1 引言
设
当
研究
成立的条件成为许多学者关注的课题. 为以示区别, 当
相对于 Max-Sum 全局等价, Max-Sum 局部等价在概率论的许多领域的应用价值更加重要. 例如, 在风险理论中, 仅仅知道索赔导致破产的可能性往往还不够, 更要关注的是相应的损失额在某个给定区间的可能性, 更深入的讨论参见 Foss[13]. 研究 Max-Sum 局部等价的动机可追溯到 Asmussen 等人[14] 对局部重尾分布的系统研究, 通过定义局部长尾分布族
众所周知, copula 函数在相依性建模方面是一个强有力的工具. 由 Sklar 定理可知, 随机向量的联合分布中关于各分量的相依结构完全由其对应的 copula 函数确定, 更详尽的讨论参见 Nelsen[23]. FGM copula 因其结构简单被广泛研究, 其联系函数
其中常数
其中, 正整数
以及
那么 (1.5) 式确为 copula 函数. 通过对 (1.5) 式关于每个变量进行求导并重新排列, 得到 Bernstein copula 的密度为
本文将在 Bernstein copula 作为连接函数的条件下来研究随机变量的 Max-Sum 局部等价式. 从上一段的讨论可知对于任意有界连续的 copula 函数, 总可以用 Bernstein copula 来逼近, 这极大地扩张了 Max-Sum 局部等价式成立的范围. 本文的主要结果如下.
定理 1.1 给定
(1) 假设对于某个
(2) 此外, 进一步假设对于某个
则
从而 Max-Sum 局部等价式 (1.11) 成立.
需要说明的是, 本文主要结果的证明, 既运用了“一次大跳”原理, 也充分挖掘了 Bernstein copula 的相关性质. 另外, 沿用刘希军和王岳宝[20] 的处理方法, 将会在一定条件下得到实值情形下的 Max-Sum 局部等价式, 限于篇幅, 本文不作展开. 本文的其余部分结构如下: 第 2 节介绍符号和预备知识, 包括 Bernstein copula 和局部重尾分布族的一些重要性质. 第 3 节给出主要结果的具体证明. 第 4 节给出相应的数值实验结果.
2 符号和预备知识
为表达简洁, 本节首先介绍证明中需要的相关记号, 类似的记号约定参见龚婵[33]. 对任意正整数
如果给定
对于给定的
若对除第
采用上述记号, 则 (1.5) 式中的 Bernstein copula 可改写为
通过比较 (1.5) 式和 (2.1) 式的系数, 有
由 (2.1) 式容易看出, FGM copula (1.4) 是 Bernstein copula 当
引理 2.1 给定
证 根据 copula 函数的性质, (2.1) 式可视为边缘分布均服从 [0,1] 上均匀分布的随机向量
上式等价于
令
因此, 当
注意到
引理 2.1 证毕.
(2.3) 式成立. 此时,
引理 2.2 如果二维随机变量
证 注意到
根据 (2.5) 式, 有
最后一步根据公式
用 (2.9) 式减去 (2.10) 式, 有
引理 2.2 证毕.
接下来, 介绍一些局部重尾分布族的概念. 更详尽的讨论可参见 Asmussen 等人[14].
定义 2.1 设分布
则称分布
则称分布
在此指出的是, 对于
如果
下面的引理 2.3 来自文献 [21,引理 2.2,2.3] 的等价描述.
引理 2.3 对固定的
另外, 如果
3 定理 1.1 的证明
3.1 定理 1.1 (1) 的证明
证 将
首先处理
根据引理 2.2, 存在正常数
结合 (3.2) 式, 有
再处理 (3.1) 式余下部分. 显然, 对于任意的
结合 (3.1) 式, (3.3) 式和 (3.4) 式, 立得 (1.9) 式.
