1 引言
所谓图像配准, 是指寻找一种空间变换, 使得待配准图像与目标图像的对应点达到空间上的一致. 设
基于以上论述, 图像配准问题可转化为能量泛函的优化问题. 即, 寻找最优的位移场
其中
基于框架 (1.1), 学者们提出了许多图像配准模型[7⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-14]. 在这些模型中,
值得注意的是, 上述大部分图像配准模型及方法并不能保证形变场是微分同胚的. 即, 形变场是存在重叠的, 会产生负体积, 这与物理规律是相违背的. 因此必须给定相关约束条件来避免网格重叠现象的产生. 在没有网格重叠现象的情况下, 形变场
上述这些模型都是在对形变场作了先验估计的前提下进行的, 即通过极小化
然而, 文献 [24] 中只是在共形集合上寻找相似性度量的全局极小. 为了在更大的集合上解决贪婪配准问题 (例如, 在
其中
其中
注 1.1 本文的结构如下: 在第二章中介绍了拟共形理论的相关知识, 给出了多尺度分数阶微分同胚图像配准模型, 并证明了该模型解的存在性及收敛性; 在第三章中提出了一种松弛的拟共形多尺度模型及其对应的数值计算方法; 第四章通过实验来论证第三章所提出算法的有效性; 在文章的最后对本文进行了总结.
2 模型及其理论分析
2.1 相关理论知识
在介绍模型之前, 我们首先介绍有关拟共形映射和 Beltrami 系数的一些基本理论知识.
给定映射
且复值函数
由 Beltrami 系数
计算得到, 这里
这里
注 2.1 形变场
注 2.2 从以上拟共形理论
2.2 多尺度微分同胚图像配准模型
受文献 [24] 启发, 为了能够在不含正则项的情况下直接寻找
第 1 步: 求解下列变分问题
其中
第 2 步: 将
其中
第 n+1 步: 依次进行, 最后求解以下变分问题的解
其中
记
因为
综上可知,
为证明以上多尺度方法解的存在性和收敛性, 定义
定理 2.1 假设
定理 2.2 设
为了证明上述定理, 先介绍几个引理. 同时为证明方便, 对于任意
引理 2.1 (i) 若
(ii) 若
证 (i) 设
因为
故
上式证明了多尺度算法无网格重叠;
(ii) 由
由 (i) 可知, 显然成立.
引理 2.2 若
证 设
引理 2.3 若
证 因为
由 (2.8) 式可得,
同理, 有
又因为
引理 2.4 设
其中
证 令
根据引理 2.3 知逆映射
由 Sobolev 嵌入定理知
所以
其中
引理 2.5 设
证 由
记
综上, 可得
引理 2.6 设
证 由引理 2.3 可知,
令
证毕.
引理 2.7 对任意的
则其满足
(i)
(ii)
(iii) 对于
(iiii) 若
证 根据引理 2.7 中对函数
介绍完上述 7 个引理后, 接下来证明定理 2.2
证
用反证法, 假设
记
也就是说,
这表明
因为
且有
以及
其中
由引理 2.6 可知
综上可得
因此
其中
因此
即
这与
故定理2.2得证.
注 2.3 由定理 2.2 可知, 多尺度方法 (2.4)--(2.6) 是收敛的, 当尺度
等价, (2.23) 式配准的结果与参数
3 基于拟共形理论的数值求解方法
3.1 基于拟共形映射的配准模型
为了克服多尺度模型 (2.6) 中的非线性不等式约束
其中
注 3.1 关于模型(3.1)解的存在性可以采用定理2.1的方法进行证明. 同样地, 令
3.2 数值计算方法
3.2.1 离散化
我们使用有限差分法将模型(3.1)离散在区域
另外, 为了方便, 记
数据项 SSD 的离散化
首先是对模型 (3.1) 中数据项
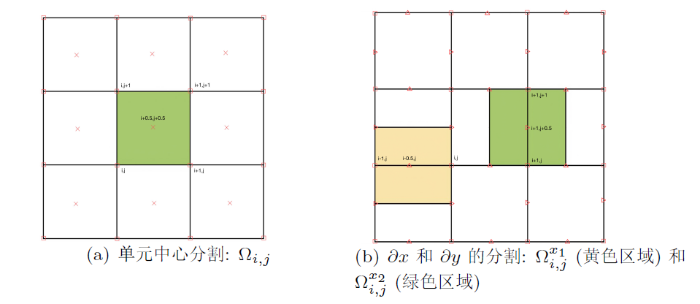
图1
设
带分数阶正则项
接下来, 我们对带分数阶导数的正则项
根据图1(b) 及数值积分中的中点法则, 可以得到
同理, 对于
另外, 对于
来估计.
