1 引言
加权线性互补问题 (weighted Linear Complementarity Problems, 简记为 wLCP ) 由著名优化专家 Potra 在 2012 年提出 [1],其数学模型为: 求
这里
本文考虑加权水平线性互补问题 (weighted Horizontal Linear Complementarity Problems, 简记为 wHLCP), 其数学模型定义如下: 求
这里
即取
近年来, 人们对求解各种数学规划问题的光滑牛顿法产生了浓厚的兴趣. 这类方法的基本思想是利用光滑函数将所求解的问题等价转化成一个光滑方程组, 然后用牛顿法求解此光滑方程组. 许多光滑牛顿法已被提出用来求解 wLCP [6⇓-8]. 注意到, 为获得局部二次收敛速率, 光滑牛顿法通常要求满足非奇异条件, 而这个条件比较强. 2021 年, Tang 和 Zhang[13] 提出了一个求解对称锥加权互补问题的非单调光滑牛顿法, 分析了算法在局部误差界条件下的收敛速率, 而局部误差界条件比非奇异条件弱. 但文献 [13] 中的非单调光滑牛顿法在每次迭代时都要求解非线性方程组的精确解, 而当问题的规模非常大时, 求解此精确解的计算代价会很昂贵.
本文在文献 [13] 的基础上, 研究一个求解 wHLCP 的非单调光滑非精确牛顿法. 相比于现有的光滑牛顿法, 我们的算法有如下优点
(a) 算法在每次迭代时只需求解非线性方程组的近似解, 相比于文献 [13] 中的非单调光滑牛顿法可节省大量的计算时间. 数值实验结果验证了这一优点.
(c) 如果
在本文中,
2 预备知识
本节首先给出函数强半光滑的定义. 设
则称
则称
接下来, 我们回顾 Sznajder 和 Gowda[14] 定义的列单调和列
本文考虑如下光滑函数
其中
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
令
这里
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
其中
而
(v) 如果
证 由引理 2.2 可知结论 (i)-(iv) 成立. 由文献 [14] 可知
这表明
3 算法
定义价值函数
下面给出我们的算法.
这里
令
令
从而得到搜索方向
的精确解
即我们只求解方程组 (3.7) 的一个近似解, 从而节省大量的计算工作. 此外, 由于非精确方向一般不是下降方向, 文献 [13] 中的非单调线搜索技术无法保证算法 3.1 的全局收敛性. 为了克服这个困难, 我们在算法 3.1 中引入一种新的非单调线搜索技术.
证 假设
不等式 (3.3) 对所有充分大的
即
再由 (3.4) 式可得
因此, 我们可以得出如下结论: 如果
证 由 (3.3) 式可知
进而由 (3.4) 式可得
由 (3.9) 式和 (3.10) 式可知
这证明了第一个结论. 假设
因为
证 由 (3.3) 式可知
结合 (3.4) 式可得
进而由引理 3.1 中的第一个结论可推出
因为
4 全局收敛性
为了分析算法 3.1 的全局收敛性, 我们做如下假设.
假设 4.1 确保
是有界的, 则由引理 3.1 可知假设 4.1 成立. 最近, Chi 等人[15]引入了
Chi 等人[15]证明了对每个
证 由引理 3.1 和 (3.1) 式可知
现在我们假设
显然,
在 (4.2) 式中令
同样地, 由 (2.1) 式可知对所有的
这表明
另一方面, 由 (4.1) 式可知对所有的
因此, 对所有的
由 (4.3) 式和 (4.4) 式可知
证 因为
接下来, 我们考虑
现在我们假设
这里第二个不等式成立是因为
这表明
再结合
由于
另一方面, 因为
这表明
由 (4.7) 式和 (4.8) 式可知
5 局部收敛速率
本节讨论算法 3.1 的局部收敛速率. 令
对任意的
这里
(II) 存在常数
(III) 存在常数
这里
对假设 5.1, 我们有如下说明.