3.2 定理 1.1 (2) 的证明
证 采用数学归纳法来证明对于任何
其中,
首先, 当
对于
注意到
类似地,
对于
其中
现假设对于所有的
由对称性, 只需考虑对任意的
注意到
再根据 (2.1) 式, 有
将被积函数简化为
由
上面的第二步利用了不等式: 如果
下证明对
有
由 (3.11) 式和 (3.12) 式, 得
再考虑
现设
最后, 考虑
综合 (3.10)-(3.15) 式, 可知当
4 数值实验
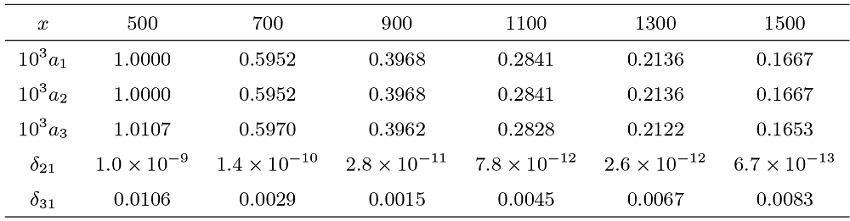
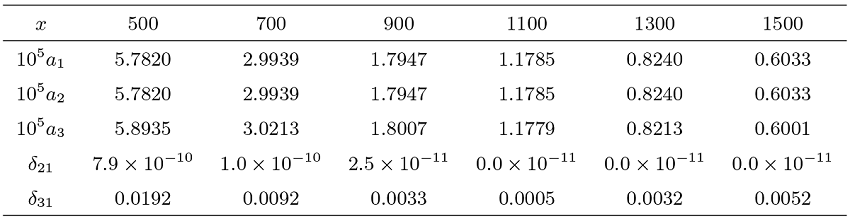
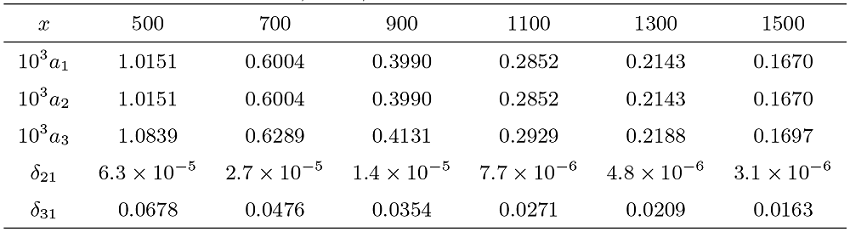
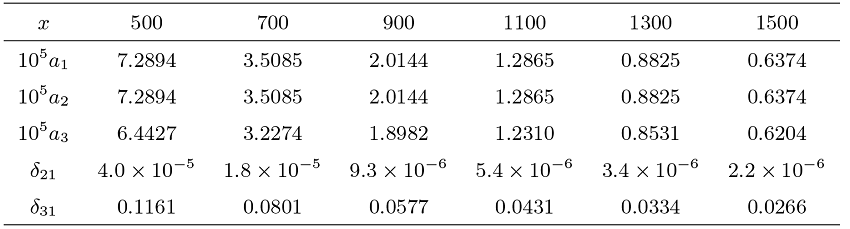
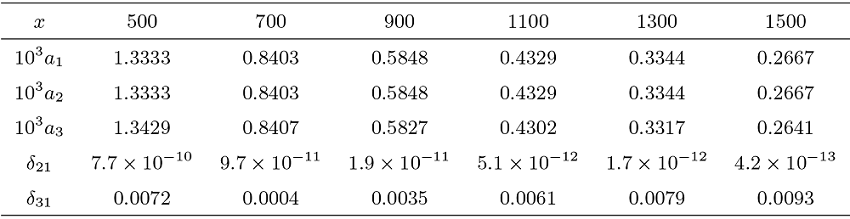
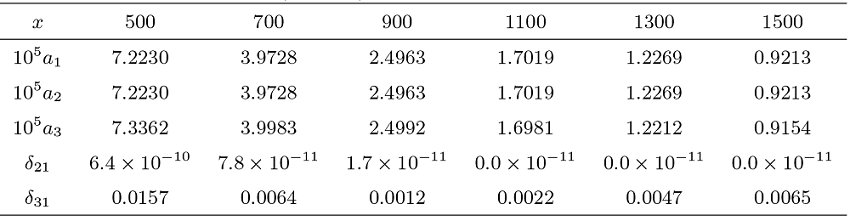
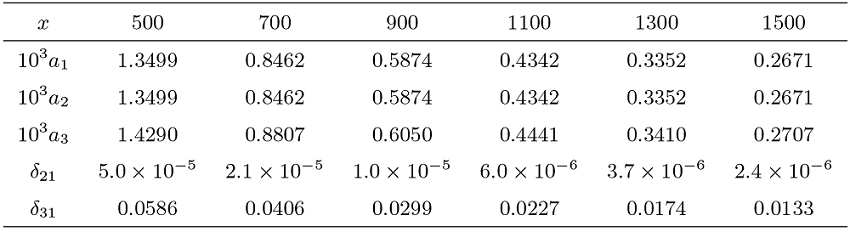
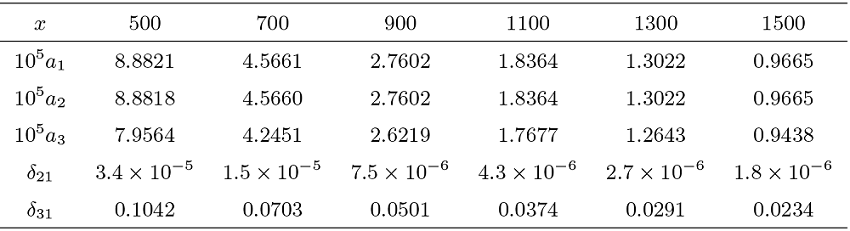
本节通过数值实验来进一步考察定理 1.1 结论的近似效果, 验证 Max-Sum 局部等价式的可行范围. 为了方便, 我们仅考虑二维情形. 假定随机变量
其参数
其中
其参数
设
由于 Pareto 分布的重尾程度主要由
(1) 两个局部分布概率之和
(2) 最大值落在给定区间的概率
(3) 部分和落在给定区间的概率
(4) 相对误差
数值结果表明, 本文关于最大值和部分和的局部渐近表达式整体精度较高. 最大值的相对误差不超过
参考文献
On closure and factorization properties of subexponential and related distributions
Weighted sums of subexponential random variables and asymptotic dependence between returns on reinsurance equities
Maxima of sums and random sums for negatively associated random variables with heavy tails
Tail asymptotics for the sum of two heavy-tailed dependent risks
Tail behavior of negatively associated heavy-tailed sums
Notes on the asymptotics of the tail probabilities of sums for negatively associated random variables with heavy tails
Sums of pairwise quasi-asymptotically independent random variables with consistent variation
Asymptotic tail probabilities of sums of dependent subexponential random variables
On sums of conditionally independent subexponential random variables
Tail behavior of sums and maxima of sums of dependent subexponential random variables
Some discussions on the local distribution classes
On pairwise quasi-asymptotically independent random variables and their applications
Asymptotics for sums of random variables with local subexponential behaviour
Asymptotic behavior of tail and local probabilities for sums of subexponential random variables
Local asymptotics of the cycle maximum of a heavy-tailed random walk