因此, 可以得到
其中有关矩阵
其中
记
其中
由以上分数阶离散理论可知
因此, 对带分数阶导数的正则项
正则项
最后, 是对正则项
其中
最终, 结合 (3.7), (3.8) 和 (3.9) 式, 我们可以得到模型 (3.1) 的离散化形式如下
3.2.2 离散化问题 (3.10) 的最优化方法
在数值计算中, 我们选择线性搜索法求解无约束优化问题 (3.10). 为了保证搜索方向是一个下降方向, 我们采用 Gauss-Newton 方向. 另外, 使用 Gauss-Newton 法时, 我们不需要计算二阶项, 可以加速 CPU 时间消耗.
其中
为了保证 Gauss-Newton 法的全局收敛性, 我们采用了线性搜索法. 其迭代过程如下
其中
接下来, 我们将研究近似的 Hessian 矩阵
Hessian 矩阵
我们分别考虑 (3.10) 式中
首先, 是离散化的 SSD 项
其梯度和 Hessian 矩阵分别为
其中
对于
另外, 对于离散带分数阶导数的正则项
最后, 对于
为了从 (3.18) 式中提取半正定部分, 我们省略其二阶项, 得到近似的 Hessian 矩阵为
因此, 对于 (3.10) 式中的函数
以及近似的 Hessian 矩阵
搜索方向
每次迭代时, 利用式 (3.20) 和 (3.21) 式, 我们需要求解高斯-牛顿系统, 找到 (3.10) 式的搜索方向
步长和终止标准
算法 1
输入: 初始化 ID=0,
a) 计算
\text { b) while } \theta\|\delta U\| \geqslant T o l \text {, 则 } U^{n e w}=U+\theta\|\delta U\| \text {; }
if \vec{r}\left(U^{n e w}\right) \leqslant 1, 则
if \theta \geqslant T 0, 退出 while 循环, 执行 c );
else \ if \theta<T 0, 执行 d );
结束 if 判断;
更新
结束 while 循环;
c) while
if
if
else if
结束 if 判断;
更新
结束 while 循环;
d) ID=1,
输出: ID,
根据文献 [38], 给定
其中 eps 是机器精度, MaxIter 是外部迭代的最大次数. 我们设置
算法 2
输入: 目标图像
a)
b) 根据 (3.10) 式计算
c) while (i)--(iii) 均不满足, 则根据
if ID=1, 则结束该算法, 输出
else
结束 if 循环;
结束 while 循环;
输出: ID,
3.2.3 多尺度图像配准算法
在本章的最后, 给出对应的二维多尺度微分同胚算法 3
算法 3
输入: 最大尺度数
for
a) 令
b) 由算法 2 得到
c) 更新
end
输出: 配准结果
4 数值实验
4.1 实验数据及对比算法
为验证算法的有效性, 本文主要采用以下几类图像数据及对比算法
实验数据
(i) 合成图像数据: A-A, A-R;
(ii) 自然图像数据: Watermelon, Pineapple-Pepper;
(iii) 医学图像数据: Liver MRI, Brain MRI, Hand CT.
