1 引言
随着资本市场的发展和人口老龄化问题日益突出, 养老金问题已成为一个热点话题, 同时制定一个可以使收益达到最优的养老金计划也显得尤为重要. 传统上主要有两种养老金计划: 确定收益型(
有关养老金计划随机控制的文献相当丰富. 从方法论角度来看, 有两种常见方法研究养老金计划的最优投资问题. 一种是鞅方法, Guan等[1]研究了损失厌恶和风险价值约束下的
在早期的养老金计划文献中, 一般假设决策者准确知道真实的概率测度. 事实上, 这一假设很难在现实中得到满足, 决策者往往无法准确知道金融模型的真实概率测度, 这意味着用于描述金融模型的任何特定概率测度都具有很大的不确定性. 因此, 有学者提出并研究了模型不确定性对养老金计划投资问题的影响. 例如, Wang等[10]研究了随机利率和随机波动率的
Li等[16]考虑了养老金计划的
2 模型建立
考虑一种集体养老金计划, 其目标收益由发起人在初始时设定, 并随时间以一定的预定比率增长. 每一时刻向退休成员群体支付的实际收益受外生工资过程控制, 其随机来源与金融市场有关. 养老基金投资于三种资产: 无风险资产、股票和可违约债券. 计划受托人管理基金的资产组合, 并调整支付给退休人员的福利, 使其福利足够接近目标, 且不会向未来的参保人借太多的钱(或余留太多的钱). 在下面前部分中, 将描述金融市场模型和
设
1) 金融市场
假设金融市场由三种资产组成: 无风险资产、股票和可违约债券. 定义
这里
定义
其中
为了研究可违约债券的价格过程, 参考Bielecki[20], 定义如下违约过程.
定义2.1 令
假定在P测度下泊松点过程
定义2.2 鞅违约过程:
根据Bielecki[20], 得到
这里
2) 成员和计划条款
该养老金计划由活跃成员和退休成员构成. 活跃成员向养老基金缴费, 退休成员从养老基金获取收益. 假定所有成员在年龄
使用Bowers[22]的记号, 用
其中
我们用
该养老金计划从退休年龄
为确定
假设该计划对养老金的生活成本进行调整的年固定比例为
这个过程包括生活成本的自动增加和因新兴经验驱动的负担能力的调整.
假设该计划在0时刻有一个预先设定的退休福利总额的目标
其中
记0时刻每位活跃成员的瞬时缴费率为
其中
3) 养老金财富过程
假设计划受托人将养老金投资于无风险资产、股票和可违约债券. 记
其中
本文考虑Makeham模型的死亡力函数形式, 即死亡函数
由(2.1)–(2.5)式, 我们可将方程
3 最优控制问题
为引入金融风险的模糊性, 下面定义一组与
在可替代测度
其中
且
(ⅰ) 对于每个
(ⅱ)
(ⅲ) 对
因为
根据Girsanov定理, 在可替代测度
且泊松过程
因此, 我们得到
其中
其中
假设
这里
本文的目标函数定义如下
其中
为了便于分析, 我们假设
其中
定义3.1 (容许策略) 对于任何固定的
4 模型求解
下面我们出示验证定理, 可以利用经典随机控制理论给出证明, 其过程省略.
