数学物理学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 1204-1217.
具时滞扩散效应的病原体-免疫模型的稳定性及分支
- 哈尔滨理工大学应用数学系 哈尔滨 150080
-
收稿日期:2019-09-28出版日期:2021-08-26发布日期:2021-08-09 -
通讯作者:王晶囡 E-mail:wangjingnan@hrbust.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(11801122);黑龙江省自然科学基金(A2018008)
Stability and Bifurcation of a Pathogen-Immune Model with Delay and Diffusion Effects
- Department of Applied Mathematics, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin 150080
-
Received:2019-09-28Online:2021-08-26Published:2021-08-09 -
Contact:Jingnan Wang E-mail:wangjingnan@hrbust.edu.cn -
Supported by:the NSFC(11801122);the NSF of Heilongjiang Province(A2018008)
摘要:
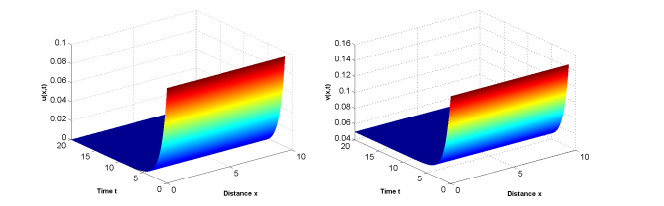
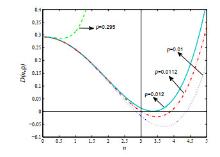
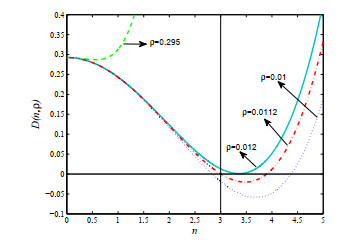
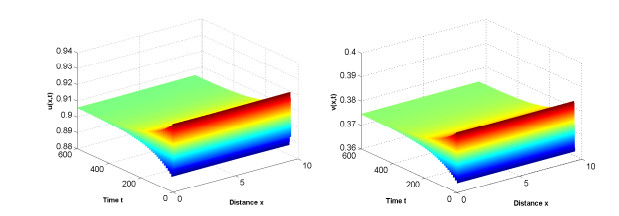
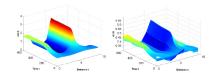
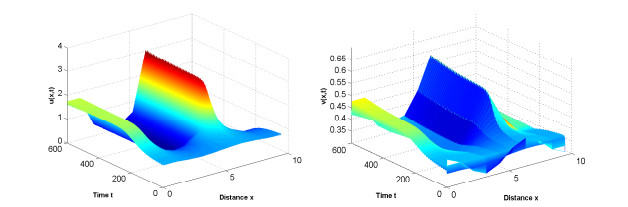
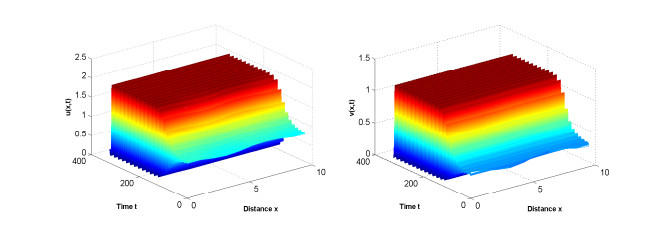
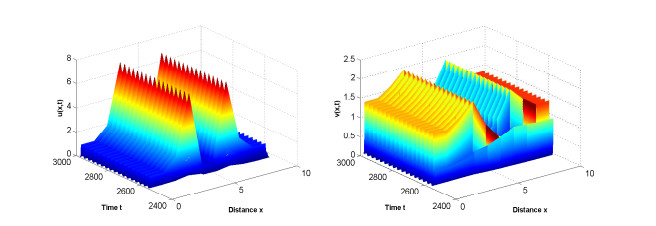
为了了解病原体与免疫细胞相互作用过程中存在的扩散因素与时滞因素对其动力学行为的影响,建立了带有齐次Neumann边界条件的具时滞病原体-免疫反应扩散模型.以病原体与免疫细胞的扩散比率和免疫时滞为参数,通过分析该模型在正稳态解处线性化系统特征根的分布,并利用泛函微分方程分支理论,得到正稳态解经历Turing失稳的充要条件以及经历Hopf分支的条件.利用Matlab数值模拟直观地展示了病原体与宿主免疫在临界点附近经历Turing失稳和Hopf分支的动力学行为,并解释了动力学行为所对应的生物医学意义,为控制病原体生长提供了一定的理论支持.
中图分类号:
- O175.29
引用本文
王晶囡,杨德中. 具时滞扩散效应的病原体-免疫模型的稳定性及分支[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(4): 1204-1217.
