
- Jun. 27, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 443-453.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20243113cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20243113
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
PANG Qifan1, WANG Zhichao2, WU Yupeng1, LI Jianqi1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-26
Published:2024-12-05
Online:2024-05-29
Contact:
* Tel: 021-62233775, E-mail: CLC Number:
PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453.
Table 2
Different K-space acquisition sequences under five K-space filling strategies
| K空间 相位编码顺序 | 单次饱和与 顺序采集 | 单次饱和与 中心优先采集 | 分段饱和与 顺序采集 | 分段饱和与 中心优先采集 | 分段饱和与 重排中心优先采集 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 127 | #1-1 | #4-31 | #3-32 |
| 2 | 2 | 125 | #1-2 | #4-29 | #1-32 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 16 | 16 | 97 | #1-16 | #4-1 | #1-25 |
| 17 | 17 | 95 | #1-17 | #3-31 | #3-24 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 32 | 32 | 65 | #1-32 | #3-1 | #1-17 |
| 33 | 33 | 63 | #2-1 | #2-31 | #3-16 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 48 | 48 | 33 | #2-16 | #2-1 | #1-9 |
| 49 | 49 | 31 | #2-17 | #1-31 | #3-8 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 63 | 63 | 3 | #2-31 | #1-3 | #3-1 |
| 64 | 64 | 1 | #2-32 | #1-1 | #1-1 |
| 65 | 65 | 2 | #3-1 | #1-2 | #2-1 |
| 66 | 66 | 4 | #3-2 | #1-4 | #4-1 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 80 | 80 | 32 | #3-16 | #1-32 | #4-8 |
| 81 | 81 | 34 | #3-17 | #2-2 | #2-9 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 96 | 96 | 64 | #3-32 | #2-32 | #4-16 |
