1 引言
乙肝病毒感染动力学的研究可以追溯到1996年Nowak等[3]提出的含有三个态变量的乙肝病毒动力学模型. 由于细胞毒性T淋巴细胞(CTL)通过作用于病毒感染细胞而在抗病毒防御机制中起着重要作用, Nowak等[4]在此前模型的基础上考虑宿主对感染细胞的免疫应答. 免疫反应的病毒动力学分析为HBV慢性感染的发病机制提供了重要见解. 此外, 时滞在生物系统中普遍存在, 病毒感染也不例外, 病毒感染宿主细胞到宿主细胞转化为感染细胞都需要一定的时间. 在讨论乙型肝炎病毒感染时, 我们引入时滞使所建立的模型更符合实际背景意义. 另外, Min等[5]指出, 非线性发生率函数更加贴近实际. 鉴于此, 近几十年来, 基于Nowak模型, 国内外许多学者进行了更为深入的研究, 建立了一系列具有免疫应答的传染病模型[6-12]. 此后, 有关乙肝病毒感染动力学和稳定性研究的文献不断涌现, 该领域的研究广度和深度有了明显的发展, 各种定性或定量研究的理论、方法以及应用实例层出不穷.
相关文献虽从不同角度和侧重点对乙肝病毒动力学和稳定性的有关问题进行了分析, 但主要侧重于整数阶领域, 所涉及到的微分方程多是整数阶的微分方程. 分数阶微积分是研究任意阶微分和积分的理论, 作为整数阶微积分在阶次上的任意推广, 其在物理学、神经网络、医学、控制工程等许多领域表现出强大的优势且具有广泛的应用背景, 已经引起国内外学者的高度关注[13-15]. 研究发现, 分数阶微积分方程非常适合于刻画具有记忆和遗传性质的材料和过程, 将分数阶微积分而不是整数阶微积分应用于数学流行病学为描述记忆特征提供了一个很好的工具, 这是许多生物系统的一个标志参见文献[16]. 分数阶模型与免疫系统中产生记忆T细胞和B细胞的类记忆系统有关, 而整数阶模型并没有关于肝细胞和游离病毒记忆的信息. 因此, 用分数阶微分方程对HBV进行建模具有更高的实际意义, 也引起了一些学者的关注, 在整数阶HBV模型的基础上进行了分数阶的推广[17-20]. 此外, 大量的研究已经证实, 实际网络中不可避免地存在时滞, 时滞对分数阶系统的动力学行为也有重要的影响. 目前时滞分数阶系统的动力学行为已经成为热门的研究课题[21-22].
然而, 时滞分数阶系统在HBV感染模型上的运用还相对较少. 鉴于此, 本文结合分数阶微积分的基本理论, 运用Caputo分数阶微分将整数阶免疫时滞HBV感染模型拓展到具有免疫反应的时滞分数阶HBV感染模型. 研究了具有免疫时滞和非线性发生率的分数阶HBV感染模型的稳定性问题. 讨论了系统解的存在唯一性、正性和有界性. 利用泛函微分方程和分数阶动力系统的稳定性理论, 通过分析模型在平衡点处超越特征方程根的分布情况, 讨论了时滞对平衡点稳定性的影响. 最后, 利用分数阶时滞稳定性原理实现了分数阶HBV感染模型的混沌控制.
2 预备知识
本节将不加证明地给出本文所涉及的一些数学知识, 以便在后面的数学证明中引用.
2.1 Caputo分数阶微分
分数阶微分存在多种定义方式, 本文选择Caputo分数阶微分进行研究. 如无特别说明, 文中的
定义2.1[23] 设
为函数
定义2.2[24](线性性) 令
定理2.1[25] 考虑如下带初值的时滞分数阶微分系统
其中: 函数
2.2 分数阶系统的稳定性
考虑Caputo分数阶非线性时滞系统
其中
定义2.3[26] 系统(2.4)的解被称为Mittag-Leffer稳定, 当且仅当
其中
定理2.2[27](一致渐进稳定性定理) 令
其中
定理2.3[28] 对于分数阶时滞非线性系统
则分数阶时滞非线性系统是Lyapunov稳定的.
