1 引言
设
其中
其中
在问题(1.1) 中, 当
其中
近年来, 两级加热流体Rayleigh-Stokes问题
在实际问题中, 大多数流体运动和运输过程都是分布参数, 其中模型方程中使用的参数, 如物理参数、源项、初始条件和边界条件等都是未知的. 通过实测数据识别这些未知参数, 提出两级加热流体的Rayleigh-Stokes反问题. 根据目前的研究现状来看, Rayleigh-Stokes问题反问题的研究还是有限的. 文献[15] 中, 作者用带高斯随机扰动的滤波正则化方法来分析Rayleigh-Stokes反向问题. 文献[16]中, 作者用带高斯随机扰动的滤波正则化方法识别Rayleigh-Stokes问题的未知源, 给出正则解与精确解之间的误差估计, 但正则化参数是通过先验来选择的, 先验正则化参数依赖于未知的先验界. 文献[17] 中, 作者考虑了一个带有控制参数的扩散方程的反问题. 介绍了几种识别控制参数的差分格式. 说明这些方法的无条件稳定性, 并对CPU时间进行了比较. 最后给出了数值实验的结果, 并说明了该反问题所需的精度和CPU时间.
本文组织结构如下. 第2节给出问题(1.1) 的不适定性和问题(1.1) 未知源识别的条件稳定性. 在第3节中, 利用分数阶Landweber正则化方法处理这个反问题, 并得到先验和后验收敛误差估计. 第4节通过数值算例证明Landweber正则化方法和分数阶Landweber正则化方法的有效性和可行性, 并对两种方法进行比较. 第5节给出本文的主要结论.
2 问题(1.1) 的不适定性分析和条件稳定性结果
在这一节, 主要讨论问题(1.1) 的不适定性分析和条件稳定性结果. 在区域
其中
其中
根据文献[42] 的结果, 问题(1.1) 存在唯一的解, 解的表达式如下
其中
其中
利用附加条件
因此
其中
其中
引理 2.1[42] 对于函数
引理 2.2[16] 假设
其中
此外, 也有如下估计成立
因为当
接下来, 将给出源项
其中
定理 2.1 假设先验界(2.8) 成立, 则条件稳定性结果如下
其中
证 通过(2.7) 式, 并且使用Hölder不等式, 可以得到
根据引理2.2, 可以得到
根据(2.7), (2.8) 和(2.11)式, 有
根据(2.10) 和(2.12)式, 有
其中
因此, 可以得到如下结果
定理2.1证毕.
在下一节, 首先引入Landweber迭代正则化方法, 得到Landweber迭代正则解, 然后给出分数阶Landweber迭代正则解. 采用分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法求解不适定问题(1.1).
3 分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法和收敛误差估计
在这一节中, 主要使用分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法来解决不适定问题(1). 在先验正则化参数选取规则和后验正则化参数选取规则的情况下, 得到精确解与正则解之间的收敛误差估计. 识别源项
其中
因为核函数
其中
因此, 通过简单计算可得
利用算子
其中
则含有测量误差
含有精确数据的分数阶Landweber正则解
其中
3.1 基于先验正则化参数选取规则的收敛误差估计
定理 3.1 设
则得到下列收敛误差估计
其中
证 利用三角不等式可得
根据(1.2)式, 可得
其中
从而
由(2.8)式, 可得
其中
根据引理2.2, 有
设
假设
因此
则
结合(3.6), (3.8), (3.9) 与(3.11)式, 可得
其中
3.2 基于后验正则化参数选取规则的收敛误差估计
在这一节, 主要考虑Morozov不一致原理[43]作为后验正则化参数选取规则, 并给出在后验正则化参数选取规则下的收敛误差估计.
假设
的
引理 3.1 令
证 根据
可以看出, 四个性质显然成立. 引理3.1证毕.
注 3.1 根据引理3.1可知, 通过(3.12) 式选取的
引理 3.2 假设先验界条件(2.8) 和假设(1.2) 成立. 对于固定的
证 因为
则
根据(2.8)式, 有
其中
根据引理2.1和引理2.2, 可得
令
根据
假设
即
因此
根据(3.15) 和(3.16)式, 有
结合(3.14) 和(3.18)式, 可得
引理3.2证毕.
引理 3.3 根据(1.2) 和(3.12)式, 有
证
引理3.3证毕.
