1 引言
互联网信息技术的迅速发展引领人们进入了大数据时代, 大数据所展现出的规模与复杂性使得传统的统计方法遭受巨大的冲击, 由于传统的统计分析理论仅适用于协变量维数远小于样本量的情形, 因此不再普遍适用于高维模型. 随着高维数据在生物信息、金融管理等领域[1]的广泛普及, 人们对高维模型中的变量选择问题提出了更高的要求, 即寻求更简约和科学的预测变量以分析与响应变量的关系, 提高模型的解释能力.
在高维模型的变量选择问题中, 高维变量间通常具有很强的相关性, 如同一行业的股票往往表现出显著的相关收益; 基因表达经常受到细胞因子的刺激或受到生物过程的调控等. 若忽视变量间的强相关性, 则会使得高维统计推断方法产生较大的系统性偏差而降低效率. 一般的线性回归模型已不足以解决这类问题, 但是引入随机效应可以有效克服该模型的缺陷, 提高模型的预测精度和建模的灵活性. 因此, 研究高维随机效应线性回归模型[2]至关重要.
下面是几种典型且应用广泛的正则化方法.
针对高维随机效应线性回归模型, 如何同时选择固定效应和随机效应是解决上述问题的关键. 很多学者提出了一些变量选择的方法, 如2011年, Joseph等[10]提出了基于SCAD和自适应Lasso的混合惩罚方法以同时选择高维随机效应线性回归模型中的固定效应和随机效应, 并证明了该方法具有渐近性质. 虽然他们通过数值实验发现该方法减小了过拟合问题, 但其在处理相关性较大的数据集上有所欠缺, 不具有分组效应.
本文其余部分结构如下: 第2节介绍了高维随机效应线性回归模型, 且提出了混合惩罚方法并在理论上证明其优良的统计性质; 第3节给出基于混合惩罚的高维随机效应线性回归模型的两步迭代算法; 第4-5节在不同信噪比和随机效应下对模型进行蒙特卡洛模拟和实例验证, 给出该惩罚方法与其他惩罚方法的对比结果; 第6节为总结与展望.
2 SCAD_L2 和SCAD混合惩罚方法及其性质
本文将研究如下形式的高维随机效应线性回归模型[12]
其中
针对模型(2.1), 本文提出了一种结合罚函数SCAD_L
其中
其中
为方便探讨模型(2.2)的性质, 这里参考文献[15]将其重新表述为如下形式
当
定理 2.1 (一致性) 对于模型(2.2), 若当
其中
注 2.1 这里对
定理 2.2 (Oracle性质) 对于模型(2.2), 若当
以概率1满足
(1)稀疏性:
(2)渐近正态性
其中
注 2.2 对固定效应中
为验证混合惩罚方法对固定效应的系数估计具有分组效果, 下面证明模型 (2.2)的分组效应.
定理 2.3[9] 记
其中
下面利用定理2.3给出模型(2.2)的分组定理.
定理 2.4 (分组定理) 对于给定的数据
其中
证 为方便起见, 将模型(2.2)改写如下形式
其中
对
令式(2.6)为 0, 且将任意两项相减可得
根据定理2.3可得
由于
所以
又因为
故
证毕.
注 2.3 定理2.4给出了两个估计系数间距离的上界. 如果两个估计系数之间相关系数的绝对值接近于
综上, 该混合惩罚方法在理论上是一种优良的变量选择和系数估计方法.
3 两步迭代算法
本节利用模型(2.2)的结构特性, 采用两步迭代法求解模型(2.2). 下面给出模型 (2.2)中惩罚参数的选取准则和算法描述.
3.1 惩罚参数的选取准则
根据模型(2.2)可以看到惩罚函数有三个调优参数
其中
3.2 算法描述
两步迭代法的描述如下.
步 1 初次迭代求解时令
步 2 将求解出的
步 3 反复迭代步 2, 当
4 蒙特卡洛模拟实验
本节将该混合惩罚方法与双 Lasso 惩罚方法, 双 SCAD 惩罚方法以及不考虑随机效应的 SCAD_
下面利用下述模型[14]生成数据
其中
下面引入三个衡量指标以比较在不同信噪比和随机效应下混合惩罚方法变量选择能力的差异.
