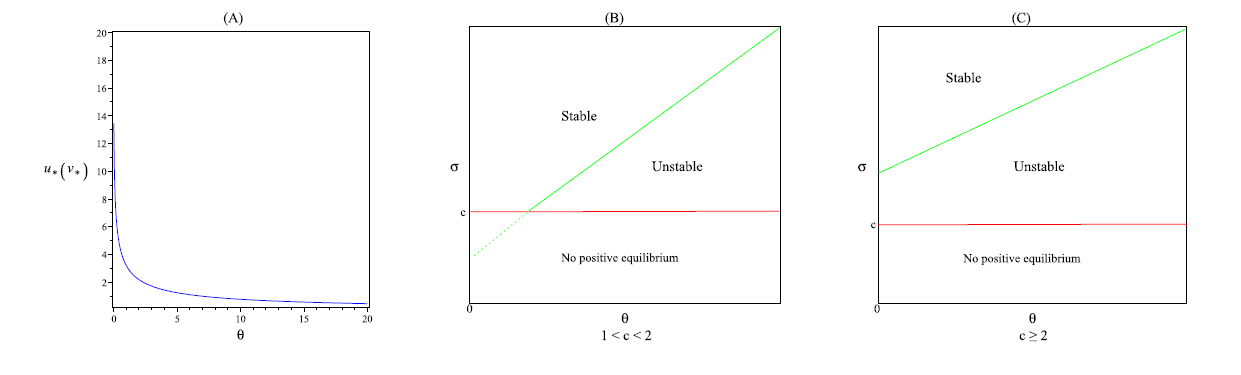
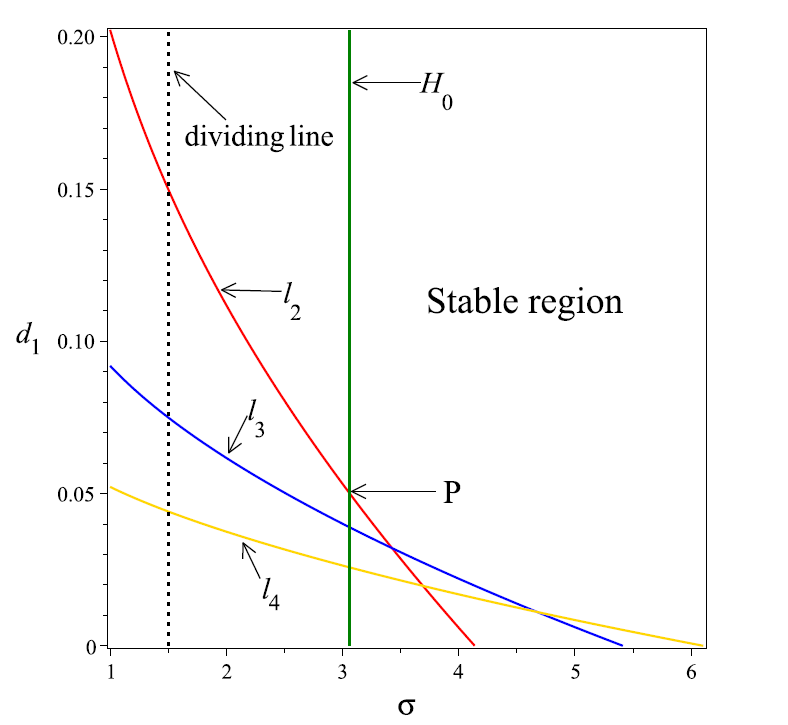
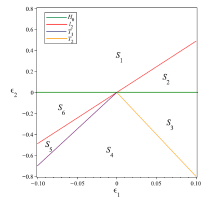
