1 引言
本文考虑如下带有列正交约束的广义Sylvester方程极小化问题.
问题1.1 给定矩阵
其中
其中
注意到问题(1.1)的可行域
基于欧氏空间上的MPRP非线性共轭梯度法, 文献[25]和[22]给出的黎曼乘积流形上的推广形式, 本文构造一类黎曼MPRP共轭梯度算法求解列正交约束下的广义Sylvester方程极小化问题: 问题1.1, 并给出算法全局收敛性. 该迭代格式的主要特点是搜索方向恒能保证该目标函数下降. 数值实验表明, 相比于基于流形的黎曼梯度下降法和几类常用的不可行方法, 该算法对于问题模型(1.1)是高效可行的. 本文余下内容组织如下: 第2节给出黎曼共轭梯度法的基本框架, 并结合Stiefel流形的几何性质, 给出求解问题模型(1.1)的黎曼MPRP共轭梯度法的迭代格式; 第3节给出算法的全局收敛性分析; 第4节给出数值算例和数值比较验证所提算法的可行性和高效性. 最后第5节给出结论.
2 求解问题1.1的黎曼MPRP共轭梯度法
欧氏空间上的MPRP非线性共轭梯度法[25]主要用于求解如下无约束优化问题
该算法的迭代格式如下
其中搜索方向
其中
由(2.2)和(2.3)式易得
其中
为了解决问题(1.1), 需将欧氏空间上的MPRP非线性共轭梯度法推广至黎曼流形
其中
通过上述变化, 可得到搜索方向
这里迭代参数
给定第
下面针对问题(1.1)的可行域介绍Stiefel流形
显然点
其中对
这里
即
下面讨论黎曼梯度的具体计算公式. 为方便记
记
同时定义
和
则
其中
下面计算
由于
此外
这里
记
根据以上讨论, 求解问题1.1的黎曼MPRP共轭梯度算法描述如算法1所示.
算法1 求解问题1.1的黎曼MPRP共轭梯度法.
给定初值
其中
选取步长
令
注2.1 类似于欧氏空间中的无约束优化问题, 我们可以用
其中
对上式第一个等式左乘
当
且当
由(2.17)和(2.18)式知当
由
上式两边对
令
结合(2.15)式, 故令初始步长为
3 算法1的全局收敛性分析
首先给出算法1的如下基本性质.
(1) 由(2.20)-(2.23)式可知对
由此可知搜索方向
(2) 由于
引理3.1
是一个紧集.
证 对
命题3.1 对算法1产生的序列
这里
证 由
由于
这里的"dist"表示
由(3.1)式知对
于是由(3.4)-(3.7) 式知对
令
在算法
由上式, (2.22)及(2.23)式可知, 对
由引理3.1知
又因目标函数序列
引理3.2 若存在常数
则存在常数
证 由命题3.1, 公式(2.20)及(3.8)-(3.12)可知, 存在整数
由
于是存在常数
再由上式及(3.13)式可知对
最后令
证毕.
定理3.1 令
证 反证法. 假设存在常数
则由(3.1)式知对
即对
由上式及(3.2)式可知
因此, 若
现假设
根据算法1的(3.24)式知, 当
由目标函数
这里
将上式与
最后由引理3.2知搜索方向序列
这也与
4 数值实验
4.1 各比较算法的主要迭代思想
首先给出各比较算法的基本迭代思路和迭代格式主要步骤.
交替方向法(ADMM)[16]. 引入辅助矩阵
问题(4.1)的拉格朗日函数为
其中
(4.2)式中的
正交分裂法(SOC)[17]. 正交分裂法的迭代思想与交替方向法相似, 即引入变量分裂正交约束, 然后交替极小两个变量矩阵. 引入变量矩阵
因为(4.3)式中第一个约束条件是线性约束, 故可以采用Bregman迭代处理, 即迭代求解
类似于交替方向乘子法和分裂Bregman迭代, (4.4)式的第一个极值问题采用交替极小变量矩阵
Majorization算法(Major)[15]. Majorization算法的基本迭代思想是对于
又因为下面不等式成立
和
其中
将
其中
则辅助函数
现若
其中
其中
其中
其中
其中
4.2 数值结果
(1) 测试模型. 测试问题(1.1)的如下具体形式
(2) 终止标准. 算法的终止标准参见文献[27]:
(3) 参数选定. 算法1中参数
例4.1 按Matlab记号的形式给定系数矩阵
其中ones
表 1 算法1与其它几类算法的数值比较结果
| l, n, p, s | CPU(s) | IT | ||grad f(Xk)|| | f(Xk) | Xfeasi | |
| Algo.1 | 0.134 | 183 | 7.202×10-4 | 0 | 9.744×10-16 | |
| OptStiefel | 0.282 | 246 | 9.431×10-4 | 0 | 4.220×10-15 | |
| Mixed | 15, 200, 10, 5 | 0.532 | 568 | 8.770×10-4 | 0 | 2.048×10-15 |
| SOC | 3.775 | 196 | 9.278×10-4 | 0 | 3.593×10-2 | |
| ADM | 3.485 | 49 | 9.823×10-4 | 0 | 5.866×10-2 | |
| Major | 11.784 | 20000 | 6.235×10-2 | 0.0003 | 5.209×10-15 | |
| Algo.1 | 0.205 | 170 | 7.973×10-4 | 0 | 1.324×10-15 | |
| OptStiefel | 0.904 | 271 | 5.123×10-4 | 0 | 1.832×10-14 | |
