
- Oct. 1, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 503-513.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212928
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiao-dong HU,Wen-xian LAN,Chun-xi WANG,Chun-yang CAO*( )
)
Received:2021-06-29
Published:2021-12-05
Online:2021-09-16
Contact:
Chun-yang CAO
E-mail:ccao@mail.sioc.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Xiao-dong HU,Wen-xian LAN,Chun-xi WANG,Chun-yang CAO. Research Advance and NMR Studies of Anti-Cancer Small Molecules Targeting c-MYC G4-DNA[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 503-513.
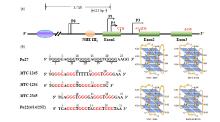
Fig.3
Reported G4 structures in the c-MYC gene promoter. (a) The promoter structure of the MYC gene and different related elements; (b) Schematic demonstration of MYC-1245, MYC-1234, MYC-2345, and Pu22(4/14/23T) G4-DNA structures. The arrowheads indicate 5'-to-3' direction of DNA strands; guanines are shown by circles, and adenines and thymines are shown by boxes
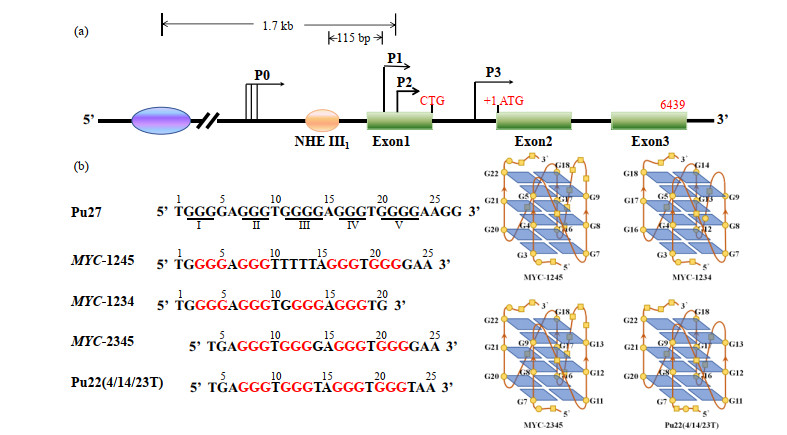
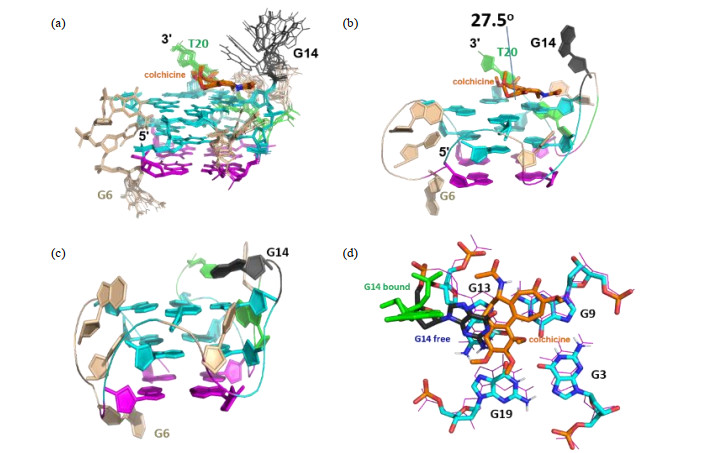
Fig.11
Structure of RET G4-DNA in complex with colchicine (in orange). (a) The ensemble of 20 structures with the lowest energy. Base G14 is flexible; (b) One conformer of the complex. An angle 27.5° was formed between aromatic seven-membered ring and phenyl ring; (c) The structure of free RET G4-DNA; (d) The position of colchicine (in orange) relative to G14 (in green) above G3-G9-G13-G19 tetrad (in cyan) at 3'-end in the complex structure, compared to structure of free RET G4-DNA (in line mode, except the base G14 which was termed as G14 free and displayed in blue stick). In (a)~(c), the G-tetrad composed by four syn guanines was in magenta line and cartoon modes, respectively. The G-tetrads composed by anti- guanines were shown in cyan lines and cartoon modes, respectively. In all figures, base G14 was in deep-gray lines and cartoon modes. Bases G16 and T20 were in green lines and cartoon modes, respectively. Bases G4, C5, G6 and C10 in loops were in wheat lines or cartoon modes. All nonpolar protons were not displayed[61]
| 1 |
WELLS R D , DERE R , HEBERT M L , et al. Advances in mechanisms of genetic instability related to hereditary neurological diseases[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2005, 33 (12): 3785- 3798.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gki697 |
| 2 |
GELLERT M , LIPSETT M N , DAVIES D R . Helix formation by guanylic acid[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1962, 48 (12): 2013- 2018.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2013 |
| 3 |
ADRIAN M , HEDDI B , PHAN A T . NMR spectroscopy of G-quadruplexes[J]. Methods, 2012, 57 (1): 11- 24.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.05.003 |
| 4 | HUPPERT J L . Four-stranded nucleic acids: structure, function and targeting of G-quadruplexes[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2008, 39 (40): 1375- 1384. |
| 5 |
BALASUBRAMANIAN S , HURLEY L H , NEIDLE S . Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: a novel anticancer strategy?[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2011, 10, 261- 275.
