1 引言
近年来, 恐惧效应对生物种群的影响引起众多学者的关注. Zanette等[1]通过对鸣禽(Songbirds)的实验研究发现, 在没有直接掠杀的情况下, 仅捕食者的恐惧效应就可导致成年鸣禽每年繁殖后代的数量减少百分之四十. 实验结果还表明, 仅捕食者给食饵带来的掠食风险感知就能在一定程度上影响食饵的行为和生理特征, 并引发连锁反应, 其影响程度甚至超过直接捕杀. 随后, Clinchy和Zanette等[2]提出了适用于野生动物的测量"恐惧神经回路"的实验室技术. 该实验研究表明, 食饵暴露在捕食者面前可以引起食饵的持续心理压力, 以至影响食饵种群规模的大小. 此外, 恐惧效应还存在于许多陆地脊椎动物种群中, 如鸟类[3-10]、麋鹿[11]、雪鞋兔[12]以及儒艮[13].
Wang和Zanette等[14]为了考虑恐惧效应对种群的影响, 首次将恐惧效应引入到捕食-食饵模型中. 基于实验数据, 在食饵出生率项上增加恐惧效应比例系数, 建立了如下具有恐惧效应的生态动力系统:
其中
其中
数值模拟能够直观地展示捕食-食饵系统的动力学现象, 如平衡点的稳定性、Hopf分支和空间斑图等. 李海银[21]考虑了密度制约且具有Beddington-DeAngelis功能反应函数的时滞捕食-被捕食系统, 利用数值模拟对系统稳定性变换和系统的Hopf分支进行了验证. 赵洪涌和张学兵等[22]提出了一种带时滞的生物经济系统, 通过理论和数值模拟展示了系统具有丰富的动力学行为. Pijush等人[23]研究了具有恐惧效应的捕食者-食饵模型, 并数值模拟了时滞使得系统动力学在稳定焦点和极限周期振荡之间多次切换, 对于更高的延迟参数值, 系统最终会进入混乱状态. 张道祥和孙光讯[24]研究了一类带有Holling Ⅲ型功能反应和线性收获效应的时滞扩散捕食者-食饵系统的空间动力学, 利用数值模拟展示了系统具有丰富的动力学行为.
基于以上讨论, 本文将从理论和数值模拟两个方面研究如下带有恐惧效应和时滞的Holling Ⅲ型反应扩散捕食- 食饵系统
其中
系统(1.3)对应的常微分方程(ODE)系统为
本文亮点工作有: (1)首先将时滞效应引入到系统(1.3), 从而首次探讨了恐惧效应对具有Holling Ⅲ型功能反应函数的生态模型Hopf分支的影响. (2)与已有的文献相比, 本文重点展现了恐惧效应
2 模型的稳定性分析
考虑到系统(1.3)的生态学意义, 我们只研究系统(1.3)的正平衡点, 令
则系统的平衡点满足如下方程组
定理2.1 若满足条件
系统(1.3)至少存在一个正平衡点
证 由方程
将其代入
其中
为了使
下面证明方程(2.1)至少存在一个正解
令函数
当
故
当
显然在
由根的存在性定理知, 存在
接下来的讨论, 我们均假设系统(1.3)已存在正平衡点
为了讨论系统(1.3)在正平衡点
系统(1.3)在正平衡点
其中
则系统(2.2)的特征方程为
其中
我们作出如下假设:
定理2.2 对任意
证 当
我们把上述特征方程(2.4)的两个根分别设为
当条件
注2.1 结合上述定理可知, 在不考虑时滞的情况下, 由于条件
3 模型的Hopf分支
本节中, 将时滞作为分支参数, 使用线性稳定性理论分析捕食-食饵系统的Hopf分支问题. 设
分离上述方程的实部和虚部, 我们推出
将方程(3.1), 方程(3.2)的左右两边平方再相加, 得到
令
我们作出如下假设:
定理3.1 对任意
证 我们设方程(3.4)有两个根
当条件
综上所述, 当条件
注3.1 条件
定理3.2 当
证 当
方程(3.5)的两个根
当
由二次函数求根公式, 方程(3.5)的正根为
又由于
定理3.3 当
证 当
因此有
易知, 数列
接下来, 我们讨论系统(1.4)的Hopf分支的横截性条件, 即式
则有
将
显然,
定理3.4 对于系统(1.3), 假设条件
注3.2 由上述定理可知, 恐惧效应参数
4 数值模拟
在这一节里, 我们使用MATLAB软件进行数值模拟, 以此来验证理论推导所得到的关于系统(1.3)的结论. 在所有数值算例中, 由于食饵和捕食者的空间斑图是类似的, 所以仅给出捕食者
4.1 时滞效应对Hopf分支的影响
当系统(1.3)的恐惧效应参数
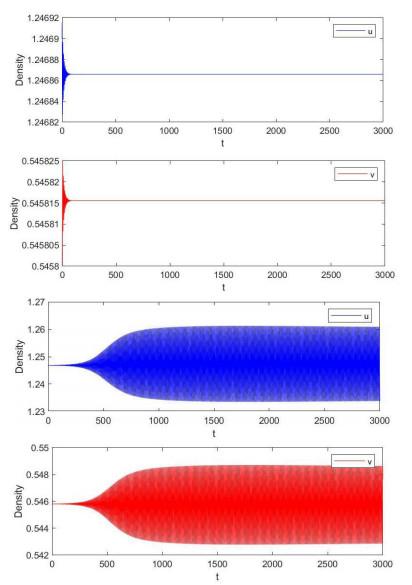
图 1和图 2显示的分别是时滞
图 1
图 1
系统(1.3)的参数:
(a)
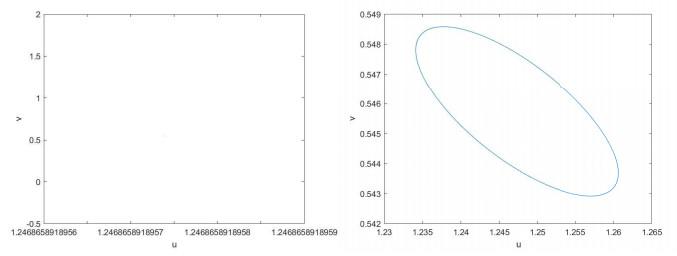
图 2
图 2
系统(1.3)的参数:
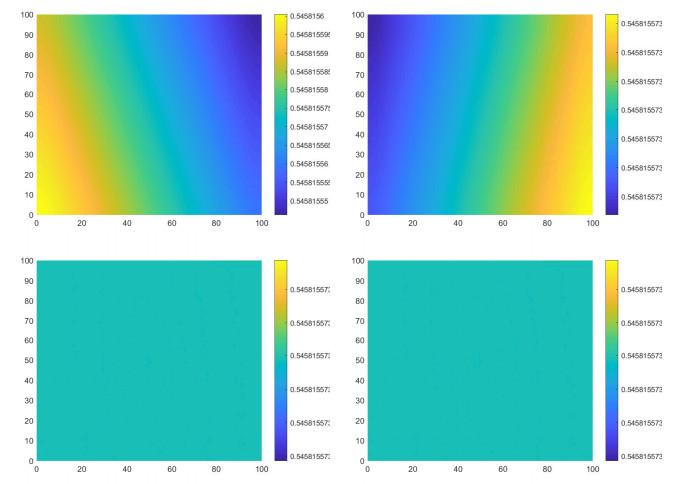
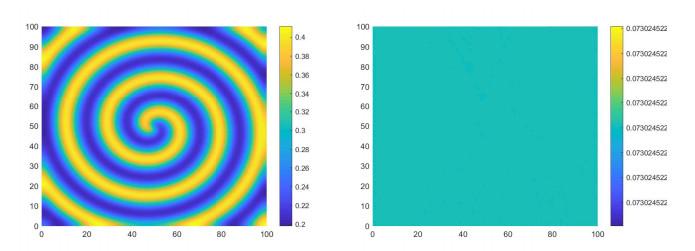
