1 引言和主要结果
本文主要考虑(1.1)的如下非局部扩散模型
其中
我们主要考虑系统(1.2)行波解的存在性和不存在性.系统(1.2)的行波解是一个形如
及边界条件
的特殊非负解,其中
定义
及
其中
因
从而
引理1.1 假设
进一步地
(Ⅰ)若
(Ⅱ)若
将
其中
引理1.2 假设
(Ⅰ)存在
(Ⅱ)若
证 (Ⅰ)因
情形1
情形2
情形3
情形4
由以上情形,令
则
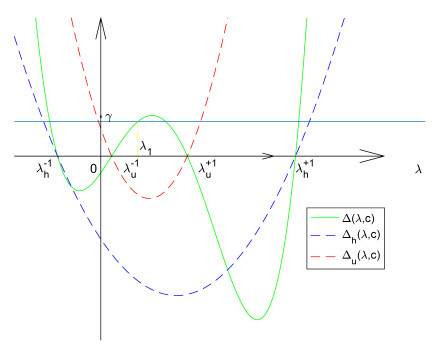
图 1
图 1
对
因
定义
因
利用隐函数定理,
则对
即
这表明
且
若
(II)假设
则
又
同理,可证若
且
现在陈述本文的主要结果.
定理1.1 (ⅰ) (存在性) 设
(H1)
(H2)
则系统(1.2)存在波速为c的行波解
(ⅱ) (不存在性) 设
(NH1)
(NH2)
则系统(1.2)不存在行波解.且若
本文的剩余部分安排如下:第2节致力于证明当波速
2 行波解的存在性
本节将在假设(H2)或
(H1')
因为系统(1.3)的第四个方程是相对独立的,从而只需考虑前三个方程
且满足边界条件
对任意小的正常数
2.1 构造上下解
定义
其中
引理2.1 对所有的
引理2.2 对
及所有的
以上两个引理的证明与文献[30]中的引理2.3、引理2.4相似,此处略去证明.
引理2.3 对充分大的
证 易知,当
从而,当
当
直接计算可得
又
充分大和充分小的
2.2 辅助问题
定义
其中
进一步地,对所有的
考虑以下系统
及初值条件
定义算子
其中
引理2.4 算子
引理2.4的证明类似于文献[27,定理2.6],故略去.
由于
要得到系统(2.3)在边界条件(2.2)下解的存在性,需要对
引理2.5 对给定
其中
证 由
且
其中
进一步地,对所有的
现在证明
则
且
同理可得
且
其他情形可类似证明.证毕.
2.3 行波解存在性的证明
引理2.6 对给定
进一步地,有
证 令
的递增序列,且当
且
在
则
进一步地,由(2.6)式可得
下面,为了叙述方便,令
事实上,假设存在某个
又
从而,由以上方程可得对
下面证明
首先证明
由系统(2.5)的第一个方程可得
从而
此外,
令
从
又
从
且
从而
且
同理
最后证明
从
从而,
定理2.1 假设(H1')或(H2)成立.则系统(2.1)存在满足边界条件(2.2)的波速为
证 令系列
由引理2.5和2.6的证明,可得
同理,存在与
从而,
在
下证
又
从而,
又
满足相应的边界条件.即
证毕.
3 c=c^{*}
假设
引理3.1 存在某个正常数
证 首先,将系统(2.1)第二个和第三个方程分别乘以
令
最后一个不等式由
可得.令
这表明
且
在(3.2)式两边从
定义
可得
又
从而,由(3.3)和(3.4)式,易得
又因为
可证得最终结论.证毕.
引理3.2 令
证 假设存在序列
且由
另一方面,由系统(1.2)的第一个方程,有
这与
下述引理是文献[29,命题3.7]的特殊情形.
引理3.3 假设
的可测非常数函数,则
的正根.
由引理3.3,可得到一个重要引理.
引理3.4 设
的可测函数.则
其中
证 由引理3.3,存在
因
可得
又
从而由引理3.3,当
注意
下面证明
对任意序列
对(3.8)式,讨论可以分为以下两种情况.
情形1
若存在一个常数
由引理3.3, (3.6)和(3.9)式,可得
其中
结合(3.5)和(3.8)式,不难得到
情形2
选取
即
根据情形1和情形2, (3.7)式成立.
同理可得
证毕.
现在用渐近法来证明结论.不失一般性,可以选取一列严格递减序列
引理3.5 序列
证 假设当
当
定理3.1 若
证 注意到
这表明
将
且
同理,由引理2.6中的讨论,可得
使得
接下来,分两步证明.
步骤1
现在证明
利用(3.11)式和文献[29,命题3.6],存在正常数
其中
注意
由
对所有的
此外,
则
注意
则
另一方面,由
同理,由文献[29,命题3.6],由(3.13)式的第一个方程可得
另一方面,令
从而,由引理3.4,对充分大的
其中
的两个正根.
