数学物理学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 646-656.
• • 上一篇
西藏自治区包虫病传播的数学建模及动力学分析
- 西北师范大学数学与统计学院 兰州 730070
-
收稿日期:2022-01-29修回日期:2022-10-17出版日期:2023-04-26发布日期:2023-04-17 -
通讯作者:韩晓玲,E-mail: hanxiaoling9@163.com -
作者简介:许越,E-mail:1206485579@qq.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(12161079);甘肃省自然科学基金(20JR10RA086)
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Analysis of Echinococcosis Transmission in Tibet Autonomous Region
- College of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou 730070
-
Received:2022-01-29Revised:2022-10-17Online:2023-04-26Published:2023-04-17 -
Supported by:NSFC(12161079);Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province(20JR10RA086)
摘要:
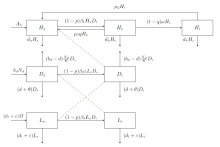
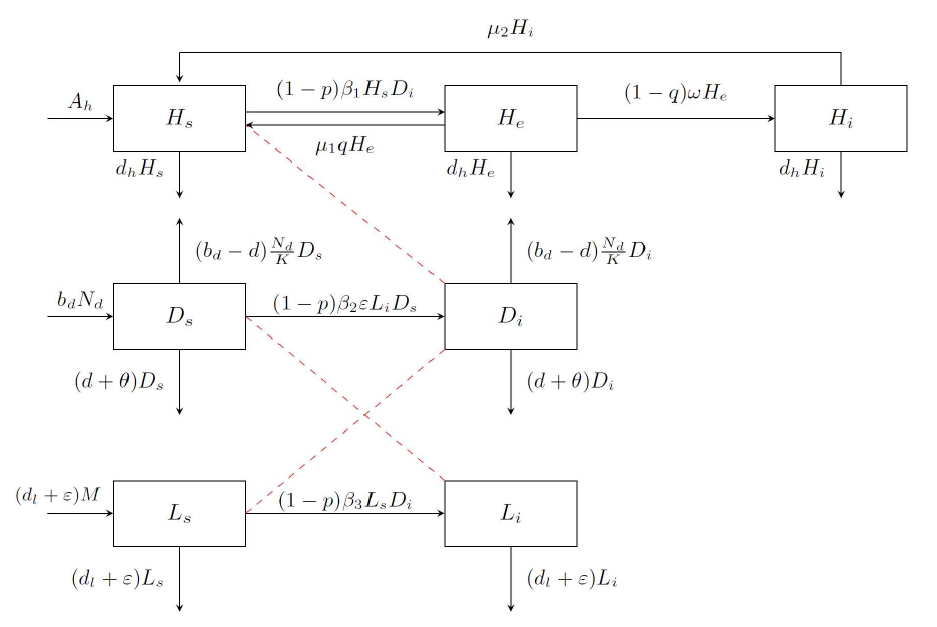
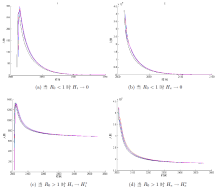
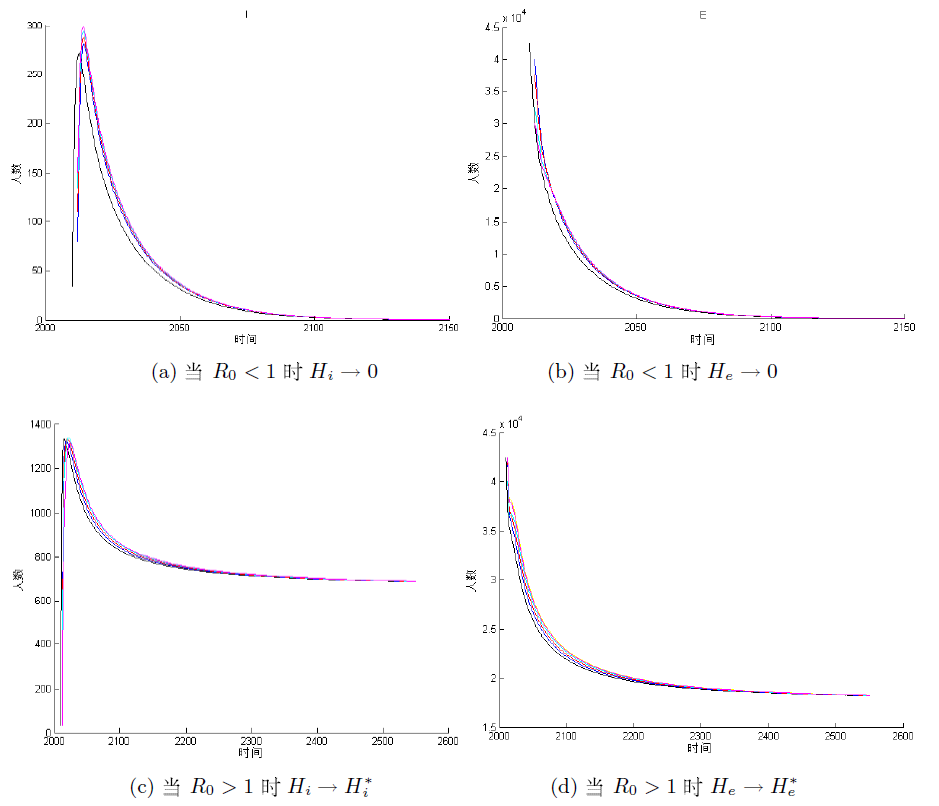
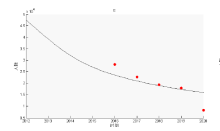
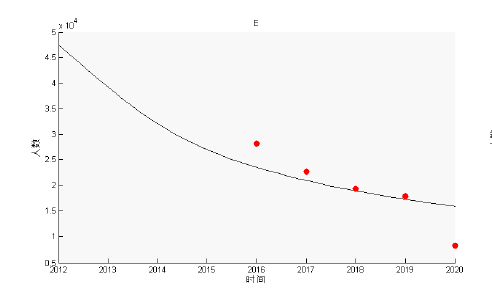
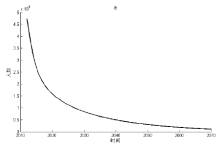
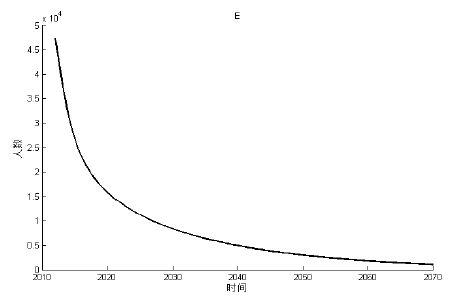
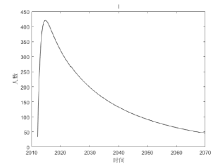
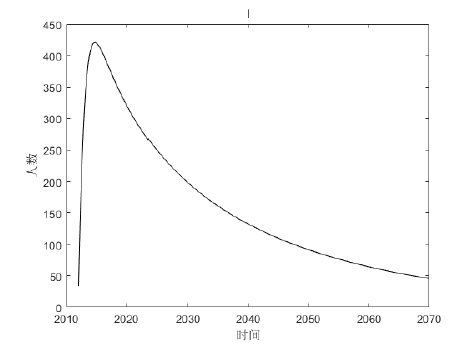
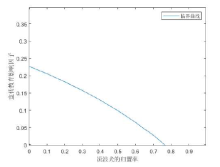
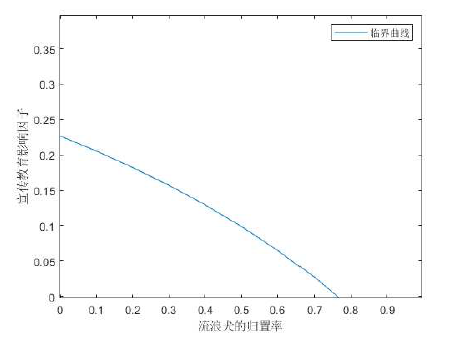
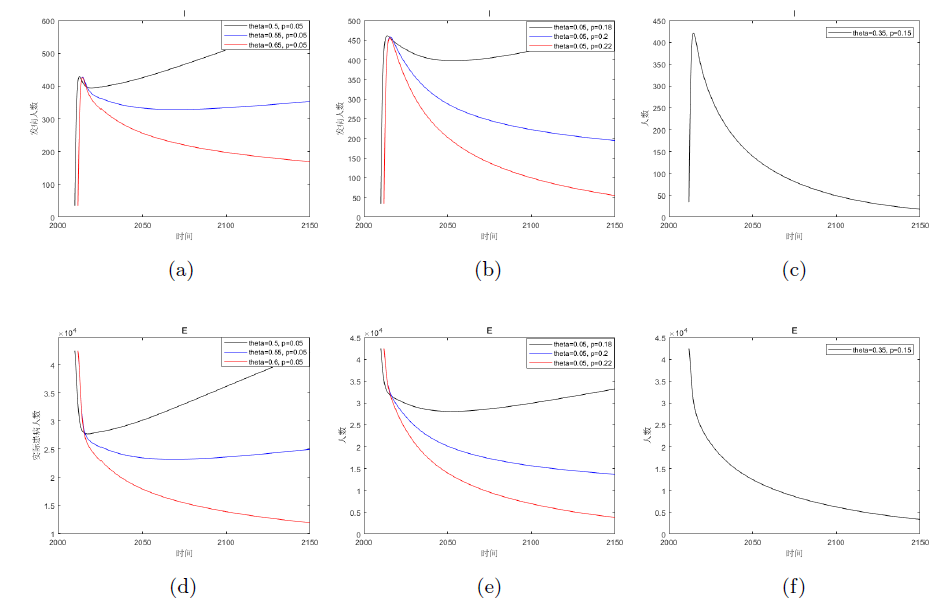
该文通过对包虫病传播机理以及西藏地区包虫病流行现状的研究, 构建了一类符合西藏地区实际情况的包虫病动力学模型. 利用 Lyapunov 函数对模型平衡点进行了稳定性分析, 证明了无病平衡点和地方病平衡点的全局稳定性. 并用收集到的数据, 依据模型对基本再生数 

中图分类号:
- O175.1
引用本文
许越, 韩晓玲. 西藏自治区包虫病传播的数学建模及动力学分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2023, 43(2): 646-656.
Xu Yue, Han Xiaoling. Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Analysis of Echinococcosis Transmission in Tibet Autonomous Region[J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2023, 43(2): 646-656.
使用本文
| [1] |
Eckert J, Deplazes P. Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of echinococ-cosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2004, 17(1): 107-135
doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.1.107-135.2004 |
| [2] |
Davidson R K, Romig T, Jenkins E, et al. The impact of globalisation on the distribution of Echinococcus multilocularis. Trends Parasitol, 2012, 28(6): 239-247
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2012.03.004 pmid: 22542923 |
| [3] | 陈伟奇, 张雅兰, 贡桑曲珍, 等. 西藏自治区棘球蚴病病例分析. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(1): 43-46 |
| Chen W Q, Zhang Y L, GongSang Q Z, et al. Analysis of hydatid disease cases in Tibet Autonomous Region. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2018, 36(1): 43-46 | |
| [4] | 韩帅, 蒉嫣, 薛垂召, 等. 2004-2020年全国棘球蚴病疫情分析. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(5): 1-6 |
| Han S, Kuai Y, Xue C Z, et al. The endemic status of echinococcosis in China from 2004 to 2020. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2021, 39(5): 1-6 | |
| [5] | 蒉嫣, 伍卫平, 韩帅, 等. 2018-2019年全国棘球蚴病监测分析. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2021, 16(9): 1025-1029 |
| Kuai Y, Wu W P, Han S, et al. Analysis of the results of echinococcosis surveillance in China from 2018 to 2019. Journal of Pathogen Biology, 2021, 16(9): 1025-1029 | |
| [6] |
Gemmell M A, Lawson J R, Roberts M G. Population dynamics in echinococcosis and cysticercosis: biological parameters of Echinococcus granulosus in dogs and sheep. Parasitology, 1986, 92(3): 599-620
doi: 10.1017/S0031182000065483 |
| [7] |
Roberts M G, Lawson J R, Gemmell M A. Population dynamics in echinococcosis and cysticercosis: mathematical model of the life-cycle of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitology, 1986, 92(3): 621-641
doi: 10.1017/S0031182000065495 |
| [8] | 杜守洪, 王蕾, 张学良, 等. 一类具有饱和发生率的包虫病传播模型研究. 数学的实践与认识, 2013, 43(20): 269-273 |
| Du S H, Wang L, Zhang X L, et al. A Echinococcosis model with saturation incidence. Journal of Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2013, 43(20): 269-273 | |
| [9] |
Liu J, Liu L, Feng X, et al. Global dynamics of a time-delayed echinococcosis transmission model. Advances in Difference Equations, 2015, 2015(1): 1-16
doi: 10.1186/s13662-014-0331-4 |
| [10] | Xu Z, Ai C. A spatial echinococcosis transmission model with time delays: stability and traveling waves. International Journal of Biomathematics, 2017, 10(6): 1-32 |
| [11] | 赵瑜, 杨诗杰. 一类随机包虫病传播模型及CDC数据拟合. 生物数学学报, 2017, 32(1): 41-48 |
| Zhao Y, Yang S J. Modeling a stochastic Echinococcosis transmission and fitting the statistical data of CDC. Journal of Biomathematics, 2017, 32(1): 41-48 | |
| [12] |
Rong X M, Fan M, Sun X D, et al. Impact of disposing stray dogs on risk assessment and control of Echinococcosis in Inner Mongolia. Mathematical Biosciences, 2018, 299: 85-96
doi: S0025-5564(17)30436-4 pmid: 29526551 |
| [13] |
Wang K, Zhang X, Jin Z, et al. Modeling and analysis of the transmission of Echinococcosis with application to Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2013, 333: 78-90
doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2013.04.020 pmid: 23669505 |
| [14] | 唐丹丹. 新疆地区包虫病模型的建立与仿真. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2016 |
| Tang D D. The Establishment and Simulation of Echinococcosis Model in Xinjiang. Urumqi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2016 | |
| [15] | Zhang Y, Xiao Y. Modeling and analyzing the effects of fixed-time intervention on transmission dynamics of echinococcosis in Qinghai province. Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2018, 76: 1249-1267 |
| [16] |
Dreessche P, Watmough J. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Mathematical Biosciences, 2002, 180: 29-48
pmid: 12387915 |
| [17] | 刘平, 吴海荣, 张伟超, 等. 我国西部地区农牧民包虫病防控认知情况及其影响因素. 中国动物检疫, 2021, 38(5): 1-4 |
| Liu P, Wu H R, Zhang W C, et al. Awareness of herdsmen for the prevention and control of echinococcosis and potential risk factors in western china. China Animal Health Inspection, 2021, 38(5): 1-4 | |
