
波谱学杂志 ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 503-513.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212928
收稿日期:2021-06-29
出版日期:2021-12-05
发布日期:2021-09-16
通讯作者:
曹春阳
E-mail:ccao@mail.sioc.ac.cn
基金资助:
Xiao-dong HU,Wen-xian LAN,Chun-xi WANG,Chun-yang CAO*( )
)
Received:2021-06-29
Online:2021-12-05
Published:2021-09-16
Contact:
Chun-yang CAO
E-mail:ccao@mail.sioc.ac.cn
摘要:
肿瘤基因MYC在人类70%癌细胞中高表达,抑制其转录是治疗肿瘤的有效手段.c-MYC启动子区P1近端的核酸酶超敏元件Ⅲ1(NHE Ⅲ1)控制MYC基因近90%的转录激活.NHE Ⅲ1区域富含碱基G序列并且形成G-四链体(G4),调控c-MYC基因转录,是抗肿瘤药物靶标.但G4-DNA和G4-RNA的三维结构高度相似,小分子与其他G4(如端粒G4、mRNA G4、c-Kit G4等)的非特异性作用会产生小分子药物“脱靶”效应,同时小分子药物会诱导其他G4形成从而干扰正常细胞的功能,造成靶向c-MYC G4抗癌药物设计困难.本文综述了近些年靶向肿瘤因子c-MYC G4-DNA的小分子药物研究进展,及核磁共振(NMR)技术在G4-DNA和G4-RNA结构确定中的作用,为靶向c-MYC G4-DNA的小分子药物设计等相关研究工作提供参考.
中图分类号:
胡晓东,蓝文贤,王春喜,曹春阳. 靶向肿瘤因子c-MYC基因启动区G4-DNA的小分子药物设计及核磁共振研究进展[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(4): 503-513.
Xiao-dong HU,Wen-xian LAN,Chun-xi WANG,Chun-yang CAO. Research Advance and NMR Studies of Anti-Cancer Small Molecules Targeting c-MYC G4-DNA[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 503-513.
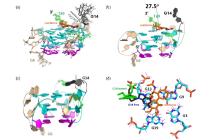
图11
RET G4-DNA与秋水仙碱复合物的结构(橙色).(a)能量最低的20个结构的集合,碱基G14构象是灵活的;(b)一个复合物的构象,芳香七元环与苯环之间呈27.5°;(c)自由态RET G4-DNA的结构;(d)秋水仙素(橙色球棍模型显示)在复合物结构中位置与自由态RET G4-DNA中的G3-G9-G13-G19四集体平面中的碱基G14对比.在图(a)~(c)中,由4个syn鸟嘌呤组成的G-四集体分别为洋红色线和卡通模式,anti鸟嘌呤组成的G-四集体分别以青色和卡通模式显示.在所有图中:碱基G14是深灰色的线条和卡通模式展示;碱基G16和T20分别为绿线和卡通模式展示;碱基G4、C5、G6和C10为小麦色或卡通模式展示.所有非极性质子都没有显示出来[61]
| 1 |
WELLS R D , DERE R , HEBERT M L , et al. Advances in mechanisms of genetic instability related to hereditary neurological diseases[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2005, 33 (12): 3785- 3798.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gki697 |
| 2 |
GELLERT M , LIPSETT M N , DAVIES D R . Helix formation by guanylic acid[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1962, 48 (12): 2013- 2018.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2013 |
| 3 |
ADRIAN M , HEDDI B , PHAN A T . NMR spectroscopy of G-quadruplexes[J]. Methods, 2012, 57 (1): 11- 24.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.05.003 |
| 4 | HUPPERT J L . Four-stranded nucleic acids: structure, function and targeting of G-quadruplexes[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2008, 39 (40): 1375- 1384. |
| 5 |
BALASUBRAMANIAN S , HURLEY L H , NEIDLE S . Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: a novel anticancer strategy?[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2011, 10, 261- 275.