4.1 衡量指标
本文采用均方误差 (Mean Square Error, MSE) 作为评价混合惩罚方法的系数估计效果的衡量指标之一. 通过综合考虑运行时间成本, 本文对模型(4.1)进行了 100 次模拟实验. 根据该模型生成的数据, MSE 的定义如下所示
其中
另外, 本文采用两个常用指标
注4.1 由
4.2 “信噪比”对混合惩罚的影响
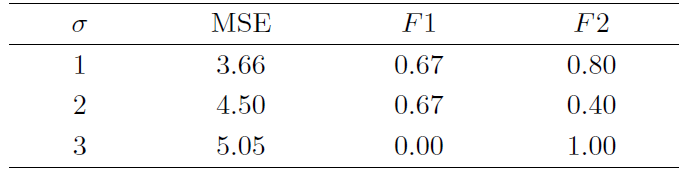
下面根据上述三个衡量指标比较不同“信噪比”下混合惩罚方法的系数估计效果和变量选择能力. 利用模型(4.1)生成模拟数据, 为进一步体现随机效应的影响, 本文设置
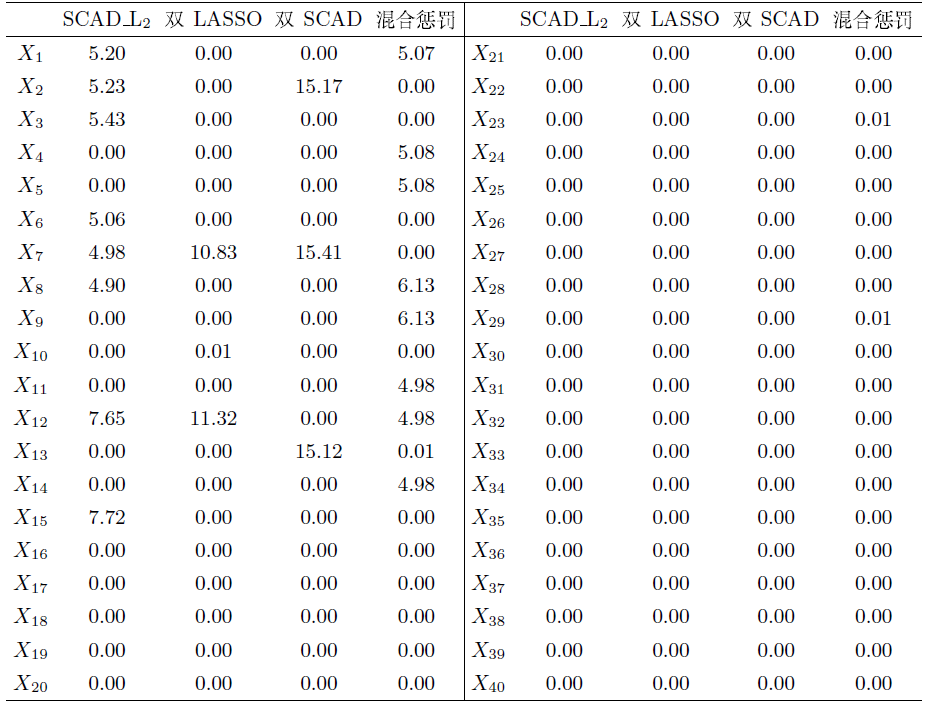
下面将根据表1给出如下模拟结果分析: 当信噪比逐渐增大时, 混合惩罚方法筛选正确变量的能力和系数估计效果均在下降; 而其排除无关变量的能力均有不同程度的变化, 当
4.3 随机效应对混合惩罚的影响
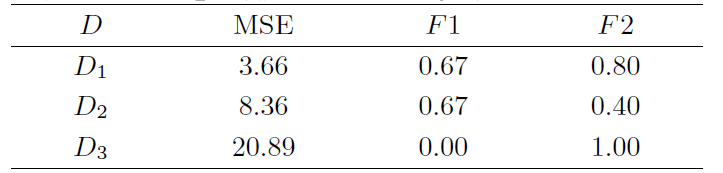
下面根据上述三个衡量指标比较不同随机效应影响下混合惩罚方法的系数估计效果和变量选择能力. 同样利用模型(4.1)产生模拟数据, 基于前述信噪比对混合惩罚方法的影响分析, 这里取
这里协方差矩阵
下面将根据表2给出如下模拟结果分析: 当随机效应增强时, 混合惩罚方法系数估计效果下降且误差受随机效应因素影响较大; 当随机效应的干扰程度较小或较大时, 混合惩罚方法的变量选择能力几乎不受影响且保持在较高水平, 故当随机效应的协方差为
4.4 不同惩罚方法的效果比较
本节将在上述实验中确定的最佳信噪比和随机效应下, 从衡量指标效果和分组效应效果两方面比较该混合惩罚方法、双Lasso惩罚方法、双SCAD惩罚方法和不考虑随机效应的SCAD_L
4.4.1 衡量指标的效果比较
下面利用模型(4.1)产生数据, 然后分别讨论固定系数在系数模型和稠密模型两种情况下的系数估计效果和变量选择能力.
