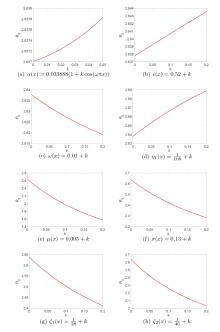
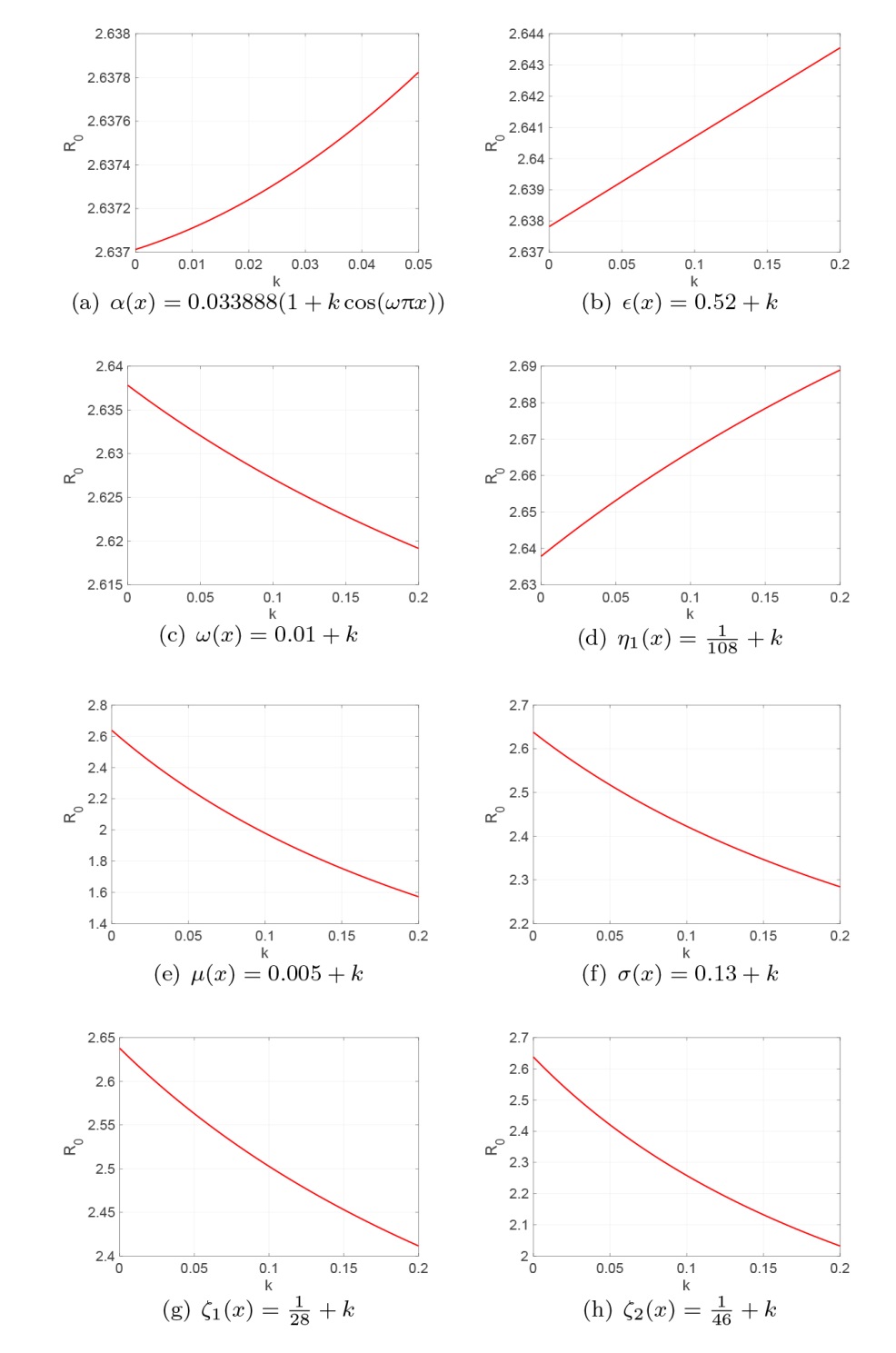
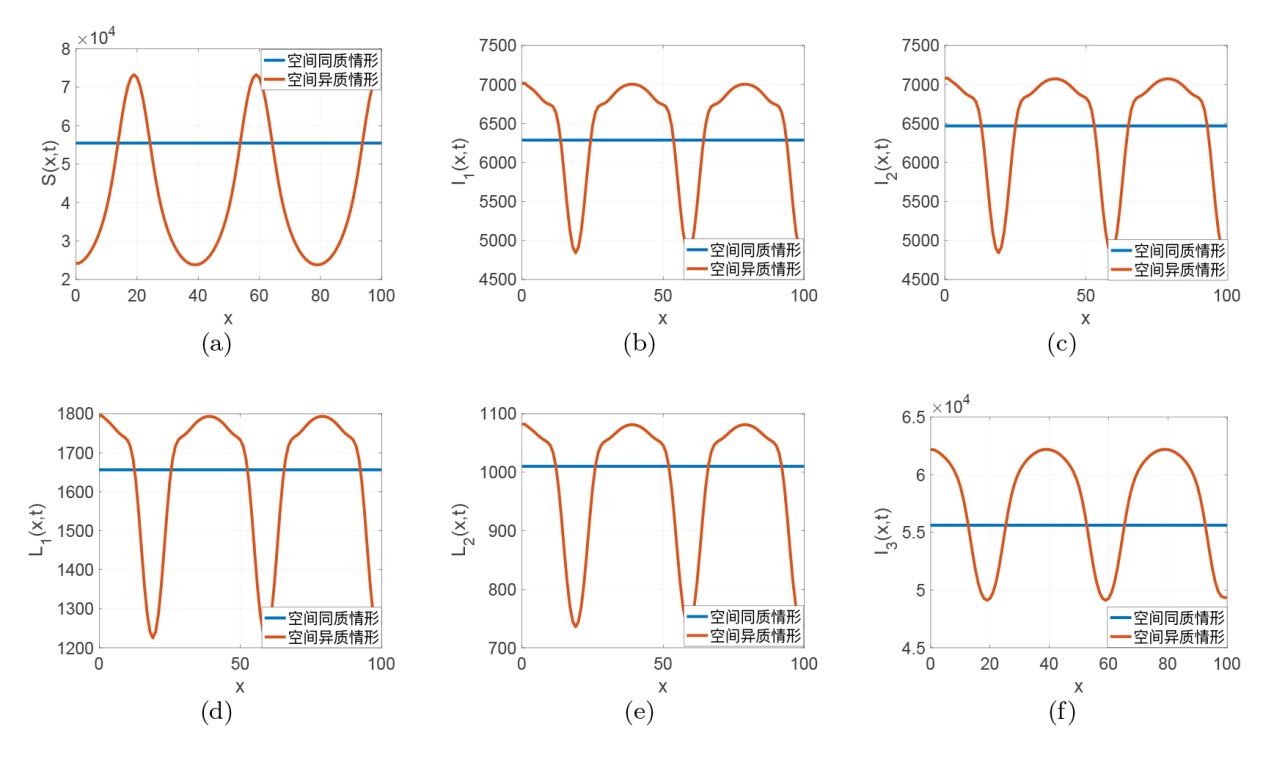
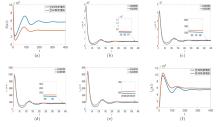
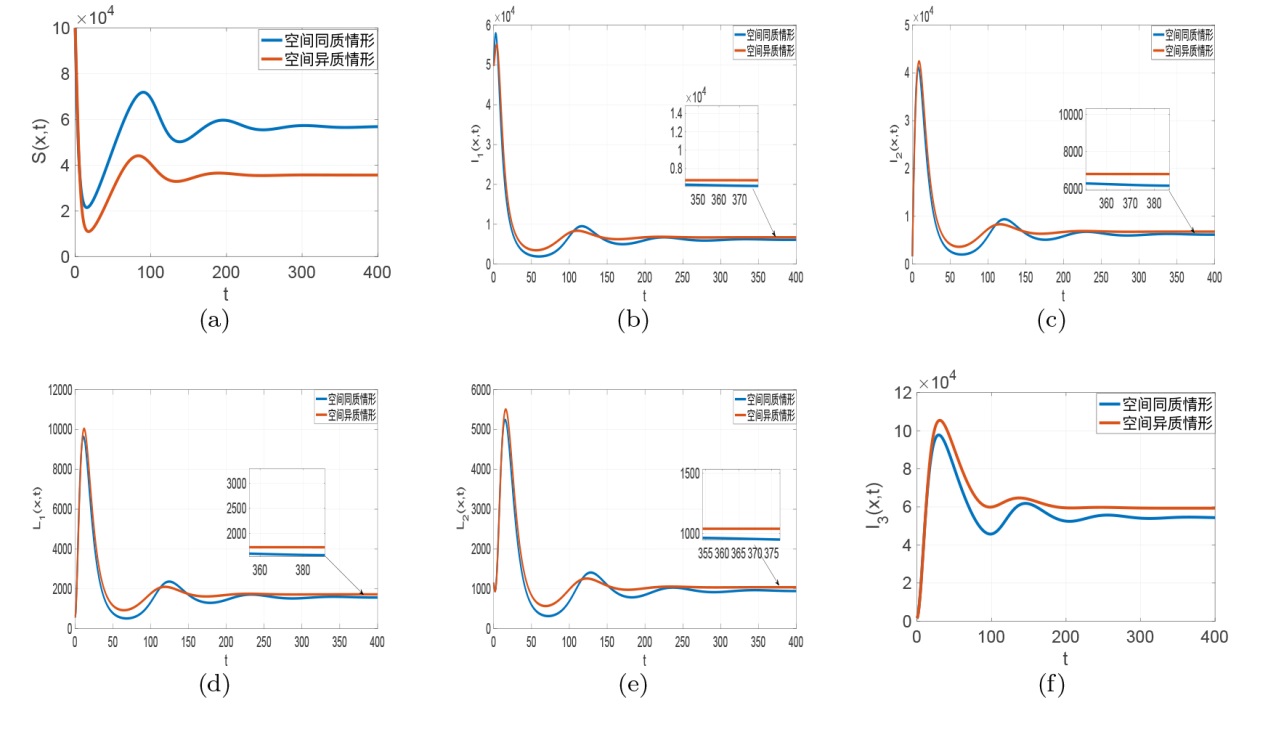
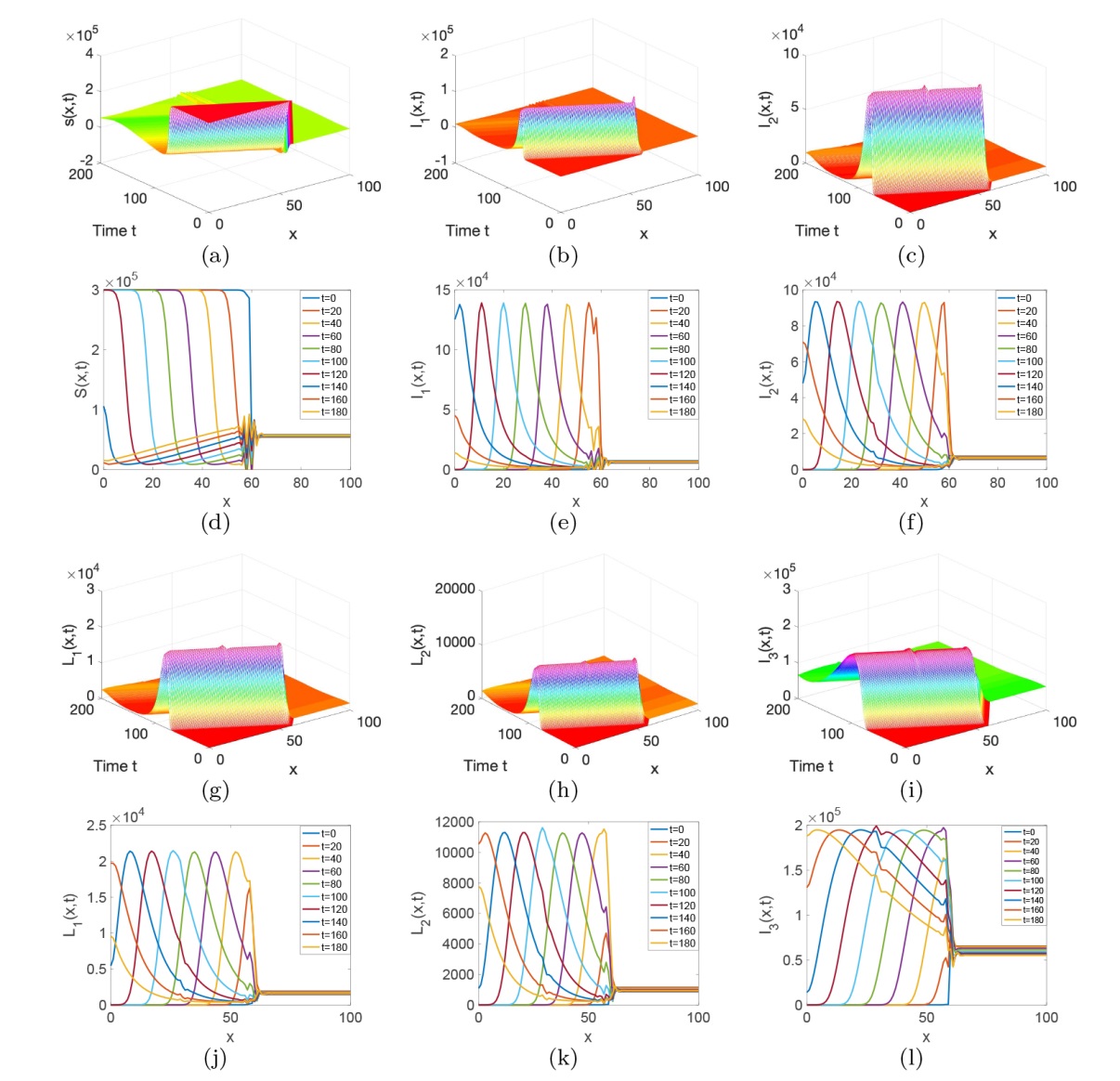
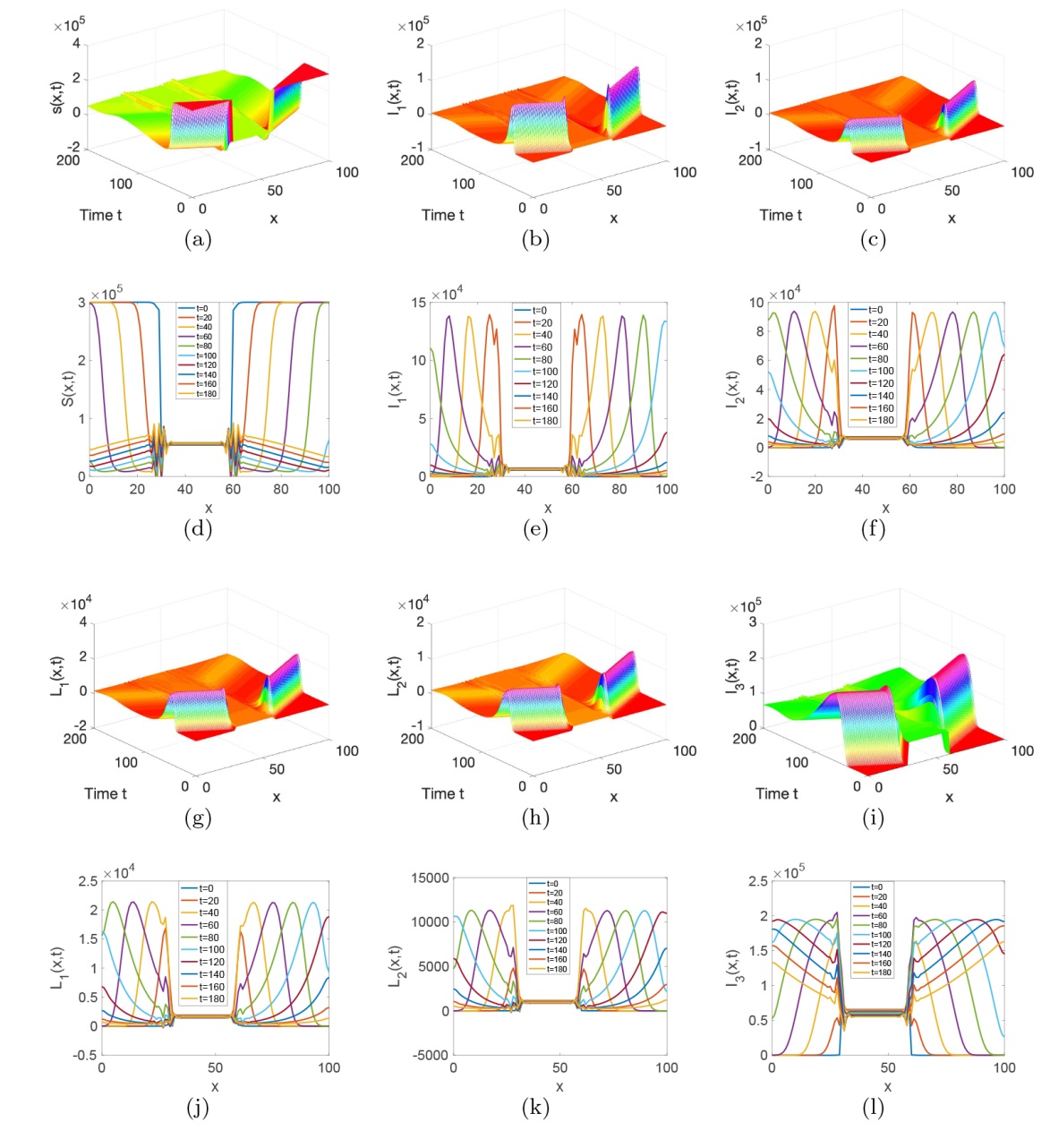
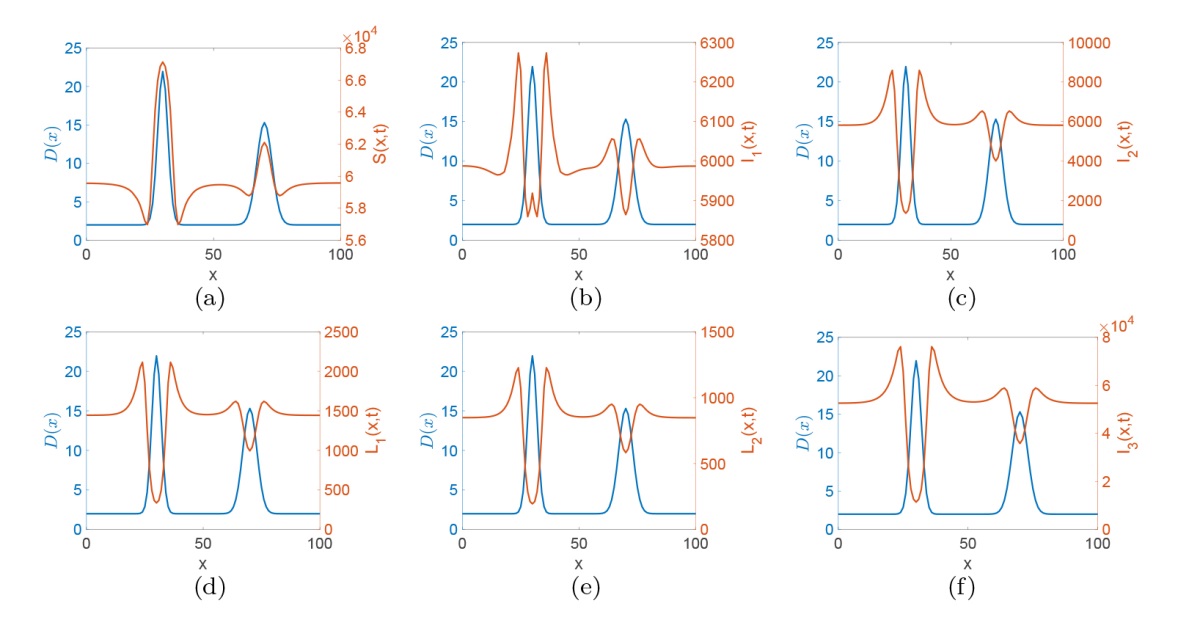
| [1] |
Sparling T F. Natural history of syphilis// Helmes KK, et al. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, New York: McGrans-Hill Book co. 1981: 298-299
|
| [2] |
Mathew A B, Michael M, et al. Global phylogeny of Treponema pallidum lineages reveals recent expansion and spread of contemporary syphilis. Nature Microbiology, 2021, 6(12): 1549-1560