doi: 10.1038/nrd3428 |
| 6 |
LIPPS H J , RHODES D . G-quadruplex structures: in vivo evidence and function[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2009, 19 (8): 414- 422.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.05.002 |
| 7 |
TORNALETTI S . Transcriptional processing of G4 DNA[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2009, 48 (4): 326- 335.
doi: 10.1002/mc.20513 |
| 8 |
COONEY M , CZERNUSZEWICZ G , POSTEL E H , et al. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro[J]. Science, 1988, 241 (4864): 456- 459.
doi: 10.1126/science.3293213 |
| 9 |
TOMONAGA T , LEVENS D . Activating transcription from single stranded DNA[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1996, 93, 5830- 5835.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.12.5830 |
| 10 |
SEENISAMY J , BASHYAM S , GOKHALE V , et al. Design and synthesis of an expanded porphyrin that has selectivity for the c-MYC G-quadruplex structure[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127 (9): 2944- 2959.
doi: 10.1021/ja0444482 |
| 11 |
SIDDIQUI-JAIN A , GRAND C L , BEARSS D J , et al. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2002, 99, 11593- 11598.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.182256799 |
| 12 |
SUN Z Y , WANG X N , CHENG S Q , et al. Developing novel G-quadruplex ligands: from interaction with nucleic acids to interfering with nucleic acid(-)protein interaction[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24 (3): 396.
doi: 10.3390/molecules24030396 |
| 13 |
BRAZDA V , HARONIKOVA L , LIAO J C , et al. DNA and RNA quadruplex-binding proteins[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15, 17493- 17517.
doi: 10.3390/ijms151017493 |
| 14 |
VARSHNEY D , SPIEGEL J , ZYNER K , et al. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21, 459- 474.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0236-x |
| 15 |
GONZALEZ V , GUO K X , HURLEY L , et al. Identification and characterization of nucleolin as a c-MYC G-quadruplex-binding protein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284 (35): 23622- 23635.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018028 |
| 16 |
GONZALEZ V , HURLEY L H . The C-terminus of nucleolin promotes the formation of the c-MYC G-quadruplex and inhibits c-MYC promoter activity[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49 (45): 9706- 9714.
doi: 10.1021/bi100509s |
| 17 |
FEDERICI L , ARCOVITO A , SCAGLIONE G L , et al. Nucleophosmin C-terminal leukemia-associated domain interacts with G-rich quadruplex forming DNA[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285 (48): 37138- 37149.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.166736 |
| 18 |
Scognamiglio P L , Di Natale C , Leone M , et al. G-quadruplex DNA recognition by nucleophosmin: new insights from protein dissection[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1840 (6): 2050- 2059.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.02.017 |
| 19 |
GALLO A , STERZO CL , MORI M , et al. Structure of nucleophosmin DNA-binding domain and analysis of its complex with a G-quadruplex sequence from the c-MYC promoter[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287 (32): 26539- 26548.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.371013 |
| 20 |
KANG H J , LE TVT , KIM K , et al. Novel interaction of the Z-DNA binding domain of human ADAR1 with the oncogenic c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex[J]. J Mol Biol, 2014, 426 (14): 2594- 2604.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.001 |
| 21 |
PETR M , HELMA R , POLÁŠKOVÁ A , et al. Wild-type p53 binds to MYC promoter G-quadruplex[J]. Biosci Rep, 2016, 36 (5): e00397.
doi: 10.1042/BSR20160232 |
| 22 |
SANDERS C M . Human Pif1 helicase is a G-quadruplex DNA-binding protein with G-quadruplex DNA-unwinding activity[J]. Biochem J, 2010, 430, 119- 128.