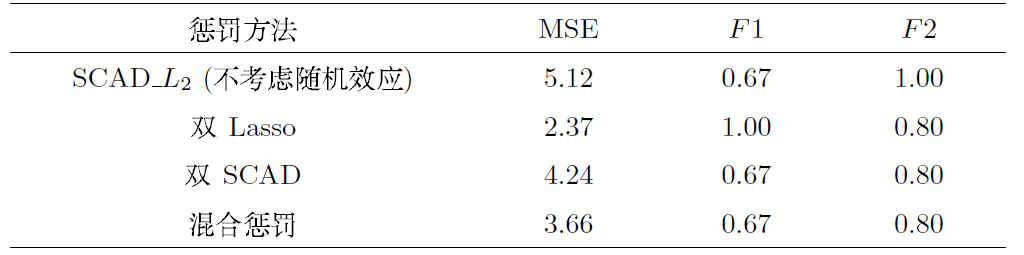
情况 1 稀疏模型取
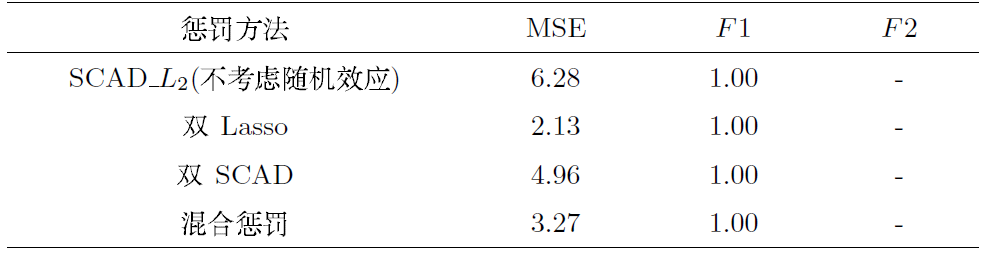
情况 2 稠密模型取
这里均选取相同的
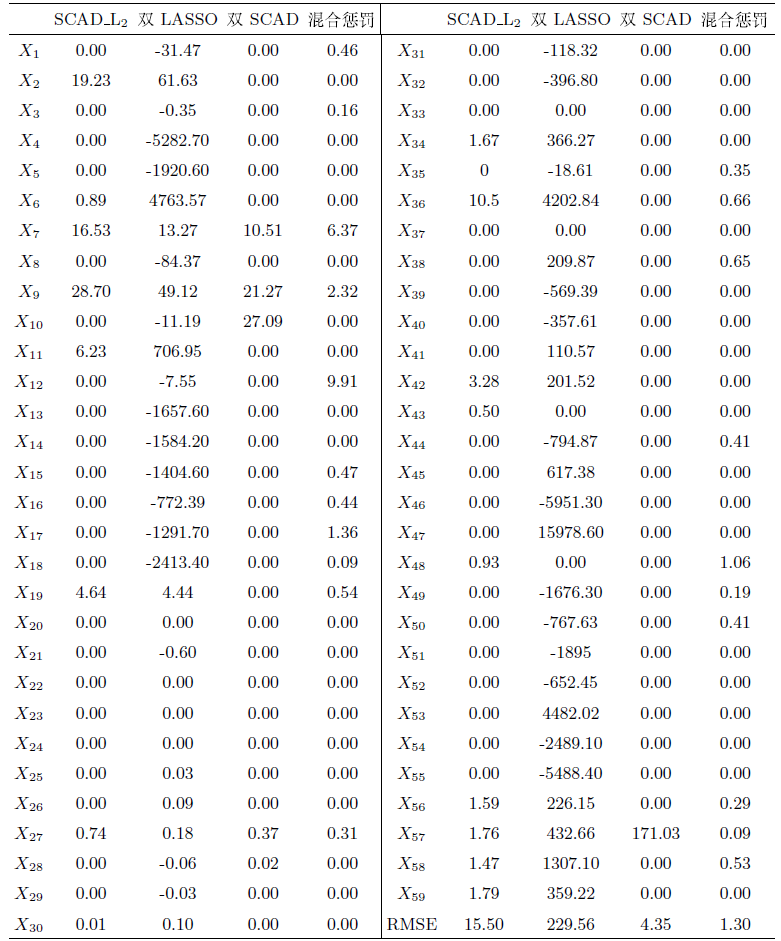
下面将根据表3给出如下模拟结果分析: 从衡量指标MSE的计算结果发现: 双Lasso惩罚方法
下面将根据表4给出如下模拟结果分析: 从衡量指标MSE的计算结果发现: 双Lasso惩罚方法
结合表3-4, 我们可以发现无论是对于高维稀疏模型还是高维稠密模型, 双 Lasso 方法均具有较好的系数估计效果和变量选择能力. 但是从理论上分析, 该方法不具有渐近性质, 故不适用于大样本数据;双SCAD方法对于高维稠密模型更加有效; 此外对于模型(4.1)而言, 仅针对固定效应系数施加惩罚是不够的, 具有一定程度的误差; 而该混合惩罚方法则更加适用于当前热门研究课题中的高维稀疏化模型.