doi: 10.1038/s41564-021-01000-z
pmid: 34819643
|
| [3] |
National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Infectious agents surveillance report, 2020, https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/iasr-e.html [2023-6-11]
|
| [4] |
Garnett G P, Aral S O, Hoyle D V, et al. The natural history of syphilis: Implications for the transmission dynamics and control of infection. Sexually Transmitted Dis, 1997, 24(4): 185-200
|
| [5] |
Fenton K A, Breban R, Vardavas R, et al. Infectious syphilis in high-income settings in the 21st century. Lancet Infect Dis, 2008, 8(4): 244-253
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70065-3
pmid: 18353265
|
| [6] |
Grassly C, Fraser C, Garnett G P. Host immunity and synchronized epidemics of syphilis across the United States. Nature, 2005, 433(7024): 417-421
|
| [7] |
Iboi E, Okuonghaea D. Population dynamics of a mathematical model for syphilis. Appl Math Model, 2016, 40: 3573-3590
|
| [8] |
Saad-Roy C M, Shuai Z, van den Driessche P. A mathematical model of syphilis transmission in an MSM population. Math Biosci, 2016, 277: 59-70
doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2016.03.017
pmid: 27071977
|
| [9] |
Gumel A B, Lubuma J M-S, Sharomi O, Terefe Y A. Mathematics of a sex-structured model for syphilis transmission dynamics. Math Meth Appl Sci, 2017, 23: 26-47
|
| [10] |
