数学物理学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 1192-1203.
具有Crowley-Martin型功能反应的捕食者-食饵模型的复杂动力学和随机敏感性分析
- 山东科技大学 数学与系统科学学院 山东青岛 266590
-
收稿日期:2019-10-29出版日期:2021-08-26发布日期:2021-08-09 -
通讯作者:孟新柱 E-mail:tengfei_wang2014@126.com;tfeng.math@gmail.com;skdmxz12@163.com -
作者简介:王腾飞, E-mail:tengfei_wang2014@126.com |冯涛, E-mail:tfeng.math@gmail.com -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2019MA003);山东省泰山学者项目研究基金
Complex Dynamics and Stochastic Sensitivity Analysis of a Predator-Prey Model with Crowley-Martin Type Functional Response
Tengfei Wang( ),Tao Feng(
),Tao Feng( ),Xinzhu Meng*(
),Xinzhu Meng*( )
)
- College of Mathematics and Systems Science, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Shandong Qingdao 266590
-
Received:2019-10-29Online:2021-08-26Published:2021-08-09 -
Contact:Xinzhu Meng E-mail:tengfei_wang2014@126.com;tfeng.math@gmail.com;skdmxz12@163.com -
Supported by:the NSF of Shandong Province(ZR2019MA003);the Research Fund for the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province
摘要:
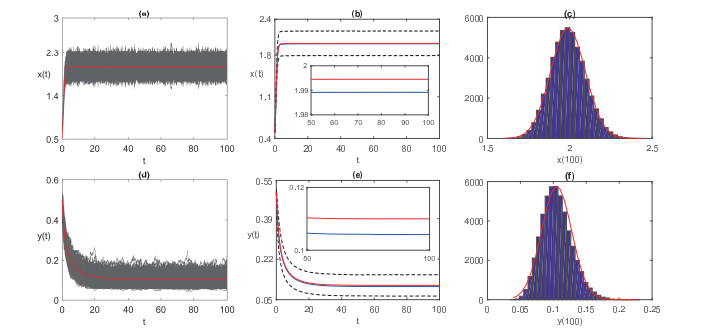
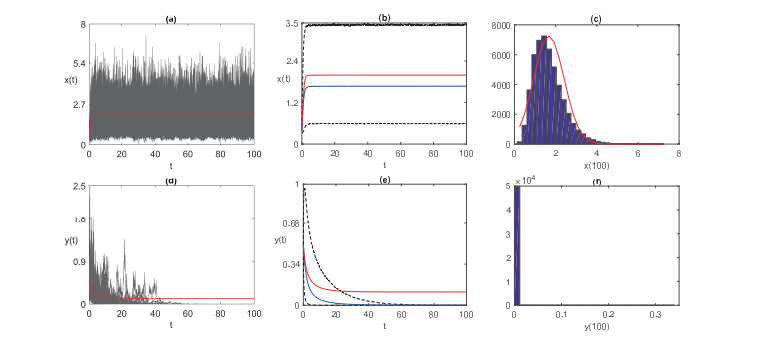
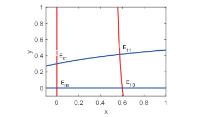
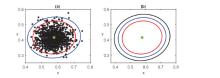
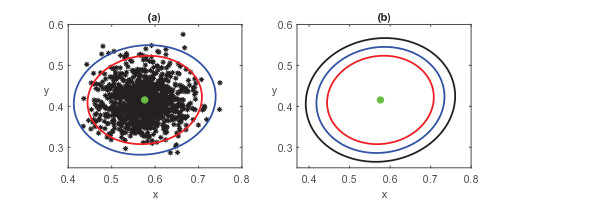
捕食者与食饵的相互作用在保护物种多样性方面起着关键作用.该文提出了一个具有Crowley-Martin型功能反应的随机捕食者-食饵模型.结果表明,当

中图分类号:
- O175
引用本文
王腾飞,冯涛,孟新柱. 具有Crowley-Martin型功能反应的捕食者-食饵模型的复杂动力学和随机敏感性分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(4): 1192-1203.
Tengfei Wang,Tao Feng,Xinzhu Meng. Complex Dynamics and Stochastic Sensitivity Analysis of a Predator-Prey Model with Crowley-Martin Type Functional Response[J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(4): 1192-1203.
