
- Jul. 11, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 258-269.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20233050
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LU Qiqi,LIAN Zifeng,LI Jialong,SI Wenbin,MAI Zhaohua,FENG Yanqiu*( )
)
Received:2023-01-09
Published:2023-09-05
Online:2023-03-02
Contact:
*Tel: +86 20 61648271, E-mail: CLC Number:
LU Qiqi, LIAN Zifeng, LI Jialong, SI Wenbin, MAI Zhaohua, FENG Yanqiu. Magnetic Resonance R2* Parameter Mapping of Liver Based on Self-supervised Deep Neural Network[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 258-269.

Fig. 3
R∗2 maps reconstructed by UNet-TVp with different λ values. The NRMSE values of R∗2 maps are shown in the bottom right corner of the maps. The change of color in the color bar on the right side of the figure from blue to red represents the R∗2 value from small to large (GT: ground truth)
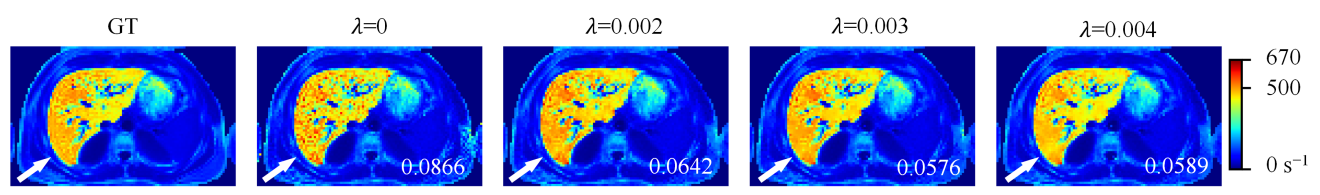
Table 1
Quantitative results of different methods on the simulated testing datasets (mean ± standard deviation)
| Methods | NRMSE | SSIM | Methods | NRMSE | SSIM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXP | 0.0616±0.0358 | 0.9571±0.0506 | UNet-EXP | 0.0623±0.0348 | 0.9572±0.0492 | |
| M2NCM | 0.0605±0.0354 | 0.9548±0.0502 | UNet-M2 | 0.0576±0.0286 | 0.9582±0.0466 | |
| M1NCM | 0.0581±0.0325 | 0.9561±0.0494 | UNet-TV | 0.0494±0.0145 | 0.9724±0.0201 | |
| PCANR | 0.0453±0.0122 | 0.9754±0.0182 | UNet-TVp | 0.0438±0.0100 | 0.9796±0.0117 |
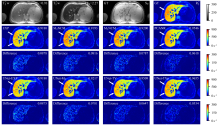
Fig. 4
R∗2maps reconstructed by different methods for one simulated severe iron-loaded liver dataset and corresponding absolute difference maps (Difference) under each R∗2 map. T∗2 w: T∗2-weighted images (TE1 = 0.93 ms, TE2 = 2.27 ms). GT: ground truth of S0 and R∗2 maps. The SSIM of each R∗2 map is shown in its top right corner, and the NRMSE is shown in the top right corner of the corresponding absolute difference map. The change of color in the color bar on the right side of the figure from blue to red represents the R∗2 value from small to large


