1 引言
其中
其中矩阵
文献 [9] 为增强算法鲁棒性, 通过最小化加权
其中
定义
和具有非负对角元的对角矩阵
模型 (1.4) 可进一步可转化为如下迹函数极小化模型
模型 (1.6) 中, 因为目标函数的复杂性且双未知变量
假定
传统上在欧氏空间中处理一些具有约束的问题常使用拉格朗日法或贪婪算法, 而这些方法往往会导致次优解的生成. 为了在数值计算中获得更精确的数值解, 黎曼流形优化开辟了一个新的方向. 采用黎曼流形优化有两个显著的优势: 第一, 对于许多具有黎曼几何结构约束的优化问题, 通过黎曼流形上的优化可以更好地利用约束空间的几何结构, 转化为黎曼流形上的无约束优化问题, 以获得更精确的数值解. 第二, 通过引入适当的度量, 可以将某些欧氏空间中的非凸问题转化为黎曼流形上的凸问题, 进而改善数值计算方法, 获得全局最优解.
黎曼流形优化问题目前已广泛应用于机器学习, 数据挖掘, 计算机视觉, 材料科学等领域. 如果将可行集限制在流形上, 流形优化问题就是一个流形上的无约束优化问题. 因此只要保证迭代点在流形上, 各种无约束优化算法都对应着流形上的优化算法, 如梯度类方法, 共轭梯度法, 信赖域方法, 牛顿法, 拟牛顿法和阻尼牛顿法等. 乘积流形黎曼优化近年来也得到了国内外学者的大量关注, 并应用于实际问题获得了一系列的研究成果. 理论和实践证明, 将具有约束的多变量矩阵优化问题转化为相应乘积流形上的无约束优化问题, 引入黎曼流形优化算法可以获得更有效的数值解. 如 Sato 和 Sato[11]提出了基于乘积流形
黎曼共轭梯度法是欧式空间非线性共轭梯度法在流形上的推广, 由于其良好的收敛特性, 目前已成为黎曼可行一阶优化方法中较常用的算法, 近年来各类黎曼非线性共轭梯度法得到了国内外学者的持续关注, 并应用于具体问题获得了相当丰富的研究成果[26⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-33]. 本文结合乘积流形
本文余下内容组织如下: 第 2 节讨论乘积流形
2 乘积流形 \mathrm{St}(m, d) \times \mathcal{P} 几何性质以及目标函数的黎曼梯度、黎曼海塞
首先给出乘积流形
由于 Stiefel 流形
同时线性流形
故乘积流形
令在欧式空间
由于乘积流形
其诱导范数为
其中
分别表示
对于乘积流形
其中
表示限制在乘积流形上点
其中,
其中对于给定的列满秩矩阵
对
其中
分别为
接下来推导问题 (1.7) 中目标函数
易知
引理 2.1
证 因为
故
利用切空间
证毕.
引理 2.2
证
结合
注意到
(2.18) 式的最后一个等式中用到了
注意到若
上式可以简化 (2.18) 式中
将 (2.19) 式代入 (2.18) 式, 并结合 (2.20) 式, 可得
将 (2.16) 和 (2.12) 式代入 (2.21) 式可得 (2.15) 式.
3 黎曼非线性共轭梯度
给定当前迭代点
其中
本文将 Zhang-Hager 技术与文献 [40] 提出的 Armijo 型线搜索相结合, 针对本文具体模型, 按如下方式选取步长: 给定
其中迭代参考值
而
对于不等式 (3.2) 中的步长
事实上, 由
结合下文引理 4.3 的结论
由极限保号性, 存在
3.1 求解问题 (1.7) 的黎曼非线性共轭梯度法及全局收敛性
结合上文中给出的乘积流形收缩映射、向量转移具体计算公式, 目标函数黎曼梯度及非单调线搜索公式, 下面给出求解问题 (1.7) 的一类非单调黎曼非线性共轭梯度法的具体迭代格式.
