1 引言
具有一般反应函数的经典恒化器模型形如
其中,
常见的功能反应函数有如下几种:
(1) IvIev功能反应函数:
(2) Sigmoidal功能反应函数:
(3) Lotka-Volterra函数:
(4) Michaelis-Menten-Monod函数:
(5) Monod-Haldane函数:
在恒化器中, 微生物可以生长在壁上或特定的表面上. 事实上, 在恒化器或其他类似模型中, 经常能观察到微生物的贴壁生长, 例如生物反应器的生长和哺乳动物大肠的微生物生长[18]. 目前具有贴壁生长现象的恒化器模型的相关研究相对较少, 考虑更符合实际现象以及从生物学的角度获得更有用的结果, 本文将研究具有贴壁现象的模型. 在经典模型的基础上考虑贴壁生长现象, 得到如下模型
其中
除了贴壁生长现象, 系统不可避免地受到环境随机波动的影响. Sun等[19]分析了受环境噪声影响的随机两种群Monod竞争恒化器模型的渐近行为和稳态分布. 文献[20]研究了最大增长率受环境中白噪声扰动的一种单物种随机恒化器模型, 结果表明, 噪声对微生物的持久性具有消极作用, 较大的噪声会使微生物灭绝. 文献[21]表明, 对于污染环境中具有非线性扰动的新型脉冲随机恒化器模型, 随机噪声和脉冲式毒素输入都对微生物的存活和灭绝有很大影响. 本文将通过白噪声输入来扰动系统(1.2), 使其更能体现实际的微生物系统. 有很多方法可以在模型中引入随机噪声扰动, 在本文中, 基于文献[22]中的方法, 假定环境噪声与变量成正比, 得到具有一般功能反应函数和贴壁生长现象的随机恒化器模型:
其中
Caraballo等[19]分析了具有贴壁生长现象和Michaelis-Menten-Monod功能反应函数的随机恒化器模型, 得到了模型解的存在唯一性, 以及随机吸引子的存在性. 本文将研究具有一般功能反应函数和贴壁生长现象的随机恒化器模型的全局动力学.
本文的结构如下: 第2节, 对系统(1.3)降维, 并证明了其存在唯一的全局正解; 第3节, 给出了系统的全局动力学行为(平稳分布的存在唯一性和灭绝性); 第4节, 具体的例子和数值模拟验证了本文的理论结果. 第5节, 进行总结与讨论; 最后, 为了文章的完整性, 在附录中给出完整的证明过程.
2 准备工作
由于复杂的三维随机模型(1.3)难以分析, 下面讨论系统的性质并对其进行降维.
定义变量
根据系统(1.3), 由伊藤公式得
定义
容易验证
此外, 显示求解(2.1)式可得
其中
也就是说
接下来, 定义
考虑(2.3)式的极限系统, 由(2.2)式知
由于本文将研究系统(1.3)的长时间行为, 不妨研究其极限系统:
考虑生物现实, 假设系统(2.4)中的参数满足以下条件
且
为了研究随机系统的动力学行为, 首先需要考虑其解是否为全局正解. 接下来, 给出系统(2.4)全局正解的存在唯一性.
定理2.1 假设
定理2.1的数学证明见附录A.
接下来给出一个引理, 它将用于主要结果的证明. 考虑
其扩散矩阵为
引理2.1 存在具有正则边界
则Markov过程
3 系统(2.4)的全局动力学行为
在考虑恒化器模型时, 通常感兴趣的是微生物什么时候会长期存在, 什么时候会灭绝. 这一节将讨论系统(2.4)中微生物的持久和灭绝.
遍历性是最重要的性质之一, 它意味着随机恒化模型具有平稳分布, 表明微生物会长时间生存. 在给出遍历性定理之前, 记
定理3.1 假设
使得
那么系统(2.4)存在平稳分布且是遍历的.
定理的严格数学证明见附录B.
接下来, 给出灭绝性定理. 记
定理3.2 假设
定理的严格数学证明见附录C.
注3.1 由于模型(2.4)是系统(1.3)的极限系统, 定理3.1和定理3.2可以反映具有一般功能反应函数和贴壁生长现象的随机恒化器模型(1.3)的长时间动力学行为.