使用本文
| 1 |
Kooi B , Ezio V . Ecoepidemic predator-prey model with feeding satiation, prey herd behavior and abandoned infected prey. Mathematical Biosciences, 2016, 274, 58- 72
doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2016.02.003 |
| 2 |
Ai S , Du Y , Rui P . Traveling waves for a generalized Holling-Tanner predator-prey model. Journal of Differential Equations, 2017, 263, 7782- 7814
doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2017.08.021 |
| 3 |
Rao F , Carlos C , Kang Y . Dynamics of a diffusion reaction prey-predator model with delay in prey: Effects of delay and spatial components. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2018, 461, 1177- 1214
doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2018.01.046 |
| 4 | Kang Y , Kumar S , Messan K . A two-patch prey-predator model with predator dispersal driven by the predation strength. Mathematical Biosciences & Engineering, 2017, 14, 843- 880 |
| 5 |
Wang H , Silogini T , Philippe G . Refuge-mediated predator-prey dynamics and biomass pyramids. Mathematical Biosciences, 2018, 298, 29- 45
doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2017.12.007 |
| 6 |
Zhang F Q , Chen Y M , Li J Q . Dynamical analysis of a stage-structured predator-prey model with cannibalism. Mathematical Biosciences, 2019, 307, 33- 41
doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2018.11.004 |
| 7 |
邓栋, 李燕. 一类带治疗项的非局部扩散SIR传染病模型的行波解. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40A (1): 72- 102
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.01.008 |
|
Deng D , Li Y . Traveling wave solutions of a nonlocal spreading SIR infectious disease model with treatment term. Acta Math Sci, 2020, 40A (1): 72- 102
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.01.008 |
|
| 8 |
曹忠威, 文香丹, 冯微, 祖力. 一类具有随机扰动的非自治SIRI流行病模型的动力学行为. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40A (1): 221- 232
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.01.017 |
|
Cao Z W , Wen X D , Feng W , Zu L . Dynamic behavior of a nonautonomous SIRI epidemic model with random perturbations. Acta Math Sci, 2020, 40A (1): 221- 232
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.01.017 |
|
| 9 |
Rajasekar S P , Pitchaimani M , Zhu Q X . Dynamic threshold probe of stochastic SIR model with saturated incidence rate and saturated treatment function. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 535, 122300
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.122300 |
| 10 |
Rajasekar S P , Pitchaimani M , Zhu Q X . Progressive dynamics of a stochastic epidemic model with logistic growth and saturated treatment. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2020, 538, 122649
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.122649 |
| 11 |
Hu Z X , Ma W B , Ruan S G . Analysis of SIR epidemic models with nonlinear incidence rate and treatment. Mathematical Biosciences, 2012, 238, 12- 20
doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2012.03.010 |
| 12 |
Qiu Z P , Michael Y , Shen Z . Global dynamics of an infinite dimensional epidemic model with nonlocal state structures. Journal of Differential Equations, 2018, 265, 5262- 5296
doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2018.06.036 |
| 13 | Rajasekar S P , Pitchaimani M . Qualitative analysis of stochastically perturbed SIRS epidemic model with two viruses. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2019, 118, 207- 221 |
| 14 |
Cai Y L , Kang Y , Banerjee M , Wang W M . A stochastic SIRS epidemic model with infectious force under intervention strategies. Journal of Differential Equations, 2015, 259, 7463- 7502
doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2015.08.024 |
| 15 |
Liu Q , Jiang D Q , Hayat T , Alsadi A . Stationary distribution of a stochastic delayed SVEIR epidemic model with vaccination and saturation incidence. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 512, 849- 863
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.08.054 |
| 16 |
Rajasekar S P , Pitchaimani M . Ergodic stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with logistic growth and nonlinear incidence. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2020, 377, 125143
doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2020.125143 |
| 17 |
Zhang X B , Zhang X H . The threshold of a deterministic and a stochastic SIQS epidemic model with varying total population size. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 91, 749- 767
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.09.050 |
| 18 |
袁海龙, 王玉萍, 李艳玲. 一类带有交叉扩散的捕食-食饵模型的正解. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39A (3): 545- 559
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.03.014 |
|
Yan H L , Wang Y P , Li Y L . Positive solution of a predator-prey model with cross diffusion. Acta Math Sci, 2019, 39A (3): 545- 559
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.03.014 |
|
| 19 |
Liu M , Du C , Deng M . Persistence and extinction of a modified Leslie-Gower Holling-type Ⅱ stochastic predator-prey model with impulsive toxicant input in polluted environments. Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems, 2018, 27, 177- 190
doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.08.001 |
| 20 |
Zhuo X L , Zhang F X . Stability for a new discrete ratio-dependent predator-prey system. Qualitative Theory of Dynamical Systems, 2018, 17 (1): 189- 202
