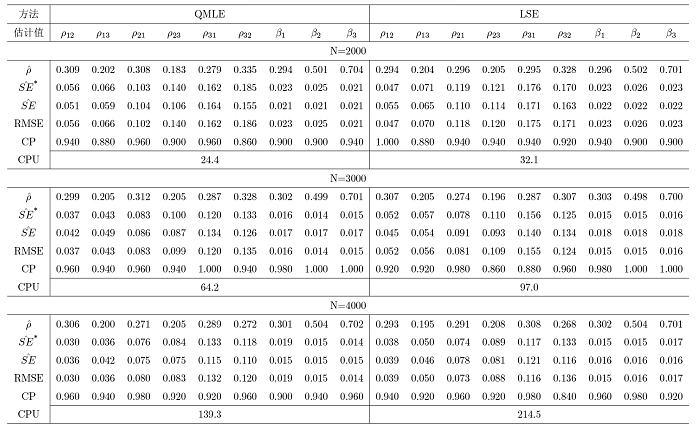
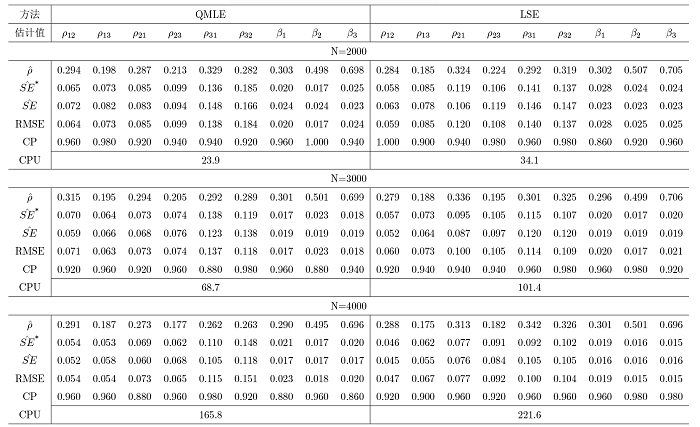
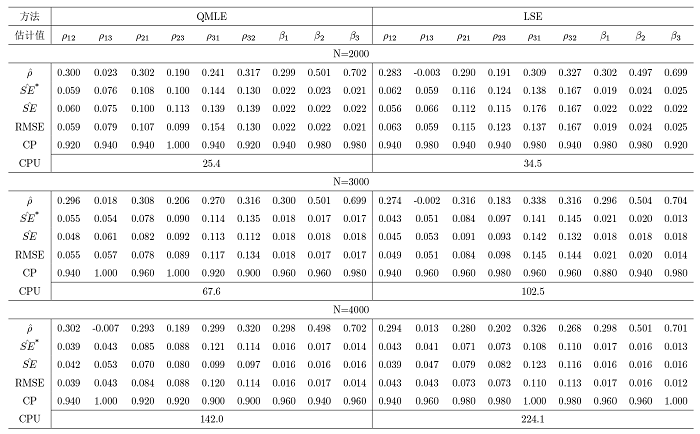
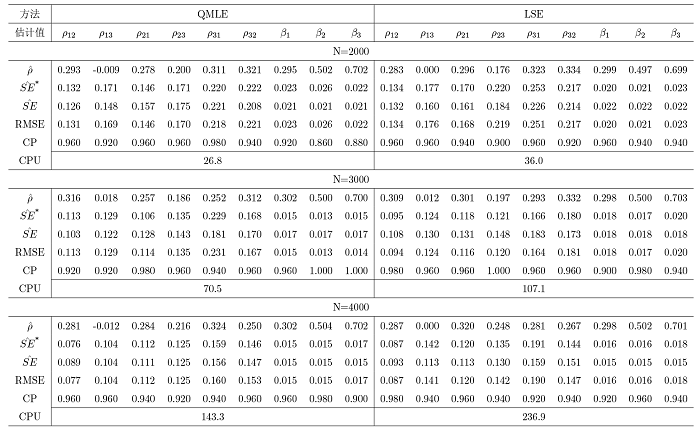
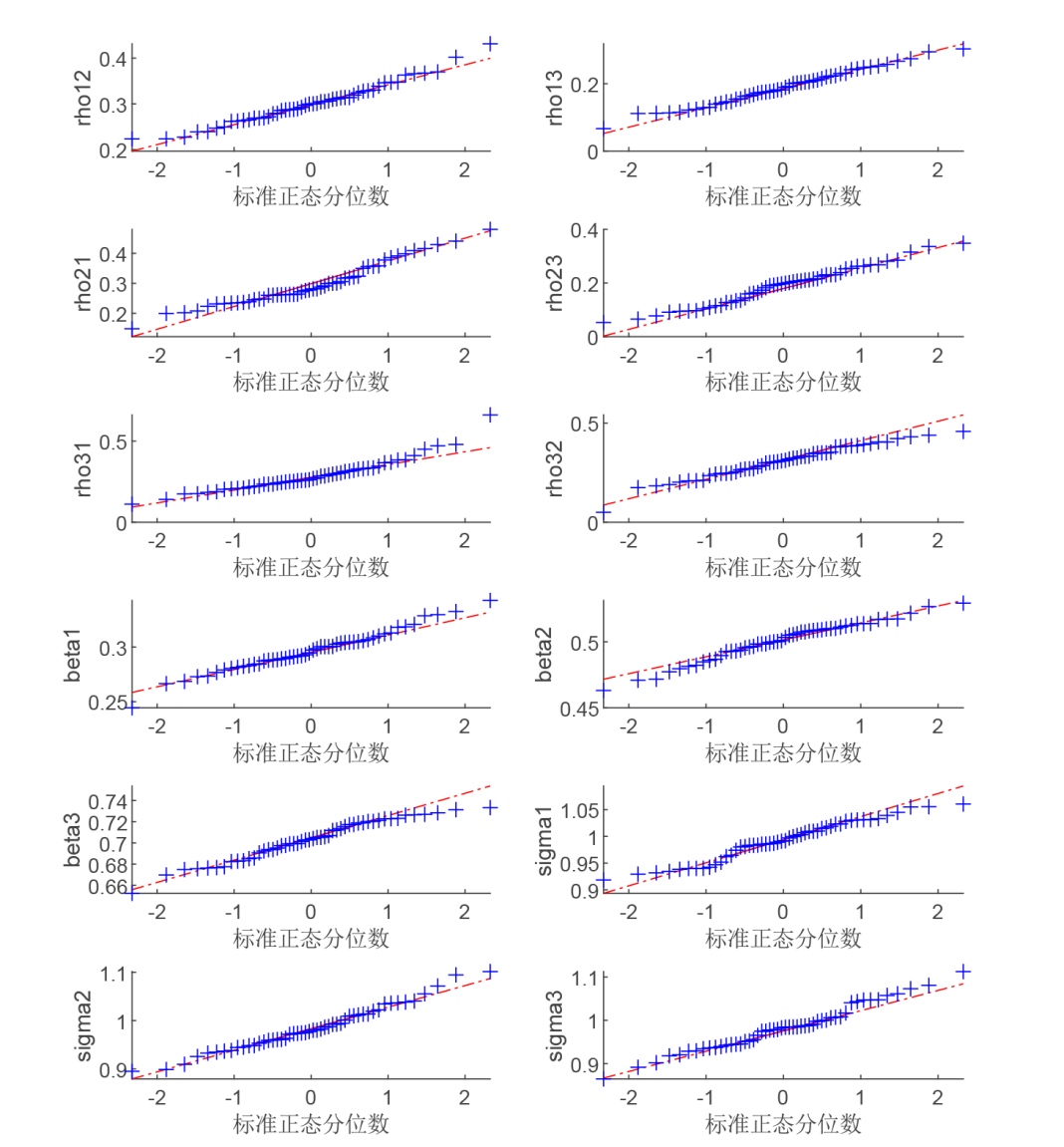
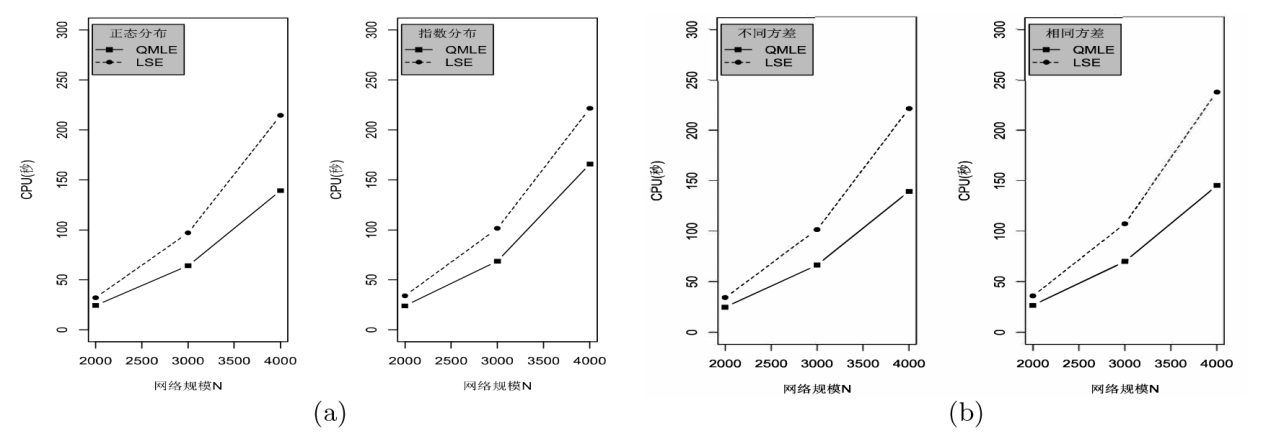
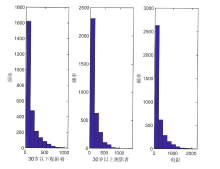
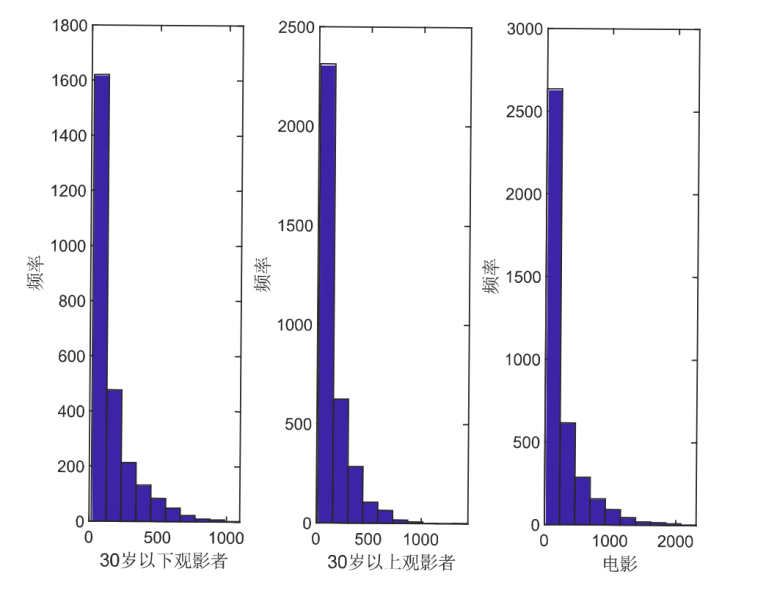
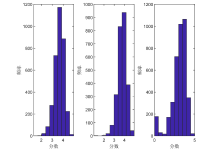
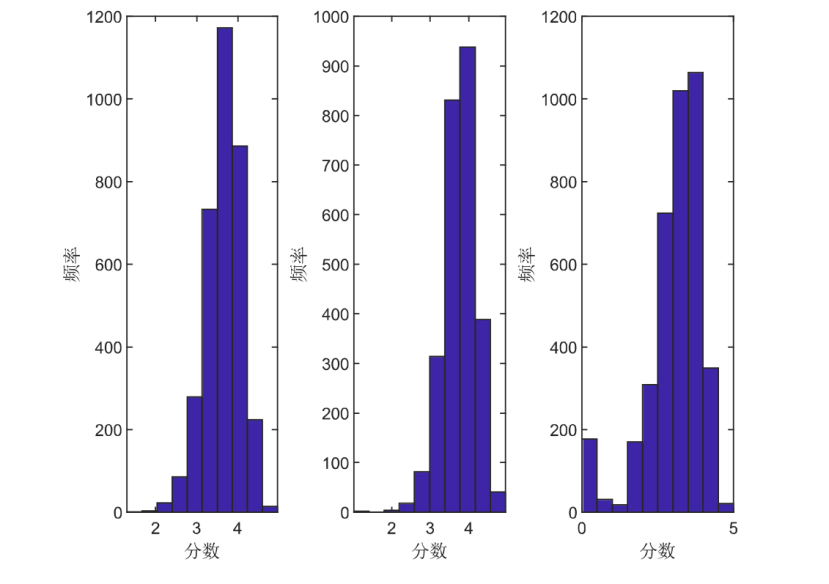
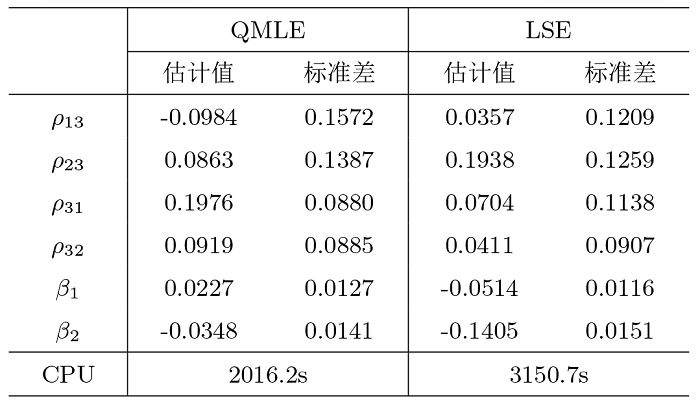
在双模网络自回归 (NAR) 模型的基础上给出了三模 NAR 模型. 该模型考虑了大规模社交网络中三种类型的节点, 且边只允许出现在不同类型的节点之间. 首先介绍了模型的定义以及模型的可逆性与参数可识别性, 考虑了拟极大似然和条件最小二乘估计方法及相应估计量的大样本性质. 其次, 在多种设定下进行了数值模拟, 对估计方法的准确性与计算效率进行了对比, 最后分析了一个实际例子.
中图分类号:
- O212
引用本文
卫奕冰, 朱复康. 大规模三模网络自回归模型[J]. 数学物理学报, 2024, 44(3): 783-803.
Wei Yibing, Zhu Fukang. Autoregressive Model for Large-scale Three-mode Networks[J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2024, 44(3): 783-803.
使用本文
| [1] | Anselin L. Spatial Econometrics:Methods and Models. New York: Springer, 1988 |
| [2] | Borgatti S P, Everett M G. Network analysis of 2-mode data. Social Networks, 1997, 19: 243-269 |
| [3] | Cai Q, Liu J M. Hierarchical clustering of bipartite networks based on multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7: 421-434 |
| [4] | Chen E, Fan J, Zhu X. Community network auto-regression for high-dimensional time serie. Journal of Econometrics, 2023, 235: 1239-1256 |
