1 引言
该文基于POD理论和矩阵分解,通过引入均值场的相关矩阵,研究了均值场对整个信号和信号波动部分的影响机制.采用数值算例验证了均值场对POD过程的影响.虽然均值场不影响POD算法的分解和重构过程,但由两种不同类型的信号(如选择适当的模态)所获得的参数都深刻受到其影响而差别很大,原因在于所获得的参数反映了原始信号,这两种不同信号不应被混淆.使用全信号时,所得参数受均值场影响而失真,尤其是低阶模态.在实际应用中,信号的均值场和波动部分有时单独被使用,因此在POD过程中,使用去除均值的信号是非常实用的,这可以避免均值场对算法的影响,从而保持原始信号的特性.
2 奇异特征值分解算法(POD)
为了方便而不失一般性,假设
矩阵
为了区别,记
其中
其中
因此
到目前为止,很少有文献提到时间系数集合
3 均值场的影响
为了分析均值对POD方法的影响,须深入分析POD结果的组成.由
定理3.1 在奇异特征分解过程中,对于任意原始信号
证 由
因而
证毕.
定理3.2 对于任意
证 由方程(2.6)以及正交集和
证毕.
定理3.3 对于任意
证 设
由于
因此
所以
证毕.
由定理3.3的结论,可以很容易地建立一个平均值获得任意能量的矩阵.
定理3.4 矩阵
证 均值矩阵
如果
因此
证毕.
由
推论3.1 矩阵
4 数值例子
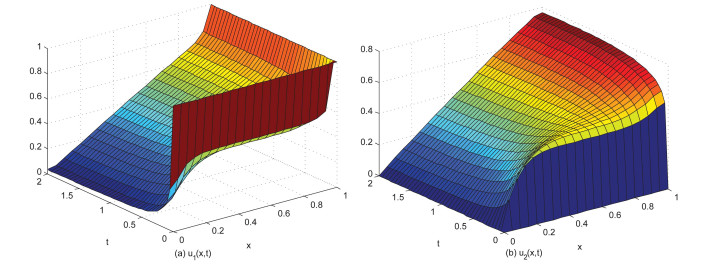
为说明均值对奇异特征分解算法的影响,考虑下面的非线性微分方程初边值问题:求
其中
图 1
本节中,给出并比较了两种试验方案.方案1:将解函数
作为一个整体函数进行POD分解.方案2:将解分量
表 1
矩阵
| 模态数 | ||||||
| 1 | 410(96.2) | 229(97.2) | 189(99.1) | 13.4(82.4) | 8.8(89) | 4.7(74.9) |
| 2 | 13.4(3.14) | 6.2(2.61) | 1.6(0.83) | 2.8(17) | 1.0(10.4) | 1.6(24.78) |
| 3 | 2.8(0.65) | 0.45(0.19) | 0.02(0.01) | 0.08(0.5) | 0.06(0.57) | 0.02(0.31) |
| 4 | 0.068(0.02) | 0.038(0.02) | 7e-4(3.8e-4) | 1.1e-2(0.07) | 2e-4(0.02) | 7e-4(0.01) |
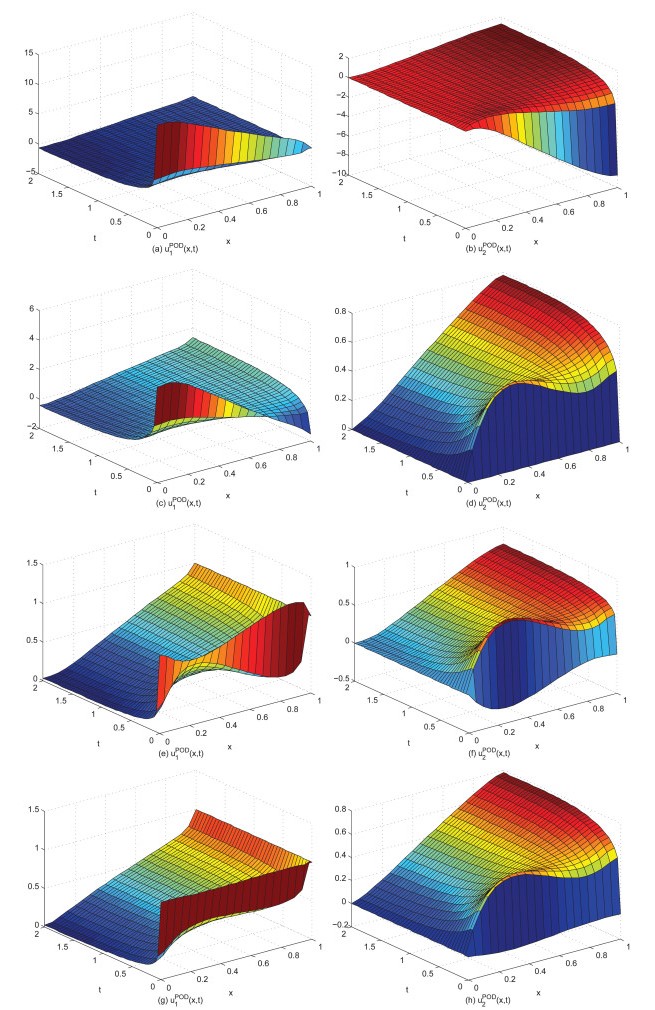
图 2
(1)显然,即使
(2)如果研究的信号中含有不同频率的组成成分,则不应将研究的信号视为一个整体,将其组成成分单独进行POD分解,重构效果更好.
