1 引言
在实践中,保险公司经常购买再保险,以降低其保险组合的风险.为简单起见,文献中通常假设一个保险公司只能从一个再保险公司购买再保险. 然而,常见的情况是,保险公司希望通过向不同风险厌恶的多家再保险公司购买再保险来分散风险.因此,研究具有多个再保险公司的最优再保险模型具有重要意义.例如, Chi和Meng[21]研究了在保险人总风险暴露的风险值或条件风险值最小化准则下,具有多个再保险人的最优再保险问题; Chen和Yuen[22]研究了扩散逼近模型下受交易费用影响的最优分红和有两个再保险公司的比例再保险问题; Meng等[23]研究了在连续时间模型下的最优再保险问题; Yao和Fan[24] 假设保险公司能够动态地控制分红、再融资和再保险策略,利用最优控制方法,研究了保险公司值函数最大化的最优策略,以及交易成本和最终价值对破产的影响.
在本文中,在风险资产价格模型受Ornstein-Uhlenbeck过程影响下,研究了保险公司最优投资和比例再保险策略. 与Liang等[26]不同的是,本文采用两个再保险公司来研究再保险问题,对于再保险保费是依据不同参数的指数保费原则计算的,并且分析了最优策略随模型参数的变化规律.比较有意思的是, Liang等[26]在复合泊松风险模型下的结果比扩散逼近风险模型下的结果复杂,而本文在扩散逼近风险模型下的结果比复合泊松风险模型下的结果复杂.论文的其余部分组织如下:第2节给出了模型和假设.第3节在复合泊松风险模型下推导出了最优投资和再保险策略的显式表达式.第4节在扩散逼近风险模型下推导出了最优投资和再保险策略的显式表达式. 第5节对最优投资和再保险策略进行了数值分析.
2 模型介绍
在经典风险模型下,盈余过程
其中
考虑具有两个再保险公司的比例再保险问题.对于给定的自留比例
其中
其中,
其中,
设
在本文中,我们假设再保险的保费根据指数保费原则进行计算.具体地,对于风险
其中常数
其中,
这里,我们假设保险公司有一个指数效用函数,其目标是最大化终端时刻
其中,
设
其终端条件为
其中
利用Yang和Zhang[32]的标准方法,可以得到如下验证定理.
对
3 复合泊松风险模型下的最优策略和值函数
来求解方程(2.6),其中
设
将(3.3)式带入方程(2.6),且由
设
对
分别对
进而可得
将
根据方程(3.5)及终端条件
其中
的解,其终端条件为
且方程(3.9)中的
将上式根据
其中
因此,如果
接下来,对
则方程(3.7)变为
这是一个带条件
其中
利用(3.12)式,带有终端条件(3.10)式的一阶线性微分方程(3.8)的解具有以下形式
其中
且
再者,根据(3.9)、(3.12)和(3.13)式,积分得到
因此,
最后,我们用下面的定理总结结果.
此外,值函数是
其中
K(t)、J(t)和L(t)分别在(3.12)-(3.14)式中给出,终端条件为(3.10)式.
4 扩散逼近风险模型下的最优策略和值函数
在本节中,我们假设(2.1)式中的总索赔过程采用扩散逼近模型,即
其中
它的值函数是
那么,相应的HJB方程为
且满足终端条件
设
对
其中
故
将
终端条件
类似于定理3.1,我们有以下结果.
最后,用下面的定理总结本节的主要结果.
此外,值函数是
其中
(ii)本文中,两家再保险公司均采用指数保费准则(公平的零效用准则),
(iii)与大多数文献不同的是,本文在复合泊松模型下的最优自留水平
5 数值分析
在本节中,我们将提供一些数值模拟来说明我们的结果.在整个数值分析过程中,除另有说明外,基本参数固定为
1) 复合泊松风险模型下,最优投资和再保险策略
(1) 模型参数
图 1
图 2
图 3
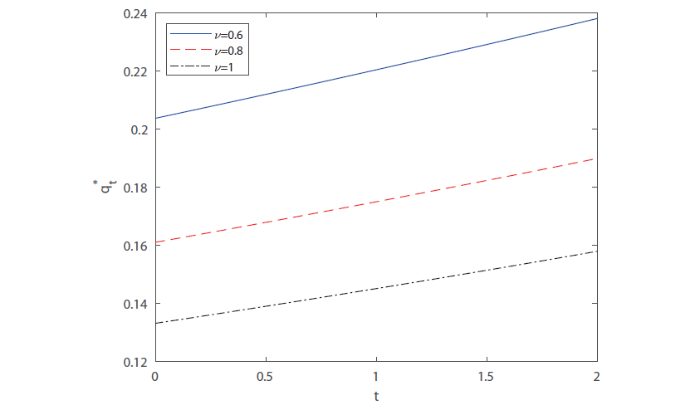
(iii) 而
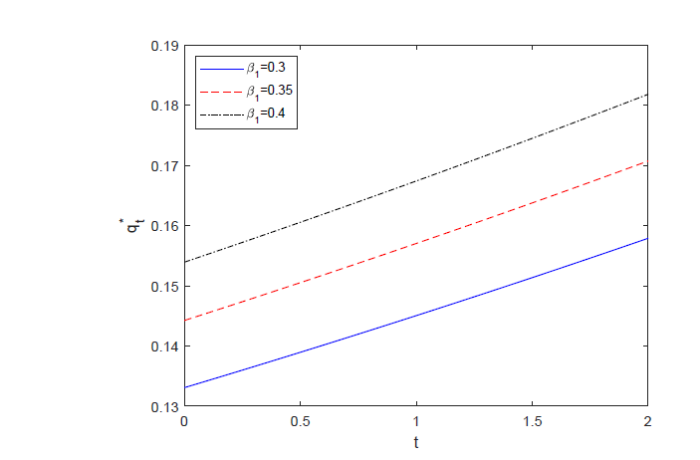
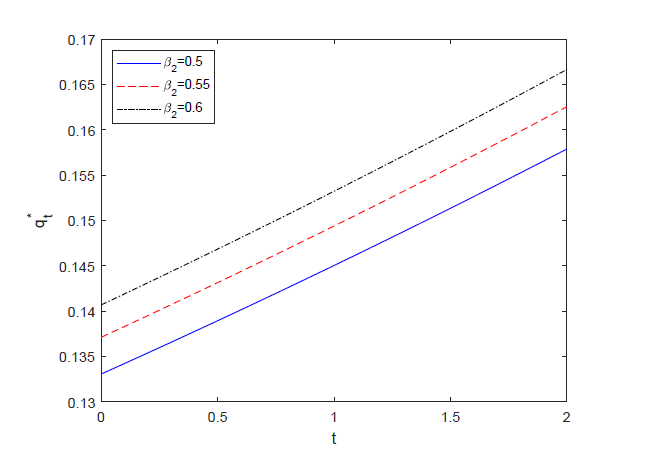
(2) 模型参数