引理2.1[29] 令
其中
引理2.2[30](Routh Hurwitz准则) 考虑特征方程
所有根具有负实部当且仅当
引理2.3[31] 考虑方程
其中
(i)
(ii) 对任意实数
(iii)
(iv) 当
(v) 对任意实数
那么下述结论成立.
(a) 假设方程
(b) 假设方程
引理2.4[32] 若Jacobian矩阵
则平衡点
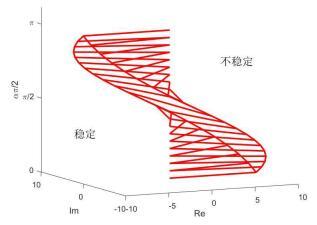
如图
图 1
3 主要结果及其证明
3.1 HBV分数阶模型建立
式中:
考虑到生物系统的记忆特性, 分数阶模型与免疫系统中产生记忆T细胞和B细胞的类记忆系统有关, 本文利用分数阶Caputo微分将系统(3.1)重新描述为
其中
3.2 解的存在唯一性
定理3.1 具有初值条件的分数阶系统可以构造如下
其中
则系统(3.2)存在唯一解.
证 取
其中
且
所以
令
取
故不等式
由此, 该系统解的存在唯一性得证. 定理3.1证毕.
3.3 解的正性和有界性
在处理一个生物模型时, 用负的解没有意义. 下面的定理证明状态变量
定理3.2 定义
证 我们将用反证法来证明这个定理.
假设其不成立, 即存在某个
1) 如果
令
因此
因为
2) 如果
由系统(3.2)的第二个方程, 我们有
因此
因为
3) 如果
由系统(3.2)的第三个方程, 我们有
因此
因为
综上, 具初值
下证有界性.
将系统(3.2)的前两个方程相加, 得
由生物学知识可知, 感染细胞发生的死亡快于自然死亡, 即
即得
因此, 我们有
由系统(3.2)的第三个方程, 得
即得
综上,
3.4 平衡点的稳定性分析
通过直接计算, 可以得到系统(3.2)存在两个非负平衡点: 无病平衡点
下面将讨论系统(3.2)中两个平衡点的稳定性.
将系统(3.2)在平衡点处线性化, 得到相应的特征行列式方程为
首先, 讨论无病平衡点
命题3.1 当
证 系统(3.2)在
若
我们可以发现特征根
若
当
当
则
在生物学上, 局部渐进稳定的感染稳态是肝细胞慢性感染的特征, 乙肝病毒的局部渐进稳定性表明乙肝病毒的感染不会持续.
命题3.1证毕.
命题3.2 当
证 考虑如下Lyapunov函数
其中
由引理2.1得
系统(3.2)的无病平衡点
同时
由(3.12)-(3.14)式, 得
令
命题3.2证毕.
接下来, 将进一步分析地方病平衡点
通过计算, 得到系统(3.2)在感染稳态
其中
命题3.3 若
证 若
显然
且
由引理2.2的Routh-Hurwitz准则, 知: 当
若
两式平方和, 可得
根据方程组(3.17),
此外, 可以通过计算证明横截条件
求方程(3.16)关于
即
因此
则
这意味着当
记
令
结合引理2.3, 给出
命题3.4 (i) 若
(ii) 若
(iii) 若
(iv) 若
4 时滞分数阶HBV感染模型的混沌控制
针对系统(3.2)设计线性反馈控制器如下
定理4.1 当
证 分别取正定矩阵
构造正定函数如下
显然, 若
由定理2.3, 控制系统(4.1)是Lyapunov稳定的, 表明HBV感染可控. 定理4.1证毕.
5 结论
本文提出了一个具有免疫时滞和非线性发生率的分数阶HBV感染模型, 作为整数阶模型的推广. 经过简单分析, 确定了模型解的存在唯一性、正性和最终一致有界性. 进而讨论了模型的稳定性问题, 通过分析系统在两个非负平衡点处特征方程的根的分布, 得到了无病平衡点和地方病平衡点的稳定性和小振幅Hopf分支周期解的存在性. 此外, 分析了该模型的混沌特性. 由于分数阶系统具有遗传和记忆特性, 系统(3.2)为我们提供了一种更真实的病毒动力学模型.
