
- Nov. 6, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 474-490.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212933
Previous Articles Next Articles
Long XIAO1,2,Xiao-lei ZHU1,Ye-qing HAN1,2,Shi-zhen CHEN1,2,*( ),Xin ZHOU1,2,*(
),Xin ZHOU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-06
Published:2021-12-05
Online:2021-11-29
Contact:
Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU
E-mail:chenshizhen@wipm.ac.cn;xinzhou@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Long XIAO,Xiao-lei ZHU,Ye-qing HAN,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Design and Application of Micellar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Molecular Probe[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 474-490.
Table 1
An application overview of commonly used polymers as micellar MRI contrast agent carriers
| 胶束链段 | 负载物 | 胶束直径 | 参考文献 |
| 聚乙二醇/聚丙烯酸-聚己内酯(PEG/PAA-PCL) | T1、T2造影剂及其他 | 100~200 nm | [ |
| 聚乙二醇-聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺(PEG-PNIPAM) | T1、T2造影剂及其他 | 50~300 nm | [ |
| 聚乙二醇-聚赖氨酸(PEG-Plys) | T1、T2造影剂及其他 | 50~200 nm | [ |
| 聚乙二醇-聚天冬氨酸(PEG-PAsp) | T1造影剂及其他 | 50~200 nm | [ |
| 聚环氧乙烷-聚N, N-二甲基丙烯酰胺(PEO-PDMA) | T1造影剂 | 70 nm | [ |
| 脂质体(lipid) | T1、T2造影剂及其他 | 50~300 nm | [ |
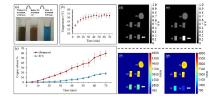
Fig.2
Influence of ultrasound heating on copper release from micelle nanocarriers and MRI detection. (a) Photos of three cuvettes containing loaded micelles with PEI: (Left) After 4 h at room temperature without US treatment; (Middle) Baseline solution (initial state); (Right) After US treatment for 50 min. (b) The temperature elevation resulting from the US. (c) The resulting copper release percentages as a function of time (n=3) for both US treated and untreated solutions. Note the substantial effect of the (d, e) MRI T1 weighted and (f, g) T1 mapping images of cuvettes (d, f) before and (e, g) after US treatment[45]
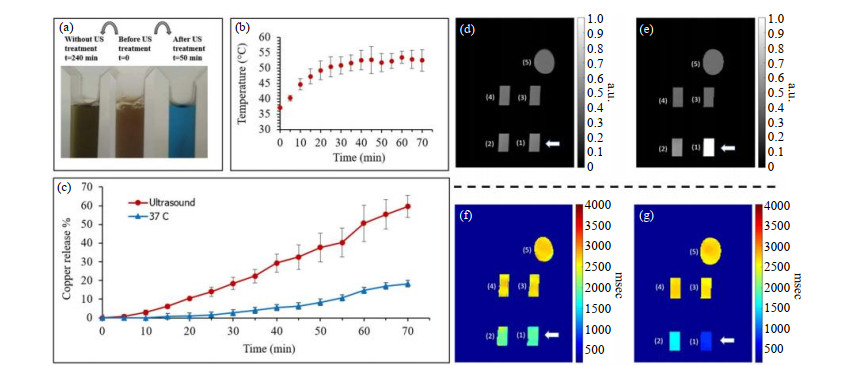
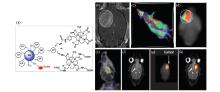
Fig.4
The structure of G5 dendrimer and detection in animal model of glioma. (a) Dylight680 (DL680) was conjugated with Gd-DOTA or Eu-DOTA-Gly4 preloaded G5 dendrimer. (b) The agent was Gd-G5-DL680 and injected at a dose of 0.03 mmol Gd/kg. In vivo optical image obtained under simultaneous white light and filtered excitation detected with the emission filter set at 750 nm demonstrating fluorescence in the glioma. (c) Ex vivo fluorescence imaging of rat brain clearly shows the selective accumulation of the Gd-G5-DL680 within the tumor. (d) Tumor is indicated as dotted white circle. (e) The in vivo fluorescent image of the rat head overlayed on an X-ray image shows the presence of Eu-DOTA-Gly4-G5-DL680 nanoparticle in the U87 tumor in the brain. (f) The coronal MR image shows the location of the U87 tumor. (g) The ex vivo fluorescence image of whole brain also detected the nanoparticle in the brain. (h) The ex vivo fluorescence image was also overlayed on the MR image to show that the nanoparticle was located in the U87 glioma[55]
