
- Jul. 13, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 341-361.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20243087cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20243087
• Review Article • Previous Articles
Received:2023-10-19
Published:2024-09-05
Online:2024-08-23
Contact:
*Tel: 13761603606, E-mail: yjusst@126.com.
CLC Number:
YANG Liming, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress of Denoising Algorithms for Diffusion Tensor Images[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(3): 341-361.
Table 1
Details of popular public datasets
| 数据集 | 成像区域 | 描述 | 网站 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IXI | 脑 | 600张健康受试者的MRI图像,包括T1图像、T2图像、DWI图像等. | https://brain-development.org/ixidataset/ |
| HCP | 脑 | 1200名健康受试者的多模态脑MRI图像,包括DWI图像、DTI图像等. | https://humanconnectome.org/ |
| OASIS | 脑 | 正常衰老和阿尔茨海默症的MRI图像,包括T1加权图像、T2加权图像、DTI图像等. | http://www.oasis-brains.org/ |
| ADNI | 脑 | 用于阿尔茨海默病的早期检测和跟踪的影像数据,包括DTI图像、功能MRI图像、结构MRI图像等. | https://adni.loni.usc.edu/ |
| MASSIVE | 脑 | 8000个三维DWI数据,包括b值为0图像、DWI扫描的噪声图像,及10个三维T1图像、T2加权图像等. | https://www.massive-data.org/ |
| fastMRI | 前列腺 | 312次检查的T2加权图像、DWI图像. | https://fastmri.med.nyu.edu/ |
Table 2
Comparison of DTI denoising algorithms based on traditional image processing
| 方法 | 第一作者 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLM | Kafali[ | 利用多次采集的共享结构,对凸集投影算法在各次采集中聚合的复值输出进行处理;能够有效校正相位误差并保留DWI图像细节. | 去噪性能受到块组尺寸的限制. |
| Liu[ | 使用张量流形来度量扩散张量的相似度,并直接正则化DTI图像;在不模糊图像边界的同时,保留了张量的几何特征,并提高了FA图和纤维束追踪的精度. | 处理时间较长;无法去除原始DWI数据产生的背景噪声. | |
| Chen[ | 在x-q空间对DWI数据去噪;在不模糊图像边缘的同时,准确去除了复杂结构(如高度弯曲的白质结构)中的噪声. | 处理时间较长. | |
| Chen[ | 基于图框架变换,充分利用DWI数据的冗余,保留图像的边缘. | 需要较大的计算机内存. | |
| PCA | Manjón[ | 利用多扩散方向dMRI数据中的冗余,对局部块组奇异值进行阈值化,避免相似块组的搜索过程,减少了处理时间. | PCA阈值的选取存在主观性. |
| Chen[ | 在两个独立的通道中,分别沿扩散维度,对具有扩散匹配特性相位校正后的DWI数据的实分量和虚分量进行去噪. | 处理时间较长. | |
| Veraart[ | 基于Marchenko-Pastur定律对空间变化的莱斯噪声进行估计,并提出客观的PCA阈值选取方法;利用多扩散方向dMRI数据的冗余. | 去噪性能严重依赖数据冗余量;存在噪声假设. | |
| Llordén[ | 在不需要满足Marchenko-Pastur定律假设的同时,充分利用了数据的线性和非线性冗余. | 去噪性能依赖核函数. | |
| Olesen[ | 修改Marchenko-Pastur分布,拓宽MPPCA的适用性;利用多维数据固有张量结构的每个维度来表征噪声,并递归估计信号成分,更好地利用多维数据中的冗余. | 去噪性能受到块组尺寸的限制;存在噪声假设, 即每个块组中的噪声是独立同分布的. | |
| LRMA | Ma[ | 联合VST和OSVS,对幅值dMRI数据去噪;在有效去除噪声和提高SNR的同时,提高了DTI图及交叉纤维估计的精度. | 基于VST的噪声估计会高估噪声标准差. |
| Zhang[ | 通过全局HOSVD预去噪,在一定程度上减少了基于块匹配HOSVD阶段噪声退化对HOSVD基的影响. | 去噪性能依赖VST算法;当图像SNR较低时,会引入伪影. | |
| Xu[ | 联合基于HOSVD稀疏约束和莱斯噪声校正模型,直接对每个局部图像块进行去噪,无需VST技术,从原理上解决了伪影问题. | 去噪性能依赖参数设置. | |