| [5] | Chen X, Chen Y, Xiao P. The impact of sampling and network topology on the estimation of social intercorrelations. Journal of Marketing Research, 2013, 50: 95-110 |
| [6] | Cohen-Cole E, Liu X, Zenou Y. Multivariate choices and identification of social interactions. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 2018, 33: 165-178 |
| [7] | D'Esposito M R, De Stefano D, Ragozini G. On the use of multiple correspondence analysis to visually explore affiliation networks. Social Networks, 2014, 38: 28-40 |
| [8] | Everett M G, Borgatti S P. The dual-projection approach for two-mode networks. Social Networks, 2013, 35: 204-210 |
| [9] |
Feng L, Zhou C, Zhao Q. A spectral method to find communities in bipartite networks. Physica A, 2019, 513: 424-437
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.022 |
| [10] | Gao M, Chen L. A projection based algorithm for link prediction in bipartite network. International Conference on Information System and Artifical Intelligence, 2016: 56-61 |
| [11] | Huang D. Least squares estimation of spatial autoregressive models for large-scale social networks. Electronic Journal of Statistics, 2019, 13: 1135-1165 |
| [12] | Huang D, Wang F, Zhu X, Wang H. Two-mode network autoregressive model for large-scale networks. Journal of Econometrics, 2020, 216: 203-219 |
| [13] |
Kelejian H H, Prucha I R. Specification and estimation of spatial autoregressive models with autoregressive and heteroskedastic disturbances. Journal of Econometrics, 2010, 157: 53-67
pmid: 20577573 |
| [14] | Lee L. Asymptotic distributions of quasi-maximum likelihood estimators for spatial autoregressive models. Econometrica, 2004, 72: 1899-1925 |
| [15] | LeSage J P, Pace R K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics. Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2009 |
| [16] | Li X, Chen H. Recommendation as link prediction in bipartite graphs: A graph kernel-based machine learning approach. Decision Support Systems, 2013, 54: 880-890 |
| [17] | Liu X. Identification and efficient estimation of simultaneous equations network models. Journal of Business & Econometrics Statistics, 2014, 32: 516-536 |
| [18] | Malikov E, Sun Y. Semiparametric estimation and testing of smooth coefficient spatial autoregressive models. Journal of Econometrics, 2017, 199: 12-34 |
| [19] | Ord K. Estimation methods for models of spatial interaction. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1975, 70: 120-126 |
