1 引言
ARZ非平衡交通流模型能够较为准确地刻画城市快速路网车辆的运行, 在黎曼坐标变换和线性化处理后呈现为二阶双曲偏微分方程组的形式[1⇓-3]. 近年来, 入口匝道控制和可变限速控制成为城市快速路网车辆交通流控制的两种有效方法[4], 将其应用于 AR/ARZ 非平衡交通流模型, 取得了一系列研究成果[5,6]. 对于线性/拟线性双曲系统柯西问题解的适定性, 文献 [7,定理 A.1,B.1] 采用 Lumer-Philipps 定理、不动点定理和能量估计等数学方法进行了证明. 在稳定性分析方面, 文献 [8] 研究了一维
在自动控制中, 时滞的出现可能由控制器造成, 也可能是人为因素, 时滞现象可能使得系统的状态变得不稳定, 但合适的时滞取值亦有可能改善系统的性能. 于是, 时滞控制策略吸引了广大学者的关注. 文献 [12] 研究了一类扩散波方程的输入控制器具有时滞的情形, 结果表明无论时滞取值多少, 只要控制参数满足某个约束条件, 即可得到闭环系统的指数稳定性. 在此基础上, 文献 [13] 建立了扩散波方程在时滞控制器下的与时滞相关及与时滞无关的指数稳定性. 针对一阶线性双曲守恒律系统, 文献 [14] 采用特征根分析方法讨论了系统的与时滞无关的稳定性和不稳定性. 此外, 当波的传播时间与控制器的反馈时滞恰好是整数倍时, 采用 Schur-Cohn 准则建立了闭环系统稳定时参数所满足的充要条件.
本文针对线性化之后的 ARZ 交通流模型, 充分考虑三个因素: 一是系统的平衡态不一定等于自由流的速度, 二是进入上游路段的交通量在交通需求的数学期望附近不可避免地出现了有界振荡, 三是利用边界状态反馈和时滞边界状态反馈的线性组合设计控制器. 一般地, 若平衡态不等于自由流的速度, 方程中会出现模型漂移项; 若进入上游路段的交通量有振荡, 导致边界条件中产生一个不确定干扰, 为闭环系统适定性的证明带来了一定困难. 此外, 控制器的时滞效应对稳定性的影响也是本文探讨的一个重要内容. 本文的主要贡献有: (1) 将时滞项用一阶运输方程边值问题的解进行刻画, 构建具有模型漂移项和边界扰动项的 PDE-PDE 无穷维耦合闭环系统; (2) 结合线性系统解与控制算子的允许性等算子半群理论, 证明了闭环系统的适定性; (3) 求得反馈参数的耗散条件以及时滞参数
2 模型建立和控制器设计
2.1 模型建立
高速公路路段的宏观交通流动态一般用 ARZ 模型描述
其中, 密度
作黎曼坐标变换
则非线性方程 (2.1) 在黎曼坐标系下的特征形式为
其中
且
不妨设
则可得如下线性化的 ARZ 模型
其中
注 2.1 显然, 当
2.2 时滞边界控制器设计
在这一部分, 结合匝道控制和可变限速控制设计时滞反馈控制器.
不妨设快速路段处于自由模态, 即
的情形, 那么特征速度的传播方向是从上游传播到下游. 因此, 本文基于下游出口处交通流密度 (
其中,
注 2.2 时滞控制器 (2.11) 由边界状态反馈和时滞边界状态反馈的线性组合构成, 考虑到从输出量测到输入控制往往具有滞后性, 因此, 可设边界条件 (2.11) 中瞬时反馈系数
定义偏差函数
则时滞控制器 (2.11) 可改写为
假设上游入口边界处交通流所满足的守恒条件和交通流稳态时的守恒条件分别为
其中,
在黎曼坐标系 (2.4) 下, 不妨令
由 (2.14) 式第二个式子知
因此, 在黎曼坐标系下的时滞边界条件为
其中
2.3 PDE-PDE 闭环系统的重建
首先引入两个辅助函数
的解可表示为
同理
的解为
从而, 时滞系统 (2.8), (2.20) 可改写为如下 PDE-PDE 耦合闭环系统的形式
注 2.3 闭环系统 (2.26) 中存在模型漂移项
3 系统 (2.26) 的适定性
设 Hilbert 状态空间为
其中的内积定义为
这里
3.1 抽象发展方程形式
定义线性算子
经过计算, 其伴随算子
将系统 (2.26) 与
其中
其中,
且
注 3.1 显然
3.2 算子 A 的性质
定理 3.1 设
从而, 算子
证 任给
即
于是,
根据一阶线性微分方程求解公式可得方程组 (3.12) 的解为
再将 (3.13) 式代入 (3.14) 式中, 得
将 (3.13)-(3.17) 式代入 (3.12) 式中的边界条件, 得到关于
根据线性方程组求解的克莱姆法则, 当且仅当系数行列式
时, 方程组 (3.18) 有唯一解, 且
其中,
因此, 根据 Sobolev 嵌入定理,
下面考虑系统算子
即
计算可得,
有解, 其中,
从而可得关于算子
定理 3.2 设
且任一
3.3 算子 A 生成 H 上的 C0 压缩半群
定义 3.1 设
则称
定理 3.3 设
其中,
那么由 (3.23) 式所诱导的范数等价于由 (3.2) 式所诱导的范数. 此外, 如果参数满足如下条件
则
因此,
证 对任意的
于是, 其实部
其中,
且
下证
条件 (a) 显然成立. 考虑到在
因此, (3.27) 式放缩为
再将边界条件 (3.4) 代入 (3.30) 式中, 利用均值不等式放缩为
于是, 当所选参数满足约束条件 (3.24) 的前四个条件时, 可得
因此, 系统算子
定理 3.4 假设
证 对于线性系统 (3.8) 的子系统
考虑其对偶系统的观测问题
其中,
4 稳定性分析
由于系统 (2.26) 具有模型漂移项以及不确定的交通需求扰动项, 因此这一部分通过构造合适的 ISS-Lyapunov 函数来证明系统的 ISS 稳定性. 不失一般性, 为方便计算, 取
定义 4.1 如果存在一个
则系统 (2.26) 在干扰
定理 4.1 如果存在
则系统 (2.26) 是 ISS 稳定的.