| Zhao[ | 有效利用不同扩散方向DWI数据的冗余,尤其适用于较少扩散方向或较低b值的DWI数据. | 去噪性能受到块组尺寸的限制. | |
| 全变分最 小化 | Knoll[ | 通过对扩散张量元素施加全变分约束,直接在目标定量域中进行压缩感知;在加快采集速度的同时,显著减少了参数图中的噪声. | 仅在有限的数据上进行评估. |
| 贝叶斯 | Krajsek[ | 基于贝叶斯框架对DTI图像进行重建和正则化;在保证张量正定性的同时,考虑了DTI的黎曼几何性质和莱斯噪声的统计特征. | 处理时间较长. |
| Liu[ | 采用黎曼相似性度量和高斯混合模型学习块组的先验分布;利用贝叶斯推理自适应去噪的同时,保留了DTI图像的非线性结构. | 块匹配过程耗时,且高度依赖图像的先验知识. | |
| 稀疏字典 | Kong[ | 利用三维DTI数据相邻切片间的冗余来训练自适应稀疏字典. | 处理时间较长. |
| St-Jean[ | 采用角度邻近匹配以提高稀疏性;通过字典学习进行局部去噪. | 处理时间较长. |
Table 3
Comparison of DTI denoising models based on deep learning
| 方法 | 第一作者 | 模型 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 监督 | Cheng[ | 1D CNN | 采用SOS-SENSE数据对训练;采用时域去噪,在有效减少训练数据量的同时,更能保留每个体素时间序列的一致性. | 两种重建方式获得的数据的噪声类型不同,影响去噪性能. |
| Jurek[ | SRCNN | 采用迁移学习方式训练模型;对复值DWI数据去噪,在一定程度上减少了莱斯偏置的影响. | 容易造成边缘模糊. | |
| Muckley[ | U-Net | 对复值DWI数据去噪,显著去除了DTI参数图中的伪影;采用ImageNet数据集训练模型,能够抑制模型的过拟合. | 仅对单幅DWI图像去噪,忽略了图像间的相关性. | |
| Wang[ | U-Net | 使用共享连接路径隐式地从多b值DWI数据中提取特征,充分利用图像间的结构相关性. | 容易造成过度去噪. | |
| Tian[ | 3D CNN | 充分利用了DWI数据的局部和非局部空间信息及扩散编码方向和图像对比度中的冗余;将MRI图像作为训练集的输入,以防止去噪图像模糊. | 传统张量拟合方法对噪声较为敏感,去噪效果受到限制. | |
| Li[ | U-Net | 直接预测高质量DTI参数图,避免了传统张量拟合方法. | 仅预测单个类型DTI参数图. | |
| 无监督 | Lin[ | CNN | 基于DIP模型对多b值DWI图像同时去噪. | 采用的数据集类型较为单一. |
| Jurek[ | SRCNN | 通过N2N范式训练去噪网络,性能优于幅度图像平均法. | 去噪图像存在部分背景噪声. | |
| Fadnavis[ | / | 利用多扩散方向DWI数据的冗余,特别适用于较少扩散方向数据;逐体素方式去噪. | 去噪性能依赖噪声假设. | |
| 自监督 | Tian[ | U-Net | 采用“先去噪后平均”的方法,保证输入图像具有更高的SNR;在有效去除噪声的同时,保留了图像的结构信息. | 去噪性能依赖扩散方向数量. |
| Yuan[ | CNN | 采用SSIM匹配算法搜索含噪图像对;引入一种新的边缘加权损失函数,更好地保留纹理细节. | SSIM指标易受原始图像中噪声的影响. | |
| Xiang[ | / | 联合自监督统计去噪理论和扩散模型;逐切片方式去噪. | 处理时间较长. |
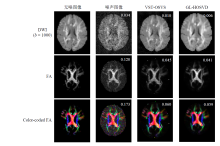
Fig. 8
Visual comparison of the denoised images, fitted FA maps, color-coded FA maps, noise-free images, and noise images of the GL-HOSVD and VST-OSVS algorithms using the simulated DWI data with 4% noise level and b-value of 1 000 s/mm2. The numbers reported are RMSE values, and the b-values are in s/mm2

| [1] | DENG L, WANG Y J. DTI brain template construction based on gaussian averaging[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(4): 413-427. |
|
邓岚, 王远军. 基于高斯平均的DTI脑模板构建方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(4): 413-427.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212957 |
|
| [2] | LIU X, WU Z, WANG X. An intrinsic anisotropic feature of DTI images derived by geometric properties on the riemannian manifold[J]. Biomed Signal Proces, 2024, 87: 105478. |