算法 1 求解问题 (1.7) 的黎曼非线性共轭梯度法
给定初始点
1. 当
2. 选择
3. 更新
4. 令
其中
5. 更新
6. 令
注 3.1 由 (3.7) 式中参数
4 收敛性分析
本节给出算法 1 的全局收敛性分析. 记
记
由文献 [35, p56] 可知,
其中
引理 4.1 对
是紧集.
证
若记
又由
故有
上式左边为关于
由于
另外, 对
其中 “dist” 表示
引理 4.2 存在非负常数
证
此时
故可得
此时
下面给出算法 1 的全局收敛性, 为此先建立序列
引理 4.3 令
此外, 序列
证 定义函数
则
从引理 4.2 和非单调 Armijo 类条件可知
这意味着对于所有的
取
另一方面, 由算法 1 和 (4.7) 式有
因此序列
引理 4.4 在算法 1 中, 当
证 由 Zhang-Hager 条件和算法 1 可知
又有
令两边取极限, 可得
(4.15) 式的第二个极限意味着存在
设
结合引理 4.3 可得
结合中值定理, 柯西-施瓦茨不等式以及 (4.17) 式可知, 存在一个
结合 (4.17) 式和引理 4.2 有
因此, 当
定理 4.1 令
证 根据 (4.15) 式中的第一个极限和 (4.7) 式有