定理 3.2 设
其中
证 利用三角不等式可得
根据引理
利用先验界条件(2.8), 有
此外, 根据定理2.3和引理3.4, 有
结合(3.22), (3.23) 和(3.24)式, 可得
其中
定理3.2证毕.
4 数值例子
在这一部分, 通过几个数值例子来证明Landweber迭代正则化方法和分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法的有效性和可行性.
设
其中
其次, 利用有限差分法离散问题(4.1). 此外, 介绍了两种离散格式, 即后向差分格式(BD)和Crank-Nicolson差分格式(C-N), 这两种离散格式都是无条件稳定的. 定义
其中
首先给出BD迭代格式. 第一步, 利用Grünwald-Letnikov公式离散Riemann-Liouville算子[45]
其中
在(4.3) 式中, 当
来计算系数
如果
计算的
第二步, 需要使用反向差分公式来离散微分算子
与
根据(4.5)–(4.7)式, 可以得到问题(4.1) 的BD迭代形式, 表达式如下
其中
接下来, 将给出问题(4.1) 的第二种迭代格式, 即Crank-Nicolson迭代方法. Crank-Nicolson迭代法具有二阶精度. 因此, 对于
其中
采用BD迭代法和Crank-Nicolson迭代法, 用MATLAB软件编程运行, 可以得到函数
最后, 通过如下表达式得到Landweber正则解
通过如下表达式得到分数阶Landweber正则解
其中
在实际应用中, 数据
其中函数randn
为了验证数值解的准确性, 使用以下方法计算相对均方根误差
其中
先验正则化参数是建立在精确解的光滑条件上的, 这在实际问题中是很难给出的. 下面的例子基于后验正则化参数选择规则(3.12) 来验证Landweber迭代正则化方法和分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法的有效性和稳定性.
通过简单计算, 在式(1.3) 中, 对于
例 1 考虑光滑函数
例 2 考虑分段光滑函数
例 3 考虑一个非光滑函数
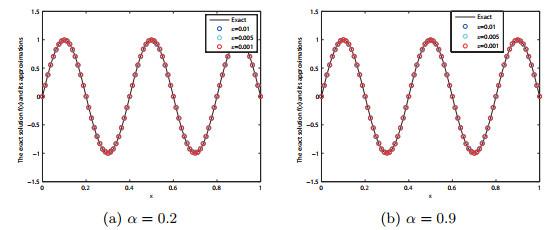
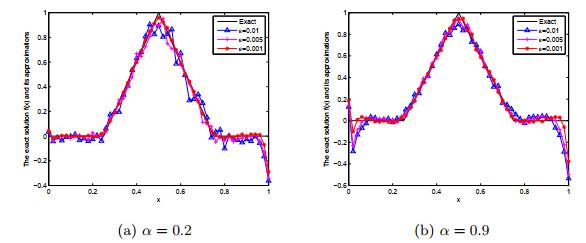
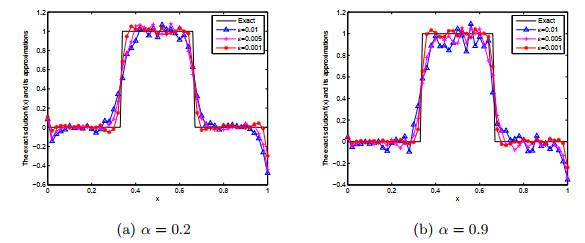
图 1
图 1
例1在BD迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x)与Landweber正则解
图 2
图 2
例1在C-N迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x)与Landweber正则解
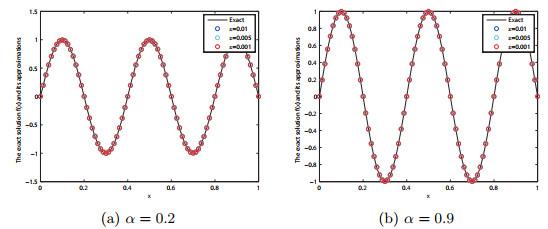
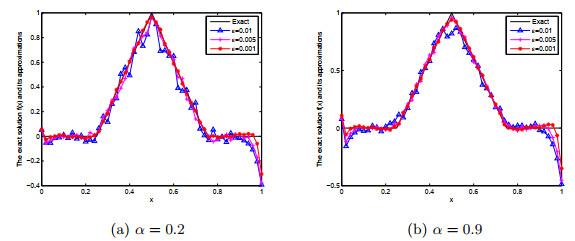
图 3
图 3
例1在BD迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x)与分数阶Landweber正则解
图 4
图 4
例1在C-N迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x)与分数阶Landweber正则解
表 1显示了例1在BD和C-N两种迭代形式下, 对于不同的
表 1 对于不同的α和ε, 例1的精确解与正则解之间的相对均方根误差
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| η(f) | ε=0.01 | Landweber | BD | 0.0099 | 0.0083 | 0.0075 |
| C-N | 0.0072 | 0.0052 | 0.0041 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0088 | 0.0076 | 0.0061 | ||
| C-N | 0.0063 | 0.0048 | 0.0039 | |||
| ε=0.005 | Landweber | BD | 0.0042 | 0.0039 | 0.0034 | |
| C-N | 0.0041 | 0.0035 | 0.0025 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0038 | 0.0035 | 0.0021 | ||
| C-N | 0.0031 | 0.0028 | 0.0011 | |||
| ε= 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 0.0025 | 0.0019 | 7.9678e-04 | |
| C-N | 0.0020 | 0.0011 | 5.5690e-04 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0018 | 0.0010 | 7.1943e-04 | ||
| C-N | 0.0011 | 8.7631e-04 | 4.6982e-04 | |||
表 2 对于不同的α和ε, 例1的精确解与正则解之间的迭代次数
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| 迭代步数(m) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 24027 | 9658 | 30 |
| C-N | 25556 | 31634 | 37652 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 19683 | 6514 | 21 | ||
| C-N | 21423 | 23963 | 29685 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 46820 | 21349 | 34 | |
| C-N | 27941 | 30652 | 39541 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 39870 | 12981 | 29 | ||
| C-N | 19685 | 23916 | 33921 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 79686 | 38679 | 44 | |
| C-N | 35719 | 42387 | 52802 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 68765 | 27695 | 38 | ||
| C-N | 26985 | 34796 | 44348 | |||
表 3 对于不同的α和ε, 例1的精确解与正则解之间的CPU时间
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| CPU时间(unit: s) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 480.54 | 193.16 | 0.60 |
| C-N | 511.12 | 632.68 | 753.04 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 393.66 | 130.28 | 0.42 | ||