4.2 评价指标
在本文中, 主要选取相对残差平方和 (
其中
其中
4.3 数值实验
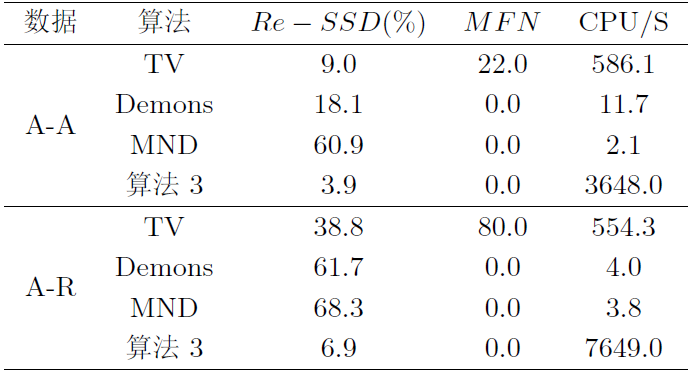
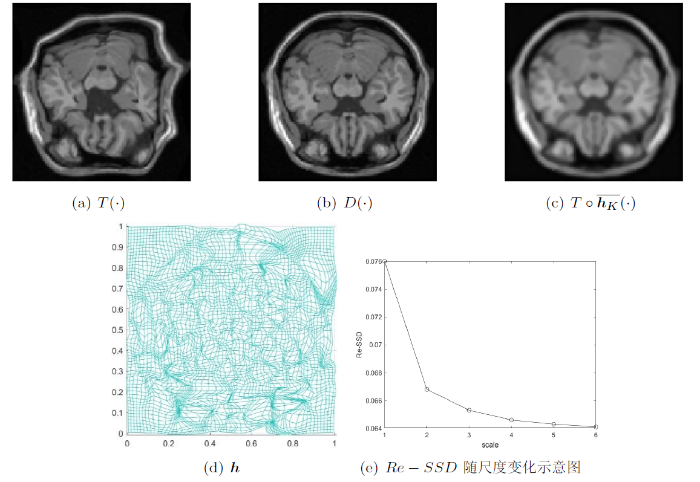
4.3.1 合成图像配准
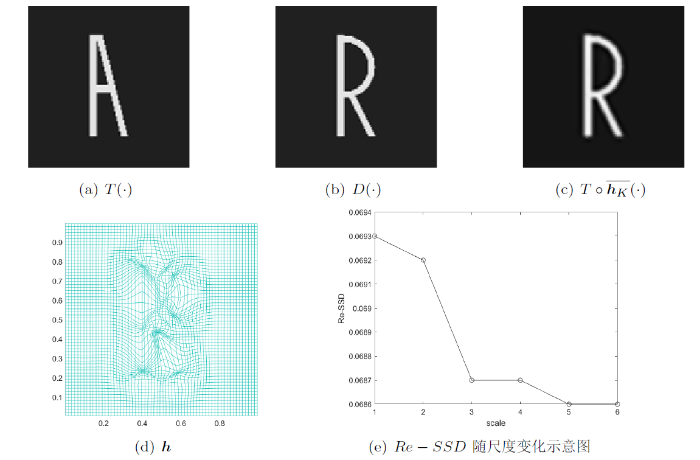
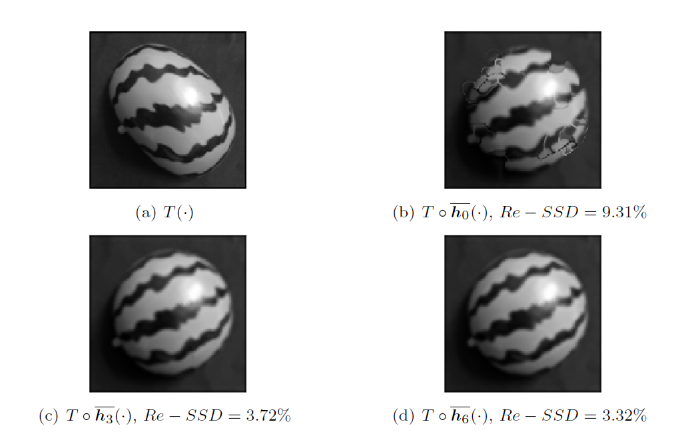
为了验证所提算法在图像配准中的有效性, 在此部分以 A-A 和 A-R 两对典型合成数据为例, 以
图2
图3
图4
图5
4.3.2 自然图像配准
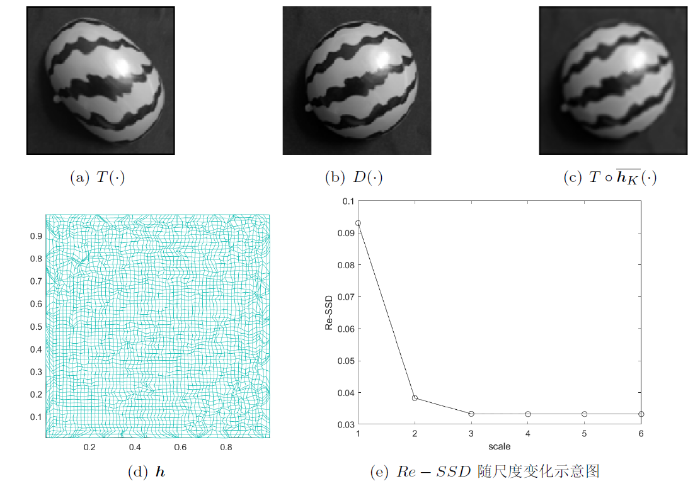
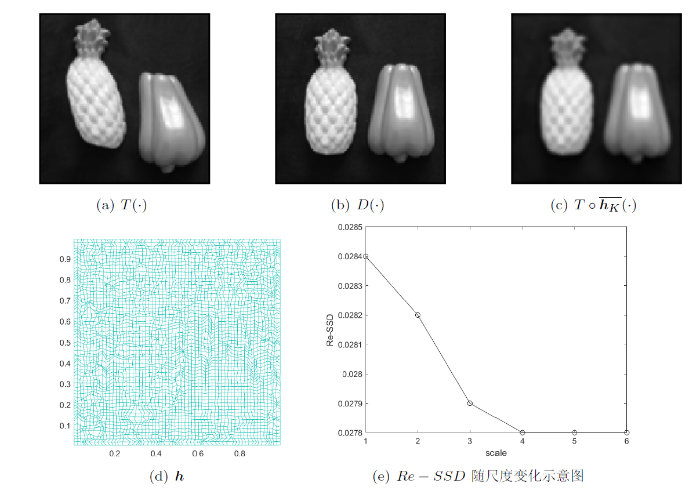
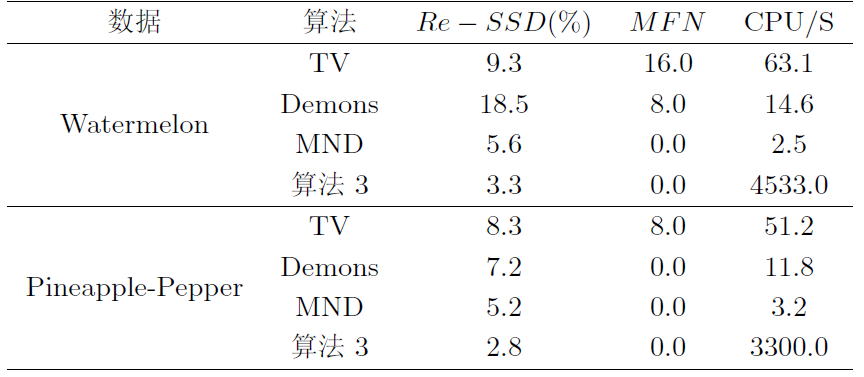
在本节中, 我们对两个不同的自然图像对“西瓜、菠萝-辣椒”进行了配准.
图6
图7
图8
图9
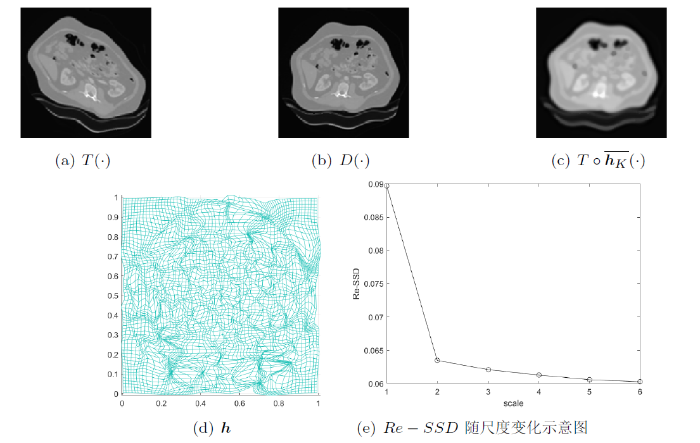
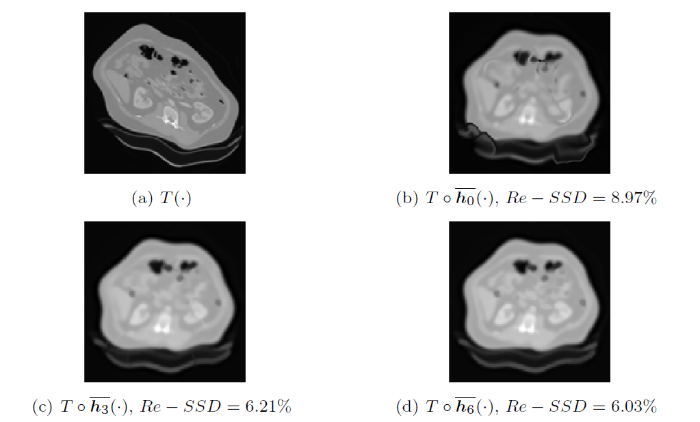
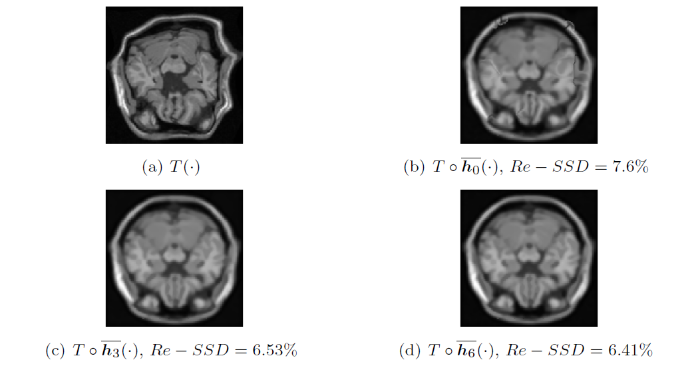
4.3.3 医学图像配准
在这个部分, 我们对三个不同的医学图像对“肝脏、大脑和手部”进行了配准.
图10
图11
图12
图13
图14
图15
5 结论
本文提出了一种基于拟共形理论的分数阶微分同胚多尺度方法, 该方法有效地避免了网格重叠, 同时在没有先验正则项的情况下找到了微分同胚图像配准的最优解, 并且通过数值实验验证了所提算法的有效性.
附录 A 3.2.1 节中矩阵 A, G, C 的计算
令矩阵 {A_1}={I_2} \otimes {I_{n + 1}} \otimes \partial _n^1 \in {R^{2n(n+1) \times 2{{(n+1)}^2}}} , {A_2} = {I_2} \otimes \partial _n^1 \otimes {I_{n + 1}} \in {R^{2n(n+1) \times 2{{(n+1)}^2}}} ,