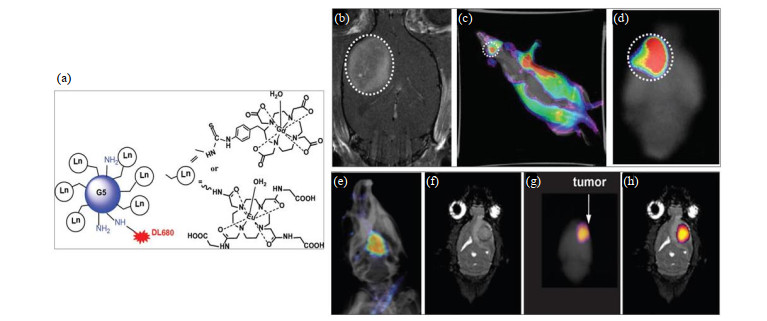
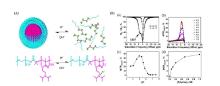
Fig.5
The use of CEST for monitoring the pH-responsive behaviors of PEG-b-PDPA polymers. (A) The micelle-unimer equilibrium in the block copolymer, PEG114-b-PDPA116, is exquisitely sensitive to pH. (B) (a) Representative CEST spectra of PEG-b-PDPA at pH 5.0 and 7.5, respectively; (b) A plot of MTRasym versus the saturation frequency offset at the pH range between 5.0 and 7.5; (c) A plot of MTRasym versus pH; (d) A plot of MTRasym versus PEG-b-PDPA copolymer concentration at a fixed pH of 5.8[56]
Table 2
Major environmentally sensitive repeat unit structures and environmental response types
| 聚合物名称 | 重复单元结构 | 类型 | 响应范围 |
| 聚(N-乙烯基吡啶) Poly(N-vinyl pyridine) | 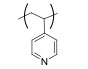 | pH敏感型 | pH:3~5 |
| 聚(丙烯酸) Poly(Acrylic acid) | 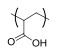 | pH敏感型 | pH:5~7 |
| 葡聚糖Dextran | 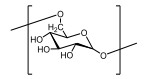 | pH敏感型 | pH:3~5 |
| 聚(L-天冬氨酸) Poly(L-aspartic acid) | 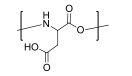 | pH敏感型 | pH:6~8 |
| 聚(L-组氨酸) Poly(L-histidine) | 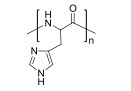 | pH敏感型 | pH:5~7 |
| 聚己内酯Poly(ε-carprolactone) | 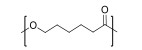 | pH及温度敏感型 | pH:5~7 T:35~40 ℃ |
| 聚(异丙基丙烯酰胺)Poly(Isopropyl-acrylamide) | 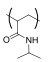 | 温度敏感型 | T:35~40 ℃ |
| 聚(丙交酯-共-乙交酯)Poly(Lacide-co-glycolide) | 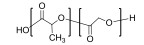 | 温度敏感型 | T:30~40 ℃ |
| 1 |
WEISSLEDER R , MAHMOOD U . Molecular imaging[J]. Radiol, 2001, 219 (2): 316- 333.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.219.2.r01ma19316 |
| 2 | BADER H , RINGSDORF H , SCHMIDT B . Watersoluble polymers in medicine[J]. Macromol Mater Eng, 1984, 123 (1): 457- 485. |
| 3 |
YANG L J , ZHANG C R , LIU J J , et al. ICG-conjugated and 125I-labeled polymeric micelles with high biosafety for multimodality imaging-guided photothermal therapy of tumors[J]. Adv Healthcare Mater, 2020, 9 (5): 1901616.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.201901616 |
| 4 |
CAO Y , LIU M , ZHANG K C , et al. Poly(glycerol) used for constructing mixed polymeric micelles as T1 MRI contrast agent for tumor-targeted imaging[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2017, 18 (1): 150- 158.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01437 |
| 5 |
LU L J , WANG Y , CAO M H , et al. A novel polymeric micelle used for in vivo MR imaging tracking of neural stem cells in acute ischemic stroke[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7 (25): 15041- 15052.
doi: 10.1039/C7RA00345E |
| 6 |
SU P F , WU H X , WANG Z , et al. Biodegradable catalase-modified micelles as ultrasound contrast agents for inflammation detection[J]. Part Part Syst Charact, 2020, 37 (10): 2000193.