| C-N | 428.46 | 479.26 | 593.70 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 936.40 | 426.98 | 0.68 | |
| C-N | 558.82 | 613.04 | 790.82 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 797.40 | 259.62 | 0.58 | ||
| C-N | 393.70 | 478.32 | 678.42 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 1593.72 | 773.58 | 0.88 | |
| C-N | 714.38 | 847.74 | 1056.04 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 1375.30 | 553.90 | 0.76 | ||
| C-N | 539.70 | 695.92 | 886.96 | |||
从表 1–3中可以发现, 在BD和C-N两种迭代格式下, 无论是Landweber迭代正则化方法还是分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法, 相对均方根误差
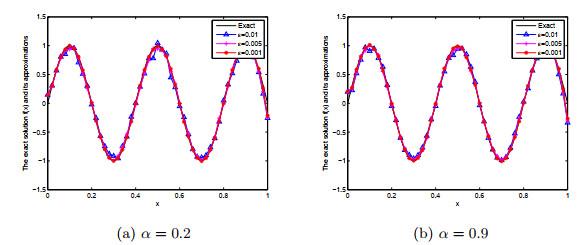
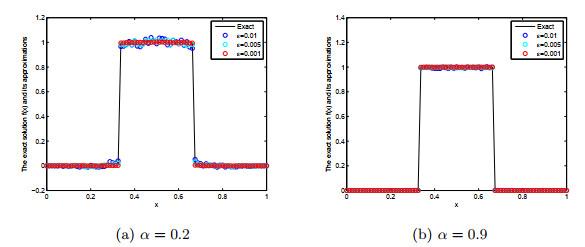
图 5
图 5
例2在BD迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与Landweber正则解
图 6
图 6
例2在C-N迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与Landweber正则解
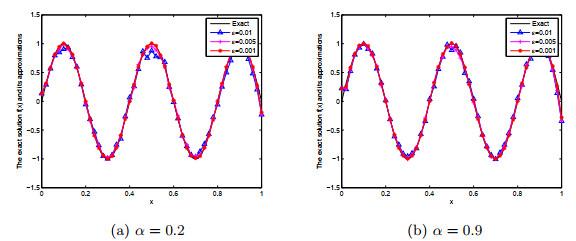
图 7
图 7
例2在BD迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与分数阶Landweber正则解
图 8
图 8
例2在C-N迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与分数阶Landweber正则解
表 4显示了例2在BD和C-N两种迭代形式下, 对于不同的
表 4 对于不同的α和ε, 例2的精确解与正则解之间的相对均方根误差
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| η(f) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 0.0243 | 0.0128 | 0.0088 |
| C-N | 0.1039 | 0.0864 | 0.0747 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0208 | 0.0106 | 0.0075 | ||
| C-N | 0.0931 | 0.0705 | 0.0628 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 0.0155 | 0.0116 | 0.0076 | |
| C-N | 0.0838 | 0.0725 | 0.0634 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0191 | 0.0103 | 0.0063 | ||
| C-N | 0.0786 | 0.0596 | 0.0413 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 0.0033 | 0.0019 | 8.6476e-04 | |
| C-N | 0.0589 | 0.0362 | 0.0295 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0021 | 0.0011 | 6.5483e-04 | ||
| C-N | 0.0412 | 0.0268 | 0.0105 | |||
表 5 对于不同的α和ε, 例2的精确解与正则解之间的迭代次数
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| 迭代步数(m) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 22348 | 6987 | 29 |
| C-N | 3717 | 5816 | 7425 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 16534 | 3768 | 19 | ||
| C-N | 2674 | 4168 | 6123 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 34258 | 12368 | 33 | |
| C-N | 6670 | 8126 | 11198 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 22369 | 6879 | 26 | ||
| C-N | 4396 | 6021 | 8934 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 79463 | 39654 | 41 | |
| C-N | 15285 | 86956 | 131965 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 54986 | 21685 | 33 | ||
| C-N | 13210 | 69663 | 113824 | |||
表 6 对于不同的α和ε, 例2的精确解与正则解之间的CPU时间
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| CPU时间(unit: s) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 446.96 | 139.74 | 0.58 |
| C-N | 74.34 | 116.32 | 148.50 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 330.68 | 75.36 | 0.38 | ||
| C-N | 53.48 | 83.36 | 122.46 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 685.16 | 247.36 | 0.66 | |
| C-N | 133.4 | 162.52 | 223.96 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 447.38 | 137.58 | 0.52 | ||
| C-N | 87.92 | 120.42 | 178.68 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 1589.26 | 793.08 | 0.82 | |