图 3和图 4展示的是捕食者的空间斑图的演化过程, 其中各子图右侧的条状图可作为密度值的参照. 图 3 (
图 3
图 3
系统(1.3)的参数:
(a)
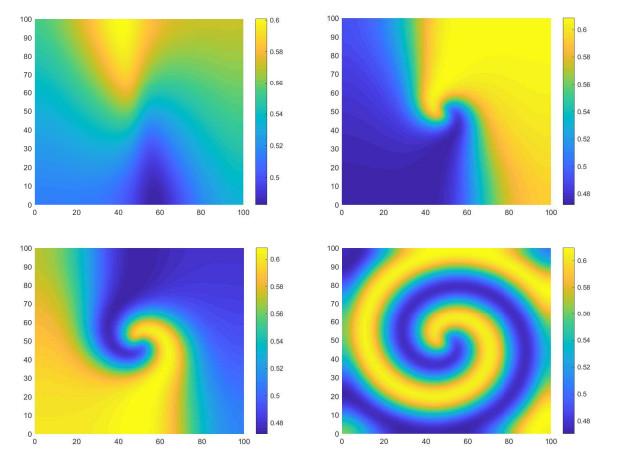
图 4
图 4
系统(1.3)的参数:
(a)
4.2 恐惧效应对稳定区间的影响
在本节的参数条件下, 我们可以根据不同的恐惧效应参数
表 1
系统(1.3)的参数:
| 恐惧交应 | Hopf分支临界值 | 平衡点 |
| 2 | 6.0441 | (1.5819, 0.6418) |
| 3 | 1.9491 | (1.2469, 0.5458) |
| 6 | 1.2727 | (0.9279, 0.3908) |
| 8 | 1.2269 | (0.8453, 0.3354) |
| 9.7 | 1.2199 | (0.7997, 0.3015) |
| 10 | 1.2201 | (0.7931, 0.2964) |
| 10.3 | 1.2205 | (0.7868, 0.2915) |
| 11 | 1.2222 | (0.7733, 0.2808) |
| 13 | 1.2308 | (0.7416, 0.2548) |
| 20 | 1.2732 | (0.6748, 0.1958) |
| 30 | 1.3265 | (0.6269, 0.1501) |
| 40 | 1.3665 | (0.5997, 0.1229) |
| 60 | 1.4222 | (0.5690, 0.0913) |
| 80 | 1.4572 | (0.5517, 0.0730) |
| 100 | 1.4822 | (0.5405, 0.0610) |
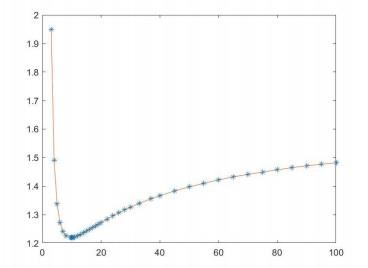
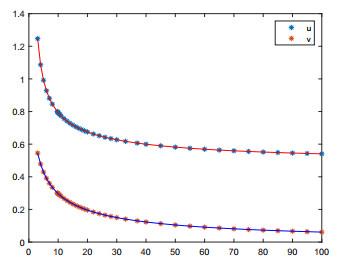
图 5直观地展现了表格1中的结论(1), 即恐惧效应参数
图 5
图 5
系统(1.3)的参数:
图 6
图 6
系统(1.3)的参数:
但恐惧效应的不断增加是否真的对捕食-食饵系统的长期发展有利?接下来, 我们通过图 7展现了表格1的结论(2), 即恐惧效应
图 7
图 7
系统(1.3)的参数:
5 结论
基于恐惧效应对食饵的出生率具有重要的影响, 本文通过理论推导和数值模拟两方面研究了恐惧效应对具有时滞的反应扩散食饵-捕食者系统的Hopf分支和稳定区间的影响. 结果表明:
(1) 不论有无时滞, 恐惧效应均会影响系统正平衡点
(2) 以时滞为参数时, 恐惧效应将影响系统的Hopf分支临界值
(3) 数值模拟结果显示, 系统具有复杂的动力学行为, 如出现了极限环, 螺旋波等现象.
参考文献
Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per year
DOI:10.1126/science.1210908 [本文引用: 1]
Predator-induced stress and the ecology of fear
DOI:10.1111/1365-2435.12007 [本文引用: 1]
Predator-induced plasticity in nest visitation rates in the Siberian jay (Perisoreus infaustus)
DOI:10.1093/beheco/arh163 [本文引用: 1]
Predation risk induces changes in nest-site selection and clutch size in the Siberian jay
Plasticity of parental care under the risk of predation: how much should parents reduce care?
Too risky to settle: avian community structure changes in response to perceived predation risk on adults and offspring
Increased perception of predation risk to adults and offspring alters avian reproductive strategy and performance
Parent birds assess nest predation risk and adjust their reproductive strategies
DOI:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00892.x
