1 引言
为了求解问题 (1.1), 自然考虑利用两分块结构, 采取交替极小化算法. 也就是, 给定一个初始点
其中
因为邻近交替极小化算法在每次迭代时都需要得到精确解, 所以 (1.3) 式中的子问题可能很难解决. 线性化技术是克服子问题没有解析解的有效方法之一. Bolte 等[7] 受邻近向前向后分裂算法的启发, 在耦合项
其中
Bregman 距离作为 2 范数平方距离的推广, 在使用时具有更大的灵活性, 生成函数不局限于 2 范数平方. 虽然 Bregman 距离不是真正的距离, 但采用 Bregman 距离正则化使得算法的适用性更广. 有时选择适当的 Bregman 距离可以得到子问题的显示解, 提高算法的收敛速度, 因此很多算法采用 Bregman 距离正则化来提高数值效果. 在文献 [28] 中, 针对问题 (1.1), 作者利用前三步迭代信息提出了如下两步惯性 Bregman 交替极小化算法 (TiBAM)
其中 D_{\phi_i}(i=1,2) 是函数 \phi_i(i=1,2) 生成的 Bregman 距离. 在效益函数满足 Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质的条件下, 证明了算法的全局收敛性. 基于交替极小化算法, Chao 等[29] 提出了如下惯性 Bregman 交替极小化算法 (BIAM) 求解问题(1.1)
在效益函数满足 Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质且合理选择参数的条件下, 给出了算法的全局收敛性分析.
本文基于邻近交替极小化算法, 结合惯性外推技术、线性化技术和 Bregman 距离, 利用前三次迭代的信息, 构造了两步惯性 Bregman 邻近交替线性极小化算法, 并在效益函数满足 Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质的假设下, 给出了所提出算法的全局收敛性分析.
本文内容组织如下: 在第二部分, 我们回顾了一些概念和重要引理, 这些概念和引理将用于证明主要的收敛结果. 在第三部分, 我们提出了两步惯性 Bregman 邻近交替线性极小化算法, 并给出收敛性分析. 最后, 在第四部分, 应用提出的算法求解稀疏非负矩阵分解、信号恢复和二次分式规划问题, 通过数值结果显示所提出算法的有效性.
2 预备知识
维数为
2.1 非凸非光滑函数的次微分
定义 2.1 设
(1) 若
为函数
为
注 2.1 根据上述定义, 可得
(a) 对于
(b) (
(c)
(d) 如果
2.2 Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质
Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质对算法的收敛结果起着至关重要的作用. 现在我们给出 Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质的定义.
设
定义 2.2 (Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 性质) 函数
都成立, 则称函数
已知实解析函数和半代数函数都是次解析的. 一般来说, 两个次解析函数的和不一定是次解析的. 然而, 对于两个次解析函数, 如果至少有一个函数将有界集映射到有界集, 那么它们的和也是次解析的, 见文献 [34]. 特别地, 次解析函数与解析函数的和函数是次解析的. 典型的次解析函数包括
2.3 Bregman 距离
定义 2.3 设
成立, 则称函数
成立.
假设函数
成立. 再者,
成立.
作为 2 范数平方距离的推广, Bregman 距离具有许多与 2 范数平方距离相似的良好性质. 然而, Bregman 距离并不是真正的距离, 因为它不满足三角不等式或对称性, 但使用 Bregman 距离使得算法的应用更加广泛.
定义 2.4 设
为
若
由 Bregman 距离定义可知, 如果
2.4 基本引理
引理 2.1 (下降引理)[20] 设
假设 2.1 设
(H1) (充分下降性). 任意
其中
(H2) (相对误差性). 任意
成立, 即
(H3) (连续性条件). {存在子序列
成立 (此时称函数
下面给出一个框架性收敛结果[28], 可应用于分析本文提出算法的收敛性.
引理 2.2[28] 设
3 两步惯性 Bregman 邻近交替线性极小化算法
下面给出两步惯性 Brgeman 邻近交替线性极小化算法 (TiBPALM) 来求解问题 (1.1). 假设
算法 3.1 选取
其中
由于
注 3.1 下面给出了算法 1 的特殊情况.
(1) 设
在这种情况下, 令
令
(2) 令
(3) 令
为了得到算法 1 的收敛性分析, 我们作如下必要的假设.
假设 3.1 (1)
(2) 对于任意固定的
同样地, 对于任意固定的
(3) 对于
记
值得注意的是, 当
引理 3.1 设
(1) 序列
其中
(2)
(3) 序列
证 (1) 根据算法 1, 可得
根据引理 2.1, 有
将 (3.5) 式和 (3.6) 式相加, 可得
则
根据 (2.1) 式和假设 3.1 (3), 再结合 (3.8) 式可得
同理,
将 (3.9) 式和 (3.10) 式相加, 可得
由于
则
因此, (3.4) 式成立, 并且序列
(2) 从 (3.4) 式中可得不等式
成立. 任取正整数
令
(3) 由效益函数定义可知
根据结论 (1) 和 (2), 可得序列
证毕.
引理 3.2 设
则
进而, 如果序列
证 根据
因为
即
同理,
即
根据函数
和
由
可得 (3.14) 式成立. 进而, 如果序列
因此, 根据序列
引理 3.3 设
(1) 序列
(2) 对任意
证 (1) 根据引理 3.1 和
显然整个序列
(2) 对于任意
所以有
则
令
根据
所以
根据(3.20) 式和
有
其中
由于
现在, 利用引理 2.2, 可以得到算法 1 生成的序列
定理 3.1 设
证 根据引理 2.2, 只需验证函数
其中
成立. 根据 (3.15) 式有
于是取
且
4 数值算例
其中
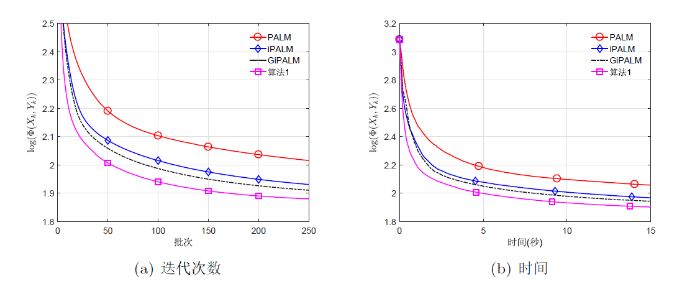
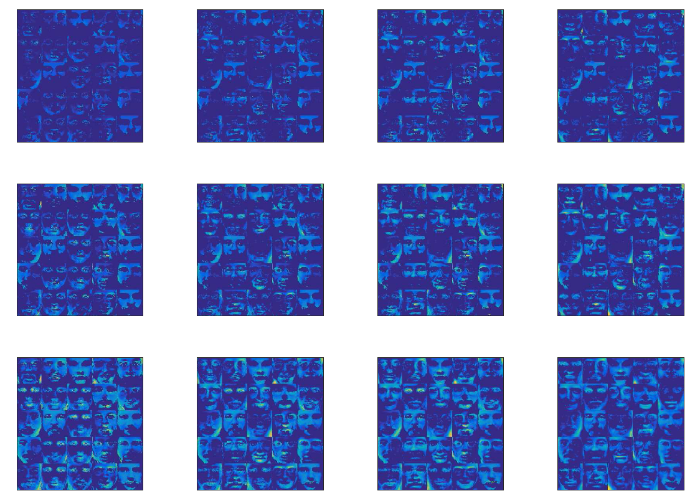
在数值实验中, 使用由人脸图像组成的标准人脸识别基准1: Yale-B 数据集和 ORL 数据集, 其中 Yale-B 数据集包含 2414 张大小为
图1
取实验参数
(1) PALM:
(2) iPALM、GiPALM: 固定惯性参数
(3) 算法 1 (TiBPALM): 固定惯性参数
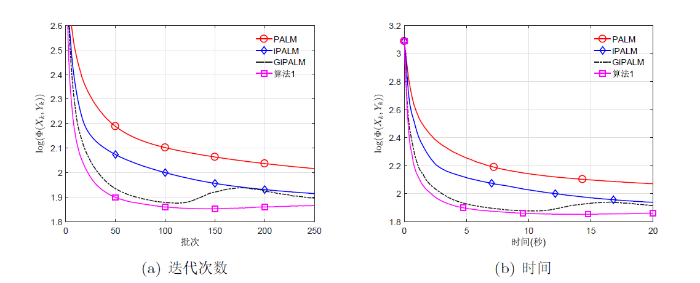
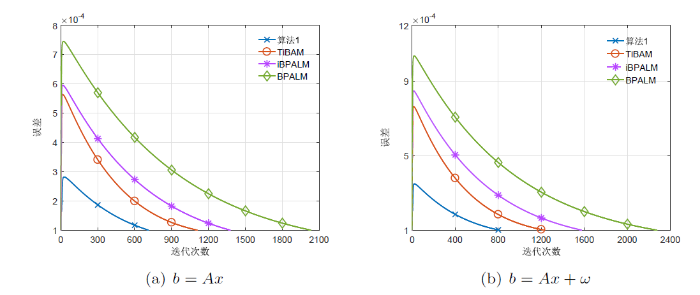
图2
图3
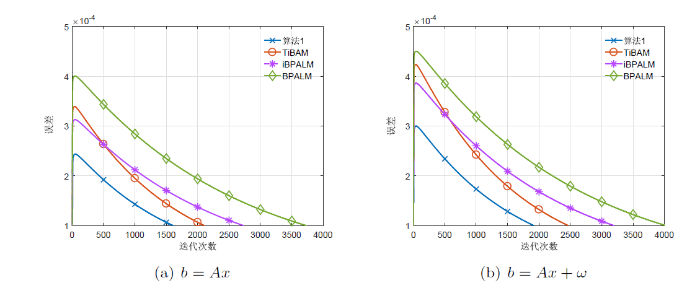
图4
图5
图6
图6
四种算法在不同稀疏度下的 25 张人脸结果图像. 从左到右分别是 PALM、iPALM、GiPALM 和算法1, 从上到下分别为
例 4.2 稀疏信号恢复问题. 假设
其中参数
通过引入辅助变量
进一步转化为
其中
由上式可知,
对于任何
其中
并且
参数选取: 设
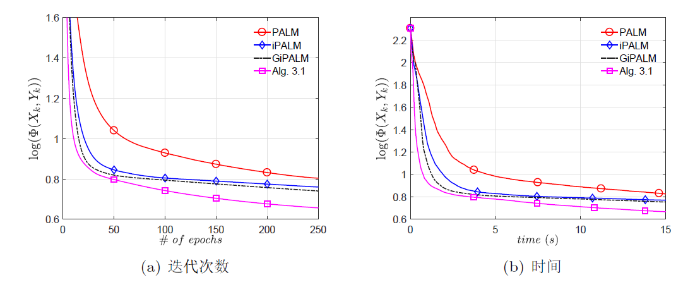
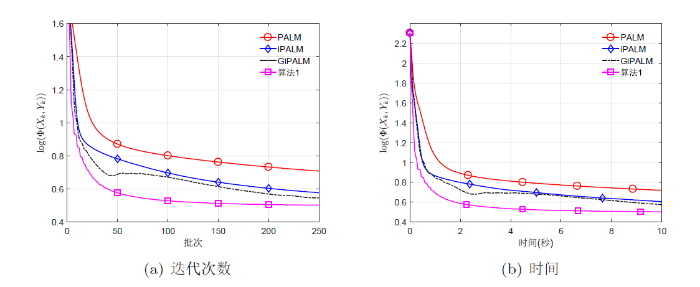
图7
图7
维数为
图8
图8
维数为
为了给出算法 1 在不同 Bregman 距离下的数值结果, 下面介绍三种不同的 Bregman 距离
(1) 定义函数
值域为
及
(2) 定义函数
值域为
及
(3) 定义函数
显然,
例 4.3 非凸二次分式规划问题
其中
上述二次分式规划问题可以转化为非凸非光滑不可分优化问题 (1.1)
其中
在本例中, 取
情形 1 取固定矩阵
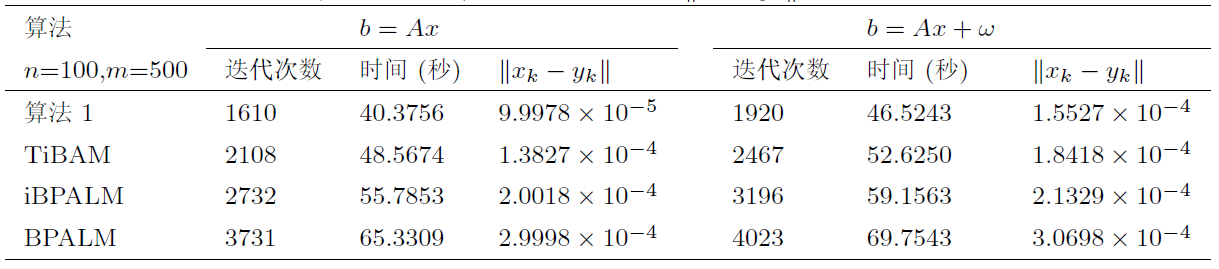
结果分析: 可以看出, 在迭代次数和 CPU 时间方面, Kullback-Leibler 距离和 Itakura-Saito 距离比 2 范数平方距离具有计算优势. 对于一步惯性算法, 计算结果表明, 算法 (23) (
情形 2 随机选择矩阵
结果分析: 表4 中数值结果显示, 当矩阵
5 总结
针对非凸非光滑不可分优化问题, 本文基于邻近交替线性极小化算法, 结合惯性外推技术和 Bregman 距离提出了两步惯性 Bregman 邻近交替线性极小化算法. 在目标函数满足 Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz 不等式且参数满足合理条件的假设下, 构造适当的效益函数, 得到算法生成的序列全局收敛到稳定点. 最后, 对稀疏非负矩阵分解、稀疏信号恢复和二次分式规划问题进行了数值实验, 并选择适当的 Bregman 距离使稀疏信号恢复问题的子问题有显示表达式, 还应用不同的 Bregman 距离来求解二次分式规划问题. 数值结果表明了所提出算法的有效性.
参考文献
大规模非凸不可分优化问题的分裂序列二次规划算法
A Splitting sequence quadratic programming algorithm for the Large-Scale nonconvex nonseparable optimization problems
具有线性化技术的三块非凸不可分优化问题 Bregman ADMM 收敛性分析
Convergence analysis of Bregman ADMM for three-block nonconvex indivisible optimization problems with linearization technique
非凸多块优化的 Bregman ADMM 的收敛率研究
Research on the convergence rate of Bregman ADMM for nonconvex multiblock optimization
Efficient reconstruction of piecewise constant images using nonsmooth nonconvex minimization
Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising
Linearly constrained non-Lipschitz optimization for image restoration
Proximal alternating linearized minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems
The forward-backward-forward method from continuous and discrete perspective for pseudo-monotone variational inequalities in Hilbert spaces
Convergence of descent methods for semi-algebraic and tame problems: proximal algorithms, forward-backward splitting, and regularized Guass-Seidel methods
Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers
Parallel and Distributed Computation: Numerical Methods
On the convergence of block coordinate descent type methods
Asymptotic properties of the Fenchel dual functional and applications to decomposition problems
Proximal alternating minimization and projection methods for nonconvex problems: an approach based on the Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz inequality
Alternating structure-adapted proximal gradient descent for nonconvex block-regularised problems
iPiano: Inertial proximal algorithm for nonconvex optimization
An inertial Tseng's type proximal algorithm for nonsmooth and nonconvex optimization problems
Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods
Inertial block proximal methods for non-convex non-smooth optimization
An inertial Douglas-Rachford splitting algorithm for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems
Inertial proximal alternating minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems
Inertial proximal alternating linearized minimization (iPALM) for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems
A Gauss-Seidel type inertial proximal alternating linearized minimization for a class of nonconvex optimization problems
A generalized inertial proximal alternating linearized minimization method for nonconvex nonsmooth problems
Some accelerated alternating proximal gradient algorithms for a class of nonconvex nonsmooth problems
Two-step inertial Bregman alternating minimization algorithm for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems
An inertial alternating minimization with Bregman distance for a class of nonconvex and nonsmooth problems
Variational Analysis and Generalized Differentiation. I: Basic Theory
The Łojasiewicz inequality for nonsmooth subanalytic functions with applications to subgradient dynamical systems
Convergence of multi-block Bregman ADMM for nonconvex composite problems
A block coordinate descent method for regularized multiconvex optimization with applications to nonnegative tensor factorization and completion
A non-Euclidean gradient descent framework for nonconvex matrix factorization
Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization
Generalized separable nonnegative matrix factorization
A semi nonnegative matrix factorization technique for pattern generalization in single-pixel imaging
Sparse nonnegative matrix factorization with
Although nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) favors a sparse and part-based representation of nonnegative data, there is no guarantee for this behavior. Several authors proposed NMF methods which enforce sparseness by constraining or penalizing the [Formula: see text] of the factor matrices. On the other hand, little work has been done using a more natural sparseness measure, the [Formula: see text]. In this paper, we propose a framework for approximate NMF which constrains the [Formula: see text] of the basis matrix, or the coefficient matrix, respectively. For this purpose, techniques for unconstrained NMF can be easily incorporated, such as multiplicative update rules, or the alternating nonnegative least-squares scheme. In experiments we demonstrate the benefits of our methods, which compare to, or outperform existing approaches.