| [3] | YUE Q, WANG Y J. A fiber tracking algorithm based on non-local constrained spherical deconvolution[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37(4): 422-433. |
|
岳晴, 王远军. 基于非局部约束球面反卷积模型的纤维追踪算法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 422-433.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20192798 |
|
| [4] | YU D, CHUANG K H, SOLLMANN N. New challenges and future perspectives in brain imaging methods[J]. Front Neurosci-Switz, 2023, 17: 1265054. |
| [5] | ZHU Y, WANG Y. Brain fiber structure estimation based on principal component analysis and RINLM filter[J]. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2023: 1-21. |
| [6] | MISHRO P K, AGRAWAL S, PANDA R, et al. A survey on state-of-the-art denoising techniques for brain magnetic resonance images[J]. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng, 2021, 15: 184-199. |
| [7] | TAX C M W, BASTIANI M, VERAART J, et al. What’s new and what’s next in diffusion MRI preprocessing[J]. NeuroImage, 2022, 249: 118830. |
| [8] | AJA-FERNÁNDEZ S, VEGAS-SÁNCHEZ-FERRERO G. Statistical analysis of noise in MRI[M]. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2016. |
| [9] |
MANJÓN J V, CARBONELL-CABALLERO J, LULL J J, et al. MRI denoising using non-local means[J]. Med Image Anal, 2008, 12(4): 514-523.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2008.02.004 pmid: 18381247 |
| [10] |
MANJÓN J V, COUPÉ P, BUADES A, et al. New methods for MRI denoising based on sparseness and self-similarity[J]. Med Image Anal, 2012, 16(1): 18-27.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2011.04.003 pmid: 21570894 |
| [11] |
KAFALI S G, ÇUKUR T, SARITAS E U. Phase-correcting non-local means filtering for diffusion-weighted imaging of the spinal cord[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 80(3): 1020-1035.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27105 pmid: 29427379 |
| [12] |
SU B, LIU Q, CHEN J, et al. Non-local mean denoising in diffusion tensor space[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2014, 8(2): 447-453.
pmid: 25009599 |
| [13] | LIU X, WU Z, WANG X. Diffusion tensor image denoising via geometric invariant nonlocal means on the tensor manifold[J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2023, 82(10): 15817-15835. |
| [14] |
CHEN G, WU Y F, SHEN D G, et al. Noise reduction in diffusion MRI using non-local self-similar information in joint x-q space[J]. Med Image Anal, 2019, 53: 79-94.