证 因为
根据引理 2.3(ii), 对所有充分大的
并且由
由 (3.2) 式, (5.4) 式, (5.5)式, 假设 5.1(II) 和假设 5.1(III) 可知对所有充分大的
其中
再结合
因此, 由线搜索 (3.3) 式可知对所有充分大的
再结合 (5.7) 式可知
进而由 (5.3)式和
根据 (3.2) 式, (5.4) 式, (5.5)式, (5.9)式, 引理 2.3(ii) 以及假设 5.1(III) 可知对所有充分大的
另外, 由 (5.8) 式可知对所有充分大的
再结合 (5.10)式可推出
由 (5.11) 式和 (5.12) 式可知对所有充分大的
这里第二个不等式成立是因为
对上面所有不等式左右相加求和可得
即
从而可知
因此, 当
根据 (5.11) 式和 (5.14) 式可知
因此, 定理成立.
6 数值结果
本节报告一些数值结果. 在实验中, 我们比较以下两个算法
这里
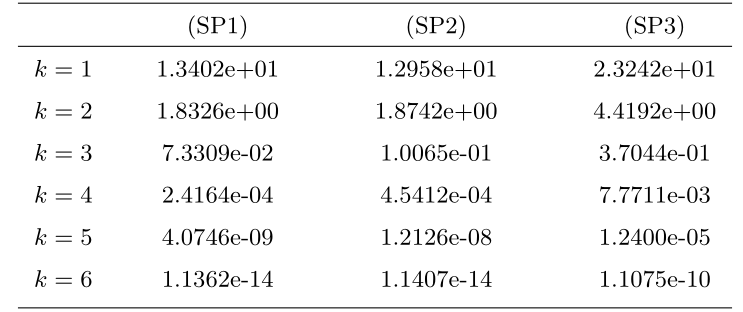
为观察 FTZ-A 的局部收敛速率, 我们随机产生一个规模为
(SP1)
(SP2)
(SP3)
表 1 给出了迭代过程中
同样的, 我们随机生成一个
接下来, 对不同规模的测试问题, 我们随机生成 10 个算例, 并使用与例 6.1 相同的初始点来求解它们. 数值结果列于表 4, 其再次表明 FTZ-A 比 TZ-A 可节省大量的计算工作. 这些数值结果证实了我们的算法具有更好的实际计算性能.
参考文献
Weighted complementarity problems-a new paradigm for computing equilibria
A full-Newton step interior-point method for monotone weighted linear complementarity problems
A modified damped Gauss-Newton method for non-monotone weighted linear complementarity problems
A derivative-free line search technique for Broyden-like method with applications to NCP, wLCP and SI
Quadratic convergence analysis of a nonmonotone Levenberg-Marquardt type method for the weighted nonlinear complementarity problem
A variant nonmonotone smoothing algorithm with improved numerical results for large-scale LWCPs
An accelerated smoothing Newton method with cubic convergence for weighted complementarity problems
A smoothing Newton algorithm for weighted linear complementarity problem
Sufficient weighted complementarity problems
A full-Newton step feasible interior-point algorithm for monotone horizontal linear complementarity problems
Limiting behavior of the derivatives of certain trajectories associated with a monotone horizontal linear complementarity problem
On the convergence of a class of infeasible interior-point algorithms for the horizontal linear complementarity problem
A nonmonotone smoothing Newton algorithm for weighted complementarity problems
Generalizations of
The weighted horizontal linear complementarity problem on a Euclidean Jordan algebra
Convergence rate of the Levenberg-Marquardt method under Hölderian local error bound
Convergence properties of inexact Levenberg-Marquardt method under Hölderian local error bound
A non-interior predictor-corrector path following algorithm for the monotone linear complementarity problem
A smoothing Levenberg-Marquardt type method for LCP
In this paper, we convert the linear complementarity problem to a system of semismoothnonlinear equations by using smoothing technique. Then we use Levenberg-Marquardttype method to solve this system. Taking advantage of the new results obtained by Dan,Yamashita and Fukushima [11, 33], the global and local superlinear convergence propertiesof the method are obtained under very mild conditions. Especially, the algorithm is locallysuperlinearly convergent under the assumption of either strict complementarity or certainnonsingularity. Preliminary numerical experiments are reported to show the efficiency ofthe algorithm.