Jingnan Wang,Dezhong Yang. Stability and Bifurcation of a Pathogen-Immune Model with Delay and Diffusion Effects[J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(4): 1204-1217.
使用本文
| 1 | Naheed A , Singh M , Lucy D . Numerical study of SARS epidemic model with the inclusion of diffusion in the system. Appl Math Comput, 2014, 229, 480- 498 |
| 2 |
Beauchemin C A A , Handel A . A review of mathematical models of influenza a infections within a host or cell culture: lessons learned and challenges ahead. BMC Public Health, 2011, 11 (Suppl 1): S7
doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-S1-S7 |
| 3 |
韩祥临, 汪维刚, 莫嘉琪. 流行性病毒传播生态动力学系统. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39A (1): 200- 208
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.01.019 |
|
Han X L , Wang W G , Mo J Q . Bionomics dynamic system for epidemic virus transmission. Acta Math Sci, 2019, 39A (1): 200- 208
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.01.019 |
|
| 4 | 唐三一, 唐彪, BragazziN L, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情数据挖掘与离散随机传播动力学模型分析. 中国科学: 数学, 2020, 50 (8): 1071- 1086 |
| Tang S Y , Tang B , Bragazzi N L , et al. Analysis of COVID-19 epidemic traced data and stochastic discrete transmission dynamic model. Sci Sin Math, 2020, 50 (8): 1071- 1086 | |
| 5 |
程欣欣, 饶亚情, 黄刚. 封闭空间中新型冠状病毒肺炎传播模型: 以日本"钻石公主号"邮轮为例. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40A (2): 540- 544
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.02.024 |
|
Cheng X X , Rao Y Q , Huang G . COVID-19 transmission model in an enclosed space: a case study of Japan Diamond Princess Cruises. Acta Math Sci, 2020, 40A (2): 540- 544
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.02.024 |
|
| 6 |
Gilchrist M A , Sasaki A . Modeling host-parasite coevolution: a nested approach based on mechanistic models. J Theor Biol, 2002, 218 (3): 289- 308
doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2002.3076 |
| 7 |
Mohtashemi M , Levins R . Transient dynamics and early diagnostics in infectious disease. J Math Biol, 2001, 43 (5): 446- 470
doi: 10.1007/s002850100103 |
| 8 | Pugliese A , Gandolfi A . A simple model of pathogen-immune dynamics including specific and non-specific immunity. Math Biosci, 2008, 214 (1): 73- 80 |
| 9 | Wang W , Ma W . Hepatitis C virus infection is blocked by HMGB1: a new nonlocal and time-delayed reaction-diffusion model. Appl Math Comput, 2018, 320, 633- 653 |
| 10 |
Stancevic O , Angstmann C N , Murray J M , et al. Turing patterns from dynamics of early HIV infection. B Math Biol, 2013, 75 (5): 774- 795
doi: 10.1007/s11538-013-9834-5 |
| 11 |
Lee M R , Huang Y T , Lee P I , et al. Healthcare-associated bacteraemia caused by Leuconostoc species at a university hospital in Taiwan between 1995 and 2008. J Hosp Infect, 2011, 78 (1): 45- 49
doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2010.11.014 |
| 12 |
崔青曼, 袁春营, 李春岭, 等. 主要海水养殖鱼类白点病和盾纤毛虫病防治技术. 水利渔业, 2007, 27 (6): 85- 87
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1278.2007.06.037 |
|
Cui Q M , Yuan C Y , Li C L , et al. Control of white - spot disease and scuticociliatida disease of some main cultured sea fishes. Reservoir Fisheries, 2007, 27 (6): 85- 87
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1278.2007.06.037 |
|
| 13 | 孙汶生. 医学免疫学. 北京: 高等教出版社, 2010 |
| Sun W S . Medical Immunology. Bei Jing: Higher Education Press, 2010 | |
| 14 | Han X L , Jin Z . A dynamic model of hepatitis B virus with delayed immune response. J North University of China, 2011, 32 (1): 197- 208 |
| 15 |
Bai Z , Peng R , Zhao X Q . A reaction-diffusion malaria model with seasonality and incubation period. J Math Biol, 2018, 77 (1): 201- 228
doi: 10.1007/s00285-017-1193-7 |
| 16 |
Zhu D D , Ren J L , Zhu H P . Spatial-temporal basic reproduction number and dynamics for a dengue disease diffusion model for a dengue disease diffusion model. Math Meth Appl Sci, 2018, 41, 5388- 5403
doi: 10.1002/mma.5085 |
| 17 |
Yamazaki K . Threshold dynamics of reaction-diffusion partial differential equations model of Ebola virus disease. Int J Biomath, 2018, 11 (8): 1850108