| Mixed | 30, 300, 15, 5 | 1.524 | 956 | 9.914×10-4 | 0 | 2.808×10-15 |
| SOC | 15.229 | 219 | 9.536×10-4 | 0 | 3.578×10-2 | |
| ADM | 14.663 | 206 | 9.741×10-4 | 0 | 3.356×10-2 | |
| Major | 32.982 | 20000 | 3.500×10-1 | 0.0018 | 6.742×10-15 | |
| Algo.1 | 0.673 | 486 | 5.942×10-4 | 0 | 1.595×10-15 | |
| OptStiefel | 1.154 | 356 | 5.515×10-4 | 0 | 1.449×10-15 | |
| Mixed | 45, 400, 20, 5 | 4.586 | 1393 | 8.224×10-4 | 0 | 4.064×10-15 |
| SOC | 54.639 | 116 | 9.679×10-4 | 0 | 5.821×10-2 | |
| ADM | 31.334 | 37 | 9.979×10-4 | 0 | 1.635×10-1 | |
| Major | 114.029 | 20000 | 4.797 | 0.2222 | 8.883×10-15 | |
| Algo.1 | 0.647 | 293 | 4.311×10-4 | 0 | 1.277×10-15 | |
| OptStiefel | 1.216 | 364 | 9.407×10-4 | 0 | 1.277×10-15 | |
| Mixed | 50, 500, 20, 5 | 5.546 | 1156 | 7.179×10-4 | 0 | 3.165×10-15 |
| SOC | 72.800 | 51 | 8.914×10-4 | 0 | 1.201×10-1 | |
| ADM | 72.570 | 46 | 8.835×10-4 | 0 | 1.313×10-1 | |
| Major | 185.344 | 20000 | 2.804 | 0.0429 | 7.434×10-15 | |
| Algo.1 | 0.609 | 239 | 5.557×10-1 | 0.0001 | 2.313×10-15 | |
| OptStiefel | 1.125 | 398 | 1.635×10-2 | 0 | 1.524×10-15 | |
| Mixed | 60, 400, 30, 5 | 9.036 | 2072 | 1.069×10-3 | 0 | 4.994×10-15 |
| SOC | 88.718 | 56 | 9.967×10-4 | 0 | 9.761×10-2 | |
| ADM | 105.745 | 99 | 9.206×10-4 | 0 | 1.023×10-1 | |
| Major | 217.668 | 20000 | 1.224×101 | 0.7462 | 9.998×10-15 | |
| Algo.1 | 1.866 | 636 | 7.307×10-4 | 0 | 1.272×10-15 | |
| OptStiefel | 1.846 | 518 | 9.739×10-4 | 0 | 8.997×10-16 | |
| Mixed | 70, 500, 15, 5 | 8.198 | 1966 | 5.506×10-4 | 0 | 2.639×10-15 |
| SOC | 58.076 | 97 | 8.202×10-4 | 0 | 1.162×10-1 | |
| ADM | 57.401 | 83 | 9.283×10-4 | 0 | 1.065×10-1 | |
| Major | 130.671 | 20000 | 7.300 | 0.4279 | 5.167×10-15 | |
| Algo.1 | 1.289 | 645 | 5.152×10-4 | 0 | 1.798×10-15 | |
| OptStiefel | 1.985 | 669 | 9.542×10-4 | 0 | 1.287×10-15 | |
| Mixed | 80, 500, 20, 5 | 11.044 | 2311 | 8.951×10-4 | 0 | 3.750×10-15 |
| SOC | 126.369 | 92 | 8.061×10-4 | 0 | 2.926×10-1 | |
| ADM | 186.829 | 198 | 8.944×10-4 | 0 | 7.416×10-2 | |
| Major | 183.599 | 20000 | 1.009×101 | 0.5858 | 7.192×10-15 |
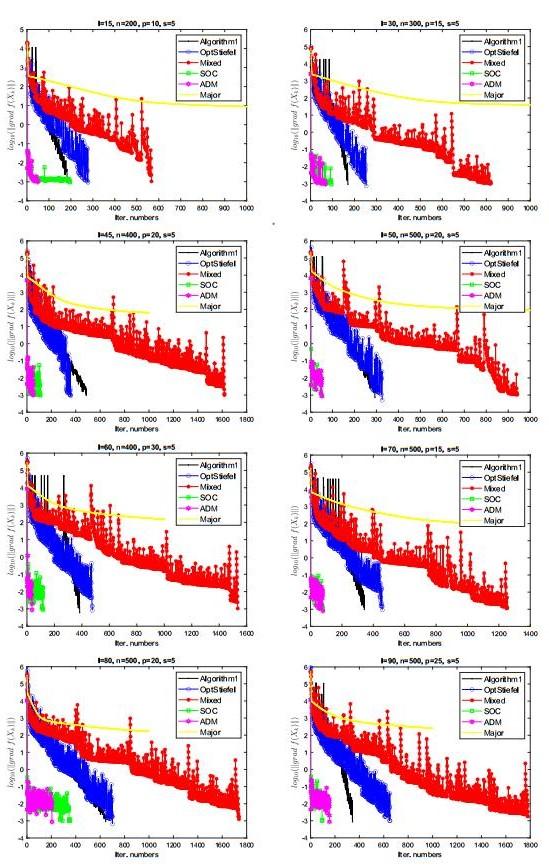
图 1
(1) 对于求解问题(1.1), 与其它几类可行算法相比, 算法1在迭代步和迭代时间上均有较大的优势. 与两类不可行算法相比, 算法1的迭代优势则更明显. 虽然算法1的总体迭代步较多, 但每步迭代成本低, 故达到相同精度下的总体迭代时间要少很多. 特别地, 文献[27]中提出的基于BB步长非单调搜索的梯度下降法(OptStiefel)是近年来求解流形优化问题的经典算法, 而对于问题模型(1.1), 本文算法1有与OptStiefel算法相当的迭代效率.