4 举例讨论与数值模拟
本文研究了具有一般反应函数的恒化器模型的全局动力学行为, 这意味着当一般功能反应函数
本章将对最常见的具有Michaelis-Menten-Monod功能反应函数的恒化器模型进行数值模拟, 以此举例验证本文的理论研究结果并展示白噪声对模型动力学行为的影响. Michaelis-Menten-Monod功能反应函数形如
其满足假设
例4.1 具有Michaelis-Menten-Monod功能反应函数和贴壁生长现象的恒化器模型形如
其中
情形1 选取系统(1.3)中的参数值如下
计算可得
其中
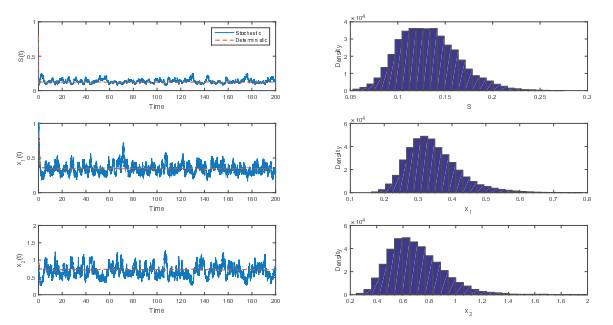
图 1
图 1
左图是随机系统及其对应的确定性系统中
情形2 选取系统(1.3)中的参数值如下
计算可得
也就是说, 定理3.2的条件成立, 即微生物
通过模拟, 可以发现微生物
图 2
图 2
左图是随机系统(1.3)及其对应的确定性系统中
5 总结与讨论
本文研究了具有一般反应函数和贴壁生长现象的随机恒化器模型的长时间行为. 通过构造合适的随机Lyapunov函数, 本文建立了模型(2.4)存在遍历平稳分布的充分条件, 这意味着微生物是持久的; 此外, 还给出了微生物灭绝的充分条件. 最后通过一个具体的算例和数值模拟验证了本文的理论结果.
本文采用新的思路和方法来分析随机恒化器模型的动态行为. 对于贴壁生长的恒化器模型的研究相对较少, 也就是说本文的结果在很大程度上改进了以前的研究成果. 另一方面, 本文成功地将特定的随机恒化器模型的结论推广到具有一般功能反应函数的随机恒化器模型.
附录A 定理2.1的证明
由于系统(2.4)的系数是局部Lipschitz连续的, 则对任意初值
其中, 约定
于是存在
定义
其中
由伊藤公式可得
其中
由于条件
其中
因此
对于
于是由(A.1)和(A.2)式可得
其中
附录B 定理3.1的证明
由定理2.1, 可知对任意初始值
显然
接下来验证条件(2). 根据文献[27]的分析, 只需证明存在非负的
其中
且
其中
容易验证
其中
由伊藤公式得
其中
则
由
即
因此
通过计算还可以得到
类似的
联合(B.2)–(B.4)式得
通过简单的计算可以发现
并且, 当
也就是说
其中
附录C 定理3.2的证明
在证明前, 为了方便, 记
引理C.1[28] 对任意的初始值
注意到
易知
根据引理C.1计算可得
由伊藤公式得
对(C.2)式两端从
根据假设A3和(C.1)式, 有
结合
也就是说
定理3.2证毕.
参考文献
Characterization of microbial compositions in a thermophilic chemostat of mixed culture fermentation
DOI:10.1007/s00253-015-7130-z [本文引用: 1]
Dynamics of the microbial community during continuous methane fermentation in continuously stirred tank reactors
DOI:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.09.014
Chemostat culture for yeast experimental evolution
DOI:10.1101/pdb.prot089011 [本文引用: 1]
Dynamical analysis of multi-nutrient and single microorganism chemostat model in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1186/s13662-018-1573-3 [本文引用: 1]
Average break-even concentration in a simple chemostat model with telegraph noise
DOI:10.1016/j.nahs.2018.03.007
Stability analysis of a chemostat model with maintenance energy
Global dynamics of a delayed chemostat model with harvest by impulsive flocculant input
The periodic solutions of a stochastic chemostat model with periodic washout rate
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2016.01.002
A note on the stationary distribution of the stochastic chemostat model with general response functions
DOI:10.1016/j.aml.2017.04.029 [本文引用: 1]
A mathematical model of the chemostat with a general class of functions describing nutrient uptake
Global dynamics of a mathematical model of competition in the chemostat: general response functions and differential death rates
A delayed chemostat model with general nonmonotone response functions and differential removal rates
DOI:10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.08.014 [本文引用: 1]
Competitive exclusion in a stochastic chemostat model with Holling type Ⅱ functional response
Dynamic behaviors of Monod type chemostat model with impulsive perturbation on the nutrient concentration
Dynamics of the stochastic chemostat with Monod-Haldane response function
DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-13294-3
The threshold of stochastic chemostat model with Monod-Haldane response function
DOI:10.22436/jnsa.010.08.29 [本文引用: 1]
Global stability in chemostat type equations with distributed time delays
DOI:10.1137/S0036141096311101 [本文引用: 1]
Dynamical behavior of a stochastic two-species Monod competition chemostat model
An analogue of break-even concentration in a simple stochastic chemostat model
DOI:10.1016/j.aml.2015.03.012 [本文引用: 1]
Extinction and stationary distribution of an impulsive stochastic chemostat model with nonlinear perturbation
DOI:10.1016/j.chaos.2018.03.038 [本文引用: 1]
Exclusion and persistence in deterministic and stochastic chemostat models
DOI:10.1016/j.jde.2005.06.017 [本文引用: 1]
Dynamics of some stochastic chemostat models with multiplicative noise
DOI:10.3934/cpaa.2017092 [本文引用: 1]
An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations
DOI:10.1137/S0036144500378302 [本文引用: 1]
Asymptotic properties of hybrid diffusion systems
DOI:10.1137/060649343 [本文引用: 1]