doi: S1361-8415(18)30391-8 pmid: 30703580 |
| [15] | KOAY C G, ÖZARSLAN E, BASSER P J. A signal tra nsformational framework for breaking the noise floor and its applications in MRI[J]. J Magn Reson, 2009, 197(2): 108-119. |
| [16] | CHEN G, DONG B, ZHANG Y, et al. Denoising of diffusion MRI data via graph framelet matching in xq space[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2019, 38(12): 2838-2848. |
| [17] | MANJÓN J V, COUPÉ P, CONCHA L, et al. Diffusion weighted image denoising using overcomplete local PCA[J]. Plos One, 2013, 8(9): e73021. |
| [18] | CHEN N, CHANG H C, BILGIN A, et al. A diffusion-matched principal component analysis (DM-PCA) based two-channel denoising procedure for high-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI[J]. Plos One, 2018, 13(4): e0195952. |
| [19] |
VERAART J, FIEREMANS E, NOVIKOV D S. Diffusion MRI noise mapping using random matrix theory[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 76(5): 1582-1593.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26059 pmid: 26599599 |
| [20] |
VERAART J, NOVIKOV D S, CHRISTIAENS D, et al. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory[J]. NeuroImage, 2016, 142: 394-406.
doi: S1053-8119(16)30394-9 pmid: 27523449 |
| [21] | TOURNIER J D, SMITH R, RAFFELT D, et al. MRtrix3: a fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation[J]. NeuroImage, 2019, 202: 116137. |
| [22] | CORDERO-GRANDE L, CHRISTIAENS D, HUTTER J, et al. Complex diffusion-weighted image estimation via matrix recovery under general noise models[J]. NeuroImage, 2019, 200: 391-404. |
| [23] | MOELLER S, PISHARADY P K, RAMANNA S, et al. Noise reduction with distribution corrected (NORDIC) PCA in dMRI with complex-valued parameter-free locally low-rank processing[J]. NeuroImage, 2021, 226: 117539. |
| [24] | RAMOS-LLORDÉN G, VEGAS-SÁNCHEZ-FERRERO G, LIAO C, et al. SNR-enhanced diffusion MRI with structure-preserving low-rank denoising in reproducing kernel hilbert spaces[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 86(3): 1614-1632. |
| [25] | OLESEN J L, IANUS A, ØSTERGAARD L, et al. Tensor denoising of multidimensional MRI data[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(3): 1160-1172. |
| [26] | MA X, UĞURBIL K, WU X. Denoise magnitude diffusion magnetic resonance images via variance-stabilizing transformation and optimal singular-value manipulation[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 215: 116852. |
| [27] | FOI A. Noise estimation and removal in MR imaging: the variance-stabilization approach[C]// IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Chicago, IL, USA: IEEE, 2011: 1809-1814. |
| [28] |
ZHANG X, PENG J, XU M, et al. Denoise diffusion-weighted images using higher-order singular value decomposition[J]. NeuroImage, 2017, 156: 128-145.
doi: S1053-8119(17)30309-9 pmid: 28416450 |
| [29] | XU P, GUO L, FENG Y Q, et al. A diffusion-weighted image denoising algorithm using HOSVD combined with rician noise corrected model[J]. J South Med Univ, 2021, 41(9): 1400-1408. |
|
徐朴, 郭莉, 冯衍秋. 基于高阶奇异值分解和Rician噪声校正模型的扩散加权图像去噪算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1400-1408.
doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.09.16 |
|
| [30] | YI S L, LI S J, HE J F, et al. Application of weighted nuclear norm denoising algorithm in diffusion-weighted image[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(7): 1005-1013. |
| 易三莉, 李思洁, 贺建峰. 加权核范数降噪算法在扩散加权图像中的应用[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(7): 1005-1013. | |
| [31] |
ZHAO Y, YI Z, XIAO L, et al. Joint denoising of diffusion-weighted images via structured low-rank patch matrix approximation[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 88(6): 2461-2474.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29407 pmid: 36178232 |
| [32] | WU H Y, YAN S L. Denoising diffusion MRI via graph total variance in spatioangular domain[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2021:4645544. |
| [33] |
KNOLL F, RAYA J G, HALLORAN R O, et al. A model-based reconstruction for undersampled radial spin-echo DTI with variational penalties on the diffusion tensor[J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28(3): 353-366.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3258 pmid: 25594167 |
| [34] | KRAJSEK K, MENZEL M I, SCHARR H. A riemannian bayesian framework for estimating diffusion tensor images[J]. Int J Comput Vision, 2016, 120: 272-299. |
| [35] | LIU S, ZHAO C, LIU M, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging denoising based on riemann nonlocal similarity[J]. J Amb Intel Hum Comp, 2019: 1-14. |
| [36] | KONG Y, LI Y, WU J, et al. Noise reduction of diffusion tensor images by sparse representation and dictionary learning[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2016, 15: 1-11. |
| [37] | ST-JEAN S, COUPÉ P, DESCOTEAUX M. Non local spatial and angular matching: enabling higher spatial resolution diffusion MRI datasets through adaptive denoising[J]. Med Image Anal, 2016, 32: 115-130. |
| [38] | PIZZOLATO M, GILBERT G, THIRAN J P, et al. Adaptive phase correction of diffusion-weighted images[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 206: 116274. |
| [39] | LIU F, FENG J, CHEN G, et al. Gaussianization of diffusion MRI data using spatially adaptive filtering[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021, 68: 101828. |
| [40] | CHEN H, DAI K, ZHONG S, et al. High-resolution multi-shot diffusion-weighted MRI combining markerless prospective motion correction and locally low-rank constrained reconstruction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(2): 605-619. |
| [41] |
TIAN C, FEI L, ZHENG W, et al. Deep learning on image denoising: an overview[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 131: 251-275.
doi: S0893-6080(20)30266-5 pmid: 32829002 |
| [42] | TRIPATHI P C, BAG S. CNN-DMRI: a convolutional neural network for denoising of magnetic resonance images[J]. Pattern Recogn Lett, 2020, 135: 57-63. |
| [43] | CHEN Z, PAWAR K, EKANAYAKE M, et al. Deep learning for image enhancement and correction in magnetic resonance imaging—state-of-the-art and challenges[J]. J Digit Imaging, 2023, 36(1): 204-230. |
| [44] | CHENG H, VINCI-BOOHER S, WANG J, et al. Denoising diffusion weighted imaging data using convolutional neural networks[J]. Plos One, 2022, 17(9): e0274396. |
| [45] | JUREK J, MATERKA A, LUDWISIAK K, et al. Supervised denoising of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images using a convolutional neural network and transfer learning[J]. Biocybern Biomed Eng, 2023, 43(1): 206-232. |
| [46] | DONG C, LOY C C, HE K, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE T Pattern Anal, 2015, 38(2): 295-307. |
| [47] |
KWAN R K S, EVANS A C, PIKE G B. MRI simulation-based evaluation of image-processing and classification methods[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 1999, 18(11): 1085-1097.
pmid: 10661326 |
| [48] | MUCKLEY M J, ADES-ARON B, PAPAIOANNOU A, et al. Training a neural network for gibbs and noise removal in diffusion MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(1): 413-428. |
| [49] | DENG J, DONG W, SOCHER R, et al. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA: IEEE, 2009: 248-255. |
| [50] |
WANG H, ZHENG R, DAI F, et al. High-field mr diffusion-weighted image denoising using a joint denoising convolutional neural network[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50(6): 1937-1947.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.26761 pmid: 31012226 |