| C-N | 305.70 | 1739.12 | 2639.3 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 1099.72 | 433.70 | 0.66 | ||
| C-N | 264.20 | 1393.26 | 2276.48 | |||
从表 4–6可以看出, 在BD和C-N迭代格式下, 无论是Landweber迭代正则化方法还是分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法, 相对均方根误差
图 9
图 9
例3在BD迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与Landweber正则解
图 10
图 10
例3在C-N迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与Landweber正则解的比较
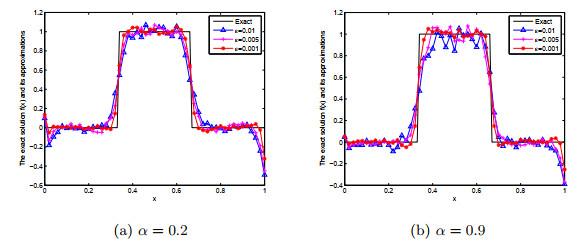
图 11
图 11
例3在BD迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与分数阶Landweber正则解
图 12
图 12
例3在C-N迭代格式下, 在α = 0.2, 0.9下对于ε = 0.01, 0.005, 0.001的精确解f(x) 与分数阶Landweber正则解
表 7显示了例3在BD和C-N两种迭代形式下, 对于不同的
表 7 对于不同的α和ε, 例3的精确解与正则解之间的相对均方根误差
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| η(f) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 0.0287 | 0.0196 | 0.0100 |
| C-N | 0.1867 | 0.2375 | 0.2735 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0234 | 0.0165 | 0.0008 | ||
| C-N | 0.1529 | 0.2143 | 0.2568 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 0.0176 | 0.0102 | 0.0050 | |
| C-N | 0.1679 | 0.2139 | 0.2228 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0153 | 0.0088 | 0.0016 | ||
| C-N | 0.1428 | 0.1796 | 0.1928 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 0.0068 | 0.0036 | 0.0010 | |
| C-N | 0.0924 | 0.1428 | 0.1522 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 0.0053 | 0.0018 | 2.5638e-04 | ||
| C-N | 0.0723 | 0.1256 | 0.1347 | |||
表 8 对于不同的α和ε, 例3的精确解与正则解之间的迭代次数
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| 迭代步数(m) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 47906 | 21398 | 29 |
| C-N | 4837 | 8878 | 19844 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 31695 | 10321 | 18 | ||
| C-N | 2968 | 5367 | 16482 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 74840 | 46709 | 33 | |
| C-N | 10244 | 168704 | 52632 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 62390 | 30987 | 28 | ||
| C-N | 7688 | 11326 | 40986 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 121803 | 76895 | 42 | |
| C-N | 238323 | 638825 | 788528 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 98465 | 54326 | 37 | ||
| C-N | 196524 | 419168 | 568238 | |||
表 9 对于不同的α和ε, 例3的精确解与正则解之间的CPU时间
| α | α = 0.2 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.9 | |||
| CPU时间(unit: s) | ε = 0.01 | Landweber | BD | 958.12 | 427.96 | 0.58 |
| C-N | 96.74 | 177.56 | 396.88 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 639.30 | 206.42 | 0.36 | ||
| C-N | 59.36 | 107.34 | 329.64 | |||
| ε = 0.005 | Landweber | BD | 1496.80 | 934.18 | 0.66 | |
| C-N | 204.88 | 3374.08 | 1052.64 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 1247.80 | 619.74 | 0.56 | ||
| C-N | 153.76 | 226.52 | 819.72 | |||
| ε = 0.001 | Landweber | BD | 2436.06 | 1537.90 | 0.84 | |
| C-N | 4766.46 | 12776.50 | 15770.56 | |||
| 分数阶Landweber | BD | 1969.30 | 1086.52 | 0.74 | ||
| C-N | 3930.48 | 8383.36 | 11364.76 | |||
5 结论
本文研究Rayleigh-Stokes方程的源项识别反问题. 采用分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法解决此类反问题(1.1). 基于条件稳定性结果, 分别在先验和后验正则化参数选择规则下得到相应的误差估计. 利用三个数值例子验证分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法和Landweber迭代正则化方法处理此反问题的有效性和稳定性. 通过误差估计(3.7) 和(3.21), 发现分数阶Landweber迭代正则化方法优于Tikhonov正则化方法, 并且这两种正则化方法得到的误差估计(3.7) 和(3.21) 不出现饱和效应. 但是用Tikhonov正则化方法来处理这个问题, 误差估计就会产生饱和现象(所谓饱和现象是在Tikhonov正则化方法中, (3.7) 和(3.21) 并不适用于所有的