doi: 10.1042/BJ20100612 |
| 23 |
BYRD A K , RANEY K D . A parallel quadruplex DNA is bound tightly but unfolded slowly by pif1 helicase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290 (10): 6482- 6494.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630749 |
| 24 |
BYRD A K , BELL M R , RANEY K D . Pif1 helicase unfolding of G-quadruplex DNA is highly dependent on sequence and reaction conditions[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293 (46): 17792- 17802.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004499 |
| 25 |
LEE S , LEE A R , RYU K S , et al. NMR investigation of the interaction between the RecQ C-terminal domain of human bloom syndrome protein and G-quadruplex DNA from the human c-MYC promoter[J]. J Mol Biol, 2019, 431 (4): 794- 806.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.010 |
| 26 |
BUDHATHOKI J B , RAY S , URBAN V , et al. RecQ-core of BLM unfolds telomeric G-quadruplex in the absence of ATP[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42 (18): 11528- 11545.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku856 |
| 27 |
CHATTERJEE S , ZAGELBAUM J , SAVITSKY P , et al. Mechanistic insight into the interaction of BLM helicase with intra-strand G-quadruplex structures[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 5556.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6556 |
| 28 |
KAROW J K , WU L , HICKSON I D . RecQ family helicases: roles in cancer and aging[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2000, 10 (1): 32- 38.
doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(99)00039-8 |
| 29 |
SUN H , KAROW J K. , HICKSON I D , et al. The Bloom's syndrome helicase unwinds G4 DNA[J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273 (42): 27587- 27592.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.42.27587 |
| 30 |
WU G H , XING Z , TRAN E J , et al. DDX5 helicase resolves G-quadruplex and is involved in MYC gene transcriptional activation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116 (41): 20453- 20461.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909047116 |
| 31 |
POSTEL E H , BERBERICH S J , FLINT S J , et al. Human c-MYC transcription factor PuF identified as nm23-H2 nucleoside diphosphate kinase, a candidate suppressor of tumor metastasis[J]. Science, 1993, 261 (5120): 478- 480.
doi: 10.1126/science.8392752 |
| 32 |
JI L , ARCINAS M , BOXER L M . The transcription factor, Nm23H2, binds to and activates the translocated c-MYC allele in Burkitt's lymphoma[J]. J Biol Chem, 1995, 270 (22): 13392- 13398.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.22.13392 |
| 33 |
FEKETE A , KENESI E , HUNYADI-GULYAS E , et al. The guanine-quadruplex structure in the human c-myc gene's promoter is converted into B-DNA form by the human poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7, e42690.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042690 |
| 34 |
OU T M , LIN J , LU Y J , et al. Inhibition of cell proliferation by quindoline derivative (SYUIQ-05) through its preferential interaction with c-MYC promoter G-quadruplex[J]. J Med Chem, 2011, 54 (16): 5671- 5679.
doi: 10.1021/jm200062u |
| 35 |
DAI J X , CARVER M , HURLEY L H , et al. Solution structure of a 2:1 quindoline-c-MYC G-quadruplex: insights into G-quadruplex-interactive small molecule drug design[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133 (44): 17673- 17680.
doi: 10.1021/ja205646q |
| 36 |
ZENG D Y , KUANG G T , WANG S K , et al. Discovery of Novel 11-triazole substituted benzofuro[3, 2-b]quinolone derivatives as c-MYC G-quadruplex specific stabilizers via click chemistry[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60, 5407- 5423.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00016 |
| 37 |
LIU H Y , CHEN A C , YIN Q K , et al. New Disubstituted quindoline derivatives inhibiting Burkitt's lymphoma cell proliferation by impeding c-MYC transcription[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60 (13): 5438- 5454.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00099 |
| 38 |
GABELICA V , BAKER E S , TEULADE-FICHOU M P , et al. Stabilization and structure of telomeric and c-MYC region intramolecular G-quadruplexes: the role of central cations and small planar ligands[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129 (4): 895- 904.
doi: 10.1021/ja065989p |
| 39 | GRAND C L , HAN H Y , MUNOZ R M , et al. The cationic porphyrin TMPyP4 down-regulates c-MYC and human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression and inhibits tumor growth in vivo[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2002, 1, 565- 573. |
| 40 |
SEENISAMY J , REZLER E M , POWELL T J , et al. The dynamic character of the G-quadruplex element in the c-MYC promoter and modification by TMPyP4[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126 (28): 8702- 8709.