doi: 10.1038/nrd3428 |
| 6 |
LIPPS H J , RHODES D . G-quadruplex structures: in vivo evidence and function[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2009, 19 (8): 414- 422.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.05.002 |
| 7 |
TORNALETTI S . Transcriptional processing of G4 DNA[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2009, 48 (4): 326- 335.
doi: 10.1002/mc.20513 |
| 8 |
COONEY M , CZERNUSZEWICZ G , POSTEL E H , et al. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro[J]. Science, 1988, 241 (4864): 456- 459.
doi: 10.1126/science.3293213 |
| 9 |
TOMONAGA T , LEVENS D . Activating transcription from single stranded DNA[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1996, 93, 5830- 5835.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.12.5830 |
| 10 |
SEENISAMY J , BASHYAM S , GOKHALE V , et al. Design and synthesis of an expanded porphyrin that has selectivity for the c-MYC G-quadruplex structure[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127 (9): 2944- 2959.
doi: 10.1021/ja0444482 |
| 11 |
SIDDIQUI-JAIN A , GRAND C L , BEARSS D J , et al. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2002, 99, 11593- 11598.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.182256799 |
| 12 |
SUN Z Y , WANG X N , CHENG S Q , et al. Developing novel G-quadruplex ligands: from interaction with nucleic acids to interfering with nucleic acid(-)protein interaction[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24 (3): 396.
doi: 10.3390/molecules24030396 |
| 13 |
BRAZDA V , HARONIKOVA L , LIAO J C , et al. DNA and RNA quadruplex-binding proteins[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15, 17493- 17517.
doi: 10.3390/ijms151017493 |
| 14 |
VARSHNEY D , SPIEGEL J , ZYNER K , et al. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21, 459- 474.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0236-x |
| 15 |
GONZALEZ V , GUO K X , HURLEY L , et al. Identification and characterization of nucleolin as a c-MYC G-quadruplex-binding protein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284 (35): 23622- 23635.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018028 |
| 16 |
GONZALEZ V , HURLEY L H . The C-terminus of nucleolin promotes the formation of the c-MYC G-quadruplex and inhibits c-MYC promoter activity[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49 (45): 9706- 9714.
doi: 10.1021/bi100509s |
| 17 |
FEDERICI L , ARCOVITO A , SCAGLIONE G L , et al. Nucleophosmin C-terminal leukemia-associated domain interacts with G-rich quadruplex forming DNA[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285 (48): 37138- 37149.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.166736 |
| 18 |
Scognamiglio P L , Di Natale C , Leone M , et al. G-quadruplex DNA recognition by nucleophosmin: new insights from protein dissection[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1840 (6): 2050- 2059.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.02.017 |
| 19 |
GALLO A , STERZO CL , MORI M , et al. Structure of nucleophosmin DNA-binding domain and analysis of its complex with a G-quadruplex sequence from the c-MYC promoter[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287 (32): 26539- 26548.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.371013 |
| 20 |
KANG H J , LE TVT , KIM K , et al. Novel interaction of the Z-DNA binding domain of human ADAR1 with the oncogenic c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex[J]. J Mol Biol, 2014, 426 (14): 2594- 2604.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.001 |
| 21 |
PETR M , HELMA R , POLÁŠKOVÁ A , et al. Wild-type p53 binds to MYC promoter G-quadruplex[J]. Biosci Rep, 2016, 36 (5): e00397.
doi: 10.1042/BSR20160232 |
| 22 |
SANDERS C M . Human Pif1 helicase is a G-quadruplex DNA-binding protein with G-quadruplex DNA-unwinding activity[J]. Biochem J, 2010, 430, 119- 128.