| [51] | ZHANG C, AREFIN T M, NAKARMI U, et al. Acceleration of three-dimensional diffusion magnetic resonance imaging using a kernel low-rank compressed sensing method[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 210: 116584. |
| [52] | QIN Y, LIU Z, LIU C, et al. Super-resolved q-space deep learning with uncertainty quantification[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021, 67: 101885. |
| [53] |
ZHANG K, ZUO W, CHEN Y, et al. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising[J]. IEEE T Image Process, 2017, 26(7): 3142-3155.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 pmid: 28166495 |
| [54] | KAYE E A, AHERNE E A, DUZGOL C, et al. Accelerating prostate diffusion-weighted MRI using a guided denoising convolutional neural network: retrospective feasibility study[J]. Radiol: Artif Intell, 2020, 2(5): e200007. |
| [55] | KAWAMURA M, TAMADA D, FUNAYAMA S, et al. Accelerated acquisition of high-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging of the brain with a multi-shot echo-planar sequence: deep-learning-based denoising[J]. Magn Reson Med Sci, 2021, 20(1): 99-105. |
| [56] | ZORMPAS-PETRIDIS K, TUNARIU N, CURCEAN A, et al. Accelerating whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI with deep learning-based denoising image filters[J]. Radiol: Artif Intell, 2021, 3(5): e200279. |
| [57] | TIAN Q, BILGIC B, FAN Q, et al. DeepDTI: high-fidelity six-direction diffusion tensor imaging using deep learning[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 219: 117017. |
| [58] |
LI H, LIANG Z, ZHANG C, et al. SuperDTI: ultrafast DTI and fiber tractography with deep learning[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 86(6): 3334-3347.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28937 pmid: 34309073 |
| [59] | KARIMI D, GHOLIPOUR A. Diffusion tensor estimation with transformer neural networks[J]. Artif Intell Med, 2022, 130: 102330. |
| [60] | LIN Y C, HUANG H M. Denoising of multi b-value diffusion-weighted MR images using deep image prior[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2020, 65(10): 105003. |
| [61] | ULYANOV D, VEDALDI A, LEMPITSKY V. Deep image prior[C]// IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018: 9446-9454. |
| [62] | LEHTINEN J, MUNKBERG J, HASSELGREN J, et al. Noise2noise: learning image restoration without clean data[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.04189, 2018. |
| [63] | BATSON J, ROYER L. Noise2self: blind denoising by self-supervision[C]// International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019: 524-533. |
| [64] | KRULL A, BUCHHOLZ T O, JUG F. Noise2void-learning denoising from single noisy images[C]// IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019: 2129-2137. |
| [65] | QUAN Y, CHEN M, PANG T, et al. Self2self with dropout: learning self-supervised denoising from single image[C]// IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020: 1890-1898. |
| [66] | HUANG T, LI S, JIA X, et al. Neighbor2neighbor: self-supervised denoising from single noisy images[C]// IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TU, USA: IEEE, 2021: 14781-14790. |
| [67] | JUREK J, MATERKA A, LUDWISIAK K, et al. Phase correction and noise-to-noise denoising of diffusion magnetic resonance images using neural networks[C]// International Conference on Computational Science, 2023, 638-652. |
| [68] | FADNAVIS S, BATSON J, GARYFALLIDIS E. Patch2self: denoising diffusion MRI with self-supervised learning[J]. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, 2020, 33: 16293-16303. |
| [69] |
GARYFALLIDIS E, BRETT M, AMIRBEKIAN B, et al. Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2014, 8: 8.
doi: 10.3389/fninf.2014.00008 pmid: 24600385 |
| [70] | TIAN Q, LI Z, FAN Q, et al. SDnDTI: self-supervised deep learning-based denoising for diffusion tensor MRI[J]. NeuroImage, 2022, 253: 119033. |
| [71] |
YUAN N, WANG L, YE C, et al. Self-supervised structural similarity-based convolutional neural network for cardiac diffusion tensor image denoising[J]. Med Phys, 2023, 50: 6137-6150.
doi: 10.1002/mp.16301 pmid: 36775901 |
| [72] | ALI H, BISWAS M R, MOHSEN F, et al. The role of generative adversarial networks in brain MRI: a scoping review[J]. Insights Imaging, 2022, 13(1): 98. |
| [73] |
RAN M, HU J, CHEN Y, et al. Denoising of 3D magnetic resonance images using a residual encoder-decoder wasserstein generative adversarial network[J]. Med Image Anal, 2019, 55: 165-180.