doi: 10.1002/ppsc.202000193 |
| 7 |
ELSAID Z , TAYLOR K M G , PURI S , et al. Mixed micelles of lipoic acid-chitosan-poly (ethylene glycol) and distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine-poly (ethylene glycol) for tumor delivery[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2017, 101, 228- 242.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.02.001 |
| 8 |
WAN Z A , ZHENG R H , MOHARIL P , et al. Polymeric micelles in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26 (5): 1220.
doi: 10.3390/molecules26051220 |
| 9 |
SHEN D , SHEN Y , CHEN Q , et al. Macrophage escape by cholesterol-polyoxyethylene sorbitol oleate micelles for pulmonary delivery[J]. Nanomedicine, 2020, 15 (5): 489- 509.
doi: 10.2217/nnm-2019-0376 |
| 10 | WANG Z , DENG X P , DING J S , et al. Mechanisms of drug release in pH-sensitive micelles for tumour targeted drug delivery system: A review[J]. Int J Pharm, 2018, 535 (1, 2): 253- 260. |
| 11 | HONG G B , ZHOU J X , YUAN R X . Folate-targeted polymeric micelles loaded with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide: combined small size and high MRI sensitivity[J]. Int J Nanomed, 2012, 7, 2863- 2872. |
| 12 |
GONG F M , ZHANG Z Q , CHEN X D , et al. A dual ligand targeted nanoprobe with high MRI sensitivity for diagnosis of breast cancer[J]. Chinese J Polym Sci, 2014, 32 (3): 321- 332.
doi: 10.1007/s10118-014-1399-8 |
| 13 |
CUI M Y , DONG Z , CAI H , et al. Folate‑targeted polymeric micelles loaded with superparamagnetic iron oxide as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging of a human tongue cancer cell line[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16 (5): 7597- 7602.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7565 |
| 14 |
XIE X X , CHEN Y , CHEN Z Y , et al. Polymeric hybrid nanomicelles for cancer theranostics: an efficient and precise anticancer strategy for the codelivery of doxorubicin/miR-34a and magnetic resonance imaging[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11 (47): 43865- 43878.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b14908 |
| 15 |
YAN L , AMIRSHAGHAGHI A , HUANG D , et al. Protoporphyrin IX (PpIX)-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION) nanoclusters for magnetic resonance imaging and photodynamic therapy[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28 (16): 1707030.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201707030 |
| 16 |
DENG L H , JIANG H , LU F L , et al. Size and PEG length-controlled PEGylated monocrystalline superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite for MRI contrast agent[J]. Int J Nanomed, 2021, 16, 201- 211.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S271461 |
| 17 |
HEMMATI , K , ALIZADEH R , GHAEMY M . Synthesis and characterization of controlled drug release carriers based on functionalized amphiphilic block copolymers and super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Polym Adv Technol, 2016, 27 (4): 504- 514.
doi: 10.1002/pat.3697 |
| 18 |
ZHANG X M , GUO K , LI L H , et al. Multi-stimuli-responsive magnetic assemblies as tunable releasing carriers[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2015, 3 (29): 6026- 6031.
doi: 10.1039/C5TB00845J |
| 19 |
DALMINA M , PITTELLA F , SIERRA J A , et al. Magnetically responsive hybrid nanoparticles for in vitro siRNA delivery to breast cancer cells[J]. Mater Sci Eng: C, 2019, 99, 1182- 1190.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.026 |
| 20 | LIN M H , DAI Y , XIA F , et al. Advances in non-covalent crosslinked polymer micelles for biomedical applications[J]. Mater Sci Eng: C, 2020, 119, 111626. |
| 21 |
QI C , MUSETTI S , FU L H , et al. Biomolecule-assisted green synthesis of nanostructured calcium phosphates and their biomedical applications[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2019, 48 (10): 2698- 2737.
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00489G |
| 22 |
LIU Y J , LI J S , LIU F X , et al. Theranostic polymeric micelles for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Biomed Nanotechnol, 2015, 11 (4): 613- 622.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2015.1945 |
| 23 | ZHANG Y H , ZHANG H Y , ZHANG H L , et al. A new Gd-based T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent: Preparation and application in stem cell imaging[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2017, 34 (3): 302- 310. |
| 张艳辉, 张宏岩, 张海禄, 等. 新型Gd基T2造影剂的制备和应用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2017, 34 (3): 302- 310. | |
| 24 |
MA J P , DONG H Q , ZHU H Y , et al. Deposition of gadolinium onto the shell structure of micelles for integrated magnetic resonance imaging and robust drug delivery systems[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2016, 4 (36): 6094- 6102.