令
其中
这意味着对所有
5 数值实验
本节利用数值实验和数值比较验证算法 1 对于求解问题 (1.7) 的有效性. 所有的数值结果均通过 Matlab(R2022a),
(1) 关于
其中
(2) 初始迭代矩阵. 本文算法及比较算法的迭代初值
其中
(3) 算法终止标准. 参考文献 [42] 中关于黎曼梯度类算法终止标准的说明, 算法 1 的终止标准取为:
其中参数
(4) 初始步长. 不等式 (3.2) 中试验步长
其中
其中
5.1 与文献 [9] 的近似交替最小二乘方法比较
对于问题 (1.6), 在变量矩阵
对于 (5.3) 式中的
对于 (5.3) 式中的
显然问题 (5.5) 关于约束变量
上述极值问题 (5.6) 的解可以通过如下特征值-特征向量分解求得
其中
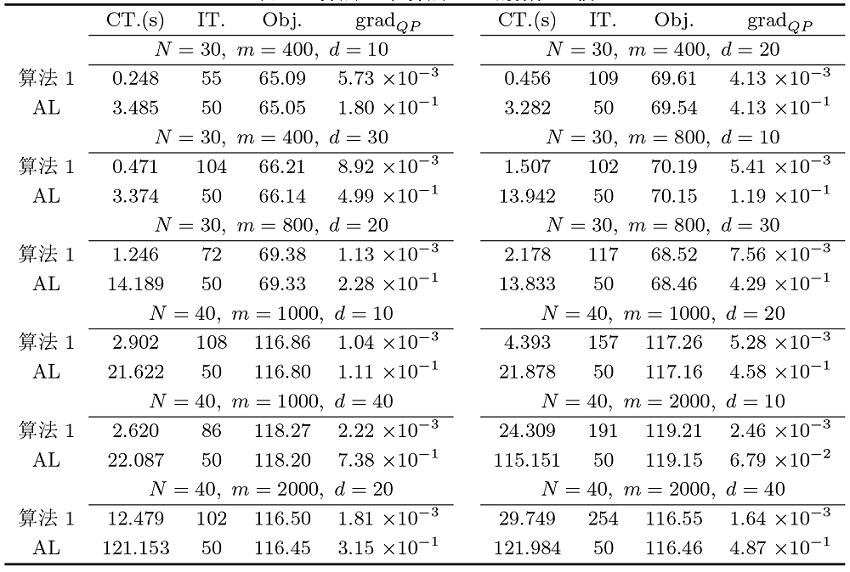
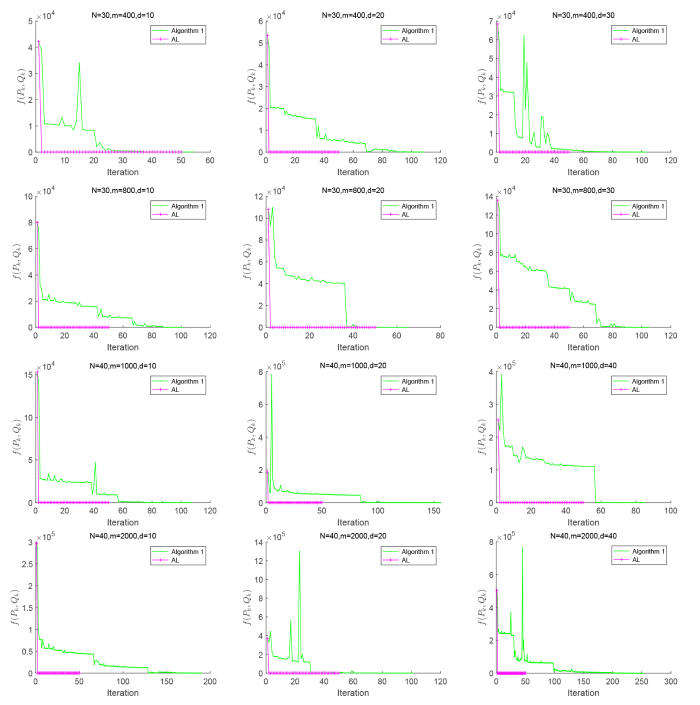
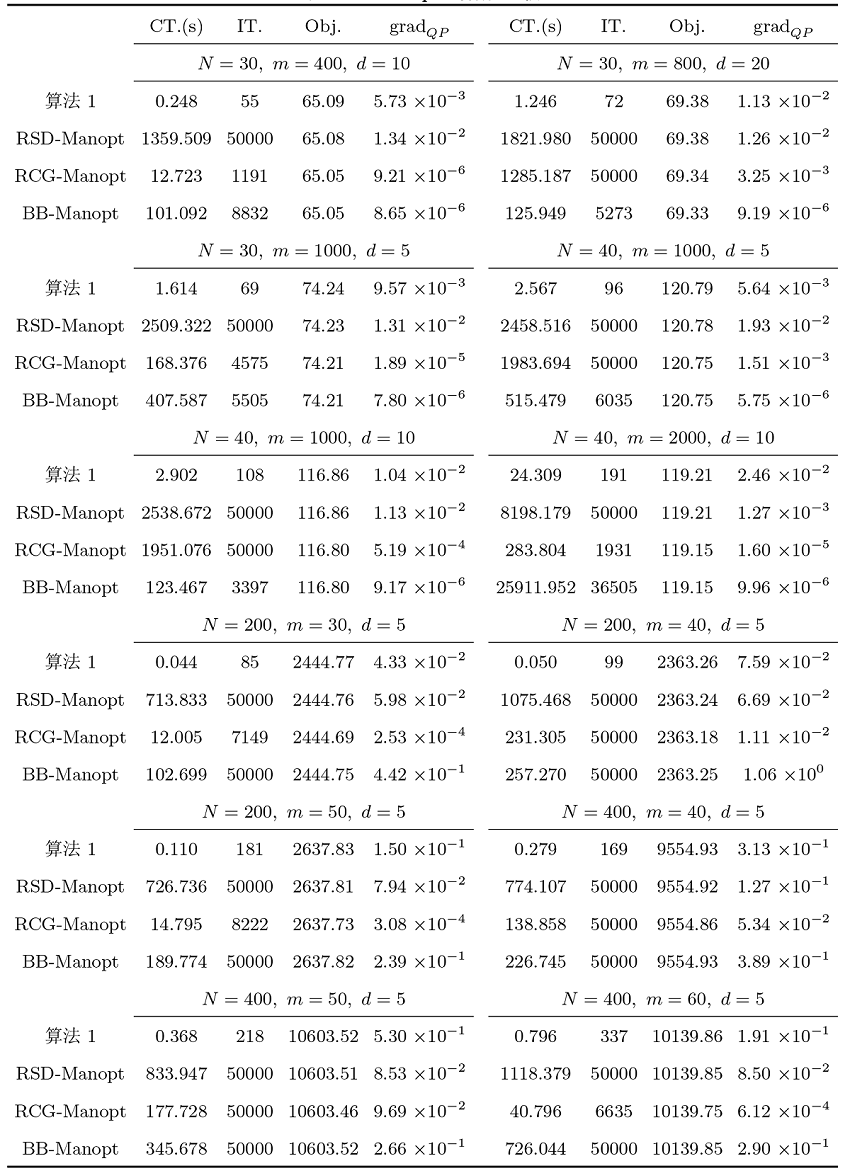
表1给出了算法 1 与文献 [9] 中近似交替最小二乘算法 (AL) 在不同系统维数下的数值比较结果, 其中算法 AL 的最大迭代步设置为 50. 表1 中“CT.” 和“IT.”分别表示迭代终止所需的计算时间和迭代次数
