1 引言
人类嗜T细胞病毒I型(HTLV-I)是一种外源性逆转录病毒, 与成人T细胞白血病(ATL)和HTLV-I相关脊髓病(HAM/TSP)密切相关. 然而, 只有一小部分感染者发展为ATL或HAM/TSP患者, 大部分HTLV-I感染者成为终身的无症状携带者(ACs). 此外, HTLV-I相关疾病的机制仍未明确, 暂无有效的治疗方法或可用的疫苗来治疗HTLV-I相关疾病[1].
与HIV-1病毒不同, 细胞外的HTLV-I病毒几乎不能被检测到. 因此, 适宜检测前病毒载量: 即外周血单核细胞携带HTLV-I整合前病毒的比例[2-3]. 在外周血中, HTLV-I主要感染CD
其中,
基于上述工作, 本文研究免疫时滞、饱和CTL免疫反应和免疫损害对HTLV-I感染动力学的影响, 为此考虑以下模型
在系统(1.2)中, 我们假设感染细胞的移除率大于有丝分裂的速率, 即
在相空间
由泛函微分方程的基本理论[15]可知, 在初始条件(1.3)下, 系统(1.2)的解存在且唯一.
容易证明, 系统(1.2)满足初始条件(1.3)的解是正的且最终有界, 集合
是系统(1.2)的正向不变集.
2 基本再生率和可行平衡点
系统(1.2)始终存在病毒未感染平衡点
若
定义
称
由(2.1)式的第四个方程可得
根据(2.4)式的前三个方程和(2.2)式, 有
由(2.2)式和(2.3)式可知,
图 1
解得
由
易知
3 可行平衡点的局部稳定性和Hopf分支
本节将研究系统(1.2)的局部动力学行为与
定理3.1 当
证 系统(1.2)在
显然, (3.1)式有两个负实根
下证当
注意到, 当
定义
显然,
当
定理3.2 当
证 系统(1.2)在
其中
以下证明方程
的根均具有负实部. 若否, 则方程(3.6)存在根
与(3.6)式矛盾. 因此, (3.6)式的所有根都具有负实部. (3.5)式的其余根由以下方程确定
其中
通过计算得到
由Routh-Hurwitz判据知, (3.7)式的所有根都有负实部. 因此, 当
系统(1.2)在
其中,
情形1 当
其中,
显然,
情形2 当
将(3.10)式的两个方程两边同时平方再相加, 得到
其中,
令
则
定义
由卡丹公式可知方程(3.13)的最大实根有以下情形
当
当
当
其中
与文献[17]的讨论类似,得到下列引理.
引理3.1 对于方程(3.12), 下列结论成立
(ⅰ) 若
(ⅱ) 若
1)
2)
3)
(ⅲ) 若
1)
2)
3)
假设(3.12)有四个正实根, 记为
其中,
对方程(3.8)关于
由(3.10)和(3.15)式可知
定理3.3 对于系统(1.2), 当
(ⅰ) 若(3.12)没有正实根, 对所有
(ⅱ) 若(3.12)至少存在一个正实根, 且
4 全局渐近稳定性
本节将通过构造适当的Lyapunov泛函并利用LaSalle不变性原理[15]研究各可行平衡点的全局渐近稳定性.
定理4.1 若
证 令
其中
若
定理4.2 若
证 令
沿着系统(1.2)的解计算
由均值不等式知,
定理4.3 若
证 令
沿着系统(1.2)的解计算
由均值不等式可知,
5 数值分析
本节利用Matlab软件对免疫激活平衡点
5.1 数值模拟
选取参数值
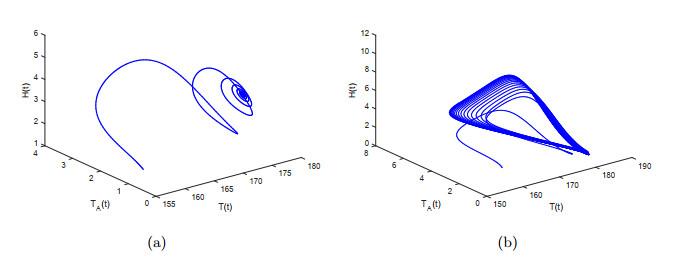
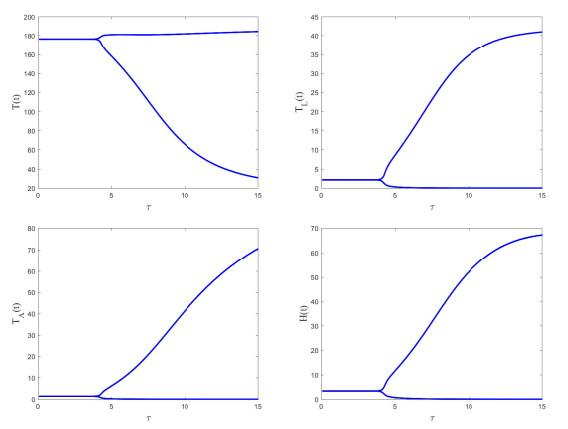
图 2
图 3
5.2 敏感性分析
由于参数的不确定性, 有必要研究再生率
根据
其中
由此得出结论:
表明相比于其他参数,
6 结论
本文研究了一类具有饱和CTL免疫反应、免疫损害和免疫时滞的HTLV-I感染模型. 通过计算, 推导出系统(1.2)的可行平衡点, 免疫未激活再生率和免疫激活再生率. 此外, 给出了每个平衡点稳定的条件: 当
参考文献
The immune response to HTLV-I
DOI:10.1016/S0952-7915(00)00107-2 [本文引用: 2]
Immunopathogenesis of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated neurologic disease
Quantifying HTLV-I dynamics
DOI:10.1038/sj.icb.7100050 [本文引用: 1]
Geometric stability switch criteria in delay differential systems with delay dependent parameters
DOI:10.1137/S0036141000376086 [本文引用: 1]
How does HTLV-I persist despite a strong cell-mediated immune response?
DOI:10.1016/j.it.2007.09.006 [本文引用: 1]
Mathematical analysis of the global dynamics of a HTLV-I infection model, considering the role of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
DOI:10.1016/j.matcom.2020.09.009 [本文引用: 1]
Global stability and hopf bifurcation of an HIV-1 infection model with saturation incidence and delayed CTL immune response
Multiple stable periodic oscillations in a mathematical model of CTL response to HTLV-I infection
DOI:10.1007/s11538-010-9591-7 [本文引用: 1]
Multistability in a model for CTL response to HTLV-I infection and its implications to HAM/TSP development and prevention
DOI:10.1007/s11538-009-9465-z [本文引用: 2]
Viral dynamics of HIV-1 with CTL immune response
DOI:10.3934/dcdsb.2020212 [本文引用: 2]
Dynamics analysis of a delayed viral infection model with immune impairment
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2011.03.043 [本文引用: 1]
Immune control of HIV-1 after early treatment of acute infection
DOI:10.1038/35035103 [本文引用: 1]
Virus dynamics: the effect of target cell limitation and immune responses on virus evolution
DOI:10.1006/jtbi.1997.0617 [本文引用: 2]
Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission
Bifurcation analysis in a predator-prey system with time delay
DOI:10.1016/j.nonrwa.2005.03.002 [本文引用: 1]
Symmetric functional differential equations and neural networks with memory
DOI:10.1090/S0002-9947-98-02083-2 [本文引用: 1]
Mathematical analysis of an HTLV-I infection model with the mitosis of CD4+ T cells and delayed CTL immune response
DOI:10.15388/namc.2021.26.21050 [本文引用: 1]