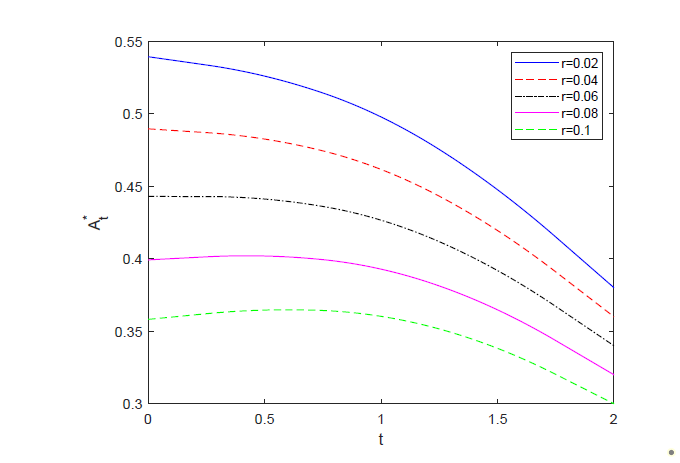
(i) 由图4知,无风险利率
图 4
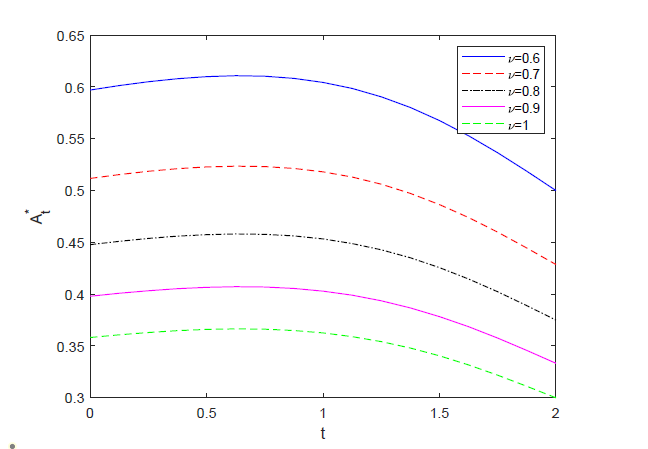
(ii) 在图5中,风险厌恶系数
图 5
2) 扩散逼近风险模型下,最优投资和再保险策略
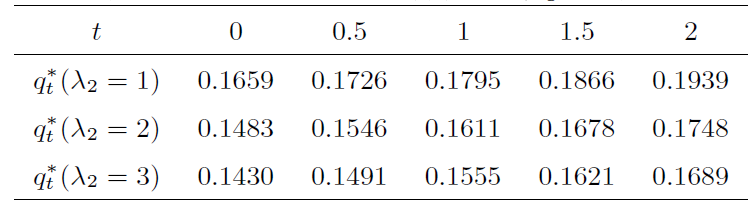
该模型下的
在表1中,固定任一指数分布,随着时间
参考文献
Optimal investment policies for a firm with random risk process: exponential utility and minimizing the probability of ruin
DOI:10.1287/moor.20.4.937
URL
[本文引用: 3]

We consider a firm that is faced with an uncontrollable stochastic cash flow, or random risk process. There is one investment opportunity, a risky stock, and we study the optimal investment decision for such firms. There is a fundamental incompleteness in the market, in that the risk to the investor of going bankrupt cannot be eliminated under any investment strategy, since the random risk process ensures that there is always a positive probability of ruin (bankruptcy). We therefore focus on obtaining investment strategies which are optimal in the sense of minimizing the risk of ruin. In particular, we solve for the strategy that maximizes the probability of achieving a given upper wealth level before hitting a given lower level. This policy also minimizes the probability of ruin. We prove that when there is no risk-free interest rate, this policy is equivalent to the policy that maximizes utility from terminal wealth, for a fixed terminal time, when the firm has an exponential utility function. This validates a longstanding conjecture about the relation between minimizing probability of ruin and exponential utility. When there is a positive risk-free interest rate, the conjecture is shown to be false. We also solve for the optimal policy for the related objective of minimizing the expected discounted penalty paid upon ruin.