图1
5.2 与两类主流非单调线搜索技术的数值比较
本文提出的线搜索 (3.2) 实质上是结合了 Zhang-Hager 非单调线搜索技术与文献 [40] 中单调 Armijo 型线搜索的一种新型非单调线搜索. 为验证其有效性, 本节与前文提到的两种主流的非单调线搜索-Zhang-Hager线搜索技术和 Max 型非单调线搜索来进行比较. 与之比较的采用两类非单调搜索技术的代表性黎曼梯度类算法包括文献 [42] 中提出的应用于流形优化的基于曲线搜索的黎曼梯度下降法 ({OptStiefelGBB}), 文献 [32,43] 推广的基于欧式空间 Dai 非线性共轭梯度法且应用于流形优化的黎曼非线性共轭梯度法 ({RCG}). 首先给出算法 {OptStiefelGBB} 和 {RCG} 应用于求解问题 (1.7) 的迭代框架.
OptStiefelGBB: 对于给定参数
其中作用于 Stiefel 流形上的收缩映射
RCG: 迭代步长
其中作用于 Stiefel 流形上的收缩映射
其中
其中
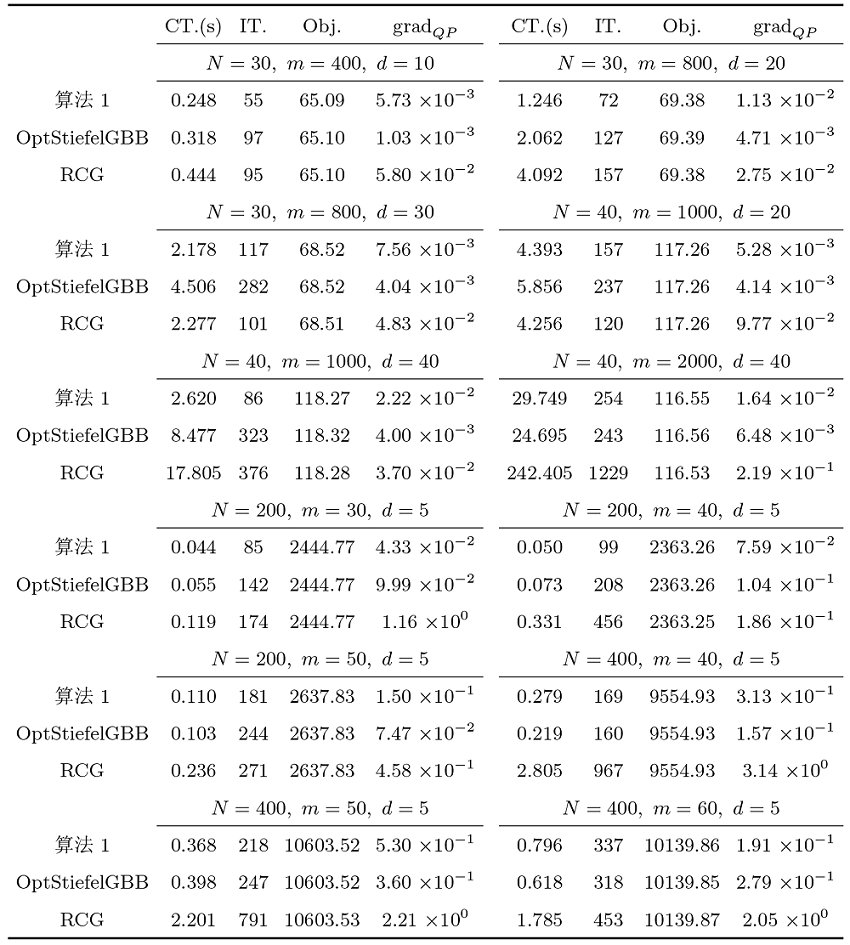
