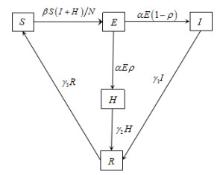
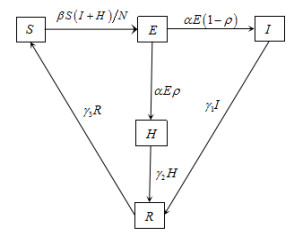
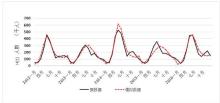
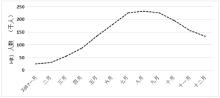
| 1 |
Huang Y , Deng T , Yu S C , et al. Effect of meteorological variables on the incidence of hand, foot, and mouth disease in children:a time-series analysis in Guangzhou, China. BMC Infectious Diseases, 2013, 13: 134
doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-134
|
| 2 |
中国疾病控制中心.手足口病疾病概述.http://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/bl/szkb/zstd/201212/t2012121072846.html
|
|
Chinese center for disease control and prevention. The overview for Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease. http://www.chinacdc.cn/jkzt/crb/bl/szkb/zstd/201212/t2012121072846.html
|
| 3 |
李超贤, 赵伟. 中西医结合治疗手足口病100例. 上海中医药杂志, 2009, 43 (9): 35- 36
|
|
Li C X , Zhao W . Treatment of 100 cases of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease by integrative Chinese and Western Medicine. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009, 43 (9): 35- 36
|
| 4 |
Seddon J H , Duff M F . Hand-foot-and-mouth disease:coxsackievirus types A5, A10, and A16 infections. N Z Med J, 1971, 74: 368- 373
|
| 5 |
Robinson C R , Doane F W , Rhodes A J . Report of an outbreak of febrile illness with pharyngeal lesions and exanthem:Toronto, summer 1957-isolation of group a coxsackie virus. The Canadian Medical Association Journal, 1958, 79 (8): 615- 621
|
| 6 |
Schmidt N J , Lennette E H , Ho H H . An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 1974, 129 (3): 304- 309
doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.304
|
| 7 |
Repass L G , Palmer W C , Stancampiano F F . Hand, foot, and mouth disease:identifying and managing an acute viral syndrome. Clevel Clin J Med, 2014, 81: 537- 543
doi: 10.3949/ccjm.81a.13132
|
| 8 |
公共卫生数据中心.手足口病.http://www.phsciencedata.cn/Share/kysjml.jsp?id=b9c93769-3e0f-413a-93c1-027d2009d8bc&show=0
|
|
Public health data center. Hand, foot, and mouth disease.http://www.phsciencedata.cn/Share/kysjml.jsp?id=b9c93769-3e0f-413a-93c1-027d2009d8bc&show=0
|
| 9 |
洪志恒, 常昭瑞, 涂文校, 等. 2016年3月全国突发公共卫生事件及需关注的传染病风险评估. 疾病监测, 2016, 31 (03): 181- 184
|
|
Hong Z H , Chang Z R , Tu R Q , et al. Risk assessment of public health emergencies and communicable diseases concerned in the mainland of China, March 2016. Disease Surrveillance, 2016, 31 (3): 181- 184
|
| 10 |
Wang J R , Tuan Y C , Tsai H P . Change of major genotype of enterovirus71 in outbreaks of hand-footand-mouth disease in tai wan between 1998 and 2000. J Clin Micro Biol, 2002, 40: 10- 15
doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.1.10-15.2002
|
| 11 |
Fujimoto T , Chikahira M , Yoshida S , et al. Outbreak of central nervous system disease associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease in Japan during the summer of 2000:detection and molecular epidemiology of enterovirus 71. Microbiol Immunol, 2002, 46: 621- 627
doi: 10.1111/mim.2002.46.issue-9
|
| 12 |
Chua K B , Kasri A R . Hand foot and mouth disease due to enterovirus 71 in malaysia. Virol Sin, 2011, 26: 221- 228
doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3195-8
|
| 13 |
Zhang Y , Tan X , Wang H , et al. An outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with subgenotype C4 of human enterovirus 71 in Shandong. China J Clin Virol, 2009, 44: 262- 267
doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2009.02.002
|
| 14 |
国家卫生计生委疾病预防控制局.卫生部关于将手足口病纳入法定传染病管理的通知.http://www.moh.gov.cn/jkj/s3577/200805/1a8bb3668b7d4540afb0531dfcef978d.shtml
|
|
Bureau of disease control and prevention of national health council of the People's Republic of China. The notice of the Ministry of health on hand foot and mouth disease into legal communicable diseases management. http://www.moh.gov.cn/jkj/s3577/200805/1a8bb3668b7d4540afb0531dfcef978d.shtml
|
| 15 |