Large deviations for random walks under subexponentiality: The big-jump domain
Asymptotics for the moments of the overshoot and undershoot of a random walk
Local precise large deviations for sums of random variables with O-regularly varying densities
不同分布的卷积的局部封闭性及局部渐近性的充分条件和必要条件
DOI:10.12341/jssms08391
[本文引用: 2]

得到了支撑在[0,\infty)上的不同分布的卷积(包括卷积根)的局部封闭性及局部渐近性的充分条件和必要条件,它揭示了不同分布的卷积及两两卷积之间的内在关系. 这一结果的充分性部分推广了Geluk等非局部的相应结果,并且两者使用的方法是不同的; 而这一结果的必要性部分是Geluk等人的结果中所没有的. 最后, 讨论了(-\infty,\infty)上不同分布卷积的局部封闭性及局部渐近性.
The sufficient condition and necessary condition of local closure and local asymptotic for the convolutions of non-identical distributions
DOI:10.12341/jssms08391
[本文引用: 2]

得到了支撑在[0,\infty)上的不同分布的卷积(包括卷积根)的局部封闭性及局部渐近性的充分条件和必要条件,它揭示了不同分布的卷积及两两卷积之间的内在关系. 这一结果的充分性部分推广了Geluk等非局部的相应结果,并且两者使用的方法是不同的; 而这一结果的必要性部分是Geluk等人的结果中所没有的. 最后, 讨论了(-\infty,\infty)上不同分布卷积的局部封闭性及局部渐近性.
Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern 联合分布的 Max-Sum 局部等价式
Max-Sum local equivalence of random variables with Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern joint distribution
服从 FGM Copula 的实值重尾随机游动的局部 Max-Sum 等价
The local max-sum equivalence of real valued random walks with heavy-tailed increments following FGM copula
The Bernstein copula and its applications to modeling and approximations of multivariate distributions
Asymptotic properties of the Bernstein density copula estimator for
Large sample behavior of the Bernstein copula estimator
Some new results on the empirical copula estimator with applications
A joint stochastic simulation method using the Bernstein copula as a flexible tool for modeling nonlinear dependence structures between petrophysical properties
A multivariate Bernstein copula model for permeability stochastic simulation
Dependence modeling in non-life insurance using the Bernstein copula
多项式 Copula 方法对市场相关结构的分析
An analysis to dependence patterns in a polynomial copula approach
Second order risk aggregation with the Bernstein copula