| [20] | Ouyang F. Using three social network analysis approaches to understand computer-supported collaborative learning. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 2021, 59: 1401-1424 |
| [21] | Seber G A. A Matrix Handbook for Statisticians. New York: Wiley, 2008 |
| [22] | Shumway R, Stoffer D. Time Series Analysis and Its Applications. New York: Springer, 2017 |
| [23] | White H. Estimation, Inference and Specification Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996 |
| [24] | Yang K, Lee L F. Identification and QML estimation of multivariate and simultaneous equations spatial autoregressive models. Journal of Econometrics, 2017, 196: 196-214 |
| [25] | Zhu X, Pan R. Grouped network vector autoregression. Statistica Sinica, 2020, 30: 1437-1462. |
| [26] | Zhu X, Pan R, Li G, et al. Network vector autoregression. Annals of Satistics, 2017, 45: 1096-1123 |
| [1] | 刘晓, 叶阳帅, 徐林. 随机时间区间通过分红和再保险最大化保险公司价值[J]. 数学物理学报, 2023, 43(6): 1843-1854. |
| [2] | 李永明,庞伟才,李乃医. 基于LENQD序列生成的线性过程误差回归函数小波估计Berry-Esseen界[J]. 数学物理学报, 2023, 43(5): 1519-1528. |
| [3] | 雷轶菊,欧祖军. U-型设计的对称化L2-偏差的下界[J]. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42(6): 1802-1811. |
| [4] | 王超,李波,王磊. 状态空间模型的正规核方法[J]. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42(3): 881-890. |
| [5] | 尹长明,石岳鑫. 纵向数据下自适应设计广义估计方程的大样本性质[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(6): 1925-1936. |