An island-wide predator manipulation reveals immediate and long-lasting matching of risk by prey
Predator-induced female behavior in the absence of male incubation feeding: an experimental study
DOI:10.1007/s00265-012-1357-9 [本文引用: 1]
Predation risk affects reproductive physiology and demography of elk
DOI:10.1126/science.1135918 [本文引用: 1]
The sensitive hare: Sublethal effects of predator stress on reproduction in snowshoe hares
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2009.01552.x [本文引用: 1]
A comparison of shark and wolf research reveals similar behavioral responses by prey
Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions
DOI:10.1007/s00285-016-0989-1 [本文引用: 1]
具有Beddington-DeAngelis功能反应及恐惧效应的捕食系统
A predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and fear effect
具有恐惧效应的Ⅰ类功能性反应的捕食系统
Predation systems with a class Ⅰ functional response to the fear effect
Fear effect in prey and hunting cooperation among predators in a Leslie-Gower model
DOI:10.3934/mbe.2019258 [本文引用: 1]
Turing-Hopf bifurcation of a delayed diffusive predator-prey system with chemotaxis and fear effect
Pattern formation of a predator-prey model with the cost of anti-predator behaviors
DOI:10.3934/mbe.2018035 [本文引用: 1]
Nonexistence of nonconstant positive steady states of a diffusive predator-prey model with fear effect
密度制约且具有时滞捕食-被捕食模型的Hopf分支
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.02.015 [本文引用: 1]
Hopf bifurcation of delayed density-dependent predator-prey model
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2019.02.015 [本文引用: 1]
Hopf bifurcation and spatial patterns of a delayed biological economic system with diffusion
DOI:10.1016/j.amc.2015.05.089 [本文引用: 1]
Delay induced multiple stability switch and chaos in a predator-prey model with fear effect
DOI:10.1016/j.matcom.2019.12.015 [本文引用: 1]
带有Holling Ⅲ功能反应和线性收获效应的时滞扩散捕食者-食饵系统Hopf分支和空间斑图
Hopf bifurcation and spatial patterns in a delayed diffusive predator-prey system with Holling Ⅲ functional response and linear harvesting effect