
- Nov. 14, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 155-162.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212904
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
De-gang TANG1,2,Hong-chuang LI1,2,Xiao-ling LIU1,2,Lei SHI1,2,Hai-dong LI1,2,Chao-hui YE1,2,Xin ZHOU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-01
Published:2022-06-05
Online:2021-05-15
Contact:
Xin ZHOU
E-mail:xinzhou@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
De-gang TANG,Hong-chuang LI,Xiao-ling LIU,Lei SHI,Hai-dong LI,Chao-hui YE,Xin ZHOU. A Simulation Study on the Effect of the High Permittivity Materials Geometrical Structure on the Transmit Field

Fig.2
The schematic simulation model diagrams of high permittivity pads (dark grey) with different geometrical structures (all coils are hidden). (a) Without pads; (b) With a quartered cylindrical pad; (c) With four cuboid pads that surround the phantom symmetrically; (d) With three cuboid pads on the same side; (e) With a single annular sector column with a degree of 120°

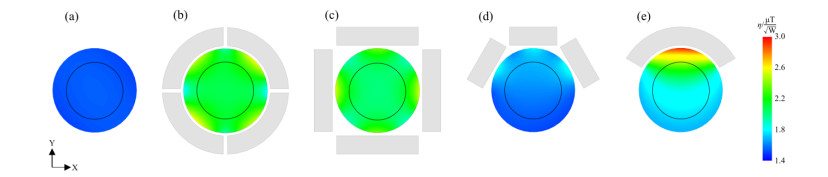
Fig.3
The simulated transmit efficiency maps in the central transverse plane of the phantom corresponding to high permittivity pads with different geometrical structures. (a) Without pads; (b) With a quartered cylindrical pad; (c) With four cuboid pads that surround the phantom symmetrically; (d) With three cuboid pads on the same side; (e) With a single annular sector column with a degree of 120°
| 1 |
UGURBIL K Imaging at ultrahigh magnetic fields: history, challenges, and solutions[J]. Neuroimage, 2018, 168, 7-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.07.007 |
| 2 |
YANG Q X, WANG J, ZHANG X, et al Analysis of wave behavior in lossy dielectric samples at high field[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2002, 47 (5):982-989.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.10137 |
| 3 |
SCHICK F Whole-body MRI at high field: technical limits and clinical potential[J]. Eur Radiol, 2005, 15 (5):946-959.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2678-0 |
| 4 |
DIETRICH O, REISER M F, SCHOENBERG S O Artifacts in 3-T MRI: Physical background and reduction strategies[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2008, 65 (1):29-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.11.005 |
| 5 |
KANGARLU A, BAERTLEIN B A, LEE R, et al Dielectric resonance phenomena in ultra high field MRI[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 1999, 23 (6):821-831.
doi: 10.1097/00004728-199911000-00003 |
| 6 |
HUANG Q H, GAO Y, XIN X G Study on the law of B1 field homogeneity and SAR inside human body varying with field strength at high and ultra-high field MR[J]. Chin J Biological Eng, 2013, 32 (1):21-27.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2013.01.004 |
|
黄绮华, 高勇, 辛学刚 高场和超高场MR下人体内B1场均匀性及SAR随场强变化规律的研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2013, 32 (1):21-27.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2013.01.004 |
|
| 7 | OSCH M J P V, WEBB A G Safety of ultra-high field MRI: What are the specific risks?[J]. Curr Radiol Rep, 2014, 2 (8):1-8. |
| 8 |
DOTY F D, ENTZMINGER G, KULKARNI J, et al Radio frequency coil technology for small-animal MRI[J]. NMR Biomed, 2007, 20 (3):304-325.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.1149 |
| 9 |
GULSEN G, MUFTULER L T, NALCIOGLU O A double end-cap birdcage RF coil for small animal whole body imaging[J]. J Magn Reson, 2002, 156 (2):309-312.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.2002.2547 |
| 10 |
DARDZINSKI B J, LI S H, COLLINS C M, et al A birdcage coil tuned by RF shielding for application at 9.4 T[J]. J Magn Reson, 1998, 131 (1):32-38.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.1997.1334 |
| 11 |
LEE K H, CHENG M C, CHAN K C, et al Performance of large-size superconducting coil in 0.21 T MRI system[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2004, 51 (11):2024-2030.
doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.831539 |
| 12 |
LIN I T, YANG H C, HSIEH C W, et al Human hand imaging using a 20 cm high-temperature superconducting coil in a 3 T magnetic resonance imaging system[J]. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107 (12):124701.
doi: 10.1063/1.3431538 |
| 13 | LIAO Z W, CHEN J F, YANG C S, et al A design scheme for 1H/31P dual-nuclear parallel MRI coil[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37 (3):273-282. |
| 廖志文, 陈俊飞, 杨春升, 等 1H/31P双核并行磁共振成像线圈的研究与设计[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37 (3):273-282. | |
| 14 | FENG T, CHEN J F, ZHANG Z, et al A design of short dead-time RF coil and RF switch for low-field NMR[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38 (1):1-11. |
| 冯涛, 陈俊飞, 张震, 等 低场核磁共振短死时间射频线圈与射频开关的设计[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38 (1):1-11. | |
| 15 |
WEBB A G, VAN DE MOORTELE P F The technological future of 7 T MRI hardware[J]. NMR Biomed, 2016, 29 (9):1305-1315.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3315 |
| 16 |
ANDREYCHENKO A, BLUEMINK J J, RAAIJMAKERS A J E, et al Improved RF performance of travelling wave MR with a high permittivity dielectric lining of the bore[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 70 (3):885-894.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24512 |
| 17 |
YANG Q X, MAO W, WANG J, et al Manipulation of image intensity distribution at 7.0 T: Passive RF shimming and focusing with dielectric materials[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2006, 24 (1):197-202.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.20603 |
| 18 |
FRANKLIN K M, DALE B M, MERKLE E M Improvement in B1-inhomogeneity artifacts in the abdomen at 3 T MR imaging using a radiofrequency cushion[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2008, 27 (6):1443-1447.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.21164 |
| 19 |
DE HEER P, BRINK W M, KOOIJ B J, et al Increasing signal homogeneity and image quality in abdominal imaging at 3 T with very high permittivity materials[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 68 (4):1317-1324.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24438 |
| 20 |
ZIVKOVIC I, TEEUWISSE W, SLOBOZHANYUK A, et al High permittivity ceramics improve the transmit field and receive efficiency of a commercial extremity coil at 1.5 tesla[J]. J Magn Reson, 2019, 299, 59-65.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2018.12.013 |
| 21 |
SICA C T, RUPPRECHT S, HOU R J, et al Toward whole-cortex enhancement with a ultrahigh dielectric constant helmet at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 83 (3):1123-1134.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27962 |
| 22 |
LEE B Y, ZHU X H, RUPPRECHT S, et al Large improvement of RF transmission efficiency and reception sensitivity for human in vivo P-31 MRS imaging using ultrahigh dielectric constant materials at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2017, 42, 158-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.07.019 |
| 23 |
RUPPRECHT S, SICA C T, CHEN W, et al Improvements of transmit efficiency and receive sensitivity with ultrahigh dielectric constant (uHDC) ceramics at 1.5 T and 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79 (5):2842-2851.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26943 |
| 24 |
VAN GEMERT J, BRINK W, REMIS R, et al A simulation study on the effect of optimized high permittivity materials on fetal imaging at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 82 (5):1822-1831.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27849 |
| 25 |
BRINK W M, WEBB A G High permittivity pads reduce specific absorption rate, improve B-1 homogeneity, and increase contrast-to-noise ratio for functional cardiac MRI at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 71 (4):1632-1640.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24778 |
| 26 | SCHMIDT R, WEBB A A new approach for electrical properties estimation using a global integral equation and improvements using high permittivity materials[J]. J Magn Reson, 2016, 262, 814. |
| 27 |
VAN GEMERT J, BRINK W, WEBB A, et al High-permittivity pad design tool for 7 T neuroimaging and 3 T body imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81 (5):3370-3378.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27629 |
| 28 |
BRINK W M, REMIS R F, WEBB A G A theoretical approach based on electromagnetic scattering for analysing dielectric shimming in high-field MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75 (5):2185-2194.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25783 |
| 29 | LUO M, HU C, ZHUANG Y, et al Numerical assessment of the reduction of specific absorption rate by adding high dielectric materials for fetus MRI at 3 T[J]. Biomed Eng-Biomed Tech, 2016, 61 (4):455-461. |
| 30 |
SEO J H, HAN S D, KIM K N Improvements in magnetic field intensity and uniformity for small-animal MRI through a high-permittivity material attachment[J]. Electron Lett, 2016, 52 (11):898-899.
