1 引言
高阶导数逼近在科学、工程和应用数学等领域具有关键作用, 对于理解、模拟和优化复杂系统以及解决许多实际问题至关重要. 但在求解高阶导数问题时, 有限差分法 (Finite Difference Method, FDM)、有限元法和谱方法等数值方法由于它们复杂的数值格式构造和计算网格划分导致在实际应用中受到一定的限制. 与这些方法相比, 无网格方法对边界条件和初始条件有更强的适应性, 在处理高维问题方面也具有特殊优势. 其中一种无网格方法是利用径向基函数 (Radial Basis Function, RBF) 逼近高阶导数.
MQ 函数是 RBF 中的重要一类, 由于它计算简单、各向同性等优点, 被广泛应用于数值计算, 最早是由 Hardy [10] 在解决航天器外形设计的问题时于 1971 年提出. MQ 函数插值采用
在处理大规模、高维度数据时, 现有的 MQ 方法时常难以提供足够的精确度. 这不仅会导致多步数值计算时的累积误差增大, 还会引发数值不稳定性问题, 造成数值溢出或数值精度丧失的情况. 为应对这一挑战, 本文在随机扰动的背景下, 研究有效逼近高阶导数的高精度方法. 通过加入噪声, 能更准确地模拟实际数据. 相比于传统的 MQ 拟插值方法, 高精度的三阶 MQ 拟插值能够更好地拟合数据的非线性特征, 具有更高的稳定性, 可以处理更广泛的随机数据逼近问题.
具体来说, 给定一个序列
当
其中
这里
这里
本文主要结构如下. 在第 2 节, 我们给出了三阶 MQ 拟插值性质的一些理论证明, 并在随机扰动背景下分析了它对高阶导数的逼近阶. 在第 3 节, 针对一元、多元和偏微分方程数值解中的具体应用分别给出算例和误差估计. 第 4 节进行简单总结.
2 三阶 MQ 拟插值方法
在测量或者采样中, 样本数据总是不可避免地带有误差. 为了更接近真实情况, 本文对采样点数据值加入一定的噪声来模拟测量采样或计算机精度所造成的误差, 即
引理2.1 如果
引理2.2 不等式
成立.
现在对三阶 MQ 拟插值在随机扰动背景下对高阶导数的逼近能力进行分析. 有如下定理
定理2.1 如果取
这里
证 计算有
注意
于是
由于
这里{u_i} \in [{x_{i - 2}},{x_{i + 2}}], 同时根据引理2.1, 我们有
利用文献 [15] 中证明 MQ 拟插值收敛性定理相同的技巧, 并结合引理2.2最终得到
所以, 三阶 MQ 拟插值的估计误差满足 (2.4) 式.
需要指出的是, 大部分函数逼近方法在满足对原函数的逼近为二阶时, 一般来说无法使得对二阶导数仍有逼近性质. 然而, 利用三阶 MQ 拟插值方法来逼近函数, 只需选取适当的参数, 不但能获得二阶导数的逼近, 甚至对更高阶导数仍有逼近性质. 不仅如此, 下面我们将分析, 相比一阶 MQ 和差商方法, 三阶 MQ 在噪声干扰时表现出了更好的稳定性.
根据文献 [13] 中所述, 如果
这里
为了得到与差商法一样的
相应的, 在定理 2.1 中我们取
可见越是高阶的导数
这意味着, 在达到相同
3 数值实验
上文关于三阶 MQ 拟插值算子对高阶导数逼近性质的讨论是基于整个实数域进行的. 但是在实际问题中, 我们往往需要在有限区间内逼近高阶导数. 因此, 本文通过在端点处人工添加辅助点的方式处理边界问题, 以便拟插值结构得以运用在有限区间内, 处理方法如下所述.
对于固定区间上的
相应的径向基函数为
以下是 Matlab 2019 的运算结果, 实验是在一个装有 16GB RAM 和 3.20 GHz 速度的 AMD R7 笔记本电脑上完成的.