参考文献
Worldwide epidemiology of HBV infection, disease burden, and vaccine prevention
Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection
DOI:10.1073/pnas.93.9.4398 [本文引用: 1]
Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses
DOI:10.1126/science.272.5258.74 [本文引用: 1]
Mathematical analysis of a basic virus infection model with application to HBV infection
Dynamics of a delay differential equation model of hepatitis B virus infection
DOI:10.1080/17513750701769873 [本文引用: 1]
具有时滞的HBV病毒动力学模型稳定性分析
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5565.2009.04.022
Stability analysis of HBV virus dynamics model with delay
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5565.2009.04.022
Global properties of an improved hepatitis B virus model
DOI:10.1016/j.nonrwa.2009.11.008
Analysis of a viral infection model with delayed immune response
Stability analysis of a model for HBV infection with cure of infected cells and intracellular delay
Dynamical behaviors of a delayed HBV infection model with logistic hepatocyte growth, cure rate and CTL immune response
考虑部分免疫和环境传播的麻疹传染病模型的全局稳定性
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.04.018 [本文引用: 1]
Global stability of a measles epidemic model with partial immunity and environmental transmission
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.04.018 [本文引用: 1]
Fractional kinetics in drug absorption and disposition processes
DOI:10.1007/s10928-009-9116-x [本文引用: 1]
An efficient spectral collocation method for the dynamic simulation of the fractional epidemiological model of the ebola virus
DOI:10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110174
带瞬时脉冲的分数阶非自制发展方程解的存在唯一性
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.01.010 [本文引用: 1]
Existence and uniqueness of the mild solutions for a class of fractional non-autonomous evolution equations with impulses
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.01.010 [本文引用: 1]
Memory effects and macroscopic manifestation of randomness
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.61.4752 [本文引用: 1]
Volterra-type Lyapunov functions for fractional-order epidemic systems
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.12.013 [本文引用: 1]
On a fractional-order model for HBV infection with cure of infected cells
DOI:10.1016/j.joems.2017.06.003
A new fractional model for the dynamics of the hepatitis B virus using the Caputo-Fabrizio derivative
DOI:10.1140/epjp/i2018-12072-4
Modeling and analysis of the fractional HBV model with Atangana-Baleanu derivative
DOI:10.1140/epjp/i2018-12120-1 [本文引用: 1]
分数阶Willis环脑迟发性动脉瘤时滞系统混沌分析
Chaotic analysis of fractional Willis delayed aneurysm system
Dynamic analysis of a delayed fractional-order SIR model with saturated incidence and treatment functions
DOI:10.1142/S0218127418501808 [本文引用: 1]
Large existence and uniqueness of solutions for a class of fractional integral-differential equations with time-delay
Mittag-Leffler stability of fractional order nonlinear dynamic systems
DOI:10.1016/j.automatica.2009.04.003 [本文引用: 1]
Stability of fractional-order nonlinear dynamic systems: Lyapunov direct method and generalized Mittag-Leffler stability
DOI:10.1016/j.camwa.2009.08.019 [本文引用: 1]
Lyapunov stability theorem about fractional system without and with delay
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.05.013 [本文引用: 1]
Lyapunov functions for fractional order systems
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.01.022 [本文引用: 1]
On zeroes of some transcendental equations
Stability results for fractional differential equations with applications to control processing
一类时滞乙肝病毒模型的稳定性分析
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-3193.2015.02.006 [本文引用: 1]
Stability analysis for a hepatitis B virus model with time delay
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-3193.2015.02.006 [本文引用: 1]
Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission
Delay effect in a model for virus replication
DOI:10.1093/imammb/16.1.29 [本文引用: 1]
Global dynamics of an in-host viral model with intracellular delay
DOI:10.1007/s11538-010-9503-x [本文引用: 1]
On the zeros of transcendental functions with applications to stability of delay differential equations with two delays