doi: S1361-8415(18)30653-4 pmid: 31085444 |
| [74] | TIAN M, SONG K. Boosting magnetic resonance image denoising with generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 62266-62275. |
| [75] | CHAN K, MARALANI P J, MOODY A R, et al. Synthesis of diffusion-weighted MRI scalar maps from flair volumes using generative adversarial networks[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2023, 17: 1197330. |
| [76] | LYU J, LI Y, YAN F, et al. Multi-channel GAN-based calibration-free diffusion-weighted liver imaging with simultaneous coil sensitivity estimation and reconstruction[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1095637. |
| [77] | YU M, GUO M, ZHANG S, et al. RIRGAN: an end-to-end lightweight multi-task learning method for brain MRI super-resolution and denoising[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 167: 107632. |
| [78] |
YE X, WANG P, LI S, et al. Simultaneous superresolution reconstruction and distortion correction for single-shot EPI DWI using deep learning[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(6): 2456-2470.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29601 pmid: 36705077 |
| [79] | HO J, JAIN A, ABBEEL P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[J]. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, 2020, 33: 6840-6851. |
| [80] | KAZEROUNI A, AGHDAM E K, HEIDARI M, et al. Diffusion models in medical imaging: a comprehensive survey[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 88: 102846. |
| [81] | XIANG T, YURT M, SYED A B, et al. DDM2: self-supervised diffusion MRI denoising with generative diffusion models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.03018, 2023. |
| [82] |
NEHER P F, LAUN F B, STIELTJES B, et al. Fiberfox: facilitating the creation of realistic white matter software phantoms[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 72(5): 1460-1470.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25045 pmid: 24323973 |
| [83] | MAIER-HEIN K H, NEHER P F, HOUDE J C, et al. The challenge of mapping the human connectome based on diffusion tractography[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 1349. |
| [1] | NING Xinzhou, HUANG Zhen, CHEN Xiqu, LIU Xinjie, CHEN Gang, ZHANG Zhi, BAO Qingjia, LIU Chaoyang. Research on Transformer Super-Resolution Reconstruction Algorithm for Ultrafast Spatiotemporal Encoding Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 454-468. |
| [2] | Dai Junlong, He Cong, Wu Jie, Bian Yun. Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms Segmentation Network Combining Dual Decoding and Global Attention Upsampling Modules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
| [3] | YANG Yu, CHEN Bo, WU Liubin, LIN Enping, HUANG Yuqing, CHEN Zhong. Spectrum Reconstruction for Laplace NMR: From Handcraft Regularization to Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 191-208. |
| [4] | CHANG Bo, SUN Haoyun, GAO Qingyu, WANG Lijia. Research Progress on Cardiac Segmentation in Different Modal Medical Images by Traditional Methods and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 224-244. |
| [5] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [6] | LAI Jiawen, WANG Yuling, CAI Xiaoyu, ZHOU Lihua. Multidimensional Information Fusion Method for Meniscal Tear Classification Based on CNN-SVM [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 423-434. |
| [7] | WANG Hui, WANG Tiantian, WANG Lijia. Squeeze-and-excitation Residual U-shaped Network for Left Myocardium Segmentation Based on Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 435-447. |
| [8] | Li Yijie, YANG Xinyu, YANG Xiaomei. Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction of Multi-scale Residual Unet Fused with Attention Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 307-319. |
| [9] | LU Qiqi, LIAN Zifeng, LI Jialong, SI Wenbin, MAI Zhaohua, FENG Yanqiu. Magnetic Resonance R2* Parameter Mapping of Liver Based on Self-supervised Deep Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 258-269. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jiajun, LU Yucheng, BAO Yifang, LI Yuxin, GENG Chen, HU Fuyuan, DAI Yakang. An Automatic Segmentation Method of Cerebral Arterial Tree in TOF-MRA Based on DBCNet [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 320-331. |
| [11] | TIAN Hui, WU Jie, BIAN Yun, ZHANG Zhiwei, SHAO Chengwei. Classification of Pancreatic Cystic Tumors Based on DenseNet and Transfer Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 270-279. |
| [12] | QIAN Chengyi,WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Imaging Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 220-238. |
| [13] | HUANG Min,LI Siyi,CHEN Junbo,ZHOU Dao. Progress of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting Technology and Its Clinical Application [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 207-219. |
| [14] | SHI Weicheng,JIN Zhaoyang,YE Zheng. Fast Multi-channel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based on PCAU-Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 39-51. |
| [15] | Qin ZHOU, Yuan-jun WANG. Groupwise Registration for Magnetic Resonance Image Based on Variational Inference [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 291-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