doi: 10.1042/BJ20100612 |
| 23 |
BYRD A K , RANEY K D . A parallel quadruplex DNA is bound tightly but unfolded slowly by pif1 helicase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290 (10): 6482- 6494.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630749 |
| 24 |
BYRD A K , BELL M R , RANEY K D . Pif1 helicase unfolding of G-quadruplex DNA is highly dependent on sequence and reaction conditions[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293 (46): 17792- 17802.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004499 |
| 25 |
LEE S , LEE A R , RYU K S , et al. NMR investigation of the interaction between the RecQ C-terminal domain of human bloom syndrome protein and G-quadruplex DNA from the human c-MYC promoter[J]. J Mol Biol, 2019, 431 (4): 794- 806.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.010 |
| 26 |
BUDHATHOKI J B , RAY S , URBAN V , et al. RecQ-core of BLM unfolds telomeric G-quadruplex in the absence of ATP[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42 (18): 11528- 11545.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku856 |
| 27 |
CHATTERJEE S , ZAGELBAUM J , SAVITSKY P , et al. Mechanistic insight into the interaction of BLM helicase with intra-strand G-quadruplex structures[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 5556.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6556 |
| 28 |
KAROW J K , WU L , HICKSON I D . RecQ family helicases: roles in cancer and aging[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2000, 10 (1): 32- 38.
doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(99)00039-8 |
| 29 |
SUN H , KAROW J K. , HICKSON I D , et al. The Bloom's syndrome helicase unwinds G4 DNA[J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273 (42): 27587- 27592.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27587 |
| 30 |
WU G H , XING Z , TRAN E J , et al. DDX5 helicase resolves G-quadruplex and is involved in MYC gene transcriptional activation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116 (41): 20453- 20461.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909047116 |
| 31 |
POSTEL E H , BERBERICH S J , FLINT S J , et al. Human c-MYC transcription factor PuF identified as nm23-H2 nucleoside diphosphate kinase, a candidate suppressor of tumor metastasis[J]. Science, 1993, 261 (5120): 478- 480.
doi: 10.1126/science.8392752 |
| 32 |
JI L , ARCINAS M , BOXER L M . The transcription factor, Nm23H2, binds to and activates the translocated c-MYC allele in Burkitt's lymphoma[J]. J Biol Chem, 1995, 270 (22): 13392- 13398.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.22.13392 |
| 33 |
FEKETE A , KENESI E , HUNYADI-GULYAS E , et al. The guanine-quadruplex structure in the human c-myc gene's promoter is converted into B-DNA form by the human poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7, e42690.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042690 |
| 34 |
OU T M , LIN J , LU Y J , et al. Inhibition of cell proliferation by quindoline derivative (SYUIQ-05) through its preferential interaction with c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex[J]. J Med Chem, 2011, 54 (16): 5671- 5679.
doi: 10.1021/jm200062u |
| 35 |
DAI J X , CARVER M , HURLEY L H , et al. Solution structure of a 2:1 quindoline-c-MYC G-quadruplex: insights into G-quadruplex-interactive small molecule drug design[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133 (44): 17673- 17680.
doi: 10.1021/ja205646q |
| 36 |
ZENG D Y , KUANG G T , WANG S K , et al. Discovery of Novel 11-triazole substituted benzofuro[3, 2-b]quinolone derivatives as c-MYC G-quadruplex specific stabilizers via click chemistry[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60, 5407- 5423.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00016 |
| 37 |
LIU H Y , CHEN A C , YIN Q K , et al. New Disubstituted quindoline derivatives inhibiting Burkitt's lymphoma cell proliferation by impeding c-MYC transcription[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60 (13): 5438- 5454.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00099 |
| 38 |
GABELICA V , BAKER E S , TEULADE-FICHOU M P , et al. Stabilization and structure of telomeric and c-MYC region intramolecular G-quadruplexes: the role of central cations and small planar ligands[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129 (4): 895- 904.
doi: 10.1021/ja065989p |
| 39 | GRAND C L , HAN H Y , MUNOZ R M , et al. The cationic porphyrin TMPyP4 down-regulates c-MYC and human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression and inhibits tumor growth in vivo[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2002, 1, 565- 573. |
| 40 |
SEENISAMY J , REZLER E M , POWELL T J , et al. The dynamic character of the G-quadruplex element in the c-MYC promoter and modification by TMPyP4[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126 (28): 8702- 8709.