doi: 10.1049/el.2016.0638 |
| 31 |
RUYTENBERG T, O'REILLY T P, WEBB A G Design and characterization of receive-only surface coil arrays at 3 T with integrated solid high permittivity materials[J]. J Magn Reson, 2020, 311, 106681.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2019.106681 |
| 32 |
CHEN W, LEE B Y, ZHU X H, et al Tunable ultrahigh dielectric constant (TuHDC) ceramic technique to largely improve RF coil efficiency and MR imaging performance[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39 (10):3187-3197.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2988834 |
| 33 | 方俊鑫, 殷之文 电介质物理学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989. |
| 34 |
WEBB A G Dielectric materials in magnetic resonance[J]. Concepts Magn Reson Part A, 2011, 38A (4):148-184.
doi: 10.1002/cmr.a.20219 |
| 35 |
HOULT D I The principle of reciprocity in signal strength calculations—A mathematical guide[J]. Concepts Magn Reson, 2000, 12 (4):173-187.
doi: 10.1002/1099-0534(2000)12:4<173::AID-CMR1>3.0.CO;2-Q |
| 36 | 罗超. 基于超材料的3 T磁共振射频接收线圈性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2016. |
| 37 | 张巍巍. 基于1.5 T磁共振系统体线圈电磁参数分析及共振频率算法实现[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. |
| 38 |
XIN S X, HUANG Q, GAO Y, et al Fetus MRI at 7 T: B1 shimming strategy and SAR safety implications[J]. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2013, 61 (5):2146-2152.
doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2247053 |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [3] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [4] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [5] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [6] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [7] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [8] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [9] | Yan MA, Cang-ju XING, Liang XIAO. Knee Joint Image Segmentation and Model Construction Based on Cascaded Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| [10] | Jun LUO, Sheng-ping LIU, Xing YANG, Jia-sheng WANG, Ye LI. Design of a 5 T Non-magnetic Magnetic Resonance Radio Frequency Power Amplifier [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 163-173. |
| [11] | Ju-min ZHANG,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Dual-modal MRI T1-T2 Contrast Agent Based on Dynamic Organic Gadolinium Nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 11-19. |
| [12] | Zhi-chao WANG,Ji-lei ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Ting HUA,Guang-yu TANG,Jian-qi LI. CEST Imaging of the Abdomen with Neural Network Fitting [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 33-42. |
| [13] | Han-wei WANG,Hao WU,Jing TIAN,Jun-feng ZHANG,Peng ZHONG,Li-zhao CHEN,Shu-nan WANG. The Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Parameters of T2/FLAIR Mismatch Sign in Evaluating the Molecular Typing of Lower-grade Gliomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 56-63. |
| [14] | Long XIAO,Xiao-lei ZHU,Ye-qing HAN,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Design and Application of Micellar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Molecular Probe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 474-490. |
| [15] | Ying-dan HU,Yue CAI,Xu-xia WANG,Si-jie LIU,Yan KANG,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN. Magnetic Resonance Imaging the Brain Structures Involved in Nicotine Susceptibility in Rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 345-355. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||