1 引言
边界层问题广泛存在于流体力学、弹性力学、声光学、化学反应、最优控制等领域, 如高雷诺数的流体流动问题、热量传输问题、多孔介质中的渗流问题等等.这类问题描述的现象往往在局部区域具有奇异性, 对应的微分方程中含有反映介质性质的某个摄动小参数, 方程的解或其导数在边界层内变化非常剧烈.
本文研究如下的边界层问题
其中扩散项系数
当对流项系数
2 Bakhvalov-Shishkin网格上的数值格式
我们在求解区间
设网格剖分数
在该网格上构造问题(1.1)的差分格式为
当问题的解具有左边界层时, 定义网格过渡点
在该网格上构造问题(1.1)的差分格式为
显然, 当小参数
引理2.1[13] 当
引理2.2[12] 当
由引理可知, 在B-S网格上求解边界层问题(1.1)的差分格式时, 不论小参数
3 优化网格参数的差分进化算法
将B-S网格(2.1)和(2.3)中的网格参数
其中
为了使误差尽可能的小, 构造如下的目标函数
以误差范数(3.2)为目标函数寻找最优的网格参数
差分进化算法将参数
下面给出采用差分进化算法结合差分格式在B-S网格上求解边界层问题(1.1)的算法步骤.
第一步 对参数
第二步 将
第三步(变异操作) 对每个个体
第四步(交叉操作) 对变异种群
其中
第五步 对个体
第六步 若
4 数值实验与结果分析
根据上节给出的算法步骤, 采用差分进化算法在B-S网格上对问题(1.1)进行数值实验.实验时取种群规模
算例1 考虑具有右边界层的问题
这里右端项
此例中
算例2 考虑具有右边界层的问题
这里右端项
此例中
算例3 考虑具有左边界层的问题
此例中
表 1 差分进化算法求解算例1的最优网格参数β1及目标函数值
| ε | N = 32 | N = 64 | N = 128 | N = 256 | ||||
| 误差 | β1 | 误差 | β1 | 误差 | β1 | 误差 | β1 | |
| 10-2 | 3.337E-02 | 0.269 | 1.766E-02 | 0.278 | 9.068E-03 | 0.296 | 4.589E-03 | 0.293 |
| 10-3 | 3.578E-02 | 0.213 | 1.861E-02 | 0.255 | 9.468E-03 | 0.279 | 4.774E-03 | 0.282 |
| 10-4 | 3.664E-02 | 0.211 | 1.896E-02 | 0.245 | 9.577E-03 | 0.265 | 4.808E-03 | 0.275 |
| 10-5 | 3.839E-02 | 0.173 | 1.962E-02 | 0.212 | 9.778E-03 | 0.238 | 4.857E-03 | 0.261 |
| 10-6 | 4.023E-02 | 0.156 | 2.062E-02 | 0.183 | 1.017E-02 | 0.211 | 4.986E-03 | 0.234 |
表 2 差分进化算法求解算例2的最优网格参数β1及目标函数值
| ε | N = 32 | N = 64 | N = 128 | N = 256 | ||||
| 误差 | β1 | 误差 | β1 | 误差 | β1 | 误差 | β1 | |
| 10-2 | 2.646E-02 | 0.842 | 1.403E-02 | 0.797 | 7.218E-03 | 0.837 | 3.657E-03 | 0.826 |
| 10-3 | 2.790E-02 | 0.711 | 1.463E-02 | 0.729 | 7.447E-03 | 0.769 | 3.749E-03 | 0.806 |
| 10-4 | 2.808E-02 | 0.710 | 1.471E-02 | 0.728 | 7.483E-03 | 0.768 | 3.765E-03 | 0.790 |
| 10-5 | 2.810E-02 | 0.709 | 1.472E-02 | 0.728 | 7.487E-03 | 0.768 | 3.766E-03 | 0.790 |
| 10-6 | 2.810E-02 | 0.709 | 1.472E-02 | 0.728 | 7.487E-03 | 0.768 | 3.767E-03 | 0.790 |
表 3 差分进化算法求解算例3的最优网格参数β2及目标函数值
| ε | N = 32 | N = 64 | N = 128 | N = 256 | ||||
| 误差 | β2 | 误差 | β2 | 误差 | β2 | 误差 | β2 | |
| 10-2 | 5.773E-03 | 0.441 | 2.879E-03 | 0.446 | 1.393E-03 | 0.430 | 6.534E-04 | 0.397 |
| 10-3 | 6.997E-03 | 0.345 | 3.638E-03 | 0.357 | 1.851E-03 | 0.364 | 9.320E-04 | 0.368 |
| 10-4 | 7.154E-03 | 0.330 | 3.733E-03 | 0.340 | 1.907E-03 | 0.346 | 9.636E-04 | 0.350 |
| 10-5 | 7.172E-03 | 0.328 | 3.743E-03 | 0.338 | 1.913E-03 | 0.344 | 9.670E-04 | 0.347 |
| 10-6 | 7.173E-03 | 0.328 | 3.744E-03 | 0.338 | 1.914E-03 | 0.344 | 9.673E-04 | 0.347 |
当问题的解具有右边界层时, 网格过渡点为
图 1
取摄动小参数
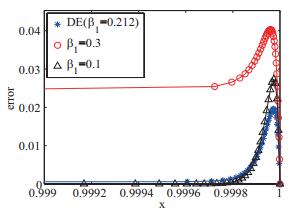
表 4 算例1中β1取不同值的误差比较
| 网格参数选取 | ε = 10-2 | ε = 10-5 | ||
| N = 64 | N = 128 | N = 64 | N = 128 | |
| 差分进化算法 | 1.766E-02 | 9.068E-03 | 1.962E-02 | 9.778E-03 |
| β1 = 2/3 | 2.486E-02 | 1.372E-02 | 3.956E+00 | 1.012E+00 |
| β1 = 0.3 | 1.769E-02 | 9.075E-03 | 4.028E-02 | 1.185E-02 |
| β1 = 0.1 | 2.676E-02 | 1.453E-02 | 2.734E-02 | 1.481E-02 |
表 5 算例2中β1取不同值的误差比
| 网格参数选取 | ε = 10-2 | ε = 10-5 | ||
| N = 64 | N = 128 | N = 64 | N = 128 | |