doi: 10.1021/ja040022b |
| 41 |
PHAN A T , KURYAVYI V , GAW H Y , et al. Small-molecule interaction with a five-guanine-tract G-quadruplex structure from the human MYC promoter[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2005, 1, 167- 173.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio723 |
| 42 |
HU M H , WANG Y Q , YU Z Y , et al. Discovery of a new four-leaf clover-like ligand as a potent c-MYC transcription inhibitor specifically targeting the promoter G-quadruplex[J]. J Med Chem, 2018, 61 (6): 2447- 2459.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01697 |
| 43 |
WU T Y , HUANG Q , HUANG Z S , et al. A drug-like imidazole-benzothiazole conjugate inhibits malignant melanoma by stabilizing the c-MYC G-quadruplex[J]. Bioorg Chem, 2020, 99, 103866.
doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103866 |
| 44 |
HU M H , WU T Y , HUANG Q , et al. New substituted quinoxalines inhibit triple-negative breast cancer by specifically downregulating the c-MYC transcription[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47 (20): 10529- 10542.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz835 |
| 45 |
GLUSZYNSKA A , JUSKOWIAK B , KUTA-SIEJKOWSKA M , et al. Carbazole ligands as c-MYC G-quadruplex binders[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 114, 479- 490.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.135 |
| 46 |
DAS T , PANDA D , SAHA P , et al. Small molecule driven stabilization of promoter G-quadruplexes and transcriptional regulation of c-MYC[J]. Bioconjug Chem, 2018, 29 (8): 2636- 2645.
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00338 |
| 47 |
SCHMIDT A W , REDDY K R , KNOLKER H J . Occurrence, biogenesis, and synthesis of biologically active carbazole alkaloids[J]. Chem Rev, 2012, 112 (6): 3193- 3328.
doi: 10.1021/cr200447s |
| 48 |
MA Y , OU T M , HOU J Q , et al. 9-N-substituted berberine derivatives: stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA and down-regulation of oncogene c-MYC[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2008, 16 (16): 7582- 7591.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.07.029 |
| 49 |
PENG D , TAN J H , CHEN S B , et al. Bisaryldiketene derivatives: A new class of selective ligands for c-myc G-quadruplex DNA[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2010, 18 (23): 8235- 8242.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.10.021 |
| 50 |
SHAN C , YAN J W , WANG Y Q , et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of isaindigotone derivatives to downregulate c-MYC transcription via disrupting the interaction of NM23-H2 with G-quadruplex[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60 (4): 1292- 1308.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01218 |
| 51 |
Islam M M , Fujii S , Sato S , et al. A selective G-quadruplex DNA-stabilizing ligand based on a cyclic naphthalene diimide derivative[J]. Molecules, 2015, 20, 10963- 10979.
doi: 10.3390/molecules200610963 |
| 52 |
CHAN D S H , YANG H , KWAN M H T , et al. Structure-based optimization of FDA-approved drug methylene blue as a c-MYC G-quadruplex DNA stabilizer[J]. Biochimie, 2011, 93 (6): 1055- 1064.
doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.02.013 |
| 53 |
ALZEER J , LUEDTKE N W . pH-mediated fluorescence and G-quadruplex binding of amido phthalocyanines[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49 (20): 4339- 4348.
doi: 10.1021/bi9020583 |
| 54 |
VORLICKOVA M , KEJNOVSKÁ I , SAGI J , et al. Circular dichroism and guanine quadruplexes[J]. Methods, 2012, 57 (1): 64- 75.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.011 |
| 55 |
SEN D , GILBERT W . Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis[J]. Nature, 1988, 334, 364- 366.
doi: 10.1038/334364a0 |
| 56 |
MARCHAND A , FERREIRA R , TATEISHI-KARIMATA H , et al. Sequence and solvent effects on telomeric DNA bimolecular G-quadruplex folding kinetics[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2013, 117 (41): 12391- 12401.