doi: 10.1007/s12346-017-0228-1 |
| 21 |
王双明, 樊馨蔓, 张明军, 梁俊荣. 具周期性潜伏期的SEIR传染病模型的动力学. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40A (2): 527- 539
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.02.023 |
|
Wang S M , Fan X M , Zhang M J , Liang J R . Dynamics of a SEIR infectious disease model with periodic incubation periods. Acta Math Sci, 2020, 40A (2): 527- 539
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2020.02.023 |
|
| 22 |
Crowley P H , Martin E K . Functional responses and interference within and between year classes of a dragony population. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 1989, 8, 211- 221
doi: 10.2307/1467324 |
| 23 |
Wang W M , Cai Y L , et al. Periodic behavior in a FIV model with seasonality as well as environment fluctuations. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2017, 354 (16): 7410- 7428
doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.08.034 |
| 24 |
Wu S , Shi J , Wu B . Global existence of solutions and uniform persistence of a diffusive predator-prey model with prey-taxis. Journal of Differential Equations, 2016, 260 (7): 5847- 5874
doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2015.12.024 |
| 25 |
Ghosh B , Zhdanova O L , Barman B , Frisman E Y . Dynamics of stage-structure predator-prey systems under density-dependent effect and mortality. Ecological Complexity, 2020, 41, 100812
doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2020.100812 |
| 26 | Feng T , Qiu Z P . Global analysis of a stochastic TB model with vaccination and treatment. Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems-B, 2019, 24 (6): 2923- 2939 |
| 27 |
Xu C , Yuan S L , Zhang T H . Average break-even concentration in a simple chemostat model with telegraph noise. Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems, 2018, 29, 373- 382
doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2018.03.007 |
| 28 | Durrett R . Stochastic Calculus: A Practical Introduction. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1996 |
| 29 | Lv J L , Liu H , Zou X L . Stationary distribution and persistence of a stochastic predator-prey model with a functional response. Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2019, 9 (1): 1- 11 |
| 30 |
Bashkirtseva I , Ryashko L . Analysis of excitability for the FitzHugh-Nagumo model via a stochastic sensitivity function technique. Physical Review E, 2011, 83, 061109
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.83.061109 |
| 31 |
Bashkirtseva I , Ryashko L , Zaitseva S . Analysis of nonlinear stochastic oscillations in the biochemical Goldbeter model. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2019, 73, 165- 176
doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2019.02.008 |
| 32 | Bashkirtseva I , Ryashko L . Stochastic sensitivity and variability of glycolytic oscillations in the randomly forced Sel'kov model. European Physical Journal B, 2017, 90 (1): 17 |
| 33 | Bashkirtseva I , Ryashko L . Analysis of noise-induced phenomena in the nonlinear tumor-immune system. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2020, 549, 123923 |
| 34 | Du N H , Nguyen D H , Yin G G . Conditions for permanence and ergodicity of certain stochastic predator-prey models. Journal of Applied Probability, 2016, 53 (1): 187- 202 |
| 35 | Bashkirtseva I , Ryazanova T , Ryashko L . Confidence domains in the analysis of noise-induced transition to chaos for Goodwin model of business cycles. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2014, 24, 1440020 |
| 36 | Freidlin M I , Wentzell A D . Random Perturbations of Dynamical Systems. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1984 |
| 37 | Bashkirtseva I , Ryashko L B . Sensitivity and chaos control for the forced nonlinear oscillations. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2005, 26, 1437- 1451 |
| 38 | Liu Z W , Shi N Z , Jiang D Q , Ji C Y . The asymptotic behavior of a stochastic Predator-Prey system with Holling Ⅱ functional response. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2012, 2012, 1- 14 |
| 39 | Qiu H , Liu M , Wang K , Wang Y . Dynamics of a stochastic predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2012, 219 (4): 2303- 2312 |
| 40 | Cantrell R S , Cosner C . On the dynamics of Predator-Prey models with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2001, 257 (1): 206- 222 |
| 41 | Feng T , Qiu Z P , Meng X Z . Stochastic hepatitis C virus system with host immunity. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems Series B, 2019, 24 (12): 6367- 6385 |
| 42 | Wang L , Jiang D Q . A note on the stationary distribution of the stochastic chemostat model with general response functions. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2017, 73, 22- 28 |
| [1] | 蓝桂杰,付盈洁,魏春金,张树文. 具有Holling Ⅲ功能性反应的随机捕食食饵模型的平稳分布和周期解[J]. 数学物理学报, 2018, 38(5): 984-1000. |
| [2] | 魏凤英, 林青腾. 一类具有校正隔离率随机SIQS模型的绝灭性与分布[J]. 数学物理学报, 2017, 37(6): 1148-1161. |
| [3] | 张水利, 张绍义. 一般状态空间跳过程的遍历性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2014, 34(4): 859-878. |
| [4] | 王健. 一般对称跳过程的Lyapunov漂移条件[J]. 数学物理学报, 2011, 31(3): 785-795. |
| [5] | 唐有荣, 刘再明, 侯振挺. 广生灭过程的遍历性及平稳分布[J]. 数学物理学报, 1998, 18(1): 25-32. |
| [6] | 陈金文. 有限维Brusseltor模型的正常返性[J]. 数学物理学报, 1995, 15(2): 121-125. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 141
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 96
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|