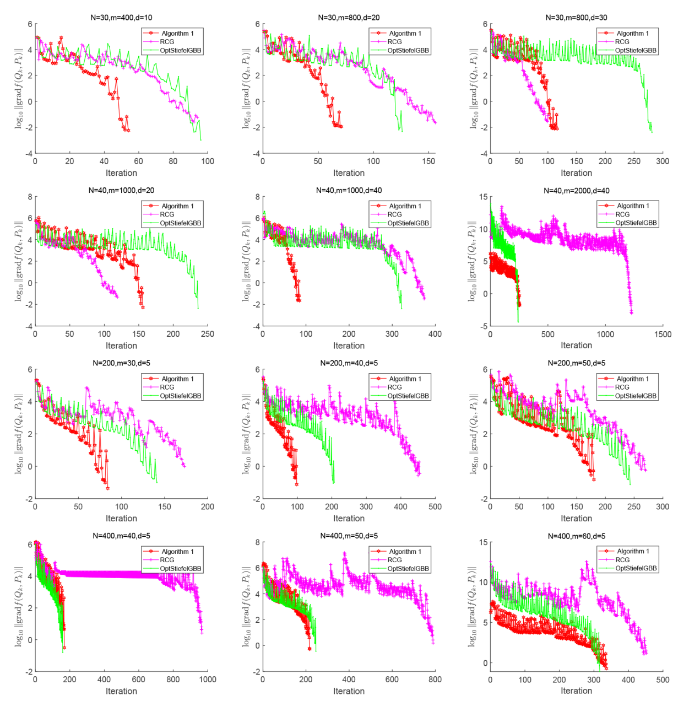
表2给出了不同系数维数下算法 1 与 OptStiefelGBB 和 RCG 的数值比较结果, 其中表头“CT.”、“IT.”、“Obj.”和“
图2
5.3 与黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt 中已有的黎曼一阶方法比较
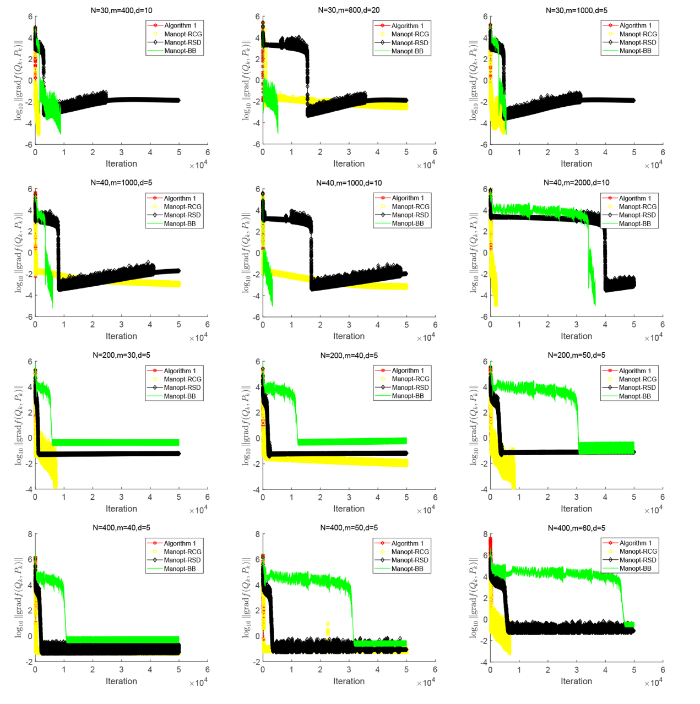
本小节给出算法 1 与黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt[44] 中已有的一阶方法进行数值比较, 与之比较的算法包括 Steepest-descent(RSD-Manopt), Conjugate-gradient(RCG-Manopt) 和 Barzilai-Borwein(BB-Manopt). 表3给出了在低样本量高维样本和高样本量低维样本两种情况下四种算法的数值比较结果. 图3给出了四种算法的黎曼梯度范数随迭代步的半对数变化曲线图. 黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt 中的三类算法其相关参数选取和终止标准均取为默认, 最大迭代步修改为 50000. 