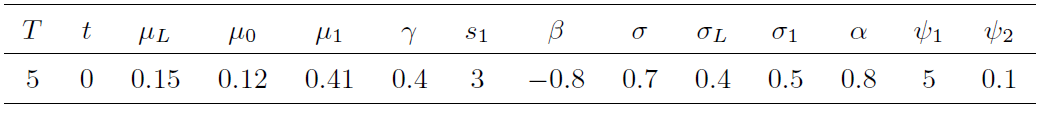1 引言
通货膨胀是指在纸币流通条件下, 因货币供给大于货币实际需求, 导致货币贬值, 而引起的一段时间内物价持续普遍上涨的现象. 该现象会直接影响经济的各个方面, 包括支出、投资和利率等. 近年来, 我国对于通货膨胀的相关研究有了一定深度, 为通货膨胀在金融保险领域的研究发展奠定了坚实基础.
在所有这些工作中, 如何将通货膨胀的影响纳入金融保险的相关模型也逐渐引起了众多学者的研究. Zhang 等[1]引入了与通货膨胀呈相同波动性的通货膨胀连接型债券对冲通胀风险, 用于研究通货膨胀下货币市场账户、股票与通胀挂钩债券中持有 DC 型养老金的最佳投资管理方式. Siu[2]考虑了金融市场含有固定利率债券、股票以及通货膨胀连接型债券, 并利用价格指数对三类资产进行折现, 研究了通胀情况下连续时间的最优投资消费问题. Kwak 和 Lim[3]同样使用价格水平指数对各类资产的价格和投资者的财富进行折现, 从而给出真实情况下人寿保险的最佳投资组合. 本文在对通胀下资产价格的处理上运用上述文献的设定方式, 将资产价格变换到真实情况下, 进而求解最优投资问题.
由于现实中无法精准估计参考模型参数, 很多文献将模型不确定性考虑在投资再保险模型中, 但这类鲁棒模型存在只考虑极端模糊厌恶态度的局限性, 与真实情况不符. 在后续的研究中, 一些学者研究了
据我们所知, 在以往的研究中, 还未有研究利用
2 基本模型
2.1 金融市场
假设在连续时间的金融市场中有三种金融资产, 分别为: 无风险资产、风险资产以及通货膨胀指数债券.
假定无风险资产在
其中
风险资产在
其中,
在很多情况下, 通货膨胀的典型指标可以使用 CPI (消费价格指数) 来表示
其中
为了对冲通货膨胀风险, 本文假设市场上存在一种通货膨胀指数债券, 该债券主要是投资者用于对冲通货膨胀风险的投资产品, 其在
其中
投资者可以通过投资上文描述的无风险资产、风险资产以及用于对冲通胀风险的通货膨胀指数债券来实现财富的积累与增值, 以获得更高的财富效用.
2.2 金融市场的通胀调整
由于通货膨胀会对各类资产价格产生一定影响, 本文需先对各类资产价格模型运用价格指数进行调整, 得到其经过调整后不受通货膨胀影响的模型[12].
经过调整后的无风险资产价格为:
其中
经过调整的风险资产价格为:
其中
经过调整的通货膨胀指数债券价格为:
可以观察到经过通胀折现调整后的三类资产中, 通货膨胀指数债券价格形式变为寻常的无风险资产价格形式, 即不受波动率影响; 而无风险资产与风险资产价格都变为带漂移的几何布朗运动形式.
此外, 假设在
其初值为
3 基于 α -鲁棒的投资模型
上述模型框架是建立在确定的概率测度
定义 3.1 过程
(1)
(2)
用
根据 Girsanov 定理, 有
其中
其初值为
接下来根据
其中
其中
其中
本文的主要目标是研究时间一致的均值方差策略下的
下面将给出可容许策略与均衡策略的定义.
定义 3.2 (可容许策略) 对任意的
(1) 对于任意的
(2) 对于任意的
(3) 对于任意的
记
为所有可容许策略构成的集合.
定义 3.3 (均衡策略) 对于一个可容许策略
定义如下策略
其中
那么
4 主要结果
为方便起见, 令
以下验证定理的证明与 Li 等[6]相似, 因此我们在此省略.