Fig. 5
Bland-Altman analysis for the agreement between the mean R∗2 values in liver parenchyma (excluding vasculatures) and the reference, and the R∗2 maps reconstructed from different methods on the simulated testing datasets. The solid lines represent mean differences and the dashed lines indicate 95% confidence intervals

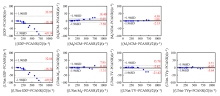
Fig. 6
Bland-Altman analysis for the agreement of the mean R∗2 values in liver parenchyma (excluding vasculatures) with the reference, and the R∗2 maps reconstructed from other methods on the clinical testing datasets. The PCANR algorithm was used as the reference method. The solid lines represent mean differences and the dashed lines indicate 95% confidence intervals
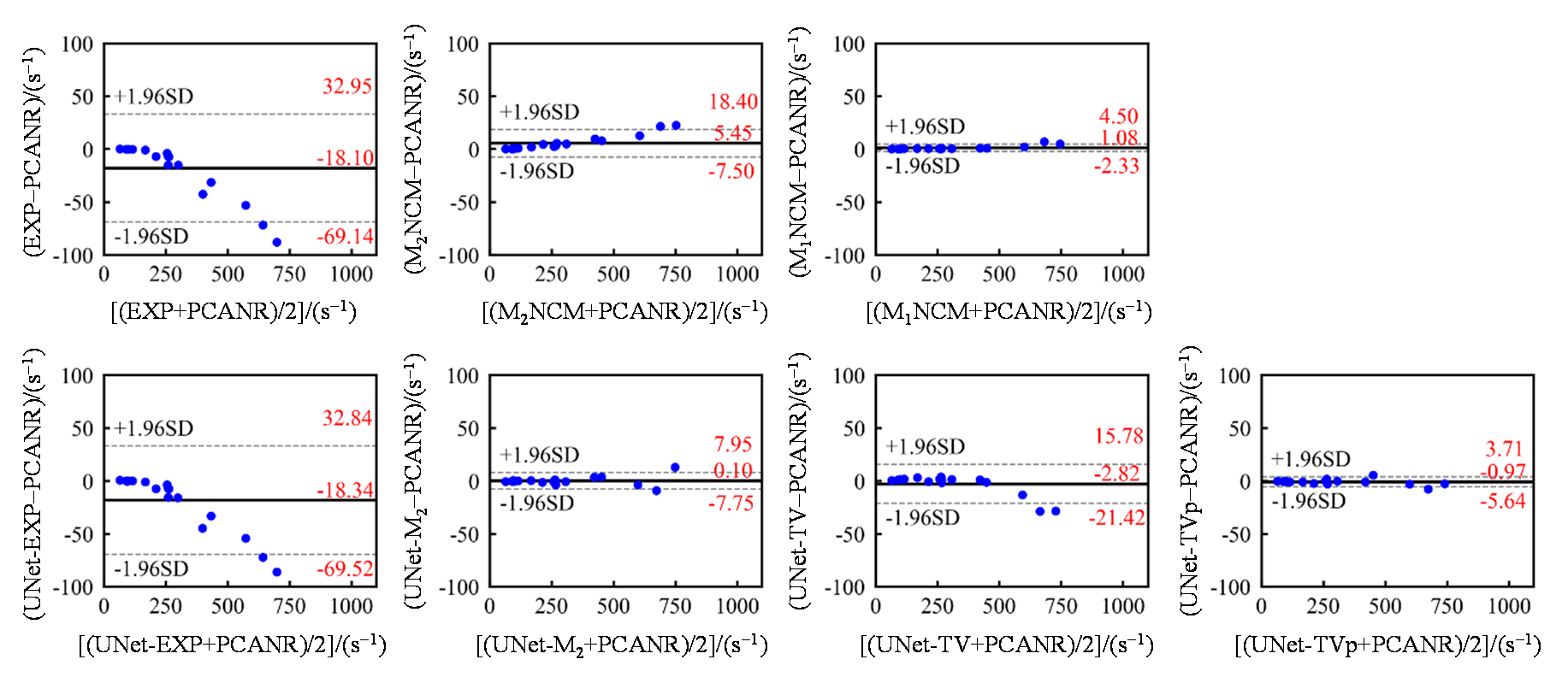
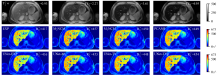
Fig. 7
R∗2 maps estimated by different reconstruction methods for one representative clinical testing data, which has moderate hepatic iron overload. First row: T∗2-weighted images (TE1 = 0.93 ms, TE2 = 2.27 ms, TE3 = 3.61 ms, TE4 = 4.95 ms). The mean R∗2 value (s-1) in liver parenchyma (excluding vasculatures) is shown in the top right corner of each R∗2 map. The change of color in the color bar on the right side of the figure from blue to red represents the R∗2 value from small to large
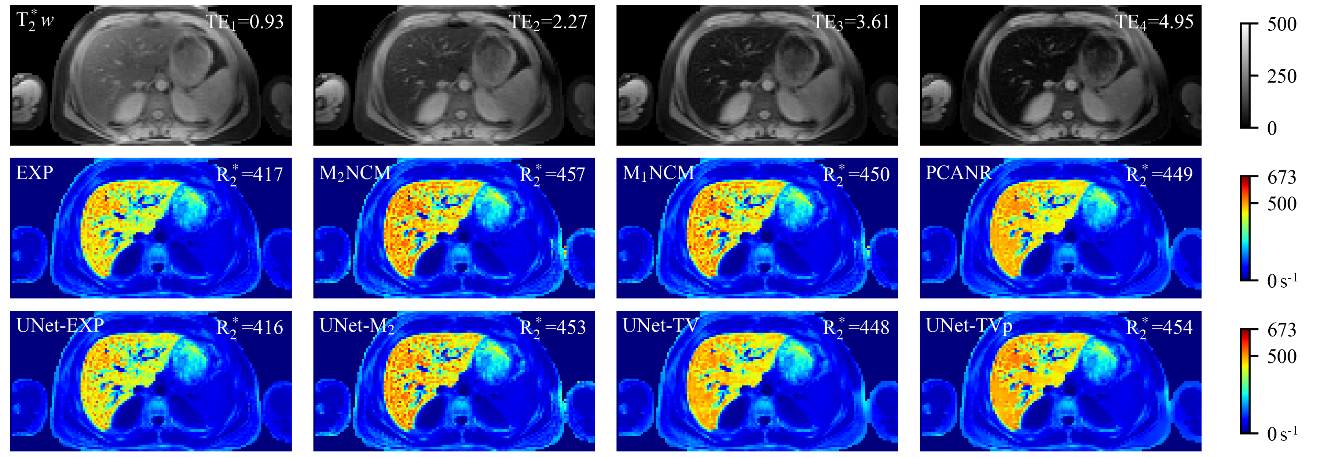
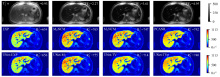
Fig. 8
R∗2 maps estimated by different reconstruction methods for one representative clinical testing data, which has severe hepatic iron overload. First row: T∗2-weighted images (TE1 = 0.93 ms, TE2 = 2.27 ms, TE3 = 3.61 ms, TE4 = 4.95 ms). The mean R∗2 value (s-1) in liver parenchyma (excluding vasculatures) is shown in the top right corner of each R∗2 map. The change of color in the color bar on the right side of the figure from blue to red represents the R∗2 value from small to large

| [1] |
LABRANCHE R, GILBERT G, CERNY M, et al. Liver iron quantification with MR imaging: A primer for radiologists[J]. Radiographics, 2018, 38(2): 392-412.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2018170079 pmid: 29528818 |
| [2] |
WOOD J C, ENRIQUEZ C, GHUGRE N, et al. MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients[J]. Blood, 2005, 106(4): 1460-1465.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3982 |
| [3] | HUANG J W, CHENG Z L, YANG Q H, et al. MRI-T2* technique in quantitative analysis of myocardium, liver and pancreas iron deposition in β-thalassemia major and the correlations with glucose metabolism[J]. Chin J Med Imaging Technol, 2021, 37(4): 557-561. |
| 黄静文, 程子亮, 杨绮华, 等. MRI-T2*技术定量分析β-重型地中海贫血心脏、肝脏、胰腺铁沉积及其与糖代谢的相关性[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2021, 37(4): 557-561. | |
| [4] | LU H M, ZHU J, WANG F, et al. Study on R2* combined with T1-mapping to evaluate iron overload in liver[J]. J Med Imaging, 2022, 32(8): 1036-1039. |
| 卢慧敏, 朱娟, 汪飞, 等. 磁共振R2*联合T1-mapping对肝脏铁过载评估的研究[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2022, 32(8): 1036-1039. | |
| [5] |
MELONI A, ZMYEWSKI H, RIENHOFF H Y, et al. Fast approximation to pixelwise relaxivity maps: Validation in iron overloaded subjects[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2013, 31(7): 1074-1080.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.05.005 pmid: 23773621 |
| [6] |
CONSTANTINIDES C D, ATALAR E, MCVEIGH E R. Signal-to-noise measurements in magnitude images from NMR phased arrays[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1997, 38(5): 852-857.
pmid: 9358462 |
| [7] |
FENG Y, HE T, GATEHOUSE P D, et al. Improved MRI R2* relaxometry of iron-loaded liver with noise correction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 70(6): 1765-1774.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.v70.6 |
| [8] |
WANG C, ZHANG X, LIU X, et al. Improved liver R2* mapping by pixel-wise curve fitting with adaptive neighborhood regularization[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 80(2): 792-801.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.v80.2 |
| [9] |
FENG L, MA D, LIU F. Rapid MR relaxometry using deep learning: An overview of current techniques and emerging trends[J]. NMR Biomed, 2022, 35(4): e4416.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.v35.4 |
| [10] | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]// Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif. Intell Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 9351, Springer, Cham, 2015: 234-241. |
| [11] |
LIU F, FENG L, KIJOWSKI R. MANTIS: Model-augmented neural network with incoherent k-space sampling for efficient MR parameter mapping[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 82(1): 174-188.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27707 pmid: 30860285 |
| [12] |
LIU F, KIJOWSKI R, EL FAKHRI G, et al. Magnetic resonance parameter mapping using model-guided self-supervised deep learning[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(6): 3211-3226.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28659 pmid: 33464652 |
| [13] |
GETREUER P. Rudin-Osher-Fatemi total variation denoising using split bregman[J]. Image Process Line, 2012, 2: 74-95.
doi: 10.5201/ipol |
| [14] | SHI B L, ZHOU Y M, PANG Z F. Image denoising via anisotropic total-variation-based method[J]. J Nantong Univ, Nat Sci Ed, 2019, 18(4): 24-33. |
| 史宝丽, 周亚美, 庞志峰. 各向异性全变分图像去噪算法[J]. 南通大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 18(4): 24-33. | |
| [15] |
LUSTIG M, DONOHO D, PAULY J M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58(6): 1182-1195.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21391 pmid: 17969013 |
| [16] | LIU J, SUN Y, XU X, et al. Image restoration using total variation regularized deep image prior[C]// IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process, IEEE, 2019: 7715-7719. |
| [17] |
STRONG D, CHAN T. Edge-preserving and scale-dependent properties of total variation regularization[J]. Inverse Probl, 2003, 19(6): S165-S187.
doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/19/6/059 |
| [18] |
ZHU W. A first-order image restoration model that promotes image contrast preservation[J]. J Sci Comput, 2021, 88(2): 1-23.
doi: 10.1007/s10915-021-01519-7 |
| [19] | HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]// 2015 IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis, IEEE, 2015: 1026-1034. |
| [20] | SANDINO C M, CHENG J Y, CHEN F, et al. Compressed sensing: From research to clinical practice with deep neural networks: shortening scan times for magnetic resonance imaging[J]. IEEE Signal Process Mag, 2020, 37(1): 117-127. |
| [21] |
WANG Z, BOVIK AC, SHEIKH HR, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(4): 600-612.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 |
| [22] |
VAN DER WALT S, SCHÖNBERGER JL, NUNEZ-IGLESIAS J, et al. scikit-image: image processing in Python[J]. Peer J, 2014, 2: e453.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.453 |
| [23] | CHENG H T, WANG S S, KE Z W, et al. A deep recursive cascaded convolutional network for parallel MRI[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2019, 36(4): 437-445 |
| 程慧涛, 王珊珊, 柯子文, 等. 基于深度递归级联卷积神经网络的并行磁共振成像方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2019, 36(4): 437-445. | |
| [24] | WANG Y S, DENG A Q, MAO J L, et al. Automatic segmentation of knee joint synovial magnetic resonance images based on 3D VNetTrans[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(3): 303-315 |
| 王颖珊, 邓奥琦, 毛瑾玲, 等. 基于3D VNetTrans的膝关节滑膜磁共振图像自动分割[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(3): 303-315. | |
| [25] |
ZHANG T, PAULY J M, LEVESQUE I R. Accelerating parameter mapping with a locally low rank constraint[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 73(2): 655-661.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25161 pmid: 24500817 |
| [26] |
ZHAO B, LU W, HITCHENS T K, et al. Accelerated MR parameter mapping with low-rank and sparsity constraints[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 74(2): 489-498.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25421 pmid: 25163720 |
| [27] |
ROMANO Y, ELAD M, MILANFAR P. The little engine that could: Regularization by Denoising (RED)[J]. SIAM J Imaging Sci, 2017, 10(4): 1804-1844.