从表3中数据和图3中黎曼梯度范数的变化曲线图可以看出, 算法 RSD-Manopt 和算法 BB-Manopt 在大多数情况下都达到最大迭代步, 其黎曼梯度范数下降相对比较缓慢, 且达到一定精度后趋于稳定. 由此可以看出, 对于求解问题 (1.7), 本文算法较黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt 中的一阶算法相比也具有一定的优势.
图3
5.4 与黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt 中已有的黎曼二阶方法比较
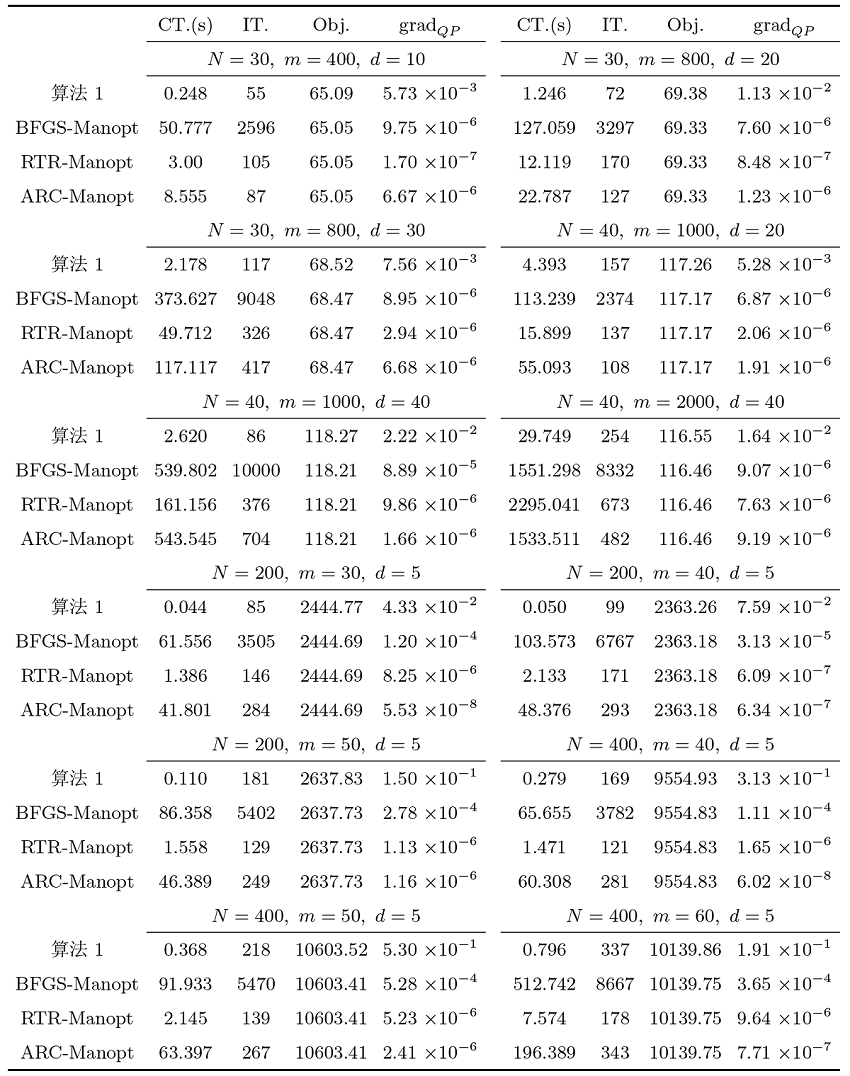
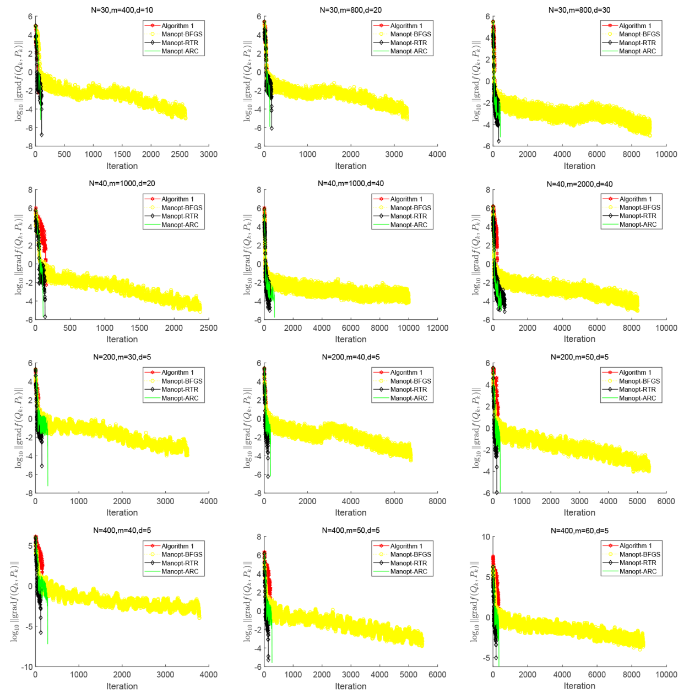
基于引理 2.2 中给出的黎曼海塞具体计算公式 (2.15), 本小节给出算法 1 与黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt 中已有的二阶算法进行数值比较, 与之比较的算法包括 BFGS(BFGS-Manopt), Trust-regions(RTR-Manopt) 和 Adaptive regularization by cubics(ARC-Manopt). 表4给出了在低样本量高维样本和高样本量低维样本两种情况下四种算法的数值比较结果. 图4给出了四种算法的黎曼梯度范数随迭代步的半对数变化曲线图. 黎曼优化工具箱 Manopt 中的三类算法其相关参数选取和终止标准均取为默认, 最大迭代步修改为 10000. 从表4的数据可以看出, 在对应的终止标准下, 算法 1 虽然总体迭代步数较多, 但因为不需要内迭代, 故总体时间较少. 算法 RTR-Manopt 因为需要用到截断共轭梯度法 (tCG) 求解相应信赖域子问题, 虽然具有超线性收敛速度, 但是总体迭代时间要比算法 1 长. 另在大多数情况下, 算法 BFGS-Manopt 的总体运行时间最长, 这是因为黎曼优化工具箱中的黎曼 BFGS 算法实质上是 Limited-memory BFGS 在黎曼流形上的推广, 且其默认的记忆规模为 30, 也即每次迭代中都需计算 30 次基于正交投影的向量转移算子, 这很大程度上主导了BFGS-Manopt 的运行时间.