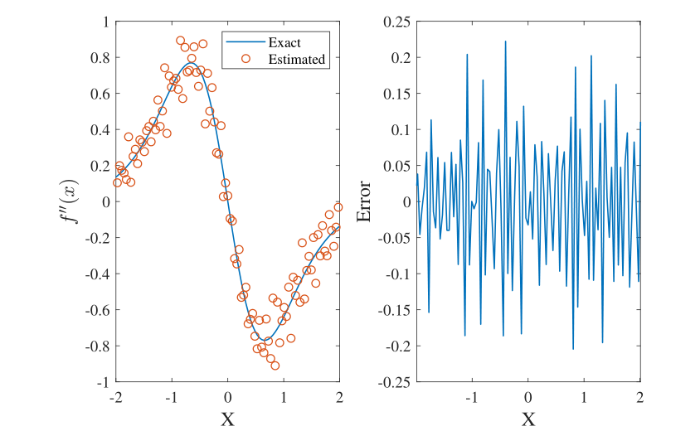
例 3.1 利用三阶 MQ 拟插值格式数值模拟函数的二阶导数. 考虑函数
其二阶导数的精确解为
图1
图2
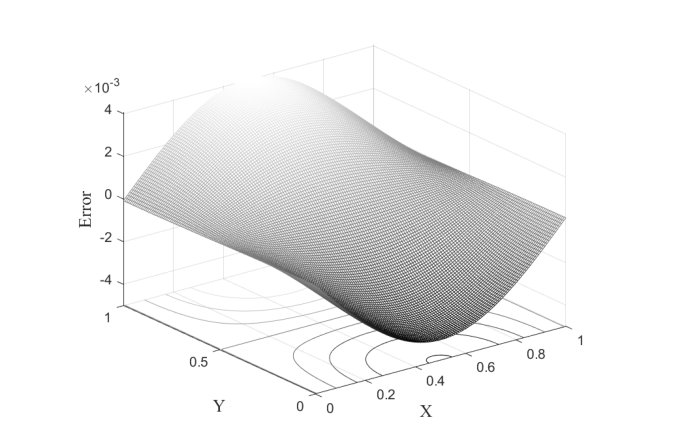
例3.2 利用三阶 MQ 拟插值计算拉普拉斯算子. 考虑如下函数
其拉普拉斯算子为
单变量三阶 MQ 拟插值结构在求解二维算例时, 使用了张量积的处理技巧, 构造了
图3
图4
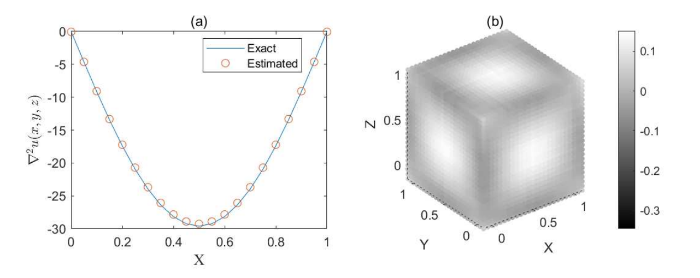
例3.3 利用三阶 MQ 拟插值计算拉普拉斯算子. 考虑如下函数
其拉普拉斯算子为
图5
在例 2 的基础上扩展研究高维算例. 同样地, 使用张量积的处理办法构造了
例3.4 利用三阶 MQ 拟插值方法求发展方程数值解. 考虑以下热方程
边界条件为
可以证实该问题精确解为
在空间方向, 利用三阶 MQ 拟插值逼近空间导数, 在时间方向, 用向前差分法进行离散. 有限差分方法在时间和空间上则分别用中心差分与向前差分离散. 在时刻
参考文献
Univariate multiquadric approximation: Quasi-interpolation to scattered data
Multivariate interpolation in odd-dimensional Euclidean spaces using multiquadrics
Applying multiquadric quasi-interpolation to solve Burgers' equation
Newton iteration with multiquadrics for the solution of nonlinear PDEs
On choosing "optimal" shape parameters for RBF approximation
Scattered data interpolation: tests of some methods
Applying multiquadric quasi-interpolation for boundary detection
Finite difference method for numerical computation of discontinuous solutions of the equations of fluid dynamics
Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces
An efficient numerical scheme for Burgers' equation
Approximation to the k-th derivatives by multiquadric quasi-interpolation method
Stability of multiquadric quasi-interpolation to approximate high order derivatives
Numerical solutions of generalized Burgers-Fisher and generalized Burgers-Huxley equations using collocation of cubic B-splines
Shape preserving properties and convergence of univariate multiquadric quasi-interpolation
Conservative multiquadric quasi-interpolation method for Hamiltonian wave equations
A multiquadric quasi-interpolations method for CEV option pricing model
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2018.03.046
[本文引用: 1]

The pricing of option contracts when the underlying process follows the constant elasticity of variance (CEV) model is considered. For CEV European options, the closed-form solutions involve the non-central chi-square distribution, whose computations by the current literatures are rather unstable and extremely expensive. Based on multiquadric quasi-interpolation methods, this study suggests a stable and fast numerical algorithm for CEV option pricing model. The method is confirmed to be a multinomial tree, in which the underlying variable moves from its initial value to an infinity of possible values of the next time step. The probabilities in the associated tree are ensured to be positive, which is a sufficient condition for stability and convergence. The method is flexible, since it is simple to implement with the nonuniform knots. Moreover, the method is easy to value the Greek letters which are important parameters in financial engineering, as the multiquadric function is infinitely continuously differentiable. Besides, the method does not require solving a resultant full matrix, the ill-conditioning problem arising when using the radial basis functions as a global interpolant can be avoided. Numerical experiments imply that the method is highly effective to calculate the stock options and its Greeks under the CEV model. (C) 2018 Elsevier B.V.
Numerical solution of Burgers-Fisher equation by cubic B-spline quasi-interpolation