doi: 10.1142/S1793524518501085 |
| 18 |
Diggles B K , Lester R J G . Influence of temperature and host species on the development of cryptocaryon irritans. J Parasitol, 1996, 82 (1): 45- 51
doi: 10.2307/3284114 |
| 19 |
Wang K , Wang W , Pang H , et al. Complex dynamic behavior in a viral model with delayed immune response. Physica D, 2007, 226 (2): 197- 208
doi: 10.1016/j.physd.2006.12.001 |
| 20 |
Xie Q , Huang D , Zhang S , et al. Analysis of a viral infection model with delayed immune response. Appl Math Model, 2010, 34 (9): 2388- 2395
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2009.11.005 |
| 21 |
Niu B , Guo Y X , Du Y F . Hopf bifurcation induced by delay effect in a diffusive tumor-immune system. Int J Bifurcat Chaos, 2018, 28 (11): 1850136
doi: 10.1142/S0218127418501365 |
| 22 | Canabarro A A , Gléria I M , Lyra M L . Periodic solutions and chaos in a nonlinear model for the delayed cellular immune response. Physica A, 2004, 342 (1/2): 234- 241 |
| 23 | Wu J H . Theory and Applications of Partial Functional Differential Equations. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1996 |
| 24 |
Jiang W , Wang H , Cao X . Turing instability and Turing-Hopf bifurcation in diffusive Schnakenberg systems with gene expression time delay. J Dynam Differential Equations, 2019, 31 (4): 2223- 2247
doi: 10.1007/s10884-018-9702-y |
| 25 |
Wang W , Liu Q X , Jin Z . Spatiotemporal complexity of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. Phys Rev E, 2007, 75 (5): 051913
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.75.051913 |
| 26 |
Baurmann M , Gross T , Feudel U . Instabilities in spatially extended predator-prey systems: spatio-temporal patterns in the neighborhood of Turing-Hopf bifurcations. J Theor Biol, 2007, 245 (2): 220- 229
doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.09.036 |
| 27 |
Song Y , Jiang H , Liu Q X , et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the diffusive Mussel-Algae model near Turing-Hopf bifurcation. SIAM J on Appl Dyn Syst, 2017, 16 (4): 2030- 2062
doi: 10.1137/16M1097560 |
| 28 |
Garvie M R . Finite-difference schemes for reaction-diffusion equations modeling predator-prey interactions in MATLAB. B Math Biol, 2007, 69 (3): 931- 956
doi: 10.1007/s11538-006-9062-3 |
| [1] | 仉志余. 具次线性中立项的二阶广义Emden-Fowler时滞微分方程的振动准则[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(3): 811-826. |
| [2] | 李喜玲,高飞,李文琴. 具有免疫时滞的分数阶HBV感染模型稳定性分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(2): 562-576. |
| [3] | 郭改慧,刘晓慧. 一类自催化可逆生化反应模型的Hopf分支及其稳定性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(1): 166-177. |
| [4] | 朱凯旋,谢永钦,周峰,邓习军. 带有时滞项的复Ginzburg-Landau方程的拉回吸引子[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(5): 1341-1353. |
| [5] | 刘健,张志信,蒋威. 分数阶非线性时滞脉冲微分系统的全局Mittag-Leffler稳定性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(4): 1053-1060. |
| [6] | 黄星寿,罗日才,王五生. 基于Gronwall积分不等式的比例时滞神经网络稳定性分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(3): 824-832. |
| [7] | 阳超,李润洁. 一类具有不连续捕获的Lasota-Wazewska模型周期解存在性及稳定性分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(4): 785-796. |
| [8] | 周庆华,万立,刘杰. 具有变时滞的神经型Hopfield神经网络的全局吸引子研究[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(4): 823-831. |
| [9] | 李文娟,李书海,俞元洪. 非线性二阶中立型分布时滞微分方程的振动性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(4): 812-822. |
| [10] | 王琼,龙芳,王珺. 关于差分Riccati方程及时滞微分方程的相关结果[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(4): 832-838. |
| [11] | 李海银. 密度制约且具有时滞捕食-被捕食模型的Hopf分支[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(2): 358-371. |
| [12] | 韩祥临,汪维刚,莫嘉琪. 一类非线性微分-积分时滞反应扩散系统奇摄动问题的广义解[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(2): 297-306. |
| [13] | 王俊,王天璐,温艳华,周先锋. N维非线性时滞分数阶微分方程初值问题的全局解[J]. 数学物理学报, 2018, 38(5): 903-910. |
| [14] | 郑立飞,郭洁,吴美华,王小瑞,万阿英. 一类具有时滞的捕食者-猎物-共生者系统的研究[J]. 数学物理学报, 2018, 38(5): 1001-1013. |
| [15] | 刘功伟, 刁林. 具记忆和变时滞项的二阶发展方程能量衰减率的凸性估计[J]. 数学物理学报, 2018, 38(3): 527-542. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 424
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 100
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|