参考文献
The Rayleigh-Stokes problem for heated second grade fluids
DOI:10.1016/S0020-7462(00)00118-9
The Rayleigh-Stokes problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivative model
DOI:10.1016/j.nonrwa.2005.09.007 [本文引用: 1]
On exact solutions for some oscillating motions of a generalized Oldroyd-B fluid
DOI:10.1007/s00033-009-0004-4 [本文引用: 1]
The Rayleigh-Stokes problem for an edge in a viscoelastic fluid with a fractional derivative model
DOI:10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.10.002 [本文引用: 1]
Numerical methods of the variable-order Rayleigh-Stokes problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivative
An inverse problem to estimate an unknown order of a Riemann-Liouville fractional derivative for a fractional Stokes' first problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid
DOI:10.1007/s10409-015-0408-7 [本文引用: 1]
Numerical method of Rayleigh-Stokes problem for heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivative
Numerical methods with fourth-order spatial accuracy for variable-order nonlinear Stokes' first problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid
DOI:10.1016/j.camwa.2011.03.065 [本文引用: 1]
Numerical solution for Stokes' first problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivative
DOI:10.1016/j.apnum.2009.05.009 [本文引用: 1]
Compact finite difference scheme and RBF meshless approach for solving 2D Rayleigh-Stokes problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivatives
DOI:10.1016/j.cma.2013.05.012 [本文引用: 1]
Two high-order numerical algorithms for solving the multi-term time fractional diffusion-wave equations
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2015.04.037 [本文引用: 1]
Fourth-order numerical method for the space time tempered fractional diffusion-wave equation
DOI:10.1016/j.aml.2017.04.011 [本文引用: 1]
New implementation of MLBIE method for heat conduction analysis in functionally graded materials
DOI:10.1016/j.enganabound.2011.11.007 [本文引用: 1]
Compact finite difference scheme and RBF meshless approach for solving 2D Rayleigh-Stokes problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivatives
DOI:10.1016/j.cma.2013.05.012 [本文引用: 1]
Identifying initial condition of the Rayleigh-Stokes problem with random noise
Identification of source term for the Rayleigh-Stokes problem with Gaussian random noise
An inverse problem of finding a source parameter in a semilinear parabolic equation
DOI:10.1016/S0307-904X(01)00010-5 [本文引用: 1]
Optimal error bound and simplified Tikhonov regularization method for a backward problem for the time-fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2014.11.026 [本文引用: 1]
The simplified Tikhonov regularization method for solving a Riesz-Feller Space-Fractional backward diffusion problem
DOI:10.1007/s11786-017-0292-6 [本文引用: 1]
Tikhonov regularization method for a backward problem for the time-fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2013.03.071 [本文引用: 1]
Tikhonov regularization method for identifying the space-dependent source for time-fractional diffusion equation on a columnar symmetric domain
DOI:10.1186/s13662-020-2542-1 [本文引用: 1]
Solving a Cauchy problem for a 3D elliptic PDE with variable coefficients by a quasi-boundary-value method