Optimal investment for an insurer to minimize its probability of ruin
DOI:10.1080/10920277.2004.10596134 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal proportional reinsurance for controlled risk process which is perturbed by diffusion
Optimal dividend problem with a nonlinear regular-singular stochastic control
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2013.02.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Stochastic optimal control models for the insurance company with bankruptcy return
Time-consistent reinsurance-investment strategy for an insurer and a reinsurer with mean-variance criterion under the CEV model
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2015.01.038 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal investment and reinsurance for an insurer under Markov-modulated financial market
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2017.02.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal investment strategies for an insurer and a reinsurer with a jump diffusion risk process under the CEV model
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2017.08.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal investment-reinsurance strategies with state dependent risk aversion and VaR constraints in correlated markets
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2018.11.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal reinsurance and dividends with transaction costs and taxes under thinning structure
DOI:10.1080/03461238.2020.1824158 URL [本文引用: 1]
A non-zero-sum reinsurance-investment game with delay and asymmetric information
DOI:10.3934/jimo.2020004 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal dividend and proportional reinsurance strategy under standard deviation premium principle
DOI:10.1007/s40840-021-01220-w [本文引用: 1]
Pricing dynamic insurance risks using the principle of equivalent utility
DOI:10.1080/03461230110106327 URL [本文引用: 1]
Equity-indexed life insurance: pricing and reserving using the principle of equivalent utility
DOI:10.1080/10920277.2003.10596078 URL [本文引用: 1]
Pricing equity-linked pure endowments via the principle of equivalent utility
DOI:10.1016/S0167-6687(03)00166-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
An example of indifference prices under exponential preferences
DOI:10.1007/s00780-003-0112-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal reinsurance with default risk: a reinsurer's perspective
DOI:10.3934/jimo.2020103 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal dynamic reinsurance with dependent risks: variance premium principle
DOI:10.1080/03461238.2014.892899 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal reinsurance to minimize the probability of drawdown under the mean-variance premium principle
DOI:10.1080/03461238.2020.1788136 URL [本文引用: 1]
Pricing catastrophe reinsurance under the standard deviation premium principle
DOI:10.3934/math.2022249 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal reinsurance arrangements in the presence of two reinsurers
DOI:10.1080/03461238.2012.723638 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal dividend and reinsurance in the presence of two reinsurers
DOI:10.1017/jpr.2016.20
URL
[本文引用: 1]

\nIn this paper the optimal dividend (subject to transaction costs) and reinsurance (with two reinsurers) problem is studied in the limit diffusion setting. It is assumed that transaction costs and taxes are required when dividends occur, and that the premiums charged by two reinsurers are calculated according to the exponential premium principle with different parameters, which makes the stochastic control problem nonlinear. The objective of the insurer is to determine the optimal reinsurance and dividend policy so as to maximize the expected discounted dividends until ruin. The problem is formulated as a mixed classical-impulse stochastic control problem. Explicit expressions for the value function and the corresponding optimal strategy are obtained. Finally, a numerical example is presented to illustrate the impact of the parameters associated with the two reinsurers' premium principle on the optimal reinsurance strategy.\n
Optimal reinsurance policies with two reinsurers in continuous time
DOI:10.1016/j.econmod.2016.07.009 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal risk control and dividend strategies in the presence of two reinsurers: Variance premium principle
DOI:10.3934/jimo.2017090 URL [本文引用: 1]
On the ruin probability of an insurance company dealing in a BS-market
Optimal proportional reinsurance and investment in a stock market with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2011.04.005 URL [本文引用: 5]
Optimal mean-variance reinsurance in a financial market with stochastic rate of return
DOI:10.3934/jimo.2020051 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal investment and proportional reinsurance strategy under the mean-reverting Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process and net profit condition
DOI:10.3934/jimo.2020143 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal reinsurance and investment strategy with delay in Heston's SV model
DOI:10.1007/s40305-020-00331-8 [本文引用: 1]
A hybrid stochastic differential reinsurance and investment game with bounded memory
DOI:10.1016/j.ejor.2021.04.046 URL [本文引用: 1]
Martingale method for optimal investment and proportional reinsurance
DOI:10.1007/s11766-021-3463-8 [本文引用: 1]
Optimal investment for insurer with jump-diffusion risk process
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2005.06.009 URL [本文引用: 2]