其中 \partial _n^1 = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&1&{}&{}&{} \\ {}&1&1&{}&{} \\ {}& \cdots & \cdots & \cdots &{} \\ {}&{}&1&1&{} \\ {}&{}&{}&1&1 \end{array}} \right] \in {R^{n,n + 1}} , \otimes 表示克罗内克积,则
设矩阵 G_1 满足 {G_{{1_{i + 1 + jn,i + 1 + jn}}}} = \left\{ \begin{gathered} 1,{\text{ }}0 \leqslant i \leqslant n - 1,{\text{ }}1 \leqslant j \leqslant n - 1 \hfill \\ \frac{1}{2},{\text{ }}0 \leqslant i \leqslant n - 1,{\text{ }}j = 0,n \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right.,{\text{ }}{G_{{1_{i,j}}}} = 0,{\text{ }}i \ne j , 矩阵 G_2 满足 {G_{{2_{i + 1 + j(n+1),i + 1 + j(n+1)}}}} = \left\{ \begin{gathered} 1,{\text{ }}1 \leqslant i \leqslant n - 1,{\text{ }}0 \leqslant j \leqslant n - 1 \hfill \\ \frac{1}{2},{\text{ }}i = 0,n,{\text{ }}0 \leqslant j \leqslant n - 1 \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right.,{\text{ }}{G_{{2_{i,j}}}} = 0,{\text{ }}i \ne j , 则
令矩阵 C_1={{I_2} \otimes {I_{n + 1}} \otimes {B_{n + 1,\alpha }}}\in {R^{ 2(n+1)^2\times 2(n+1)^2}} , {C_2} = \left[ {{I_2} \otimes {B_{n + 1,\alpha }} \otimes {I_{n + 1}}} \right](list,:) \in {R^{ 2(n+1)^2\times 2(n+1)^2}} ,其中 list = \big( 1 + 0(n+1), \cdots, 1 + n(n+1), \cdots, n + 1 + 0(n+1), \cdots, n + 1 + n(n+1) \big)^T\in{R^{(n+1)^2\times 1}} ,则
参考文献
A survey of image registration techniques
A survey of hierarchical non-linear medical image registration
A survey of medical image registration
DOI:10.1016/s1361-8415(01)80026-8
PMID:10638851
[本文引用: 1]

The purpose of this paper is to present a survey of recent (published in 1993 or later) publications concerning medical image registration techniques. These publications will be classified according to a model based on nine salient criteria, the main dichotomy of which is extrinsic versus intrinsic methods. The statistics of the classification show definite trends in the evolving registration techniques, which will be discussed. At this moment, the bulk of interesting intrinsic methods is based on either segmented points or surfaces, or on techniques endeavouring to use the full information content of the images involved.