doi: 10.1137/16M1102884 |
| [28] |
LANDMAN B A, BAZIN P L, SMITH S A, et al. Robust estimation of spatially variable noise fields[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2009, 62(2): 500-509.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22013 pmid: 19526510 |
| [29] |
HENNINGER B, ALUSTIZA J, GARBOWSKI M, et al. Practical guide to quantification of hepatic iron with MRI[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(1): 383-393.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06380-9 pmid: 31392478 |
| [1] | Li Yijie, YANG Xinyu, YANG Xiaomei. Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction of Multi-scale Residual Unet Fused with Attention Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 307-319. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jiajun, LU Yucheng, BAO Yifang, LI Yuxin, GENG Chen, HU Fuyuan, DAI Yakang. An Automatic Segmentation Method of Cerebral Arterial Tree in TOF-MRA Based on DBCNet [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 320-331. |
| [3] | TIAN Hui, WU Jie, BIAN Yun, ZHANG Zhiwei, SHAO Chengwei. Classification of Pancreatic Cystic Tumors Based on DenseNet and Transfer Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 270-279. |
| [4] | QIAN Chengyi,WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Imaging Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 220-238. |
| [5] | HUANG Min,LI Siyi,CHEN Junbo,ZHOU Dao. Progress of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting Technology and Its Clinical Application [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 207-219. |
| [6] | SHI Weicheng,JIN Zhaoyang,YE Zheng. Fast Multi-channel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based on PCAU-Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 39-51. |
| [7] | Qin ZHOU, Yuan-jun WANG. Groupwise Registration for Magnetic Resonance Image Based on Variational Inference [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 291-302. |
| [8] | Xiao CHANG,Xin CAI,Guang YANG,Sheng-dong NIE. Applications of Generative Adversarial Networks in Medical Image Translation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 366-380. |
| [9] | Ying-shan WANG, Ao-qi DENG, Jin-ling MAO, Zhong-qi ZHU, Jie SHI, Guang YANG, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Hong-zhi WANG. Automatic Segmentation of Knee Joint Synovial Magnetic Resonance Images Based on 3D VNetTrans [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 303-315. |
| [10] | Meng CHEN, Chen GENG, Yu-xin LI, Dao-ying GENG, Yi-fang BAO, Ya-kang DAI. Automatic Detection for Cerebral Aneurysms in TOF-MRA Images Based on Fuzzy Label and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 267-277. |
| [11] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [12] | Lu HUO,Xiao-xin HU,Qin XIAO,Ya-jia GU,Xu CHU,Luan JIANG. Automatic Segmentation of Breast and Fibroglandular Tissues in DCE-MR Images Based on nnU-Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 367-380. |
| [13] | LIU Peng, ZHONG Yu-min, WANG Li-jia. Automatic Segmentation of Right Ventricle in Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Image Based on a Dense and Multi-Scale U-net Method [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(4): 456-468. |
| [14] | ZHAO Shang-yi, WANG Yuan-jun. Classification of Alzheimer's Disease Patients Based on Magnetic Resonance Images and an Improved UNet++ Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(3): 321-331. |
| [15] | GONG Jin-chang, WANG Yu, WANG Yuan-jun. A Method for Segmentation of Glioma on Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Images Based on Wavelet Fusion and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(2): 131-143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||