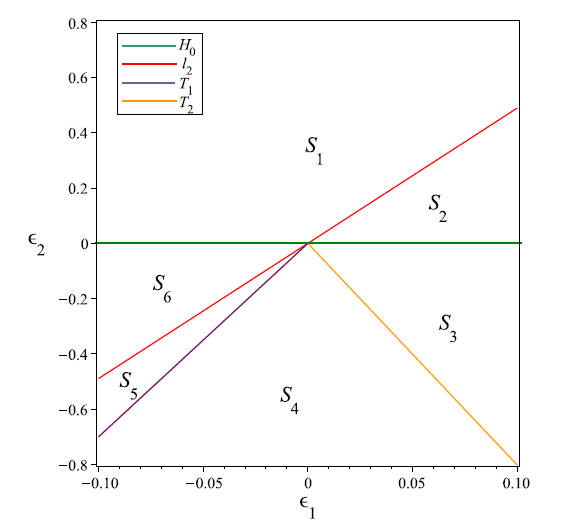
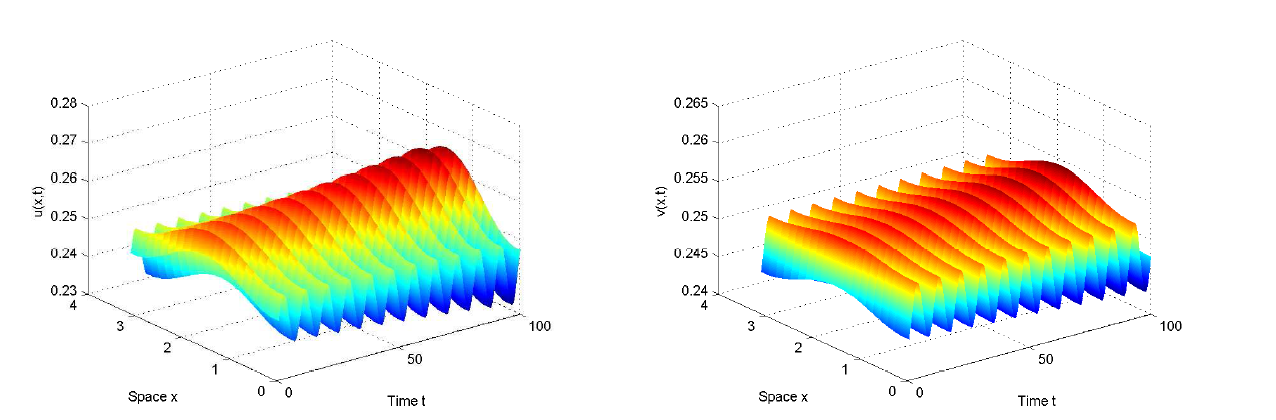
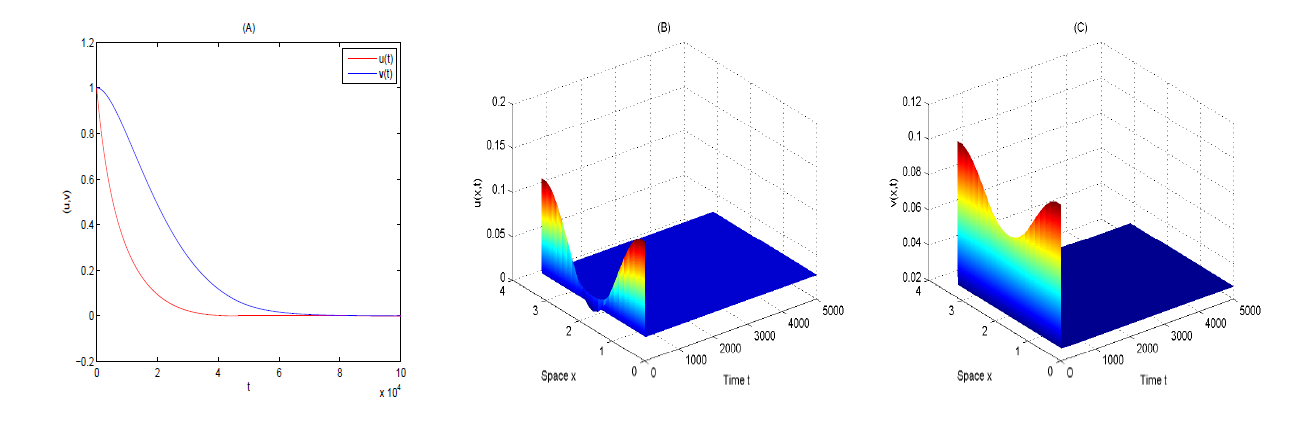
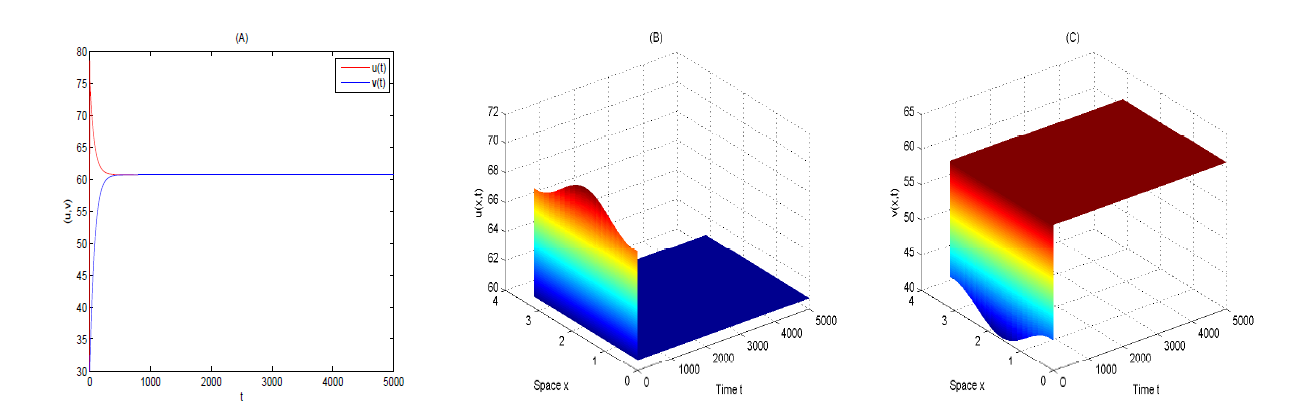