定理 4.1 (验证定理) 假设存在函数
(1)
(2) 函数
(3)
那么
定理 4.2 问题 (3.8) 的均衡策略及值函数如下
(1) 均衡投资策略为
(2) 相应的均衡值函数为
其中,
证 (4.2)式可写成
对 (4.7) 式应用一阶最优性条件有
及
将 (4.8) 式和 (4.9) 式代入 (4.7) 式中, 有
受边界条件 (4.3) 式的启发, 假定 (4.10) 式的解形式如下
其中,
则有
将 (4.13) 式代入 (4.10) 式中, 化简有
对 (4.14) 式的
将 (4.15)、(4.16) 式代入 (4.14) 式化简后变量分离, 有
而后再结合 (4.1)式, 将 (4.8)、(4.9)、(4.13)、(4.15)、(4.16)式的值代入 (4.3) 式的
化简后变量分离, 分别有
运用 (4.12) 式的边界条件, 求解 (4.17)、(4.20) 式和 (4.23) 式, 得
将 (4.26) 式代回 (4.18)、(4.19)、(4.21)、(4.22)、(4.24) 及 (4.25)式, 得
这里将 (4.29) 式乘上系数
求解过程涉及解黎卡提方程, 为计算简便, 这里采用 Sun 等[13]的方法, 求解可得
其中
将 (4.34) 式代回 (4.27)-(4.32) 式, 求解可得
其中
这里将 (4.13)、(4.26)、(4.34)-(4.42) 式结合, 代入(4.8)、(4.9)、(4.11) 式与 (4.15)、(4.16) 式可得
最后可以验证上述结果满足验证定理的条件, 从而定理证毕.
推论 4.1 若
(1) 均衡投资策略为
(2) 相应的均衡值函数为
其中, 当
对应的
由上述推论可得, 若
5 数值分析
本节主要通过曲线变化趋势简洁描述参数对最优投资策略的影响, 除特别说明外, 基本参数设置见表1.
图1 显示: 风险资产的投资数量随着时间
图1
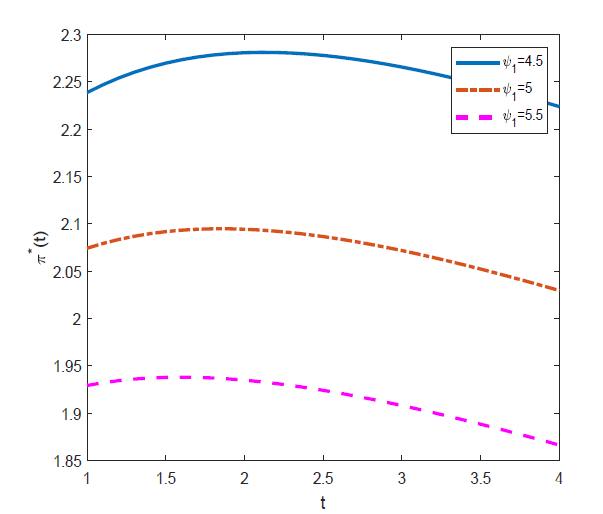
图2 显示: 无风险资产的投资数量随着时间
图2
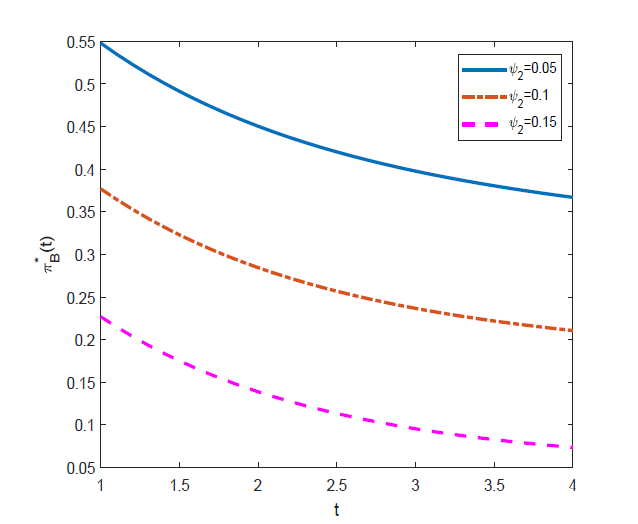
图3 显示: 风险资产的投资数量随着模糊厌恶型投资者模糊态度
图3
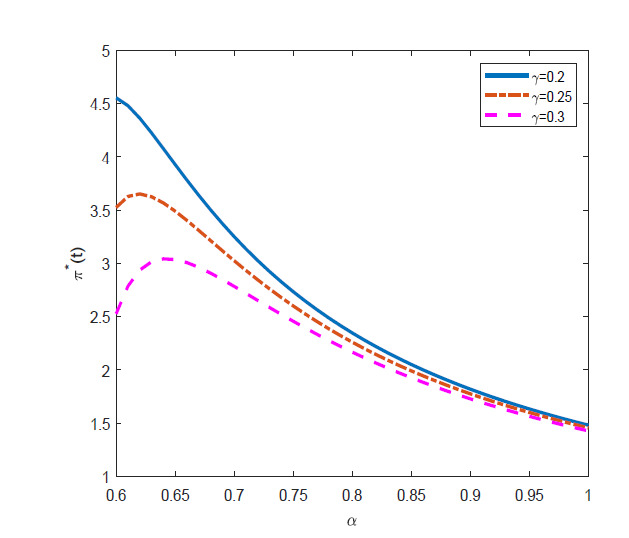
图4 显示: 无风险资产的投资数量随着模糊偏好型投资者模糊态度的增加呈现先减后增的趋势, 且随着风险厌恶系数
图4
参考文献
Optimal management and inflation protection for defined contribution pension plans
Long-term strategic asset allocation with inflation risk and regime swiching
Optimal portfolio selection with life insurance under inflation risk
Equilibrium strategies for alpha-maxmin expected utility maximization
DOI:10.1137/18M1178542
[本文引用: 1]

In the existing literature of robust utility maximization with ambiguity, agents are generally assumed to be extremely ambiguity-averse as they tend to only consider expected payoffs in the worst-case scenario. However, experimental studies have shown that agents' attitude to ambiguity is not systematically negative and can even be ambiguity-seeking when they consider themselves knowledgeable or competent. To conceptually distinguish between an agent's perception of ambiguity and ambiguity aversion, the so-called alpha-maxmin expected utility (alpha-MEU) was proposed in the economics literature as a linear aggregation of the most and least favorable prior beliefs. Although the axiomatic characterization of alpha-MEU has been well studied, there has been little work on the benchmark maximization problem for alpha-MEU. The main difficulty stems from the dynamic inconsistency of two distinct extreme priors and nonconvexity (and nonconcavity) of the value function. In this paper, we study the maximization problem for alpha-MEU and solve for the equilibrium strategies of open-loop type. Under logarithmic risk preference, we obtain the explicit form of equilibrium investment strategies, which involves a two-dimensional system of fully coupled quadratic backward stochastic differential equations (BSDE). The main challenge in completing the verification theorem is to study the existence, uniqueness, and stability of this system of BSDE. For this purpose, we consider a general Markov model of the financial market, which leads to a system of quadratic Markovian BSDE. We find that the equilibrium investment strategy becomes more conservative if the agent is more ambiguity-averse or the agent perceives more ambiguity in the financial market. The equilibrium strategy is close to the classical nonrobust strategy (without ambiguity) if the agent is ambiguity-neutral. As time approaches maturity, ambiguity-seeking (ambiguity-averse) agents adopt more aggressive (conservative) equilibrium strategies. Additionally, the equilibrium strategy of an ambiguity-neutral agent converges to the classical nonrobust strategy at maturity.
违约风险下目标收益型养老金计划的
Alpha-robust mean-variance reinsurance-investment strategy
Portfolio selection with parameter uncertainty under
Optimal reinsurance under the
Alpha-robust mean-variance investment strategy for DC pension plan with uncertainty about jump-diffusion risk
Robust optimal reinsurance-investment for
A Stackelberg reinsurance-investment game under
A kind of optimal investment problem under inflation and uncertain time horizon
Robust optimal investment-reinsurance strategies for an insurer with multiple dependent risks