图4
6 结论
本文研究了来源于特征提取的一类鲁棒判别回归模型, 该模型可重构为由 Stiefel 流形和线性流形所组成的黎曼乘积流形上的一类矩阵迹函数极小化问题, 即问题 (1.6). 因模型 (1.6) 的目标函数中矩阵
本文只针对问题 (1.7) 进行数值求解, 如何设计有效算法进一步求解问题 (1.6) 是下一步的研究工作, 可行的研究方案是采用交替更新的迭代思想, 其迭代框架为
1. 给定数据矩阵
2.
3. 生成
4. 通过算法1更新
但终止标准的建立和算法的收敛性分析值得进一步研究.
参考文献
Discriminating joint feature analysis for multimedia data understanding
Multimedia event detection using a classifier-specific intermediate representation
A shared-subspace learning framework for multi-label classification
The manifold ways of perception
One of the great puzzles of visual perception is how an image that is in perpetual flux can still be seen by the observer as the same object. In an informative Perspective, Seung and Lee explain the mathematical intricacies of two new algorithms for modeling the variability of perceptual stimuli and other types of high-dimensional data (Tenenbaum et al., and Roweis and Saul).
Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding
DOI:10.1126/science.290.5500.2323
PMID:11125150
[本文引用: 1]

Many areas of science depend on exploratory data analysis and visualization. The need to analyze large amounts of multivariate data raises the fundamental problem of dimensionality reduction: how to discover compact representations of high-dimensional data. Here, we introduce locally linear embedding (LLE), an unsupervised learning algorithm that computes low-dimensional, neighborhood-preserving embeddings of high-dimensional inputs. Unlike clustering methods for local dimensionality reduction, LLE maps its inputs into a single global coordinate system of lower dimensionality, and its optimizations do not involve local minima. By exploiting the local symmetries of linear reconstructions, LLE is able to learn the global structure of nonlinear manifolds, such as those generated by images of faces or documents of text.
Laplacian eigenmaps and spectral techniques for embedding and clustering//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
On the equivalence of HLLE and LTSA
Robust discriminant regression for feature extraction
Structure-preserving
Riemannian optimal model reduction of linear port-Hamiltonian systems
Riemannian optimal control and model matching of linear port-Hamiltonian systems
Riemannian optimal identification method for linear systems with symmetric positive-definite matrix
Riemannian inexact Newton method for structured inverse eigenvalue and singular value problems
Best low multilinear rank approximation of higher-order tensors, based on the Riemannian trust-region scheme
A Riemannian optimization approach to the matrix singular value decomposition
Riemannian Newton-CG methods for constructing a positive doubly stochastic matrix from spectral data
A riemannian fletcher-reeves conjugate gradient method for doubly stochastic inverse eigenvalue problems
A geometric Gauss-Newton method for least squares inverse eigenvalue problems
A geometric nonlinear conjugate gradient method for stochastic inverse eigenvalue problems
A Riemannian inexact Newton-CG method for constructing a nonnegative matrix with prescribed realizable spectrum
A Riemannian under-determined BFGS method for least squares inverse eigenvalue problems
A Riemannian inexact Newton dogleg method for constructing a symmetric nonnegative matrix with prescribed spectrum
Riemannian modified Polak-Ribière-Polyak conjugate gradient order reduced model by tensor techniques
Global convergence of Riemannian line search methods with a Zhang-Hager-type condition
A new, globally convergent Riemannian conjugate gradient method
A Dai-Yuan-type Riemannian conjugate gradient method with the weak Wolfe conditions
Hybrid Riemannian conjugate gradient methods with global convergence properties
A Riemannian conjugate gradient method for optimization on the Stiefel manifold
Low-rank matrix completion by Riemannian optimization
A nonmonotone line search technique and its application to unconstrained optimization
Optimization methods on Riemannian manifolds and their application to shape space
A nonmonotone line search technique for Newton's method
Global convergence of a modified Fletcher-Reeves conjugate gradient method with Armijo-type line search
A feasible method for optimization with orthogonality constraints
A Riemannian optimization approach for solving the generalized eigenvalue problem for nonsquare matrix pencils
Manopt, a Matlab toolbox for optimization on manifolds