doi: 10.1021/jp406857s |
| 57 |
TONG X T , LAN W X , ZHANG X , et al. Solution structure of all parallel G-quadruplex formed by the oncogene RET promoter sequence[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2011, 39 (15): 6753- 6763.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr233 |
| 58 |
LI M M , WU S , LIU Z , et al. Arenobufagin, a bufadienolide compound from toad venom, inhibits VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through suppression of VEGFR-2 signaling pathway[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2012, 83 (9): 1251- 1260.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.023 |
| 59 |
LIU Y P , LAN W X , WANG C X , et al. A putative G-quadruplex structure in the proximal promoter of VEGFR-2 has implications for drug design to inhibit tumor angiogenesis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293 (23): 8947- 8955.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002666 |
| 60 |
CALABRESE D R , CHEN X , LEON E C , et al. Chemical and structural studies provide a mechanistic basis for recognition of the MYC G-quadruplex[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 4229.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06315-w |
| 61 |
WANG F , WANG C X , LIU Y P , et al. Colchicine selective interaction with oncogene RET G-quadruplex revealed by NMR[J]. Chem Commun (Camb), 2020, 56 (14): 2099- 2102.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC00221F |
| 62 |
WANG F , WANG C X , LIU Y P , et al. NMR studies on the interaction between oncogene RET G-quadruplex and berberine[J]. Chinese J Chem, 2020, 38 (12): 1656- 1662.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202000301 |
| [1] | KOU Xinhui, ZHANG Yubing. Study on the Enantiomeric Recognition of Chiral Ureas Containing Amino Acid Units [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 221-230. |
| [2] | DU Qunjie. Experimental Study on Accurate Determination of Shale Porosity by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 275-284. |
| [3] | SHEN Zhiqiang, DENG Yabo, YANG Peiju, HU Xiaoxue, HUANG Xiaojuan, XU Chuanzhi, SONG Huanling. Design and Application of an in situ NMR Device for Light-Induced Reaction Systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 22-33. |
| [4] | XU Xiaojie, CHEN Yan’an, LI Xufei, ZHANG Yuncai, ZHANG Yong, ZHAN Dongkai, PAN Ting. Structural Elucidation of Hybutimibe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 43-55. |
| [5] | WANG Feng, LIU Tingwei, XU Yajie, YU Peng, WANG Ya, PENG Bowen, YANG Xiaodong. A Miniaturised NMR RF Probe Design with External Field-locking Channel [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 332-340. |
| [6] | WANG Yuanfang,WANG Xiaohua,SHU Chang,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili,ZENG Danyun. The Aggregation of ATAD2 Bromodomain in Solution [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 169-178. |
| [7] | ZHAO Chang,GONG Zhou. Investigation of Dynamic Structure of Protein Encountering Complex with Paramagnetic NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 148-157. |
| [8] | ZHAN Jianhua,HU Qin,ZHU Qinjun,JIANG Bin,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili. Track the Conformational Change of Unlabeled Yeast Cytochrome c in Cell Homogenate Using NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 22-29. |
| [9] | CI Jie,YANG Xue,XIN Jiaxiang,WEI Daxiu,YAO Yefeng. Preparation and Lifetime Studies of the Singlet State of Five Spins in Hexene Molecules Used to Guide the Preservation of the Parahydrogen-induced Nuclear Polarization State [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 30-38. |
| [10] | Yun-shan PEI, Cai ZHANG, Xiao-li LIU, Kai CHENG, Ze-ting ZHANG, Cong-gang LI. Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by the Interaction Between Protein Disulfide Isomerase and α-Synuclein [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 381-392. |
| [11] | Xiao-yang ZHANG, Shou-quan YAO, Jun-cheng XU, Yu JIANG. Magnetic Field Locking System Based on Fluxgate and Time Domain Digital Frequency Discrimination [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 448-458. |
| [12] | Han HU,Wei-yu WANG,Jun XU,Feng DENG. 1, 3-Butadienen Hydrogenation on Supported Pd-Sn Bimetallic Catalysts Investigated by Parahydrogen-induced Polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 133-143. |
| [13] | Qian XU,Lang CHEN,Xiang-ying HU,Cong-gang LI,Yi-xiang LIU,Ling JIANG. The Effect of T69E-mimicked Phosphorylation on the Interaction Between Bcl-2 and Nur77 [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 87-95. |
| [14] | Xiao-qing LIN,Shi-jia DU,Hao-lin ZHAN,Yu-qing HUANG,Zhong CHEN. Two-Dimensional Homonuclear Orthogonal-Pattern Phase-Sensitive J-Resolved NMR Spectroscopy Based on Pure Shifts [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 448-459. |
| [15] | Yao XIAO,Chang-jiu XIA,Xian-feng YI,Feng-qing LIU,Shang-bin LIU,An-min ZHENG. Progress in the Studies on Sn-Zeolites by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 571-584. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||