DOI:10.1088/0266-5611/30/1/015005 [本文引用: 1]
A modified quasi-boundary value method for an inverse source problem of the time-fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1016/j.apnum.2013.12.002
, The quasi-boundary regularization value method for identifying the initial value of heat equation on a columnar symmetric domain
The quasi-boundary value method for identifying the initial value of the space-time an fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1007/s10473-020-0304-5 [本文引用: 1]
On a quasi-reversibility regularization method for a Cauchy problem of the Helmholtz equation
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2009.09.031 [本文引用: 1]
The quasi-reversibility regularization method for identifying the unknown source for time fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2014.08.010 [本文引用: 1]
A potential-free field inverse schrödinger problem: optimal error bound analysis and regularization method
DOI:10.1080/17415977.2019.1700243 [本文引用: 1]
A potential-free field inverse time-fractional Schrödinger problem: Optimal error bound analysis and regularization method
A mollification regularization method for unknown source in time-fractional diffusion equation
Fourier regularization method of a sideways heat equation for determining surface heat flux
DOI:10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.12.010 [本文引用: 1]
An a posteriori Fourier regularization method for identifying the unknown source of the space-fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1186/1029-242X-2014-434
The Fourier regularization method for identifying the unknown source for the modified Helmholtz equation
Landweber iteration regularization method for identifying unknown source on a columnar symmetric domain
DOI:10.1080/17415977.2017.1384825 [本文引用: 1]
Landweber iteration regularization method for identifying unknown source of the modified Helmholtz equation
Landweber iterative method for identifying the initial value problem of the time-space fractional diffusion-wave equation
DOI:10.1007/s11075-019-00734-6
Landweber iterative method for an inverse source problem of time-fractional diffusion-wave equation onspherically symmetric domain
Landweber iteration regularization method for identifying the initial value problem of the time-space fractional diffusion-wave equation
DOI:10.1007/s11075-019-00734-6 [本文引用: 1]
The fractional Landweber method for identifying the space source term problem for time-space fractional diffusion equation
DOI:10.1007/s11075-020-01006-4 [本文引用: 1]
Two-step regularization methods for linear inverse problems
DOI:10.1515/156939406778474523 [本文引用: 1]
Regularization by fractional filter methods and data smoothing
DOI:10.1088/0266-5611/24/2/025018 [本文引用: 1]
An analysis of the Rayleigh-Stokes problem for a generalized second-grade fluid
DOI:10.1007/s00211-014-0685-2 [本文引用: 2]
A finite element method for the numerical solution of Rayleigh-Stokes problem for a heated generalized second grade fluid with fractional derivatives
Weighted average finite difference methods for fractional diffusion equations
DOI:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.12.006 [本文引用: 2]
A posteriori error analysis for the Crank-Nicolson method for linear Schrödinger equations
DOI:10.1051/m2an/2010101 [本文引用: 1]