| 97 | 97 | 66 | #4-1 | #3-2 | #2-17 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 112 | 112 | 96 | #4-16 | #3-32 | #4-24 |
| 113 | 113 | 98 | #4-17 | #4-2 | #2-25 |
| : | : | : | : | : | : |
| 127 | 127 | 126 | #4-31 | #4-30 | #2-32 |
| 128 | 128 | 128 | #4-32 | #4-32 | #4-32 |
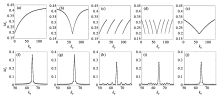
Fig. 2
Amplitude modulation curves after fat signal saturation for five different K-space filling strategies (the first row) and the corresponding point spread functions in image space (the second row). (a, f) single saturation with sequential acquisition; (b, g) single saturation with center-out acquisition; (c, h) multiple saturations with sequential acquisition; (d, i) multiple saturations with center-out acquisition; (e, j) multiple saturations with reordered center-out acquisition

Fig. 3
Simulated saturation images with saturation frequency at δ -3.5 (the first row) and δ 3.5 (the second row), and MTRasym maps (the third row), obtained without considering scalp fat. (a, f, k) single saturation with sequential acquisition; (b, g, l) single saturation with center-out acquisition; (c, h, m) segmental saturation with sequential acquisition; (d, i, n) segmental saturation with center-out acquisition; and (e, j, o) segmental saturation with reordered center-out acquisition
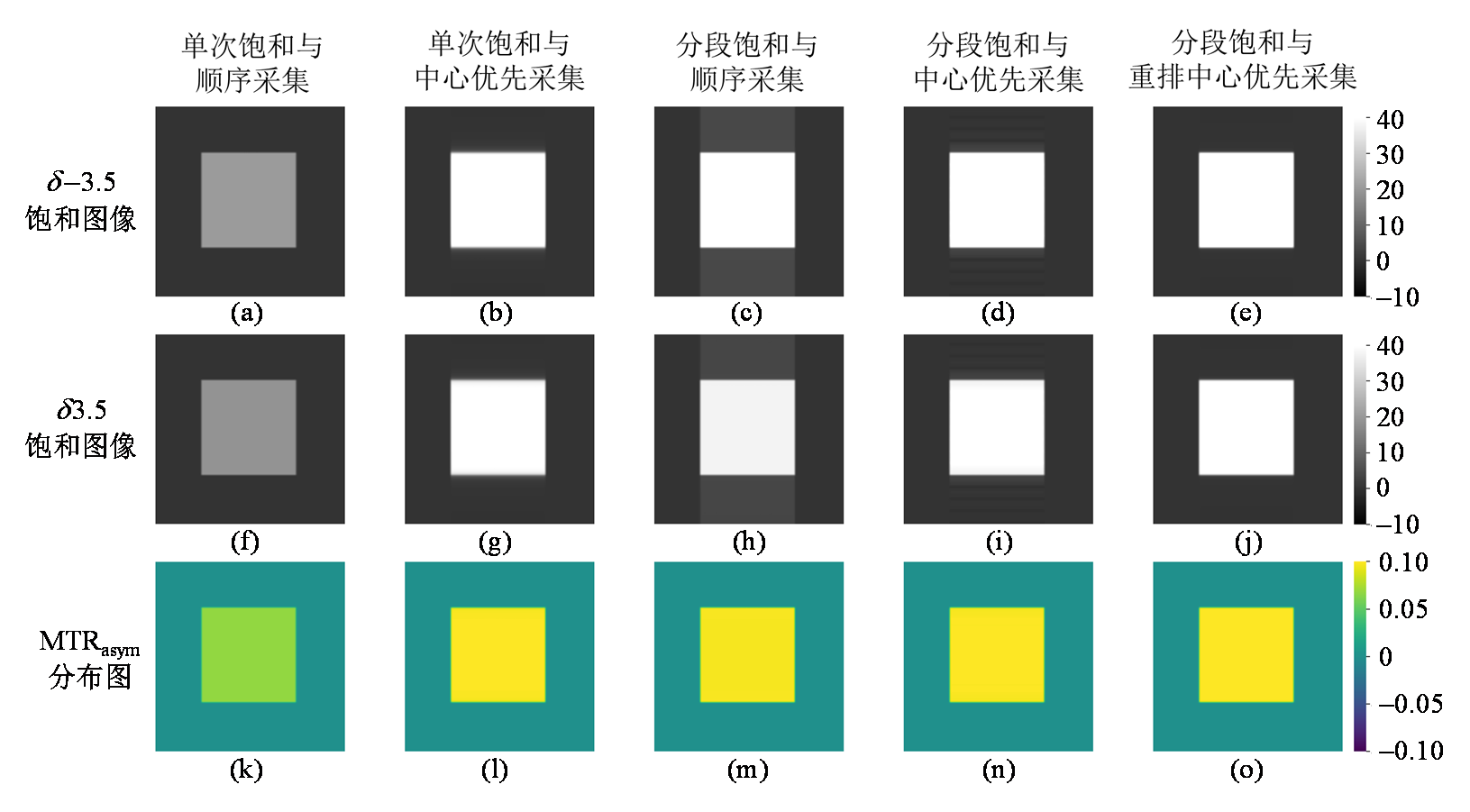

Fig. 4
Simulated saturation images with saturation frequency at δ -3.5 (the first row) and δ 3.5 (the second row), and MTRasym maps (the third row), obtained when considering scalp fat. (a, f, k) single saturation with sequential acquisition; (b, g, l) single saturation with center-out acquisition; (c, h, m) segmental saturation with sequential acquisition; (d, i, n) segmental saturation with center-out acquisition; and (e, j, o) segmental saturation with reordered center-out acquisition