Deformable registration of brain tumor images via a statistical model of tumor-induced deformation
An approach to the deformable registration of three-dimensional brain tumor images to a normal brain atlas is presented. The approach involves the integration of three components: a biomechanical model of tumor mass-effect, a statistical approach to estimate the model's parameters, and a deformable image registration method. Statistical properties of the sought deformation map from the atlas to the image of a tumor patient are first obtained through tumor mass-effect simulations on normal brain images. This map is decomposed into the sum of two components in orthogonal subspaces, one representing inter-individual differences in brain shape, and the other representing tumor-induced deformation. For a new tumor case, a partial observation of the sought deformation map is obtained via deformable image registration and is decomposed into the aforementioned spaces in order to estimate the mass-effect model parameters. Using this estimate, a simulation of tumor mass-effect is performed on the atlas image in order to generate an image that is similar to tumor patient's image, thereby facilitating the atlas registration process. Results for a real tumor case and a number of simulated tumor cases indicate significant reduction in the registration error due to the presented approach as compared to the direct use of deformable image registration.
Deformable medical image registration: a survey
DOI:10.1109/TMI.2013.2265603
PMID:23739795
[本文引用: 1]

Deformable image registration is a fundamental task in medical image processing. Among its most important applications, one may cite: 1) multi-modality fusion, where information acquired by different imaging devices or protocols is fused to facilitate diagnosis and treatment planning; 2) longitudinal studies, where temporal structural or anatomical changes are investigated; and 3) population modeling and statistical atlases used to study normal anatomical variability. In this paper, we attempt to give an overview of deformable registration methods, putting emphasis on the most recent advances in the domain. Additional emphasis has been given to techniques applied to medical images. In order to study image registration methods in depth, their main components are identified and studied independently. The most recent techniques are presented in a systematic fashion. The contribution of this paper is to provide an extensive account of registration techniques in a systematic manner.
Image registration methods: a survey
Large deviations for stochastic flows of diffeomorphisms
Deformable multi-modal image registration by maximizing rényi's statistical dependence measure
Inverse consistent deformable image registration
A combination of the total variation filter and a fourth-order filter for image registration
A novel diffeomorphic model for image registration and its algorithm
Variational image registration by a total fractional-order variation model
An improved discontinuity-preserving image registration model and its fast algorithm
A novel high-order functional based image registration model with inequality constraint
Recent history of fractional calculus
On conformable fractional calculus
A variational model with fractional-order regularization term arising in registration of diffusion tensor image
The random walk's guide to anomalous diffusion: a fractional dynamics approach
An alternating direction implicit scheme of a fractional-order diffusion tensor image registration model
Numerical methods for volume preserving image registration
Optimized conformal surface registration with shape-based landmark matching
Optimization of surface registrations using Beltrami holomorphic flow
Landmark and intensity-based registration with large deformations via quasi-conformal maps
Multi-scale approach for two-dimensional diffeomorphic image registration
Quasiconformal Teichmuller Theory
Lectures on Quasiconformal Mappings
A diffeomorphic image registration model with fractional-order regularization and Cauchy-Riemann constraint
Numerical analysis of fully discretized Crank-Nicolson scheme for fractional-in-space Allen-Cahn equations
A class of second order difference approximations for solving space fractional diffusion equations
Templates for the Solution of Linear Systems: Building Blocks for Iterative Methods
Solution of sparse indefinite systems of linear equations
A hyperelastic regularization energy for image registration
Iterative Methods for Optimization
Multimodality Non-rigid Demon Algorithm Image Registration
MRI modalitiy transformation in demon registration//IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro