1 引言
其中
在现实世界中种群难免会受到各种环境噪声的影响, 正如 May[8] 指出环境噪声会不同程度地影响种群系统中的内禀增长率、环境容纳量、竞争系数以及系统中的其它参数. 注意到模型的参数通过噪声的连续频谱输出在均值周围波动, 这种现象可用 Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 过程来描述. 最近有部分学者研究了模型参数满足 Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 过程[9⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-15] 的情形, 特别地, 文献 [15] 考虑了一类具有 Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 过程的随机模型并分析了该模型的平稳分布和概率密度函数. 受文献 [15] 的启发, 本文考虑对模型 (1.1) 中捕食者的内禀增长率
其中
2 全局解的存在唯一性和指数绝灭
为方便后面的讨论, 记
定理 2.1 对任意初值
证 定义一个
其中 R1 = sup(x,s)∈R + ×R{−cx6 + ax5 + x5 + cx−s6 + ¯ss5 + 15s5 + 5σ22ηs4−s}, R2 = supy∈R+{−hy2 + 23y32 + 4b5y54 + hy}, J 为正常数.
余下的证明与文献 [16, 定理 3.3] 的证明类似, 故省略.
定理 2.2 若
证 令
结合模型 (1.2) 的第三个式子可知, 当
即服从高斯分布
结合当
选取
这就意味着
3 平稳分布的存在性
考虑积分方程
引理 3.1[19] 假设上述方程的参数与时间
若存在一个非负的
定理 3.1 若
证 构造一个
其中
分别对
根据 Young 不等式可知
将式 (3.4) 代入式 (3.3) 有
再次应用 Young 不等式可得
将式 (3.6) 代入式 (3.5) 进而得到
对
回顾式 (3.1) 并结合式 (3.2)、(3.7) 和 (3.8) 可得
构造一个有界闭集
其中
取充分小的
其中
下面将验证对任意的
情况 1 对任意的
情况 2 对任意的
取
可以得到
情况 3 对任意的
情况 4 对任意的
情况 5 对任意的
联立上述 5 种情况, 再由式 (3.10) 可得
这就意味着当
4 概率密度函数
在上一节中已知当
易得
为方便后续分析, 简记参数
定理 4.1 假设
其中
其中
证 令
由定理 4.1 条件可知
其中
由文献 [20] 可知模型 (4.3) 存在的唯一正态密度函数
类似于文献 [21] 的证明方法可知式 (4.3) 存在唯一显式解
易得
显然
因此矩阵
接下来推导
并且
由
当
证毕.
5 数值模拟
对于模型 (1.2), 本节将通过一些数值例子来验证理论分析结果的可行性. 选择初值
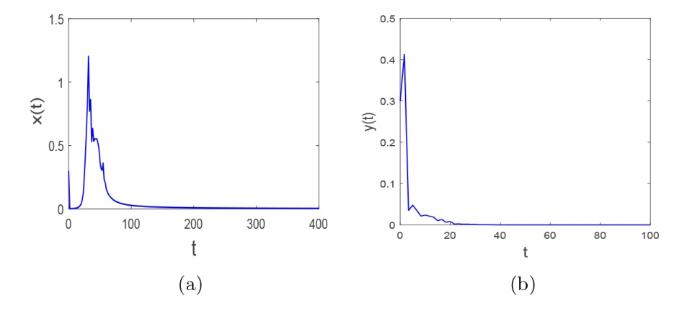
例 1 选取
图1
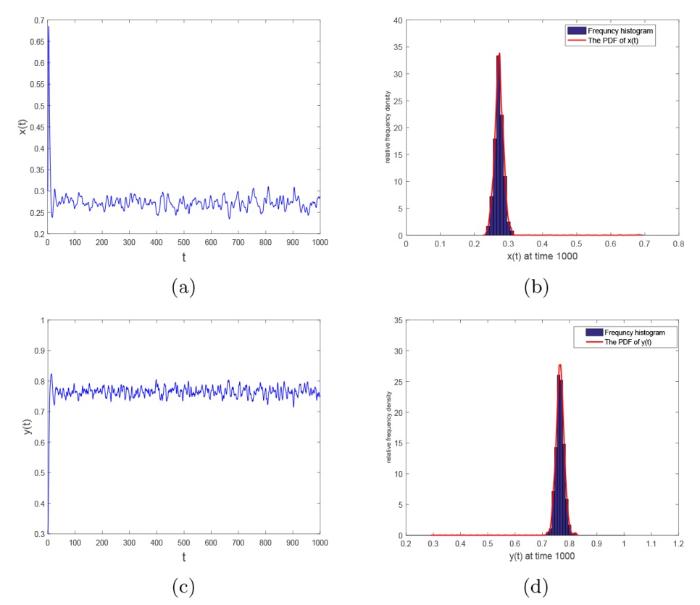
例 2 取
图2
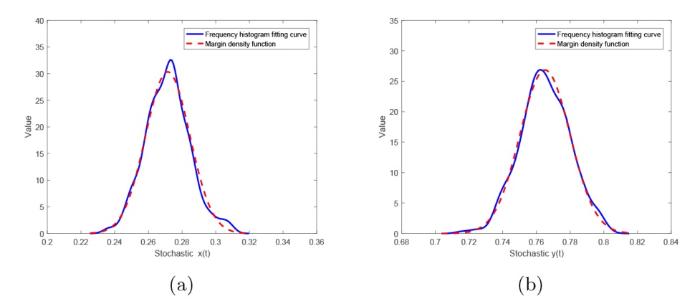
图3
相应的概率密度函数为
前文具体分析了一类具有 Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 过程的随机模型 (1.2) 的长期动力学行为. 首先证明了模型 (1.2) 全局解的存在唯一性. 其次, 分别给出了两种群指数绝灭和平稳分布存在的充分条件. 最后, 分析并得到了模型 (1.2) 在其唯一拟正平衡附近概率密度函数的具体表达式. 现将上述主要结论总结如下
(i) 基于定理 2.2 可知当
(ii) 平稳分布在随机过程的生物统计意义上表示一种关于随机变量的概率分布. 由定理 3.1 可知, 当
(iii) 概率密度函数是平稳分布的进一步表征, 反映了模型在拟稳态情形下随机变量精确输出值的概率分布. 若
综上所述, 两种群指数绝灭和平稳分布存在的充分条件以及唯一概率密度函数的存在条件揭示了两种群密度与捕食者的内禀增长率
参考文献
Global stability and canard explosions of the predator-prey model with the sigmoid functional response
DOI:10.1137/21M1437755 URL [本文引用: 1]
Bifurcation and chaos of a discrete predator-prey model with Crowley-Martin functional response incorporating proportional prey refuge
Hopf bifurcation analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling-II type functional response and a prey refuge
Impact of fear effect on the growth of prey in a predator-prey interaction model
Influence of Allee effect and delay on dynamical behaviors of a predator-prey system
Spatial pattern formation and delay induced destabilization in predator-prey model with fear effect
A stochastic predator-prey system with modified LG-Holling type II functional response
A generalized stochastic competitive system with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process
A stochastic predator-prey model with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process: Characterization of stationary distribution, extinction and probability density function
A stochastic turbidostat model with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process: Dynamics analysis and numerical simulations
Analysis of a stochastic population model with mean-reverting Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process and Allee effects
Dynamical behaviors of a stochastic food chain system with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process
Environmental variability in a stochastic HIV infection model
Stationary distribution and periodic solution for stochastic predator-prey systems with nonlinear predator harvesting
Environmental variability and mean-reverting processes