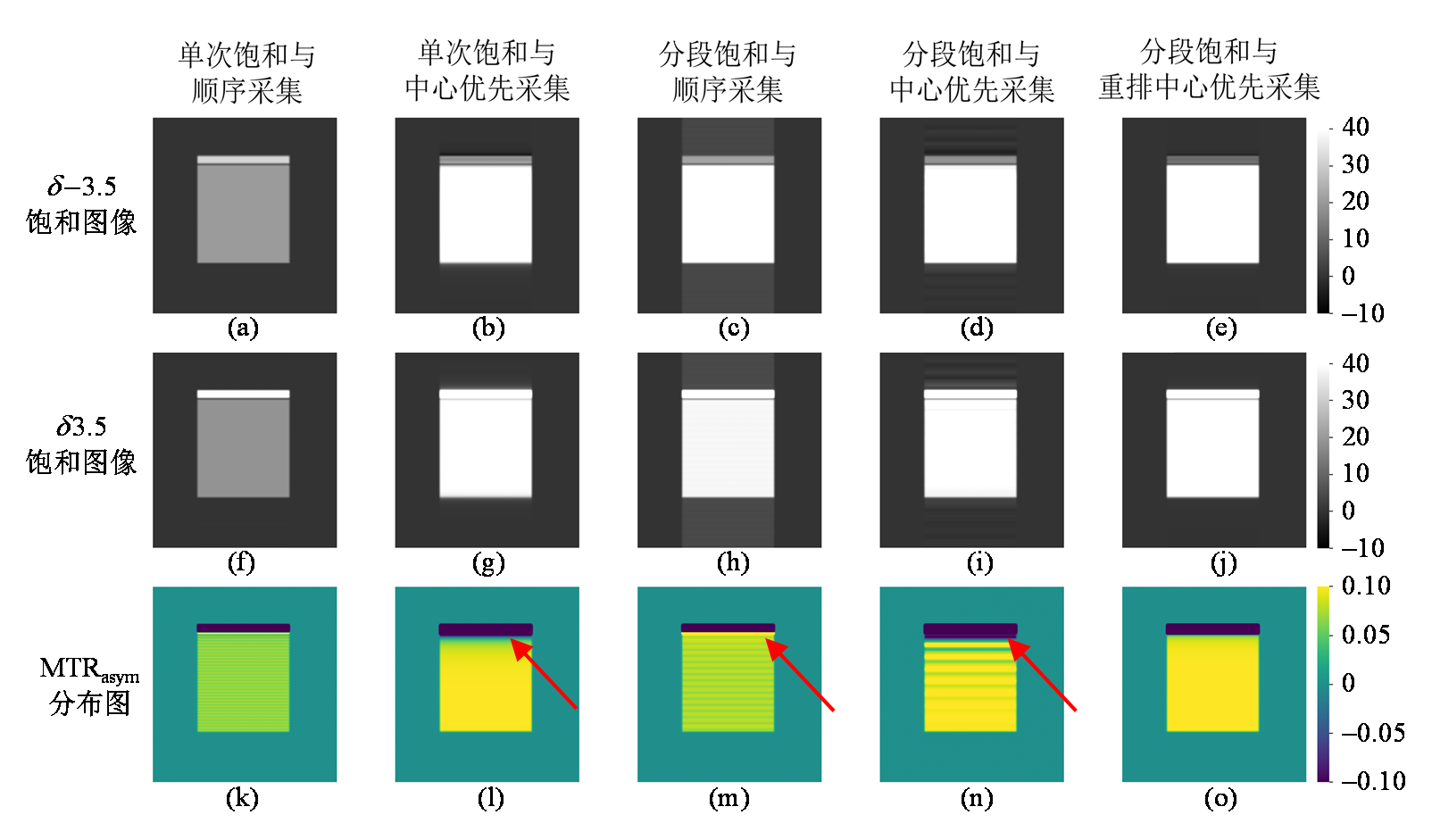
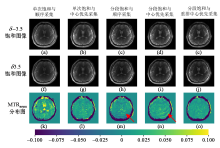
Fig. 6
Brain saturation images with saturation frequency at δ -3.5 (the first row) and δ 3.5 (the second row), and MTRasym maps (the third row), obtained from a healthy volunteer. (a, f, k) single saturation with sequential acquisition; (b, g, l) single saturation with center-out acquisition; (c, h, m) segmental saturation with sequential acquisition; (d, i, n) segmental saturation with center-out acquisition; and (e, j, o) segmental saturation with reordered center-out acquisition

| [1] |
WARD K M, ALETRAS A H, BALABAN R S. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST)[J]. J Magn Reson, 2000, 143(1): 79-87.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.1999.1956 pmid: 10698648 |
| [2] | ZHANG Y, LOU F Y, FANG K, et al. Review of a new molecular imaging method——deuterium metabolic spectroscopy and imaging[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(3): 356-365. |
|
张怡, 楼飞洋, 方可, 等. 分子影像新技术——氘代谢波谱及成像的综述与展望[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(3): 356-365.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20222999 |
|
| [3] |
WARD K M, BALABAN R S. Determination of pH using water protons and chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST)[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2000, 44(5): 799-802.
pmid: 11064415 |
| [4] |
ZHOU J Y, PAYEN J F, WILSON D A, et al. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI[J]. Nat Med, 2003, 9(8): 1085-1090.