| [18] | 马知恩, 周义仓, 王稳地, 靳帧. 传染病动力学的数学建模与研究. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004 |
| Ma Z E, Zhou Y C, Wang W D, Jin Z. Mathematical Modeling and Research on the Dynamics of Infectious Diseases. Beijing: Science Press, 2004 |
| [1] | 胡振祥,聂麟飞. 具有水平传播和环境传播的反应扩散传染病模型研究[J]. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42(6): 1849-1860. |
| [2] | 王凯,赵洪涌. 一类具有时滞的反应扩散登革热传染病模型的行波解[J]. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42(4): 1209-1226. |
| [3] | 郑雯丽,唐嘉,陈彩荣. 求解一类新的广义绝对值方程组的动力学模型[J]. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42(3): 818-825. |
| [4] | 张太雷,刘俊利,韩梦洁. 具有时滞和季节性的炭疽模型的动力学分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42(3): 851-866. |
| [5] | 孙丹丹,李盈科,滕志东,张太雷. 具有年龄结构的麻疹传染病模型的稳定性分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(6): 1950-1968. |
| [6] | 丰利香,王德芬. 具有隔离和不完全治疗的传染病模型的全局稳定性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(4): 1235-1248. |
| [7] | 刘永建,黄秋健. Rabinovich系统的Jacobi分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2021, 41(3): 783-796. |
| [8] | 王双明,樊馨蔓,张明军,梁俊荣. 具周期性潜伏期的SEIR传染病模型的动力学[J]. 数学物理学报, 2020, 40(2): 527-539. |
| [9] | 靖晓洁, 赵爱民, 刘桂荣. 考虑部分免疫和环境传播的麻疹传染病模型的全局稳定性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2019, 39(4): 909-917. |
| [10] | 李华,刘三红,方奕乐,张兴安. 儿童手足口病的数学建模和计算机模拟[J]. 数学物理学报, 2018, 38(5): 1032-1040. |
| [11] | 张丽萍, 赵瑜, 原三领. 一类具有非线性发生率的随机SIS传染病模型阈值动力学行为研究[J]. 数学物理学报, 2018, 38(1): 197-208. |
| [12] | 韦爱举, 张新建, 王俊义, 李科赞. 一类埃博拉传染病模型的动力学分析[J]. 数学物理学报, 2017, 37(3): 577-592. |
| [13] | 尹逊武, 李德生. 小时滞梯度系统的动力学行为[J]. 数学物理学报, 2015, 35(3): 464-477. |
| [14] | 冯春华. 一类简化的n个神经元时滞BAM神经网络模型的振动性[J]. 数学物理学报, 2011, 31(6): 1490-1501. |
| [15] | 徐为坚;. 具有种群Logistic增长及饱和传染率的SIS模型的稳定性和Hopf分支[J]. 数学物理学报, 2008, 28(3): 578-584. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 128
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 82
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|