定理4.1 (验证定理) 假设存在函数
其中
边界条件
这里
则
定理4.2 对于目标收益养老金计划的
其中
其中
证 (ⅰ) 违约后情况(
当
这里
由
将
对
我们假设
将
令
得到
其中
将
(ⅱ) 违约前情况(
接下来推导违约前的
这里
假设
由边界条件
由
将
因此
令
得到
其中
将
命题4.1(ⅰ) 若
证 (ⅰ)
(ⅱ)
(ⅲ)
令
对
推论4.1 若
其中
其中
模糊厌恶的概率扭曲函数为
注4.1 由上述推论知, 若
推论4.2 若
其中
其中
注4.2 若
5 数值分析
在这一节, 将通过数值算例来分析目标收益养老金计划的
类似文献[5, 9, 16], 假定参数取值如下:
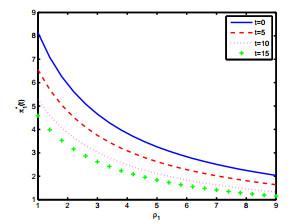
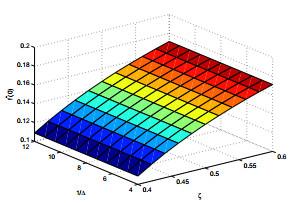
我们首先研究
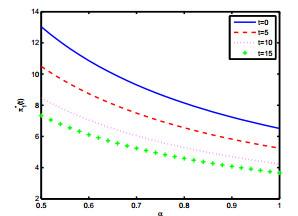
图 (a)
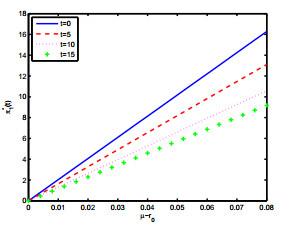
图 (b)
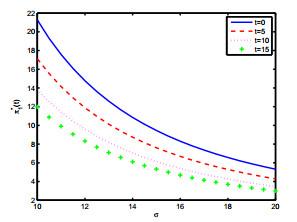
图 (c)
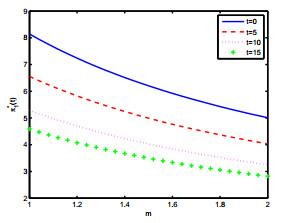
图 (d)
图 (e)
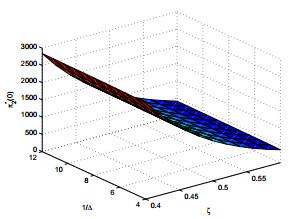
然后我们给出一个确定时刻
图 (f)
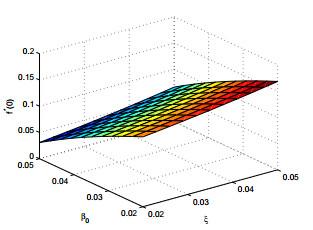
最后我们分别研究参数
图 (g)
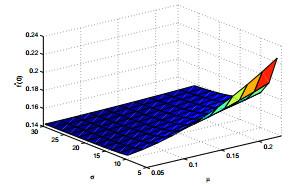
图 (h)反映
图 (h)
图 (i)
参考文献
Optimal management of DC pension plan under loss aversion and Value-at-Risk constraints
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2016.05.014 [本文引用: 1]
Asset allocation under loss aversion and minimum performance constraint in a DC pension plan with inflation risk
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2017.05.009 [本文引用: 1]
Optimal investment and benefit payment strategy under loss aversion for target benefit pension plans
Optimal DB-PAYGO pension management towards a habitual contribution rate
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2020.07.005 [本文引用: 1]
Optimal portfolios for DC pension plans under a CEV model
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2009.01.005 [本文引用: 2]
Equilibrium investment strategy for DC pension plan with default risk and return of premiums clauses under CEV model
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2016.10.007 [本文引用: 3]
Optimal investment strategies and intergenerational risk sharing for target benefit pension plans
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2018.02.003 [本文引用: 2]
Optimal investment strategies and risk-sharing arrangements for a hybrid pension plan
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2019.09.005 [本文引用: 1]
Robust optimal investment and benefit payment adjustment strategy for target benefit pension plans under default risk
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2021.113382 [本文引用: 9]
Robust optimal investment strategy for an AAM of DC pension plans with stochastic interest rate and stochastic volatility
DOI:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2018.03.003 [本文引用: 1]
Ambiguity aversion and optimal derivative-based pension investment with stochastic income and volatility
DOI:10.1016/j.jedc.2018.01.023 [本文引用: 1]
Preference and belief: ambiguity and competence in choice under uncertainty
DOI:10.1007/BF00057884 [本文引用: 1]
Alpha-robust mean-variance reinsurance-investment strategy
DOI:10.1016/j.jedc.2016.07.001 [本文引用: 1]
Data-driven robust mean-CVaR portfolio selection under distribution ambiguity
DOI:10.1080/14697688.2018.1466057
Equilibrium strategies for alpha-maxmin expected utility maximization
Alpha-robust mean-variance investment strategy for DC pension plan with uncertainty about jump-diffusion risk
DOI:10.1051/ro/2020132 [本文引用: 4]
Probabilistic sophistication and multiple priors
DOI:10.1111/1468-0262.00303 [本文引用: 2]
Differentiating ambiguity and ambiguity attitude
DOI:10.1016/j.jet.2003.12.004 [本文引用: 1]
A smooth model of decision making under ambiguity
DOI:10.1111/j.1468-0262.2005.00640.x [本文引用: 2]
Portfolio optimization with a defaultable security