| [6] | 郑金辉,余旌胡,丁义明,鲍泽宇. 回归模型参数的变点检测方法研究[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(4): 1124-1134. |
| [7] | 吕洋,丁义明,谭秋衡. 基于非平稳性度量的数字印章信息匹配[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(3): 892-901. |
| [8] | 雷轶菊,欧祖军,赵国喜. 混水平列扩充设计的混偏差的下界[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(3): 882-891. |
| [9] | 刘晓,姚鹏,陈振龙. 扩散风险模型中随机时间区间最优分红和再保险问题[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(2): 538-547. |
| [10] | 叶仁道,王仲池,罗堃,林雅. 多个偏正态总体共同位置参数的Bootstrap置信区间[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(1): 194-216. |
| [11] | 杨柳,邓醉茶. 退化抛物型方程的一个初值反演问题[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(4): 891-903. |
| [12] | 王志刚,丁义明. 信噪比在AR模型定阶方法选择中的研究[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(3): 811-823. |
| [13] | 邓迎春,李满,黄娅,周杰明. 非时齐复合Poisson风险模型的破产特征量分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(2): 501-514. |
| [14] | 傅可昂,丁丽,李君巧. 重尾非线性自回归模型自加权M-估计的渐近分布[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(2): 475-483. |
| [15] | 马奕佳,薛留根,芦飞. 缺失数据下部分非线性变系数EV模型的统计推断[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(2): 460-474. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 89
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 63
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|