Wang L , Zhu B , Li Z , et al. Epidemiologic characteristics of hand, foot, and mouth disease in China from 2006 to 2015. J Infect, 2016, 73: 512- 515
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2016.08.007
|
| 16 |
Tiing F C S , Labadin J . A Simple Deterministic Model for the Spread of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (hfmd) in Sarawak//Second Asia International Conference on Modeling and Simulation. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia:IEEE, 2008, 947- 952
|
| 17 |
Liu J L . Threshold dynamics for a HFMD epidemic model with periodic transmission rate. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2011, 64: 89- 95
doi: 10.1007/s11071-010-9848-6
|
| 18 |
MaY J , Liu M X , Hou Q , et al. Modeling seasonal HFMD with the recessive infection in shandong. China Math Biosci Eng, 2013, 10: 1159- 1171
doi: 10.3934/mbe
|
| 19 |
Yang J Y , Chen Y M , Zhang F Q . Stability analysis and optimal control of a hand-foot-mouth disease (hfmd) model. J Appl Math Comput, 2013, 41: 99- 117
doi: 10.1007/s12190-012-0597-1
|
| 20 |
Li Y , Zhang J H , Zhang X A . Modeling and preventive measures of hand, foot and mouth disease(hfmd) in china. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2014, 11 (3): 3108- 3117
doi: 10.3390/ijerph110303108
|
| 21 |
Li Y , Wang L W , Pang L Y , et al. The data fitting and optimal control of a hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) model with stage structure. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2016, 276: 61- 74
doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2015.11.090
|
| 22 |
Wang J Y , Xiao Y N , Peng Z H . Modeling seasonal HFMD infections with the effects of contaminated environments in mainland China. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2016, 274: 615- 627
doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2015.11.035
|
| 23 |
Wang J Y , Xiao Y N , Cheke R A . Modeling the effects of contaminated environments on HFMD infections in mainland China. Biosystems, 2016, 140: 1- 7
doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2015.12.001
|
| 24 |
Chou A H , Liu C C , Chang P C , et al. Pilot scale production of highly efficacious and stable enterovirus 71 vaccine candidates. PloS One, 2012, 7: e34834
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034834
|
| 25 |
Liang Z , Mao Q , Gao F , et al. Progress on the research and development of human enterovirus 71(ev71) vaccines. Front Med, 2013, 7: 111- 121
doi: 10.1007/s11684-012-0237-z
|
| 26 |
Zhu F C , Xu W B , Xia J L , et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an enterovirus 71 vaccine in China. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370 (9): 818- 828
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1304923
|
| 27 |
中华人民共和国国家卫生委科技教育司.重大新药创制科技重大专项取得重大成果——世界首个预防手足口病疫苗获批生产上市.http://www.nhfpc.gov.cn/qjjys/s3594r/201512/fa403581683d4b619bcee477aa15423e.shtml
|
|
Department of science and technology education of national health council of the People's Republic of China. Creative technology of major new drugs made significant achievements and hand foot and mouth disease prevention vaccine in the world was firstly approved to be manufactured and marketed.http://www.nhfpc.gov.cn/qjjys/s3594r/201512/fa403581683d4b619bcee477aa15423e.shtml
|
| 28 |
Zhang X A , Zhao Y D , Neumann A U . Partial immunity and vaccination for influenza. J Comput Biol, 2010, 17 (12): 1689- 1696
doi: 10.1089/cmb.2009.0003
|
| 29 |
Van den Driessche P , Watmough J . Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Mathematical Biosciences, 2002, 180 (1): 29- 48
|
| 30 |
Li R C , Liu L D , Mo Z J , et al. An inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine in healthy children. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370 (9): 829- 837
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1303224
|
 ),Sanhong Liu2,*,Yile Fang3,Xingan Zhang1
),Sanhong Liu2,*,Yile Fang3,Xingan Zhang1