doi: 10.1038/nm907 pmid: 12872167 |
| [5] | TAO Q, YI P W, WEI G J, et al. pH Imaging based on chemical exchange saturation transfer: Principles, methods, applications and recent progresses[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2018, 35(4): 505-519. |
|
陶泉, 易佩伟, 魏国境, 等. 基于CEST机制的pH成像方法、原理和应用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2018, 35(4): 505-519.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20182664 |
|
| [6] |
TERRENO E, CASTELLI D D, CRAVOTTO G, et al. Ln(iii)-dotamgly complexes: A versatile series to assess the determinants of the efficacy of paramagnetic chemical exchange saturation transfer agents for magnetic resonance imaging applications[J]. Invest Radiol, 2004, 39(4): 235-243.
pmid: 15021328 |
| [7] |
ZHAO X, WEN Z, HUANG F, et al. Saturation power dependence of amide proton transfer image contrasts in human brain tumors and strokes at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 66(4): 1033-1041.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22891 pmid: 21394783 |
| [8] | HEO H Y, JONES C K, HUA J, et al. Whole-brain amide proton transfer (APT) and nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE) imaging in glioma patients using low-power steady-state pulsed chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging at 7T[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 44(1): 41-50. |
| [9] |
SUN C, ZHAO Y, ZU Z. Validation of the presence of fast exchanging amine CEST effect at low saturation powers and its influence on the quantification of APT[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 90(4): 1502-1517.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29742 pmid: 37317709 |
| [10] | FOO L S, HARSTON G, MEHNDIRATTA A, et al. Clinical translation of amide proton transfer (APT) MRI for ischemic stroke: A systematic review (2003-2020)[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2021, 11(8): 3797-3811. |
| [11] | ZAISS M, EHSES P, SCHEFFLER K. Snapshot-CEST: Optimizing spiral-centric-reordered gradient echo acquisition for fast and robust 3D CEST MRI at 9.4 T[J]. NMR Biomed, 2018, 31(4): e3879. |
| [12] |
ZHOU J, BLAKELEY J O, HUA J, et al. Practical data acquisition method for human brain tumor amide proton transfer (APT) imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2008, 60(4): 842-849.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21712 pmid: 18816868 |
| [13] |
DESHMANE A, ZAISS M, LINDIG T, et al. 3D gradient echo snapshot CEST MRI with low power saturation for human studies at 3T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81(4): 2412-2423.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27569 pmid: 30431179 |
| [14] |
KRISHNAMOORTHY G, NANGA R P R, BAGGA P, et al. High quality three-dimensional gagCEST imaging of in vivo human knee cartilage at 7 Tesla[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2017, 77(5): 1866-1873.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26265 pmid: 27174078 |
| [15] | HAN P, CHEEMA K, LEE H L, et al. Whole-brain steady-state CEST at 3 T using MR multitasking[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 87(5): 2363-2371. |
| [16] |
JONES C K, POLDERS D, HUA J, et al. In vivo three-dimensional whole-brain pulsed steady-state chemical exchange saturation transfer at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 67(6): 1579-1589.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.23141 pmid: 22083645 |
| [17] |
SCHMITT B, ZAISS M, ZHOU J, et al. Optimization of pulse train presaturation for CEST imaging in clinical scanners[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 65(6): 1620-1629.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22750 pmid: 21337418 |
| [18] |
ZAID ALKILANI A, CUKUR T, SARITAS E U. Fd-Net: An unsupervised deep forward-distortion model for susceptibility artifact correction in EPI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2024, 91(1): 280-296.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29851 pmid: 37811681 |
| [19] |
LI H, FOX-NEFF K, VAUGHAN B, et al. Parallel EPI artifact correction (PEAC) for N/2 ghost suppression in neuroimaging applications[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2013, 31(6): 1022-1028.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.03.021 pmid: 23601363 |
| [20] |
HAASE A, FRAHM J, MATTHAEI D, et al. FLASH imaging: Rapid NMR imaging using low flip-angle pulses. 1986[J]. J Magn Reson, 2011, 213(2): 533-541.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2011.09.021 pmid: 22152368 |
| [21] |
SUN P Z, CHEUNG J S, WANG E, et al. Fast multislice pH-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI with unevenly segmented RF irradiation[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 65(2): 588-594.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22628 pmid: 20872859 |
| [22] |
KIM H, PARK S, HU R, et al. 3D CEST MRI with an unevenly segmented RF irradiation scheme: A feasibility study in brain tumor imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 90(6): 2400-2410.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29810 pmid: 37526017 |
| [23] | 李建奇, 林江. 现代体部磁共振诊断学原理及技术分册[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2022. |
| [24] | HELD C, JUNKER D, WU M, et al. Intraindividual difference between supraclavicular and subcutaneous proton density fat fraction is associated with cold-induced thermogenesis[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2022, 12(5): 2877-2890. |
| [25] |
ZHAO Y, YAN X, ZHANG Z, et al. Self-adapting multi-peak water-fat reconstruction for the removal of lipid artifacts in chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 82(5): 1700-1712.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27859 pmid: 31241219 |
| [26] | HUANG J, LAI J H C, TSE K H, et al. Deep neural network based CEST and AREX processing: Application in imaging a model of alzheimer's disease at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 87(3): 1529-1545. |
| [27] | 王志超. 化学交换饱和转移成像对比度优化及信号提取方法的研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2021. |
| [28] | HAACKE E M. Magnetic resonance imaging : Physical principles and sequence design[M]. New York: Wiley, 1999. |
| [29] |
YUSHKEVICH P A, PIVEN J, HAZLETT H C, et al. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability[J]. Neuroimage, 2006, 31(3): 1116-1128.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.015 pmid: 16545965 |
| [30] |
KIM M, GILLEN J, LANDMAN B A, et al. Water saturation shift referencing (WASSR) for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) experiments[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2009, 61(6): 1441-1450.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21873 pmid: 19358232 |
| [31] |
ZHANG J, ZHU W, TAIN R, et al. Improved differentiation of low-grade and high-grade gliomas and detection of tumor proliferation using APT contrast fitted from Z-Spectrum[J]. Mol Imaging Biol, 2018, 20(4): 623-631.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1154-y pmid: 29313159 |
| [32] |
TIETZE A, BLICHER J, MIKKELSEN I K, et al. Assessment of ischemic penumbra in patients with hyperacute stroke using amide proton transfer (APT) chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI[J]. NMR Biomed, 2014, 27(2): 163-174.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3048 pmid: 24288260 |
| [33] |
ZHU H, JONES C K, VAN ZIJL P C, et al. Fast 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging of the human brain[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2010, 64(3): 638-644.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22546 pmid: 20632402 |
| [34] |
MCMAHON M T, GILAD A A, ZHOU J, et al. Quantifying exchange rates in chemical exchange saturation transfer agents using the saturation time and saturation power dependencies of the magnetization transfer effect on the magnetic resonance imaging signal (QUEST and QUESP): pH calibration for poly-L-lysine and a starburst dendrimer[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2006, 55(4): 836-847.
pmid: 16506187 |
| [35] | ZAISS M, ANGELOVSKI G, DEMETRIOU E, et al. QUESP and QUEST revisited-fast and accurate quantitative CEST experiments[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79(3): 1708-1721. |
| [36] |
DESMOND K L, STANISZ G J. Understanding quantitative pulsed CEST in the presence of MT[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 67(4): 979-990.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.23074 pmid: 21858864 |
| [37] | SUN P Z, WANG Y, DAI Z, et al. Quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (qCEST) MRI-RF spillover effect-corrected omega plot for simultaneous determination of labile proton fraction ratio and exchange rate[J]. Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2014, 9(4): 268-275. |
| [38] | MCVICAR N, LI A X, GONCALVES D F, et al. Quantitative tissue pH measurement during cerebral ischemia using amine and amide concentration-independent detection (AACID) with MRI[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2014, 34(4): 690-698. |
| [39] | JONES C K, HUANG A, XU J, et al. Nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE) imaging in the human brain at 7 T[J]. NeuroImage, 2013, 77: 114-124. |
| [40] | HEO H Y, ZHANG Y, LEE D H, et al. Quantitative assessment of amide proton transfer (APT) and nuclear overhauser enhancement (NOE) imaging with extrapolated semi-solid magnetization transfer reference (EMR) signals: Application to a rat glioma model at 4.7 Tesla[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75(1): 137-149. |
| [41] |
ZHOU J Y, ZAISS M, KNUTSSON L, et al. Review and consensus recommendations on clinical APT-weighted imaging approaches at 3T: Application to brain tumors[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 88(2): 546-574.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29241 pmid: 35452155 |
| [42] |
GLANG F, DESHMANE A, PROKUDIN S, et al. DeepCEST 3T: Robust MRI parameter determination and uncertainty quantification with neural networks-application to CEST imaging of the human brain at 3T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 84(1): 450-466.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28117 pmid: 31821616 |
| [43] | WANG Z C, ZHANG J L, ZHAO Y, et al. CEST imaging of the abdomen with neural network fitting[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(1): 33-42. |
|
王志超, 张记磊, 赵羽, 等. 基于神经网络拟合的腹部化学交换饱和转移成像[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(1): 33-42.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212903 |
|
| [44] | SHI W C, JIN Z Y, YE Z. Fast multi-channel magnetic resonance imaging based on PCAU-Net[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2023, 40(1): 39-51. |
|
施伟成, 金朝阳, 叶铮. 基于PCAU-Net的快速多通道磁共振成像方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2023, 40(1): 39-51.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20222992 |
|
| [45] | LI Y J, YANG X Y, YANG X M. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction of multi-scale residual Unet fused with attention mechanism[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2023, 40(3): 307-319. |
|
李奕洁, 杨馨雨, 杨晓梅. 融合注意力机制的多尺度残差Unet的磁共振图像重建[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2023, 40(3): 307-319.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20223040 |
|
| [46] |
WINDSCHUH J, ZAISS M, EHSES P, et al. Assessment of frequency drift on CEST MRI and dynamic correction: Application to gagCEST at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81(1): 573-582.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27367 pmid: 29851141 |
| [47] |
KASAHARA S, MIKI Y, MORI N, et al. Spin-echo T1-weighted imaging of the brain with interleaved acquisition and presaturation pulse at 3 T: A feasibility study before clinical use[J]. Acad Radiol, 2009, 16(7): 852-857.
doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2008.12.026 pmid: 19375955 |
| [48] | DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE T Inform Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306. |
| [49] | ZHAO Y, SUN C S, ZU Z L. Assignment of molecular origins of NOE signal at -3.5 ppm in the brain[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 90(2): 673-685. |
| [50] |
HUA J, JONES C K, BLAKELEY J, et al. Quantitative description of the asymmetry in magnetization transfer effects around the water resonance in the human brain[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58(4): 786-793.
pmid: 17899597 |
| [1] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [2] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [3] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [4] |
De-gang TANG,Hong-chuang LI,Xiao-ling LIU,Lei SHI,Hai-dong LI,Chao-hui YE,Xin ZHOU.
A Simulation Study on the Effect of the High Permittivity Materials Geometrical Structure on the Transmit Field    |
| [5] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [6] | Yan MA, Cang-ju XING, Liang XIAO. Knee Joint Image Segmentation and Model Construction Based on Cascaded Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| [7] | Jun LUO, Sheng-ping LIU, Xing YANG, Jia-sheng WANG, Ye LI. Design of a 5 T Non-magnetic Magnetic Resonance Radio Frequency Power Amplifier [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 163-173. |
| [8] | Ju-min ZHANG,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Dual-modal MRI T1-T2 Contrast Agent Based on Dynamic Organic Gadolinium Nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 11-19. |
| [9] | Zhi-chao WANG,Ji-lei ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Ting HUA,Guang-yu TANG,Jian-qi LI. CEST Imaging of the Abdomen with Neural Network Fitting [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 33-42. |
| [10] | Han-wei WANG,Hao WU,Jing TIAN,Jun-feng ZHANG,Peng ZHONG,Li-zhao CHEN,Shu-nan WANG. The Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Parameters of T2/FLAIR Mismatch Sign in Evaluating the Molecular Typing of Lower-grade Gliomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 56-63. |
| [11] | Long XIAO,Xiao-lei ZHU,Ye-qing HAN,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Design and Application of Micellar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Molecular Probe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 474-490. |
| [12] | Chong-wu WANG,Xi HUANG,Lei SHI,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Cathepsin B Triggered Hyperpolarization 129Xe MRI Probe for Ultra-Sensitive Lung Cancer Cells Detection [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 336-344. |
| [13] | Ying-dan HU,Yue CAI,Xu-xia WANG,Si-jie LIU,Yan KANG,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN. Magnetic Resonance Imaging the Brain Structures Involved in Nicotine Susceptibility in Rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 345-355. |
| [14] | Shi-ju YAN,Yong-sen HAN,Guang-yu TANG. An Improved Level Set Algorithm for Prostate Region Segmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 356-366. |
| [15] | HE Hong-yan, WEI Shu-feng, WANG Hui-xian, YANG Wen-hui. Matrix Gradient Coil: Current Research Status and Perspectives [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(1): 140-153. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 83
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 126
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||