为了更加具体地分析均值的影响,引入如下几种范数来衡量POD重构解与真解之间的误差.
表 2 全信号及去除均值部分信号重构解的最大绝对误差
| 模态数 | ||||||
| 1 | 0.77 | 0.49 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| 2 | 9.7e-2 | 1.7e-2 | 6.6e-3 | 1.3e-2 | 7.1e-3 | 2.3e-3 |
| 3 | 1.2e-2 | 1.3e-2 | 2.6e-3 | 1.3e-2 | 4.7e-3 | 1.3e-3 |
| 4 | 8.9e-3 | 4.7e-3 | 5.5e-4 | 6.5e-3 | 2.6e-3 | 5.5e-4 |
表 3 全信号及去除均值部分信号重构解的最大相对误差
| 模态数 | ||||||
| 1 | 21.1 | 14.0 | 0.42 | 0.95 | 0.36 | 0.41 |
| 2 | 0.97 | 0.49 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.37 | 0.10 |
| 3 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| 4 | 2.3e-2 | 8.0e-2 | 1.1e-2 | 2.1e-2 | 3.8e-2 | 1.1e-2 |
表 4
全信号及去除均值部分信号重构解的
| 模态数 | ||||||
| 1 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| 2 | 3.2e-1 | 3.9e-2 | 1.6e-2 | 4.8e-2 | 3.1e-2 | 1.6e-2 |
| 3 | 3.0e-2 | 2.5e-2 | 6.0e-3 | 2.7e-2 | 7.7e-3 | 6.0e-3 |
| 4 | 1.4e-2 | 7.7e-3 | 1.4e-3 | 4.8e-3 | 3.0e-3 | 1.4e-3 |
5 结论
该文主要研究了POD方法中的时间系数集合
(1)基于POD方法的理论和矩阵分析,通过引入全信号和去除均值部分信号的相关矩阵,分析了均值对POD方法的影响机制,比较了全信号和去除均值部分信号重构解的结果,推导出这两种信号之间的关系,最后使用一个数值例子来说明这一理论的合理性.首先消除信号的均值部分对整体信号重建的影响,这就是为什么大多数研究人员在实际应用中使用选择去除均值部分信号的原因.
(2)在POD方法中,无论随机场是否包括均值,求得的时间系数集合都是正交的.因此,可以使用不同个数的空间模态来重构原始随机场.如果使用所有空间模态,所得重构解将是真解.
(3)虽然均值场不影响POD过程中的分解和重构,但是否去除均值,所得的奇异特征值、空间模态和主坐标等参数都差别很大,因此,在实际应用中,不该混淆这些系数的物理意义.
(4)仅使用一阶空间模态来重构解是远远不够的,即使最大奇异特征值能捕获任意多的系统能量.
参考文献
Statistics in function space
On the physcal interpretation of proper orthogonal modes in vibrations
DOI:10.1006/jsvi.1997.1386 [本文引用: 1]
Experimental measurements of dimensionality and spatial coherence in the dynamics of a flexible-beam impact oscillator
Identification of muscle determinant for different gait speeds by proper orthogonal decomposition
Using svd to detect damage in structures with different operational conditions
DOI:10.1006/jsvi.1999.2305 [本文引用: 1]
Proper orthogonal decomposition and its applicaitons-part Ⅰ:Theory
DOI:10.1006/jsvi.2001.4041 [本文引用: 1]
Proper orthogonal decomposition of roof pressure
DOI:10.1016/0167-6105(93)90057-U [本文引用: 1]
Proper orthogonal decomposition and reconstruction of multichannel roof pressure
DOI:10.1016/0167-6105(94)00066-M [本文引用: 1]
Spatial extrapolation of pressure time series on low buildings using proper orthogonal decomposition
DOI:10.12989/was.2004.7.6.373 [本文引用: 1]
Proper orthogonal decomposition of random wind pressure field
DOI:10.1006/jfls.1999.0242 [本文引用: 1]
An introduction to proper orthogonal decomposition
Reduced order modeling of the upper tropical pacific ocean model using proper orthogonal decompositon
DOI:10.1016/j.camwa.2006.11.012
A POD-based reduced-order TSCFE extrapolation iterative format for two-dimensional heat equations
A class of three-weight linear codes and their complete weight enumerators
A pod reduced-order spdmfe extrapolating algorithm for hyperbolic equations
DOI:10.1016/S0252-9602(14)60056-4