doi: 10.1039/C6TB01013J |
| 25 |
JIANG D D , ZHANG X P , YU D X , et al. Tumor-microenvironment relaxivity-changeable Gd-loaded poly (L-lysine)/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles as cancer-recognizable magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents[J]. J Biomed Nanotechnol, 2017, 13 (3): 243- 254.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2017.2346 |
| 26 |
LIU Y J , FENG L X , LIU T X , et al. Multifunctional pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles for theranostics evaluated experimentally in cancer[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6 (6): 3231- 3242.
doi: 10.1039/c3nr05647c |
| 27 |
ZHU D R , LIU F Y , MA L N , et al. Nanoparticle-based systems for T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2013, 14 (5): 10591- 10607.
doi: 10.3390/ijms140510591 |
| 28 | ZHAN Y Y , XUE R , ZHU Y L , et al. A biocompatible gadolinium-based amino acid copolymer contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2016, 33 (4): 635- 645. |
| 湛游洋, 薛蓉, 祝云龙, 等. 氨基酸共聚物修饰的生物相容性MRI造影剂[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2016, 33 (4): 635- 645. | |
| 29 |
KUMAGAI M , IMAI Y , NAKAMURA T , et al. Iron hydroxide nanoparticles coated with poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (aspartic acid) block copolymer as novel magnetic resonance contrast agents for in vivo cancer imaging[J]. Colloids Surf., B, 2007, 56 (1-2): 174- 181.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.12.019 |
| 30 |
ZHANG Z Q , SUN Q Q , ZHONG J L , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-visible and pH-sensitive polymeric micelles for tumor targeted drug delivery[J]. J Biomed Nanotechnol., 2014, 10 (2): 216- 226.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2014.1729 |
| 31 |
JIANG B , LIU M , ZHNG K C , et al. Oligoethylenimine grafted PEGylated poly (aspartic acid) as a macromolecular contrast agent: properties and in vivo studies[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2016, 4 (19): 3324- 3330.
doi: 10.1039/C6TB00278A |
| 32 |
WILSON M P , PATEL D , MURAD M H , et al. Diagnostic performance of MRI in the detection of renal lipid-poor angiomyolipomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Radiol, 2020, 296 (3): 511- 520.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020192070 |
| 33 |
SUN J , ZHAO X Q , BALU N , et al. Carotid plaque lipid content and fibrous cap status predict systemic CV outcomes: the MRI substudy in AIM-HIGH[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2017, 10 (3): 241- 249.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.06.017 |
| 34 |
ALKHALIL M , BIASIOLLI L , AKBAR N , et al. T2 mapping MRI technique quantifies carotid plaque lipid, and its depletion after statin initiation, following acute myocardial infarction[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2018, 279, 100- 106.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.08.033 |
| 35 |
BASTIAANSEN J A M , STUBER M . Flexible water excitation for fat-free MRI at 3T using lipid insensitive binomial off-resonant RF excitation (LIBRE) pulses[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79 (6): 3007- 3017.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26965 |
| 36 |
ROMEO V , MAUREA S , GUARINO S , et al. The role of dynamic post-contrast T1-w MRI sequence to characterize lipid-rich and lipid-poor adrenal adenomas in comparison to non-adenoma lesions: preliminary results[J]. Abdom Radiol, 2018, 43 (8): 2119- 2129.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1429-4 |
| 37 |
XIA J , YIN A Y , LI Z Z , et al. Quantitative analysis of lipid-rich necrotic core in carotid atherosclerotic plaques by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and clinical outcomes[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2017, 23, 2745- 2750.
doi: 10.12659/MSM.901864 |
| 38 |
LU C Y , JI J S , ZHU X L , et al. T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of hepatic tumor guided by SPIO-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers and ferritin reporter genes[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9 (41): 35548- 35561.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b09879 |
| 39 |
ZHANG Y , UDAYAKUMAR D , CAI L , et al. Addressing metabolic heterogeneity in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with quantitative Dixon MRI[J]. JCI insight, 2017, 2 (15): e94278.
doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.94278 |
| 40 |
WEINMANN H J , BRASCH R C , PRESS W R , et al. Characteristics of gadolinium-DTPA complex: a potential NMR contrast agent[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1984, 142 (3): 619- 624.