doi: 10.1021/ja040022b |
| 41 |
PHAN A T , KURYAVYI V , GAW H Y , et al. Small-molecule interaction with a five-guanine-tract G-quadruplex structure from the human MYC promoter[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2005, 1, 167- 173.
doi: 10.1038/nchembio723 |
| 42 |
HU M H , WANG Y Q , YU Z Y , et al. Discovery of a new four-leaf clover-like ligand as a potent c-MYC transcription inhibitor specifically targeting the promoter G-quadruplex[J]. J Med Chem, 2018, 61 (6): 2447- 2459.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01697 |
| 43 |
WU T Y , HUANG Q , HUANG Z S , et al. A drug-like imidazole-benzothiazole conjugate inhibits malignant melanoma by stabilizing the c-MYC G-quadruplex[J]. Bioorg Chem, 2020, 99, 103866.
doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103866 |
| 44 |
HU M H , WU T Y , HUANG Q , et al. New substituted quinoxalines inhibit triple-negative breast cancer by specifically downregulating the c-MYC transcription[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47 (20): 10529- 10542.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz835 |
| 45 |
GLUSZYNSKA A , JUSKOWIAK B , KUTA-SIEJKOWSKA M , et al. Carbazole ligands as c-MYC G-quadruplex binders[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 114, 479- 490.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.135 |
| 46 |
DAS T , PANDA D , SAHA P , et al. Small molecule driven stabilization of promoter G-quadruplexes and transcriptional regulation of c-MYC[J]. Bioconjug Chem, 2018, 29 (8): 2636- 2645.
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00338 |
| 47 |
SCHMIDT A W , REDDY K R , KNOLKER H J . Occurrence, biogenesis, and synthesis of biologically active carbazole alkaloids[J]. Chem Rev, 2012, 112 (6): 3193- 3328.
doi: 10.1021/cr200447s |
| 48 |
MA Y , OU T M , HOU J Q , et al. 9-N-substituted berberine derivatives: stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA and down-regulation of oncogene c-MYC[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2008, 16 (16): 7582- 7591.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.07.029 |
| 49 |
PENG D , TAN J H , CHEN S B , et al. Bisaryldiketene derivatives: A new class of selective ligands for c-myc G-quadruplex DNA[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2010, 18 (23): 8235- 8242.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.10.021 |
| 50 |
SHAN C , YAN J W , WANG Y Q , et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of isaindigotone derivatives to downregulate c-MYC transcription via disrupting the interaction of NM23-H2 with G-quadruplex[J]. J Med Chem, 2017, 60 (4): 1292- 1308.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01218 |
| 51 |
Islam M M , Fujii S , Sato S , et al. A selective G-quadruplex DNA-stabilizing ligand based on a cyclic naphthalene diimide derivative[J]. Molecules, 2015, 20, 10963- 10979.
doi: 10.3390/molecules200610963 |
| 52 |
CHAN D S H , YANG H , KWAN M H T , et al. Structure-based optimization of FDA-approved drug methylene blue as a c-MYC G-quadruplex DNA stabilizer[J]. Biochimie, 2011, 93 (6): 1055- 1064.
doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.02.013 |
| 53 |
ALZEER J , LUEDTKE N W . pH-mediated fluorescence and G-quadruplex binding of amido phthalocyanines[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49 (20): 4339- 4348.
doi: 10.1021/bi9020583 |
| 54 |
VORLICKOVA M , KEJNOVSKÁ I , SAGI J , et al. Circular dichroism and guanine quadruplexes[J]. Methods, 2012, 57 (1): 64- 75.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.011 |
| 55 |
SEN D , GILBERT W . Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis[J]. Nature, 1988, 334, 364- 366.
doi: 10.1038/334364a0 |
| 56 |
MARCHAND A , FERREIRA R , TATEISHI-KARIMATA H , et al. Sequence and solvent effects on telomeric DNA bimolecular G-quadruplex folding kinetics[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2013, 117 (41): 12391- 12401.