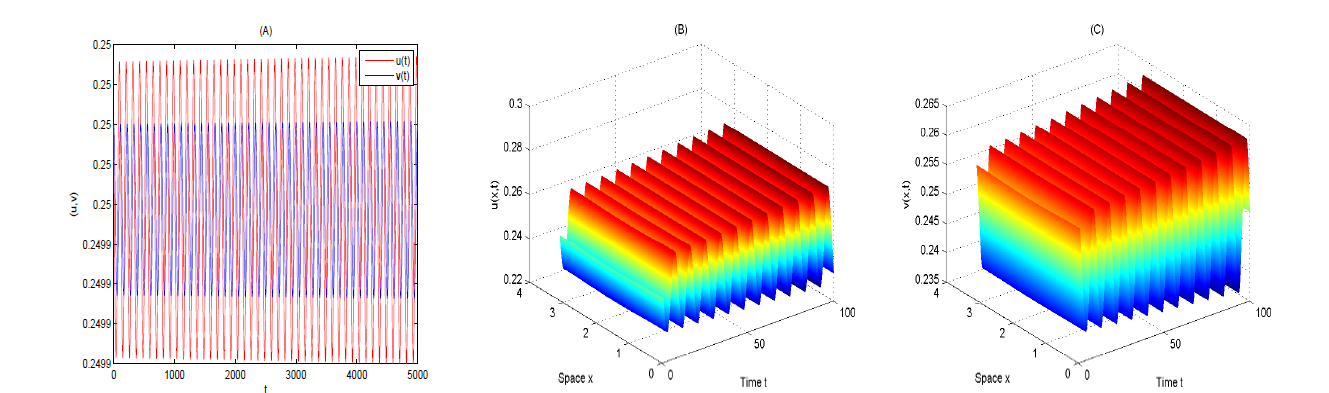
Acta mathematica scientia,Series A ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1577-1594.