下面从分组效应角度来分析上述不同惩罚方法的效果差异.
4.4.2 分组效应的效果比较
下面将考虑在更高维数的稀疏模型下比较四种不同惩罚方法的分组效果, 这里根据模型 (4.1)生成数据. 为使分组效应[17]在实验中有更明显的结果, 这里需要重新确定各变量的取值, 取
其中
(1) 在高维稀疏模型中, 利用混合惩罚方法所得系数估计结果更加准确, 并且在以每五个相关性很高的变量为一组的情况下, 相应筛选出来的变量系数近似相等且与真实系数最为接近, 即混合惩罚方法表现了很好的分组效果.
(2) 不考虑随机效应的SCAD_L
(3) 在高维稀疏模型下, 无论是对模型(2.1)施加双SCAD惩罚方法还是双Lasso惩罚方法, 所得结果均不具备分组效应.
(4) 结合上述三条分析得出: 对于更高维数的稀疏模型, 混合惩罚方法具有很好的分组效应.综上, 该混合惩罚方法具有很好的分组效应, 表现出更优良的系数估计效果和变量选择能力.
5 实例分析
本节将通过实例验证该混合惩罚方法的统计效果. 本文将混合惩罚方法应用于在线新闻流行度数据集[18]研究中, 该数据集总结了一组关于在两个阶段发布的全球之声文章的异构特性, 其研究目的在于使得所发布的文章在社交网络中获得更多的人气.
本文从HTML代码中提取了一个广泛的特性集, 其描述了文章不同方面的特征, 这些特征被认为可能是影响文章流行度的相关因素, 如表6所示. 其中一些特性依赖于Mashable服务的特殊性: 如文章经常引用在同一服务中发布的其他文章等. 本文还提取了一些自然言语处理的特征, 如LDA算法应用于所有Mashable文本, 并据此确定5个最重要的相关主题, 衡量当前文章与这些主题的密切程度. 这里用
本文借鉴了Fernandes[18]所提出的方法以判断文章是否受欢迎, 这里采用Scikit学习库对预测模型进行拟合, 首先假设一个二元分类任务, 如果其中一篇文章的分享数高于一个固定的决策阈值(这里选用1000), 则认为其是“受欢迎的”, 否则认为是“不受欢迎的”. 对于预测实验, Fernandes在文献[18]中采用了滚动窗口方案, 即取训练窗口大小为10000进行29次迭代, 每次迭代进行1000个样本的预测, 并据此测试了五种分类模型. 结果表明, 随机森林(RF)模型在AUC度量方面的表现最佳, 得到的最佳结果(AUC=0.73)比随机分类器高23%, 达到了较好的辨别水平, 是一个良好的分类器. 本文据此对上述四种不同的分类方法做了相似的实验, 结果表明, 该混合惩罚方法在AUC度量方面的表现最佳, 达到72.8%, 与RF模型的分类水平相近, 表明了混合惩罚在该阈值下同样有较好的分类效果.
根据表7发现针对
综上,该混合惩罚方法具有的优良统计性质有利于筛选出影响在线新闻流行度的相关变量以使发布的文章获得最佳人气.
6 总结与展望
本文对模型(2.1)提出了一种基于SCAD_L
仍有大量工作值得今后继续研究, 如: 将混合惩罚方法进一步应用到随机效应分位回归模型等其他模型中; 对两步迭代算法加以改进以节约模拟实验中计算机的运行时间; 在基因表达和前列腺癌症等实例中验证混合惩罚方法的系数估计和分组效应效果等.