doi: 10.2214/ajr.142.3.619 |
| 41 |
AKAI H , SHIRAISHI K , YOKOYAMA M , et al. PEG-poly (L-lysine)-based polymeric micelle MRI contrast agent: Feasibility study of a Gd-micelle contrast agent for MR lymphography[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 47 (1): 238- 245.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25740 |
| 42 |
ZHANG N N , YU S S , MIN X , et al. Visual targeted therapy of hepatic cancer using homing peptide modified calcium phosphate nanoparticles loading doxorubicin guided by T1 weighted MRI[J]. Nanomed-Nanotechnol, 2018, 14 (7): 2167- 2178.
doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2018.06.014 |
| 43 |
YAN Q D , DONG X , XIE R Z , et al. Preparation of Mn2+@PolyDOPA-b-polysarcosine micelle as MRI contrast agent with high longitudinal relaxivity[J]. J Macromol Sci A, 2021, 58 (3): 175- 181.
doi: 10.1080/10601325.2020.1840918 |
| 44 |
JOHNSON N J J , HE S , NGUYEN HUU V A , et al. Compact micellization: a strategy for ultrahigh T1 magnetic resonance contrast with gadolinium-based nanocrystals[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10 (9): 8299- 8307.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b02559 |
| 45 | ARESTEANU R N S , BORODETSKY A , AZHARI H , et al. Ultrasound-induced and MRI-monitored CuO nanoparticles release from micelle encapsulation[J]. Nanotechnology, 2020, 32 (5): 055705. |
| 46 |
SUN C J , LIN H Y , GONG X Q , et al. DOTA-branched organic frameworks as giant and potent metal chelators[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2020, 142 (1): 198- 206.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b09269 |
| 47 | WANG Y X J . Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: Current status of clinical application[J]. Quant Imag Med Surg, 2011, 1 (1): 35- 40. |
| 48 |
RAY S , LI Z , HSU C H , et al. Dendrimer-and copolymer-based nanoparticles for magnetic resonance cancer theranostics[J]. Theranostics, 2018, 8 (22): 6322- 6349.
doi: 10.7150/thno.27828 |
| 49 |
YE S , LIU Y , LU Y , et al. Cyclic RGD functionalized liposomes targeted to activated platelets for thrombosis dual-mode magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2020, 8 (3): 447- 453.
doi: 10.1039/C9TB01834D |
| 50 |
YAN L , LUO L J , AMIRSHAGHAGHI A , et al. Dextran-benzoporphyrin derivative (BPD) coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION) micelles for T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and photodynamic therapy[J]. Bioconjugate Chem, 2019, 30 (11): 2974- 2981.
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00676 |
| 51 |
WARD K M , ALETRAS A H , BALABAN R S . A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST)[J]. J Magn Reson, 2000, 143 (1): 79- 87.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.1999.1956 |
| 52 |
SUN P Z , VAN ZIJL P C M , ZHOU J Y . Optimization of the irradiation power in chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer experiments[J]. J Magn Reson, 2005, 175 (2): 193- 200.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2005.04.005 |
| 53 | WOESSNER D E , ZHANG S R , MERRITT M E , et al. Numerical solution of the Bloch equations provides insights into the optimum design of PARACEST agents for MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2010, 53 (4): 790- 799. |
| 54 |
FERRAUTO G , BEAUPREZ F , DI GREGORIO E , et al. Development and characterization of lanthanide-HPDO3A-C16-based micelles as CEST-MRI contrast agents[J]. Dalton Trans, 2019, 48 (16): 5343- 5351.
doi: 10.1039/C8DT04621B |
| 55 | GONAWALA S , ALI M M . Application of dendrimer-based nanoparticles in glioma imaging[J]. J Nanomed Nanotechnol, 2017, 8 (3): 444. |
| 56 |
ZHANG S R , ZHOU K J , HUANG G , et al. A novel class of polymeric pH-responsive MRI CEST agents[J]. Chem Commun, 2013, 49 (57): 6418- 6420.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc42452a |
| 57 |
HAN Z , LIU G S . CEST MRI trackable nanoparticle drug delivery systems[J]. Biomed Mater, 2021, 16 (2): 024103.
doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/abdd70 |
| 58 |
HILL L K , FREZZO J A , KATYAL P , et al. Protein-engineered nanoscale micelles for dynamic 19F magnetic resonance and therapeutic drug delivery[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13 (3): 2969- 2985.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b07481 |
| 59 |
FU C K , DEMIR B , ALCANTARA S , et al. Low-fouling fluoropolymers for bioconjugation and in vivo tracking[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2020, 59 (12): 4729- 4735.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201914119 |
| 60 |
LI B , CAI M Y , LIN L , et al. MRI-visible and pH-sensitive micelles loaded with doxorubicin for hepatoma treatment[J]. Biomater Sci, 2019, 7 (4): 1529- 1542.