Previous Articles Next Articles
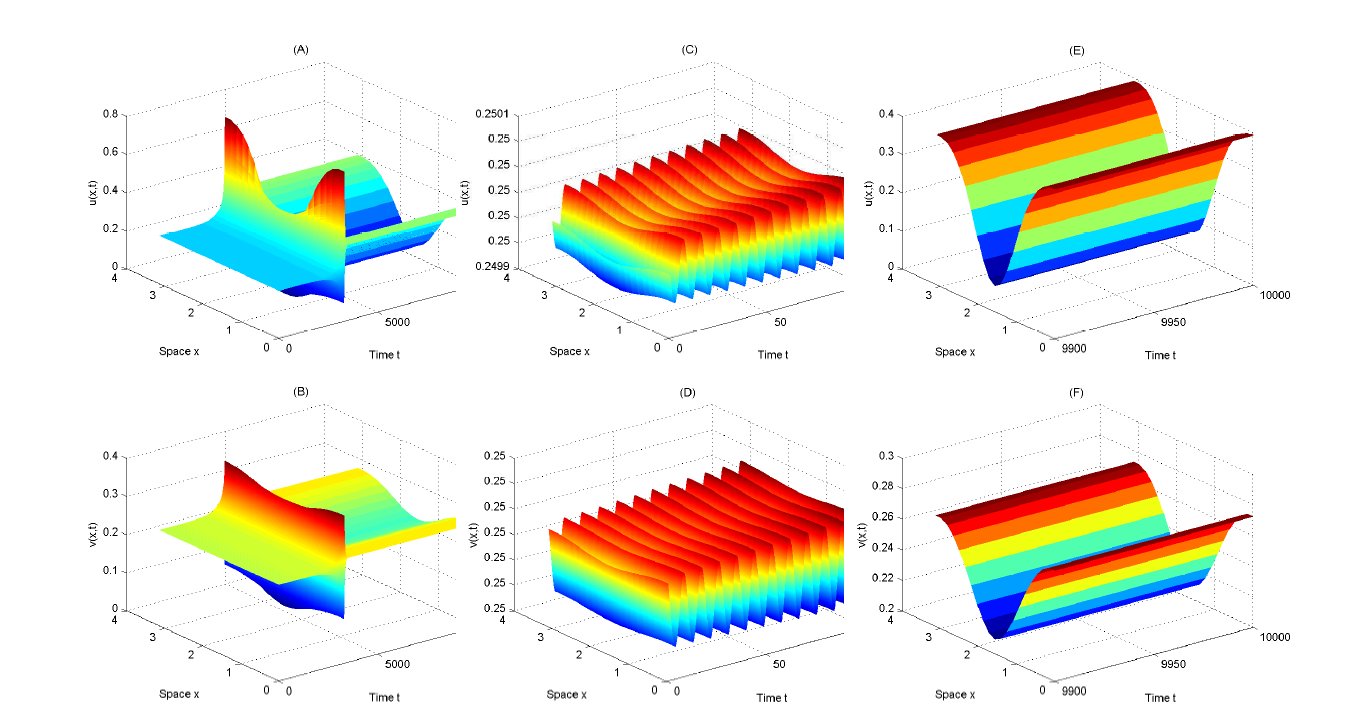
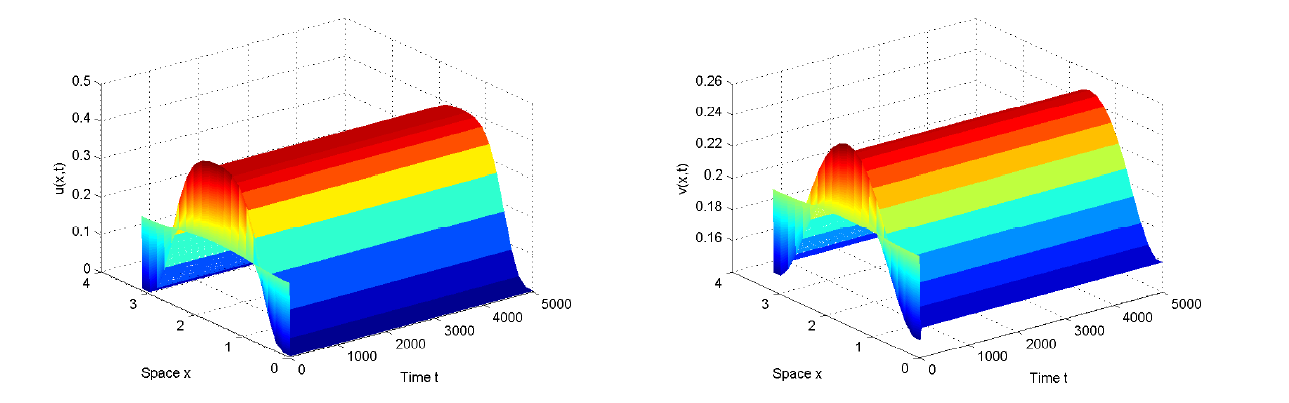
Spatiotemporal Dynamics Induced by the Interaction Between Fear and Schooling Behavior in a Diffusive Model
Xiao Jianglong1( ),Song Yongli2(
),Song Yongli2( ),Xia Yonghui3,*(
),Xia Yonghui3,*( )
)
- 1School of Mathematical Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Zhejiang Jinhua 321004
2School of Mathematics, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 311121
3School of Mathematics, Foshan University, Guangdong Foshan 528000
-
Received:2023-08-02Revised:2024-04-16Online:2024-12-26Published:2024-11-22 -
Supported by:NSFC(11931016);Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province(LZ23A010001);Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province(LZ24A010006)
CLC Number:
- 0175.23
Cite this article
Xiao Jianglong, Song Yongli, Xia Yonghui. Spatiotemporal Dynamics Induced by the Interaction Between Fear and Schooling Behavior in a Diffusive Model[J].Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2024, 44(6): 1577-1594.
share this article
| [1] | Yang J, Yuan S, Zhang T. Complex dynamics of a predator-prey system with herd and schooling behavior: with or without delay and diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn, 2021, 104: 1709-1735 |
| [2] |
Zanette L, White A, Allen M, et al. Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per year. Science, 2011, 334(6061): 1398-1401
doi: 10.1126/science.1210908 pmid: 22158817 |
| [3] | Suraci J, Clinchy M, Dill L, et al. Fear of large carnivores causes a trophic cascade. Nat Commun, 2016, 7(1): Article 10698 |
| [4] | Hua F, Sieving K, Fletcher R, et al. Increased perception of predation risk to adults and offspring alters avian reproductive strategy and performance. Behav Ecol, 2014, 25(3): 509-519 |
| [5] | Wirsing A, Ripple W. A comparison of shark and wolf research reveals similar behavioral responses by prey. Front Ecol Environ, 2011, 9: 335-341 |
| [6] | Bauman A G, Seah J C L, Januchowski-Hartley F A, et al. Fear effects associated with predator presence and habitat structure interact to alter herbivory on coral reefs. Biol Lett, 2019, 15(10): 20190409 |
| [7] |
Wang X, Zanette L, Zou X. Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions. J Math Biol, 2016, 73(5): 1179-1204
pmid: 27002514 |
| [8] | Sasmal S. Population dynamics with multiple Allee effects induced by fear factors-A mathematical study on prey-predator interactions. Appl Math Model, 2018, 64: 1-14 |
| [9] | Panday P, Samanta S, Pal N, et al. Delay induced multiple stability switch and chaos in a predator-prey model with fear effect. Math Comput Simul, 2020, 172: 134-158 |
| [10] | Wang J, Cai Y, Fu S, et al. The effect of the fear factor on the dynamics of a predator-prey model incorporating the prey refuge. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2019, 29: 083109 |