Nwankwo A, Okuonghae D. Mathematical analysis of the transmission dynamics of HIV syphilis co-infection in the presence of treatment for syphilis. Bull Math Biol, 2018, 80: 437-492
|
| [11] |
Omame A, Okuonghae D, Nwafor U E, et al. A co-infection model for HPV and syphilis with optimal control and cost-effectiveness analysis. Int J Biomath, 2021, 14: 2150050
|
| [12] |
吴鹏, 赵洪涌. 基于空间异质反应扩散 HIV 感染模型的最优治疗策略. 应用数学学报, 2022, 45(5): 752-766
|
|
Wu P, Zhao H. Optimal treatment strategies for a reaction-dffusion HIV infection model with spatial heterogeneity. Acta Math Appl Sinica, 2022, 45(5): 752-766
|
| [13] |
Wang X, Wang H, Michael Y L. Modeling rabies transmission in spatially heterogeneous environments via θ-diffusion. Bull Math Biol, 2021, 83: Article 16
|
| [14] |
Gao Y, Wang J. Threshold dynamics of a delayed nonlocal reaction-diffusion HIV infection model with both cell-free and cell-to-cell transmissions. J Math Anal Appl, 2020, 488: 1-21
|
| [15] |
Smith H L. Monotone Dynamical Systems: An Introduction to the Theory of Competitive and Cooperative Systems. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, 1995
|
| [16] |
叶其孝, 李元正, 王明新, 吴雅萍. 反应扩散方程引论. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016
|
|
Ye Q X, Li Z Y, Wang M X, Wu Y P. Introduction to Reaction Diffusion Equations. Beijing: Science Press, 2016
|
| [17] |
Martin R H, Smith H L. Abstract functional differential equations and reaction-diffusion systems. Trans Am Math Soc, 1990, 321: 1-44
|
| [18] |
Wu J. Theory and Applications of Partial Functional-Differential Equations. Vol 119. New York: Springer, 1996
|
| [19] |
Hale J. Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems. Province, RI: American Mathematical Society, 1988
|
| [20] |
Pazy A. Semigroups of Linear Operators and Applications to Partial Differential Equations. Applied Mathematical Science. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1983
|
| [21] |
Ren X, Tian Y, Liu L, Liu X. A reaction-diffusion within-host HIV model with cell-to-cell transmission. J Math Biol, 2018, 76(7): 1831-1872
doi: 10.1007/s00285-017-1202-x
pmid: 29305736
|