(2) Mixed算法因在
5 结论
本文从Stiefel流形的角度设计黎曼MPRP共轭梯度法求解列正交约束下广义Sylvester方程极小化问题. 该算法可视为欧氏空间上MPRP共轭梯度法在Stiefel流形上的推广. 仿照欧氏空间上MPRP共轭梯度法的全局收敛性分析, 基于Stiefel流形的基本性质, 本文给出了该黎曼MPRP共轭梯度法的完整收敛性分析. 同时数值实验部分给出数值比较结果, 说明本文算法在迭代效率上与几类不可行算法和几类基于Stiefel流形的梯度下降法有较大的优势.
参考文献
An iterative method for solving the generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations over generalized bisymmetric matrices
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2009.06.018 [本文引用: 1]
Developing BiCOR and CORS methods for coupled Sylvester-transpose and periodic Sylvester matrix equations
Extending the CGLS algorithm for least squares solutions of the generalized Sylvester-transpose matrix equations
DOI:10.1016/j.jfranklin.2015.05.024
LSQR iterative method for generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2011.10.030 [本文引用: 1]
On iterative solutions of general coupled matrix equations
DOI:10.1137/S0363012904441350 [本文引用: 1]
Convex constrained optimization for large-scale generalized Sylvester equations
DOI:10.1007/s10589-009-9253-6 [本文引用: 1]
Conditional gradient Tikhonov method for a convex optimization problem in image restoration
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2013.06.011 [本文引用: 1]
An efficient method for solving a matrix least squares problem over a matrix inequality constraint
DOI:10.1007/s10589-015-9783-z [本文引用: 1]
Dykstra's algorithm for a constrained least-squares matrix problem
DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1506(199611/12)3:6<459::AID-NLA82>3.0.CO;2-S [本文引用: 1]
Dykstra's algorithm for constrained least-squares rectangular matrix problems
Selective alternating projections to find the nearest SDD+ matrix
Dykstra's algorithm for constrained least-squares doubly symmetric matrix problems
A Riemannian optimization approach for solving the generalized eigenvalue problem for nonsquare matrix pencils
DOI:10.1007/s10915-020-01173-5 [本文引用: 1]
The skew-symmetric orthogonal solutions of the matrix equation AX=B
DOI:10.1016/j.laa.2005.01.022 [本文引用: 1]
Setting up alternating least squares and iterative majorization algorithms for solving various matrix optimization problems
Numerical study of learning algorithms on Stiefel manifold
DOI:10.1007/s10287-013-0181-7 [本文引用: 3]
A splitting method for orthogonality constrained problems
DOI:10.1007/s10915-013-9740-x [本文引用: 3]
An augmented Lagrangian method for 1-regularized optimization problems with orthogonality constraints
DOI:10.1137/140988875 [本文引用: 1]
A Riemannian optimization approach to the matrix singular value decomposition
DOI:10.1137/120872887 [本文引用: 2]
A Riemannian conjugate gradient method for optimization on the Stiefel manifold
DOI:10.1007/s10589-016-9883-4 [本文引用: 1]
Low-rank matrix completion by Riemannian optimization
DOI:10.1137/110845768 [本文引用: 1]
A geometric nonlinear conjugate gradient method for stochastic inverse eigenvalue problems
DOI:10.1137/140992576 [本文引用: 4]
A Riemannian Fletcher-Reeves conjugate gradient method for doubly stochastic inverse eigenvalue problems
A Riemannian variant of the Fletcher-Reeves conjugate gradient method for stochastic inverse eigenvalue problems with partial eigendata
DOI:10.1002/nla.2221 [本文引用: 2]
A descent modified Polak-Ribière-Polyak conjugate gradient method and its global convergence
DOI:10.1093/imanum/drl016 [本文引用: 5]
A feasible method for optimization with orthogonality constraints
A non-monotone linear search algorithm with mixed direction on Stiefel manifold
DOI:10.1080/10556788.2017.1415337 [本文引用: 2]