| [11] | Antwi-Fordjour K, Parshad R D, Thompson H E, et al. Fear-driven extinction and (de) stabilization in a predator-prey model incorporating prey herd behavior and mutual interference. AIMS Math, 2023, 8(2): 3353-3377 |
| [12] | Dai B, Sun G. Turing-Hopf bifurcation of a delayed diffusive predator-prey system with chemotaxis and fear effect. Appl Math Lett, 2021, 111: 106644 |
| [13] | Zhang X, An Q, Wang L. Spatiotemporal dynamics of a delayed diffusive ratio-dependent predator-prey model with fear effect. Nonlinear Dyn, 2021, 105: 3775-3790 |
| [14] | Tiwari V, Tripathi J, Mishra S, et al. Modeling the fear effect and stability of non-equilibrium patterns in mutually interfering predator-prey systems. Appl Math Comput, 2020, 371: 124948 |
| [15] | Major P. Predator-prey interactions in two schooling fishes, caranx ignobilis and stolephorus purpureus. Anim Behav, 1978, 26: 760-777 |
| [16] | Scheel D, Packer C. Group hunting behaviour of lions: a search for cooperation. Anim Behav, 1991, 41(4): 697-709 |
| [17] | Ajraldi V, Pittavino M, Venturino E. Modeling herd behavior in population systems. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl, 2011, 12(4): 2319-2338 |
| [18] | Xu C, Yuan S, Zhang T. Global dynamics of a predator-prey model with defense mechanism for prey. Appl Math Lett, 2016, 62: 42-48 |
| [19] | Manna D, Maiti A, Samanta G. Analysis of a predator-prey model for exploited fish populations with schooling behavior. Appl Math Comput, 2018, 317: 35-48 |
| [20] | Melchionda D, Pastacaldi E, Perri C, et al. Social behavior-induced multistability in minimal competitive ecosystems. Theor Biol, 2017, 439: 24-38 |
| [21] | Jiang H. Turing bifurcation in a diffusive predator-prey model with schooling behavior. Appl Math Lett, 2019, 96: 230-235 |
| [22] | Yang J, Zhang T, Yuan S. Turing pattern induced by cross-diffusion in a predator-prey model with pack predation-herd behavior. Int J Bifurcation Chaos, 2020, 30(7): 2050103 |
| [23] | Zhou Y, Yan X, Zhang C. Turing patterns induced by self-diffusion in a predator-prey model with schooling behavior in predator and prey. Nonlinear Dyn, 2021, 105: 3731-3747 |
| [24] | Lou Y, Ni W. Diffusion, self-diffusion and cross-diffusion. J Differ Equations, 1996, 131(1): 79-131 |
| [25] | Lou Y, Ni W, Yotsutani S. Pattern formation in a cross-diffusion system. Discrete Contin Dyn A, 2015, 35(4): 1589-1607 |
| [26] | Wang S, Zhang J, Xu F, et al. Dynamics of virus infection models with density-dependent diffusion. Comput Math Appl, 2017, 74(10): 2403-2422 |
| [27] | Zhou X, Shi X, Song X. Analysis of nonautonomous predator-prey model with nonlinear diffusion and time delay. Appl Math Comput, 2008, 196(1): 129-136 |