的两个正根.再由文献[29,命题3.6],易得存在正常数
下一步,令
对充分大的
的两个正根,且
的两个正根.令
从而,由(3.16)式可得
由于
这表明
步骤2
首先,假设存在
这与
其次,要证
由
又
令
又
矛盾.另一方面,由引理2.5的类似讨论可得
4 行波解的不存在性
在本节中,主要考虑行波解的不存在性.准确地说,通过双边拉普拉斯变换得到了当
4.1 R_{0}>1
现在证明以下引理.
引理4.1 假设(NH1)或(NH2)成立.若
证 由
以上不等式两边同乘
令
从
进一步地,通过简单计算可得
从而对任意
易得
又
同理可得
将(4.3)式和(4.4)式相加,有
又
令
从而存在一个正常数
因此,对任意
令
从而,由
对一切
又
可得
即
同理可证,
定理4.1 假设(NH1)或(NH2)成立,则系统(1.3)不存在波速为
证 首先,对
显然
令
根据引理4.1,
令
其中
下面证明
又
进一步地,下证
则由
这与(4.7)式的第二个等式矛盾.从而,
这与(4.8)式矛盾.证毕.
4.2 R_{0}<1
定理4.2 假设
证 假设对所有
可得
由Fubini定理,可得
把以上不等式代入(4.9)式,得到
从而
又
即
从而
矛盾.证毕.
参考文献
A model for influenza with vaccination and antiviral treatment
DOI:10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.02.026 [本文引用: 1]
A vaccination model for transmission dynamics of influenza
DOI:10.1137/030600370 [本文引用: 1]
Uniqueness and existence of traveling waves for discrete quasilinear monostable dynamics
DOI:10.1007/s00208-003-0414-0 [本文引用: 1]
Travelling wave solution for an infection-age strutured model with diffusion
DOI:10.1017/S0308210507000455 [本文引用: 4]
Travelling wave solutions in Mltigroup Age-Structured Epidemic Models
DOI:10.1007/s00205-008-0203-8 [本文引用: 1]
Travelling wave solution for an infection-age strutured epidemic model with external supplies
DOI:10.1088/0951-7715/24/10/012 [本文引用: 1]
Uniqueness and existence of traveling waves for discrete quasilinear monostable dynamics
DOI:10.1007/s00208-003-0414-0 [本文引用: 1]
Strategies for mitigating an influenza pandemic
DOI:10.1038/nature04795 [本文引用: 1]
Traveling waves of a simple diffusive epidemic model
DOI:10.1142/S0218202595000504 [本文引用: 1]
Traveling waves in a model of influenza a drift
DOI:10.1016/S0022-5193(03)00056-0 [本文引用: 1]
Antiviral resistantce and the control of pandemic influenza
DOI:10.1371/journal.pmed.0040111 [本文引用: 2]
Traveling waves for a nonlocal dispersal SIR model with delay and external supplies
The role of population heterogeneity and human mobility in the spread of pandemic influenza
DOI:10.1098/rspb.2009.1605 [本文引用: 1]
Dynamics of two-strain influenza with isolation and partial crossimmunity
DOI:10.1137/S003613990343882X [本文引用: 1]
Asymptotic estimates of the the solutions of nonlinear integral equations and asymptotic speeds for the spread of populations
Asymptotic speeds of spread and traveling waves for integral equations and delayed reaction-diffusion models
DOI:10.1016/S0022-0396(03)00175-X
Existence of traveling waves with the critical speed for a discrete diffusive epidemic model
DOI:10.1016/j.jde.2016.09.022 [本文引用: 1]
Traveling waves in a nonlocal dispersal SIR model with nonlocal delayed transmission
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.03.005 [本文引用: 1]
Traveling waves of diffusive predator-prey systems:disease outbreak propagation
Traveling waves of the spread avian influenza
DOI:10.1090/S0002-9939-2012-11246-8
Asymptotic speed of spread and traveling waves for a nonlocal epidemic model
Travelling waves in a nonlocal dispersal Kermack-Mckendrick epidemic model
DOI:10.3934/dcdsb.2013.18.1969 [本文引用: 3]
Traveling waves in a nonlocal dispersal SIR epidemic model
DOI:10.1016/j.nonrwa.2014.12.001 [本文引用: 3]
Traveling waves in a nonlocal dispersal SIR epidemic with critical wave speed
DOI:10.1016/j.jmaa.2017.10.016 [本文引用: 1]
Spreading speed and traveling waves for nonlocal dispersal equations with degenerate monostable nonlinearity
DOI:10.1016/j.jde.2012.01.014 [本文引用: 4]
Existence of traveling wave solutions for influenza model with treatment
DOI:10.1016/j.jmaa.2014.04.068 [本文引用: 5]