| 差分进化算法 | 1.403E-02 | 7.218E-03 | 1.472E-02 | 7.487E-03 |
| β1 = 1 | 1.441E-02 | 7.411E-03 | 1.580E-02 | 7.983E-03 |
| β1 = 0.3 | 2.085E-02 | 1.116E-02 | 2.123E-02 | 1.135E-02 |
| β1 = 0.1 | 4.362E-02 | 2.522E-02 | 4.441E-02 | 2.565E-02 |
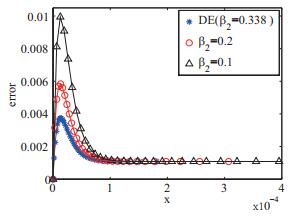
表 6 算例3中β2取不同值的误差比较
| 网格参数选取 | ε = 10-2 | ε = 10-5 | ||
| N = 64 | N = 128 | N = 64 | N = 128 | |
| 差分进化算法 | 2.879E-03 | 1.393E-03 | 3.742E-03 | 1.912E-03 |
| β2 = 1 | 3.233E-03 | 1.621E-03 | 3.743E-03 | 1.913E-03 |
| β2 = 0.2 | 5.293E-03 | 2.936E-03 | 5.840E-03 | 3.146E-03 |
| β2 = 0.1 | 2.638E-02 | 1.351E-02 | 9.939E-03 | 5.692E-03 |
我们将网格参数
图 2
图 3
图 4
因此, 与人为选择B-S网格中的网格参数相比, 利用差分进化算法优化选择网格参数进而求解边界层问题能得到更好的数值结果.该方法经过少量次数的迭代可得到最优网格参数, 在计算精度、收敛性方面均有优势.
5 结语
本文采用差分进化算法优化选择Bakhvalov-Shishkin网格中参数, 提出了求解具有左、右边界层的奇异摄动问题的差分进化算法.实验结果表明, 与选择固定的网格参数相比, 采用差分进化算法计算能极大提高计算精度, 特别是边界层的计算精度, 并且数值结果具有收敛性.本文的方法也可以推广到Bakhvalov-Shishkin网格上其它问题的计算或高维问题的计算中.
参考文献
Layer-adapted meshes for convection-diffusion problems
DOI:10.1016/S0045-7825(02)00630-8 [本文引用: 2]
Discrete spline solution of singularly perturbed problem with two small parameters on a Shishkin-type mesh
DOI:10.1007/s10598-018-9416-3 [本文引用: 1]
A singularly perturbed problem with two parameters on a Bakhvalov-type mesh
A second-order hybrid finite difference scheme for a system of coupled singularly perturbed initial value problems
求解二阶双曲型方程的自适应网格方法
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.04.021 [本文引用: 1]
Adaptive mesh method for solving a second-order hyperbolic equation
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.04.021 [本文引用: 1]
Approximation of singularly perturbed reaction-diffusion problems by quadratic-splines
Layer-adapted meshes for parameterized singular perturbation problem
DOI:10.1016/j.proeng.2015.11.342
Improved uniform convergence of a finite difference approximation to a kind of singularly perturbed problems
Uniform convergence analysis of finite difference approximations for singular perturbation problems on an adapted grid
Two improved algorithms and implementation for a singularly perturbed problem on moving meshes
DOI:10.1007/s11424-011-8138-9 [本文引用: 1]
Analysis of a streamline-diffusion finite element method on Bakhvalov-Shishkin mesh for singularly perturbed problem
Sufficient conditions for uniform convergence on layer-adapted grids
DOI:10.1007/s006070050049 [本文引用: 1]
一类奇异摄动问题差分格式的一致收敛性分析
Analysis of uniform convergence for difference scheme of a singularly perturbed problem
多尺度有限元结合Bakhvalov-Shishkin网格法高效处理边界层问题的研究
Combining the multiscale finite element and Bakhvalov-Shishkin grid to solve the boundary layer problems
Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces
基于泛化反向学习的多目标约束差分进化算法
Multi-objective constrained differential evolution using generalized opposition-based learning
基于改进差分进化算法的云制造资源优化组合方法
Resource optimization combination method based on improved differential evolution algorithm for cloud manufacturing