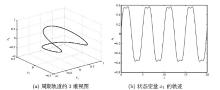
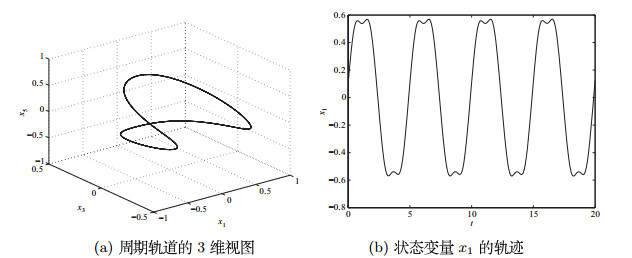
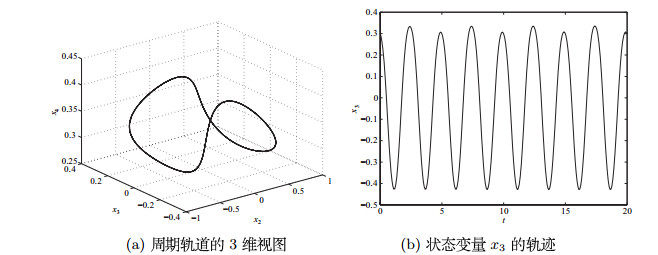
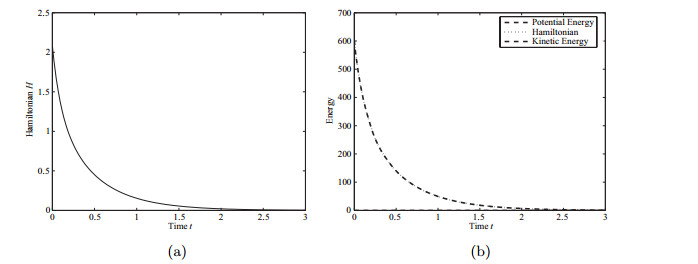
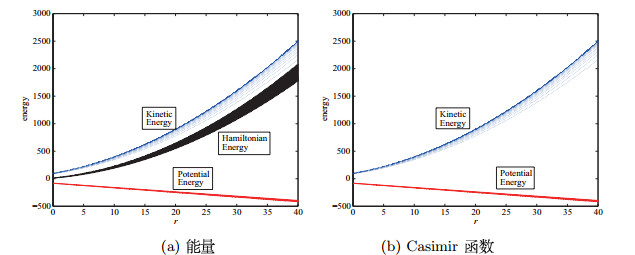
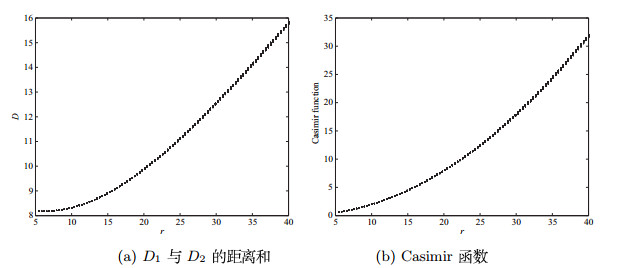
| 1 |
Lorenz N E . Deterministic nonperiodic flow. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1963, 20, 130- 141
doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1963)020<0130:DNF>2.0.CO;2
|
| 2 |
Teman R. Infinite Dimensional Dynamic System in Mechanics and Physics. New York: Springer-Verlog, 2000
|
| 3 |
Pchelintsev A N . Numerical and physical modeling of the dynamics of the lorenz system. Numerical Analysis and Applications, 2014, 7 (2): 159- 167
doi: 10.1134/S1995423914020098
|
| 4 |
Boldrighini C , Franceschini V . A five-dimensional truncation of the plane incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Communications in Mathematical Physics, 1979, 64, 159- 170
doi: 10.1007/BF01197511
|
| 5 |
Sparrow C. The Lorenz Equations: Bifurcations, Chaos, and Strange Attractors. New York: Springer Verlag, 1982
|
| 6 |
Franceschini V , Tebaldi C . A seven-modes truncation of the plane incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1981, 25 (3): 397- 417
|
| 7 |
Hilborn R C . Chaos and Nonlinear Dynamics. Landon: Oxford Univ Press, 1994
|
| 8 |
Franceschini V , Inglese G , Tebaldi C . A five-mode truncation of the Navier-Stokes equations on a three-dimensional torus. Commun Mech Phys, 1988, 64, 35- 40
|
| 9 |
Leonov G A , Kuznetsov N V , Korzhemanova N A , Kusakin D V . Lyapunov dimension formula for the global attractor of the Lorenz system. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2016, 41, 84- 103
doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2016.04.032
|
| 10 |
Leonov G A , Kuznetsov N V . On differences and similarities in the analysis of Lorenz, Chen, and Lu systems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 256, 334- 343
doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2014.12.132
|
| 11 |
Franceschini V , Zanasi R . Three-dimensional Navier-Stokes equations trancated on a torus. Nonlinearity, 1992, 4, 189- 209
|
| 12 |
Franceschini V , Tebaldi C . Breaking and disappearance of tori. Commun Math Phys, 1984, 94, 317- 329
doi: 10.1007/BF01224828
|
| 13 |
Arnold V . Kolmogorov's hydrodynamic attractors. Proc R Soc Lond A, 1991, 434 (19): 19- 22
|
| 14 |
Pasini A , Pelino V , Potesta S . Torsion and attractors in the Kolmogorov hydrodynamical system. Phys Lett A, 1998, 241, 77- 83
doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(98)00113-3
|
| 15 |
Pasini A , Pelino V . A unified view of Kolmogorov and Lorenz systems. Phys Lett A, 2000, 275, 435- 446
doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(00)00620-4
|
| 16 |
Pelino V , Pasini A . Dissipation in Lie-Poisson systems and the Lorenz-84 model. Phys Lett A, 2001, 291, 389- 396
doi: 10.1016/S0375-9601(01)00764-2
|
| 17 |
Liang X Y , Qi G Y . Mechanical analysis and energy conversion of Chen chaotic system. General and Applied Physics, 2017, 47 (4): 288- 294
|
| 18 |
Liang X Y , Qi G Y . Mechanical analysis of Chen chaotic system. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 2017, 98, 173- 177
doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2017.03.021
|
| 19 |
Qi G , Liang X . Mechanical analysis of Qi four-wing chaotic system. Nonlinear Dyn, 2016, 86 (2): 1095- 1106
doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2949-0
|
| 20 |
Pelino V , Maimone F , Pasini A . Energy cycle for the Lorenz attractor. Chaos Soliton Fract, 2014, 64, 67- 77
doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2013.09.005
|
| 21 |
Marsden J, Ratiu T. Introduction to Mechanics and Symmetry: A Basic Exposition of Classical Mechanical Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2002
|
| 22 |
Strogatz S H. Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1994
|
| 23 |
Morrison P J . Thoughts on brackets and dissipation:old and new. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2009, 169 (1): 012006
|
| 24 |
Doering C R , Gibbon J D . On the shape and dimension of the Lorenz attractor. Dyn Stab Syst, 1995, 10 (3): 255
|