证 构造 ISS-Lyapunov 函数如下
其中
沿系统 (2.26) 的解, 将 (4.3) 式对
运用 Cauchy-Schwarz 不等式和 Young 不等式将 (4.5) 式放缩为
令
且
下证
考虑到当
沿系统 (2.26) 的解, 将 (4.4) 式对
将系统 (2.26) 的边界条件代入 (4.5) 和 (4.10) 式中, 并利用均值不等式整理得
于是, 由约束条件 (4.1) 的前四个条件可得
其中
在 (4.12) 式两边从 0 到
因此, 带有时滞控制器的系统 (2.26) 在有界干扰
注 4.1 根据定理 4.1 可知, 要使系统 (2.26) ISS 稳定, 控制器中的时滞参数
也就是说, 定理 4.1 建立的是与时滞相关的稳定性结论.
注 4.2 当不考虑漂移项
5 与时滞无关的稳定性分析结果
在这一部分, 不妨设 \lambda_1^*=\lambda_2^*\doteq\lambda^* , 我们考虑系统 (2.8) 在单纯时滞反馈 (2.12) 下的特征方程. 此时,
i.e.
其中,
令
显然, 特征值的实部 Re
命题 5.1 实系数多项式
的全体根位于单位圆内, 当且仅当
且
的内子矩阵的行列式均大于 0.
根据命题 5.1, 易得如下结论
定理 5.1 无论时滞
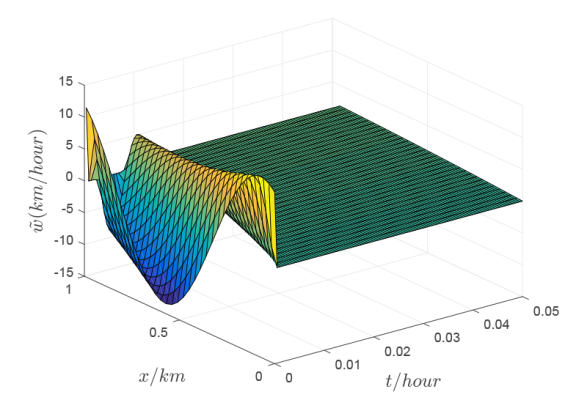
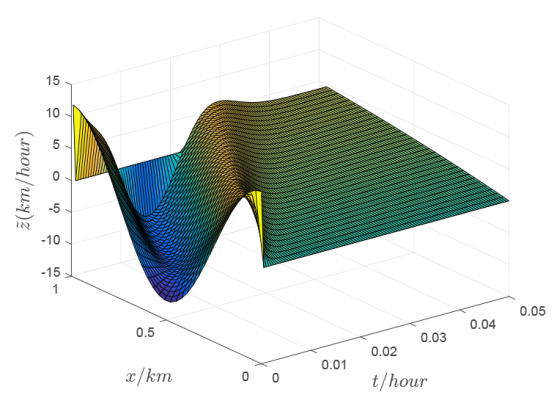
6 数值模拟
本节通过 MATLAB 数值仿真实例来验证所设计的时滞控制器的有效性和可行性. 考虑自由模态下的快速路段, 其道路参数为
由 (2.4) 和 (2.9) 式计算可得
进而, 选取参数
控制器的时滞参数
则根据定理 4.1, 反馈参数
不妨取满足上述条件的
图1
图2
注 6.1 从定理
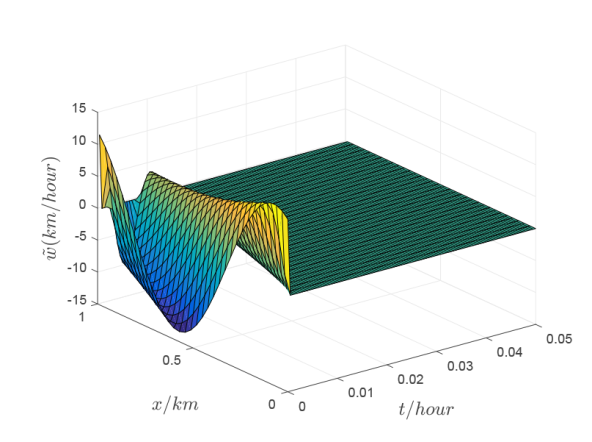
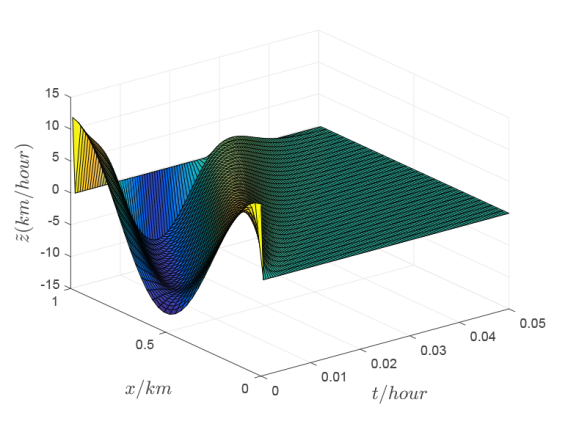
特别地, 当不考虑漂移项, 即
图3
图4
7 结论
本文首先对宏观 ARZ 交通流模型进行黎曼坐标变换及线性化处理, 在自由模态下, 结合匝道控制和可变限速控制建立了状态反馈与时滞状态反馈相结合的控制策略. 其次, 将时滞项用一阶运输方程初值问题的解进行刻画, 构建了 PDE-PDE 无穷维耦合闭环系统. 然后, 结合线性系统解与控制算子的允许性理论, 证明了闭环系统的适定性. 通过构建加权 Lyapunov 函数证明了系统的 ISS 稳定性, 并得到了与时滞相关的稳定性条件. 最后, 若仅考虑时滞反馈, 在特征速度
此外, 若系统处于拥堵模态的情形, 即
参考文献
Resurrection of “second order” models of traffic flow
A non-equilibrium traffic model devoid of gas-like behavior
Prediction of traffic convective instability with spectral analysis of the Aw-Rascle-Zhang model
Comparing the effects of ramp metering and variable speed limit on reducing travel time and crash risk at bottlenecks
Necessary and sufficient conditions on the exponential stability of positive hyperbolic systems
PI boundary control of linear hyperbolic balance laws with stabilization of ARZ traffic flow models
Boundary feedback stabilization of freeway traffic networks: ISS control and experiments
Traffic congestion control for Aw-Rascle-Zhang Model
DOI:10.1016/j.automatica.2018.10.040
[本文引用: 1]