参考文献
高维因子模型及其在统计机器学习中的应用
High-dimensional factor and its applications to statistical machine learning
Flexible modelling of random effects in linear mixed model-a bayesian approach
Predicting the clinical status of human breast cancer by using gene expression profiles
Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net
Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems
DOI:10.1080/00401706.2000.10485983 URL [本文引用: 1]
Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: a retrospective
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-9868.2011.00771.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In the paper I give a brief review of the basic idea and some history and then discuss some developments since the original paper on regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso.
Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties
DOI:10.1198/016214501753382273 URL [本文引用: 2]
Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B
Fixed and random effects selection in mixed effects models
DOI:10.1111/j.1541-0420.2010.01463.x
PMID:20662831
[本文引用: 1]

We consider selecting both fixed and random effects in a general class of mixed effects models using maximum penalized likelihood (MPL) estimation along with the smoothly clipped absolute deviation (SCAD) and adaptive least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (ALASSO) penalty functions. The MPL estimates are shown to possess consistency and sparsity properties and asymptotic normality. A model selection criterion, called the IC(Q) statistic, is proposed for selecting the penalty parameters (Ibrahim, Zhu, and Tang, 2008, Journal of the American Statistical Association 103, 1648-1658). The variable selection procedure based on IC(Q) is shown to consistently select important fixed and random effects. The methodology is very general and can be applied to numerous situations involving random effects, including generalized linear mixed models. Simulation studies and a real data set from a Yale infant growth study are used to illustrate the proposed methodology.© 2010, The International Biometric Society.
基于双SCAD惩罚的随机效应分位回归模型
Random effects quantile regression model based on double SCAD punishment
Joint variable selection for fixed and random effects in linear mixed-effects models
DOI:10.1111/j.1541-0420.2010.01391.x
PMID:20163404
[本文引用: 1]

It is of great practical interest to simultaneously identify the important predictors that correspond to both the fixed and random effects components in a linear mixed-effects (LME) model. Typical approaches perform selection separately on each of the fixed and random effect components. However, changing the structure of one set of effects can lead to different choices of variables for the other set of effects. We propose simultaneous selection of the fixed and random factors in an LME model using a modified Cholesky decomposition. Our method is based on a penalized joint log likelihood with an adaptive penalty for the selection and estimation of both the fixed and random effects. It performs model selection by allowing fixed effects or standard deviations of random effects to be exactly zero. A constrained expectation-maximization algorithm is then used to obtain the final estimates. It is further shown that the proposed penalized estimator enjoys the Oracle property, in that, asymptotically it performs as well as if the true model was known beforehand. We demonstrate the performance of our method based on a simulation study and a real data example.© 2010, The International Biometric Society.
Variable selection in linear mixed effects models
混合效应模型的多惩罚回归过程及其算法收敛性研究
Research of multi-penalty regression process of mixed effects models and its convergence
高维模型选择方法综述
A review of high-dimensional model selection methods
Variable selection in quantile regression
Adaptive elastic net for group testing
DOI:10.1111/biom.12973
PMID:30267535
[本文引用: 1]

For disease screening, group (pooled) testing can be a cost-saving alternative to one-at-a-time testing, with savings realized through assaying pooled biospecimen (eg, urine, blood, saliva). In many group testing settings, practitioners are faced with the task of conducting disease surveillance. That is, it is often of interest to relate individuals' true disease statuses to covariate information via binary regression. Several authors have developed regression methods for group testing data, which is challenging due to the effects of imperfect testing. That is, all testing outcomes (on pools and individuals) are subject to misclassification, and individuals' true statuses are never observed. To further complicate matters, individuals may be involved in several testing outcomes. For analyzing such data, we provide a novel regression methodology which generalizes and extends the aforementioned regression techniques and which incorporates regularization. Specifically, for model fitting and variable selection, we propose an adaptive elastic net estimator under the logistic regression model which can be used to analyze data from any group testing strategy. We provide an efficient algorithm for computing the estimator along with guidance on tuning parameter selection. Moreover, we establish the asymptotic properties of the proposed estimator and show that it possesses "oracle" properties. We evaluate the performance of the estimator through Monte Carlo studies and illustrate the methodology on a chlamydia data set from the State Hygienic Laboratory in Iowa City.© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
A proactive intelligent decision support system for predicting the popularity of online news
Unbiasedness of two-stage estimation and prediction procedures for mixed linear models