doi: 10.1021/jp406857s |
| 57 |
TONG X T , LAN W X , ZHANG X , et al. Solution structure of all parallel G-quadruplex formed by the oncogene RET promoter sequence[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2011, 39 (15): 6753- 6763.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr233 |
| 58 |
LI M M , WU S , LIU Z , et al. Arenobufagin, a bufadienolide compound from toad venom, inhibits VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through suppression of VEGFR-2 signaling pathway[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2012, 83 (9): 1251- 1260.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.023 |
| 59 |
LIU Y P , LAN W X , WANG C X , et al. A putative G-quadruplex structure in the proximal promoter of VEGFR-2 has implications for drug design to inhibit tumor angiogenesis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293 (23): 8947- 8955.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002666 |
| 60 |
CALABRESE D R , CHEN X , LEON E C , et al. Chemical and structural studies provide a mechanistic basis for recognition of the MYC G-quadruplex[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 4229.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06315-w |
| 61 |
WANG F , WANG C X , LIU Y P , et al. Colchicine selective interaction with oncogene RET G-quadruplex revealed by NMR[J]. Chem Commun (Camb), 2020, 56 (14): 2099- 2102.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC00221F |
| 62 |
WANG F , WANG C X , LIU Y P , et al. NMR studies on the interaction between oncogene RET G-quadruplex and berberine[J]. Chinese J Chem, 2020, 38 (12): 1656- 1662.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.202000301 |
| [1] | 徐倩,陈朗,胡翔颖,李从刚,刘乙祥,姜凌. T69E模拟磷酸化修饰对Bcl-2与Nur77相互作用的影响[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(1): 87-95. |
| [2] | 王子豪,徐赫,汪涛,杨善中,丁运生,魏海兵. 外型和内型C-2位单取代降冰片烯衍生物的核磁共振波谱研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(3): 323-335. |
| [3] | 王崇武,黄曦,石磊,陈世桢,周欣. 组织蛋白酶B响应的超极化129Xe MRI探针对肺癌细胞的超灵敏探测[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(3): 336-344. |
| [4] | 吴嘉敏,贺玉成,徐征,朱延河,姜文正. 用于土壤水分测量的磁共振射频线圈宽频匹配方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(3): 414-423. |
| [5] | 赵心怡,韩冬,罗红军,沈文斌,杨功俊. 德拉沙星葡甲胺波谱学数据解析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(2): 268-276. |
| [6] | 余锦波,张偲,张则婷,徐国华,李从刚. Alpha-突触核蛋白与完整线粒体相互作用的NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(2): 164-172. |
| [7] | 廖怀玉, 韩红园, 陈飞, 张海艳, 杨静, 赵天增. 苦皮藤中两个新的 β-二氢沉香呋喃型化合物的 NMR 数据解析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 101-109. |
| [8] | 李玉江, 赵伟, 郭晓河, 陶乐, 张祥, 张海艳, 赵天增. 盐酸马尼地平的核磁共振数据解析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 110-117. |
| [9] | 王睿迪, 徐贝贝, 宋艳红, 王雪璐, 姚叶锋. 原位核磁共振技术研究光催化甲醇重整过程中甲醇与水的相互作用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 43-57. |
| [10] | 柯汉平, 蔡宏浩. 基于哈德曼编码的新型高分辨定域谱[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 524-532. |
| [11] | 刘思, 安艳捧, 唐惠儒. 冷冻干燥对人类体液代谢组影响的NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 484-489. |
| [12] | 李英俊, 杨鸿境, 刘季红, 靳焜, 林乐弟, 刘雪洁. 基于咔唑-三嗪并吲哚的N-酰腙衍生物的NMR数据归属[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 496-504. |
| [13] | 尹田鹏, 李幸, 汪泽, 王雅溶, 王敏. 石斛属植物中石斛碱类成分的波谱学特征[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 381-389. |
| [14] | 刘欢, 徐锦绣, 郑炀, 熊镭. 渤海J油田储层核磁共振测井孔隙度影响因素分析及校正[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 370-380. |
| [15] | 张宫, 何宗斌, 曹文倩, 陈瑶. 回波间隔对核磁共振表观孔隙度的影响及矫正方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(2): 172-181. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 424
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 213
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||