This paper develops boundary feedback control laws to reduce stop-and-go oscillations in congested traffic. The macroscopic traffic dynamics are governed by Aw-Rascle-Zhang (ARZ) model, consisting of second-order nonlinear partial differential equations (PDEs). A criterion to distinguish free and congested regimes for the ARZ traffic model leads to the study of hetero-directional hyperbolic PDE model of congested traffic regime. To stabilize the oscillations of traffic density and speed in a freeway segment, a boundary input through ramp metering is considered. We discuss the stabilization problem for freeway segments respectively, upstream and downstream of the ramp. For the more challenging upstream control problem, our full-state feedback control law employs a backstepping transformation. Both collocated and anti-collocated boundary observers are designed. The exponential stability in L-2 sense and finite time convergence to equilibrium are achieved and validated with simulation. In the absence of relaxation time and boundary parameters' knowledge, we propose adaptive output feedback control design. Control is applied at outlet and the measurement is taken from inlet of the freeway segment. We use the backstepping method to obtain an observer canonical form in which unknown parameters multiply with measured output. A parametric model based on this form is derived and gradient-based parameter estimators are designed. An explicit state observer involving the delayed values of the input and the output is introduced for state estimation. Using the parameter and state estimates, we develop an adaptive output feedback control law which achieves convergence to the steady regulation in the L-2 sense. (C) 2018 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Stop-and-go suppression in two-class congested traffic
Time-Delayed feedback control of a hydraulic model governed by a diffusive wave system
一类扩散波方程的PDP反馈控制和稳定性分析
The PDP feedback control and stability analysis of a diffusive wave equation
The stability analysis for a 2 × 2 conservation law with PI controller and PDP Controller