| [28] | Zhang X, Chen L. The linear and nonlinear diffusion of the competitive Lotka-Volterra model. Nonlinear Anal, 2007, 66(12): 2767-2776 |
| [29] | Wang J, Wei J, Shi J. Global bifurcation analysis and pattern formation in homogeneous diffusive predator-prey systems. J Differ Equations, 2016, 260(4): 3495-3523 |
| [30] | Tang X, Song Y. Bifurcation analysis and Turing instability in a diffusive predator-prey model with herd behavior and hyperbolic mortality. Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2015, 81(A): 303-314 |
| [31] | Yi F, Wei J, Shi J. Bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a homogeneous diffusive predator-prey system. J Differ Equations, 2009, 246(5): 1944-1977 |
| [32] | Shi J, Wang C, Wang H, et al. Diffusive spatial movement with memory. J Dyn Differ Equations, 2020, 32: 979-1002 |
| [33] | Song Y, Peng Y, Zhang T. The spatially inhomogeneous Hopf bifurcation induced by memory delay in a memory-based diffusion system. J Differ Equations, 2021, 300: 597-624 |
| [34] | Shi J, Wang C, Wang H. Spatial movement with diffusion and memory-based self-diffusion and cross-diffusion. J Differ Equations, 2021, 305: 242-269 |
| [35] | Jiang W, Wang H, Cao X. Turing instability and Turing-Hopf bifurcation in diffusive Schnakenberg systems with gene expression time delay. J Dyn Differ Equations, 2019, 31: 2223-2247 |
| [36] | Chen S, Lou Y, Wei J. Hopf bifurcation in a delayed reaction-diffusion-advection population model. J Differ Equations, 2018, 264(8): 5333-5359 |
| [37] | Wu D, Zhao H. Spatiotemporal dynamics of a diffusive predator-prey system with Allee effect and threshold hunting. J Nonlinear Sci, 2020, 30: 1015-1054 |
| [38] | Zhou P, Xiao D. Global dynamics of a classical Lotka-Volterra competition-diffusion-advection system. J Funct Anal, 2018, 275(2): 356-380 |
| [39] | Chen M, Wu R. Spatiotemporal patterns induced by Turing and Turing-Hopf bifurcations in a predator-prey system. Appl Math Comput, 2020, 380: 1-15 |
| [40] | Luo D, Wang Q. Global bifurcation and pattern formation for a reaction-diffusion predator-prey model with prey-taxis and double Beddington-DeAngelis functional responses. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl, 2022, 67: 103638 |
| [41] | Song Y, Zhang T, Peng Y. Turing-Hopf bifurcation in the reaction-diffusion equations and its applications. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul, 2016, 33: 229-258 |
| [1] | Zhang Wenwen, Liu Zhijun, Wang Qinglong. Exponential Extinction, Stationary Distribution and Probability Density Function of A Stochastic Predator-Prey Model with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Process [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2024, 44(5): 1368-1379. |
| [2] | Wang Qiufen, Zhang Shuwen. Stochastic Predator-Prey System with Fear Effect and Holling-Type III Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2024, 44(5): 1380-1391. |