doi: 10.1039/C8BM01501E |
| 61 | CAI M Y , LV G , YANG Q , et al. MRI-visible and pH-sensitive nanomicelles for targeting delivery of sorafenib to hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Radiology, 2019, 11, 1005- 1011. |
| 蔡明岳, 吕格, 杨琴, 等. MRI可视化pH敏感纳米胶束用于肝癌靶向输送索拉非尼的可行性[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 11, 1005- 1011. | |
| 62 |
ZHOU G Y , XIAO H , LI X X , et al. Gold nanocage decorated pH-sensitive micelle for highly effective photothermo-chemotherapy and photoacoustic imaging[J]. Acta Biomater, 2017, 64, 223- 236.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.10.018 |
| 63 |
ZHU X L , TANG X X , LIN H Y , et al. A fluorinated ionic liquid-based activatable 19F MRI platform detects biological targets[J]. Chem, 2020, 6 (5): 1134- 1148.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2020.01.023 |
| 64 |
YANG H K , MIAO Y L , CHEN Y P , et al. Redox-responsive nanoparticles from disulfide bond-linked poly-(N-ε-carbobenzyloxy-L-lysine)- grafted hyaluronan copolymers as theranostic nanoparticles for tumor-targeted MRI and chemotherapy[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 148, 483- 492.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.071 |
| 65 |
ZHAI S D , HU X L , HU Y J , et al. Visible light-induced crosslinking and physiological stabilization of diselenide-rich nanoparticles for redox-responsive drug release and combination chemotherapy[J]. Biomater, 2017, 121, 41- 54.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.002 |
| 66 |
HSU J C , NAHA P C , LAU K C , et al. An all-in-one nanoparticle (AION) contrast agent for breast cancer screening with DEM-CT-MRI-NIRF imaging[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10 (36): 17236- 17248.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR03741H |
| 67 |
MIURA Y , TSUJI A B , SUGYO A , et al. Polymeric micelle platform for multimodal tomographic imaging to detect scirrhous gastric cancer[J]. ACS Biomater Sci Eng, 2015, 1 (11): 1067- 1076.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5b00142 |
| 68 | MOUKHEIBER D , CHITGUPI U , CARTER K A , et al. Surfactant-stripped pheophytin micelles for multimodal tumor imaging and photodynamic therapy[J]. ACS Appl Bio Mater, 2018, 2 (1): 544- 554. |
| 69 |
CARAVAN P . Strategies for increasing the sensitivity of gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2006, 35 (6): 512- 523.
doi: 10.1039/b510982p |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [3] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [4] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [5] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [6] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [7] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [8] |
De-gang TANG,Hong-chuang LI,Xiao-ling LIU,Lei SHI,Hai-dong LI,Chao-hui YE,Xin ZHOU.
A Simulation Study on the Effect of the High Permittivity Materials Geometrical Structure on the Transmit Field |
| [9] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [10] | Yan MA, Cang-ju XING, Liang XIAO. Knee Joint Image Segmentation and Model Construction Based on Cascaded Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| [11] | Jun LUO, Sheng-ping LIU, Xing YANG, Jia-sheng WANG, Ye LI. Design of a 5 T Non-magnetic Magnetic Resonance Radio Frequency Power Amplifier [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 163-173. |
| [12] | Ju-min ZHANG,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Dual-modal MRI T1-T2 Contrast Agent Based on Dynamic Organic Gadolinium Nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 11-19. |
| [13] | Zhi-chao WANG,Ji-lei ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Ting HUA,Guang-yu TANG,Jian-qi LI. CEST Imaging of the Abdomen with Neural Network Fitting [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 33-42. |
| [14] | Han-wei WANG,Hao WU,Jing TIAN,Jun-feng ZHANG,Peng ZHONG,Li-zhao CHEN,Shu-nan WANG. The Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Parameters of T2/FLAIR Mismatch Sign in Evaluating the Molecular Typing of Lower-grade Gliomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 56-63. |
| [15] | Ying-dan HU,Yue CAI,Xu-xia WANG,Si-jie LIU,Yan KANG,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN. Magnetic Resonance Imaging the Brain Structures Involved in Nicotine Susceptibility in Rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 345-355. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 267
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||