| [3] | Bo Li,Ziwei Liang. Stability of Stage-Structured Predator-Prey Models with Beddington-DeAngelis Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2022, 42(6): 1826-1835. |
| [4] | Tong Zhao,Hailong Yuan,Gaihui Guo. Positive Solutions of a Predator-Prey Model with Modified Leslie-Gower Type [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2022, 42(1): 176-186. |
| [5] | Yue Sun,Daoxiang Zhang,Wen Zhou. The Influence of Fear Effect on Stability Interval of Reaction-Diffusion Predator-Prey System with Time Delay [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(6): 1980-1992. |
| [6] | Xin Wu,Rong Yuan,Zhaohai Ma. Analysis on Critical Waves and Non-Critical Waves for Holling-Tanner Predator-Prey System with Nonlocal Diffusion [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(6): 1705-1717. |
| [7] | Tengfei Wang,Tao Feng,Xinzhu Meng. Complex Dynamics and Stochastic Sensitivity Analysis of a Predator-Prey Model with Crowley-Martin Type Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(4): 1192-1203. |
| [8] | Gaihui Guo,Xiaohui Liu. Hopf Bifurcation and Stability for an Autocatalytic Reversible Biochemical Reaction Model [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(1): 166-177. |
| [9] | Tingting Jiang,Zengji Du. Periodic Solutions of a Neutral Impulsive Predator-Prey Model with Holling-Type IV Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(1): 178-193. |
| [10] | Changxu Shao,Shutang Liu. Fractal Feature and Control of Three-Species Predator-Prey Model [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2019, 39(4): 951-962. |
| [11] | Yingjie Fu,Guijie Lan,Shuwen Zhang,Chunjin Wei. Dynamics of a Stochastic Predator-Prey Model with Pulse Input in a Polluted Environment [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2019, 39(3): 674-688. |
| [12] | Guijie Lan,Yingjie Fu,Chunjin Wei,Shuwen Zhang. Stationary Distribution and Periodic Solution for Stochastic Predator-Prey Systems with Holling-Type Ⅲ Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2018, 38(5): 984-1000. |
| [13] | Lifei Zheng,Jie Guo,Meihua Wu,Xiaorui Wang,Aying Wan. The Research on a Class of the Predator-Prey-Mutualist System with Delays [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2018, 38(5): 1001-1013. |
| [14] | Zhou Jun. Turing Instability and Hopf Bifurcation of a Bimolecular Model with Autocatalysis and Saturation Law [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2017, 37(2): 366-373. |
| [15] | Yang Wenbin, Wu Jianhua. Some Dynamics in Spatial Homogeneous and Inhomogeneous Activator-Inhibitor Model [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2017, 37(2): 390-400. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 225
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 87
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|