1 引言
随着现代工业和农业的迅速发展,大量的毒物和污染物进入了全球生态系统.因此,环境污染是最重要的一个社会生态问题.环境中各种有毒物质的存在对无保护种群的生存有着极大的威胁,有毒物质的无控制输入将会导致种群走向灭绝,所以环境污染下种群的持续生存问题,成为了生物数学研究的又一个热门课题.目前,已有许多学者对此做了大量的研究,得到了许多成果[1-6].同时,我们注意到,在现实环境中,存在许多随机或偶然的因素影响着生物种群的变化[7-11],比如:地震,洪水,海啸等会对种群产生瞬时的影响,而环境噪声会不断在不同程度上影响着种群的增长率、环境容量、竞争系数和系统的其他参数.因此,研究随机环境下具有脉冲效应的种群动力学行为,得到广大学者的青睐.
其中
在本文中,我们总假设
2 预备知识
给出本文所需要的定义、引理、定理和一些记号如下:
设
的解,其中
定义2.1[14] (1)若种群
(2)若种群
(3)若存在常数
(4)若存在常数
定义2.2[14] 设
均成立,则称
考虑如下非自治随机单种群Logstic模型
其中
引理2.1[15] 系统(2.1)存在以
引理2.2[16] 系统
存在一个正周期解
其中
引理2.3[11] 设
(1)若存在正数
成立,其中
(2)若存在正数
成立,其中
定理2.1[14](伊藤公式) 设
其中
3 主要结论
定理3.1 对于任意给定的初值
证 由系统的第一个方程知
构造比较系统
由引理2.1知系统(3.1)存在唯一全局连续正解如下
再由随机微分方程的比较定理得
由系统(1.1)的第二个方程和(3.2)式知
构造比较系统
易知系统(3.3)存在唯一的全局连续正解
根据随机微分方程的比较定理可知
最后,由系统(1.1)的第三个方程, (3.2)和(3.4)式知
构造如下比较系统
根据引理2.2,可得上述脉冲微分方程的全局渐近稳定周期解为
由脉冲微分方程的比较定理得
因此,由(3.2), (3.4)和(3.6)式可知,对任意的初始值
定理3.2 如果
证 定义
当
对上式两边取期望有
易知
由于
另一方面,由(3.8)式可知
结合(3.9)和(3.10)式可知,若考虑如下脉冲微分方程
则系统(3.11)的解为
其中
由脉冲微分方程比较定理得
即系统是均值有界的.
为进一步研究系统,令
由引理2.2知系统(3.12)存在唯一正周期解
显然,在任意脉冲区间
定理3.3 如果系统(1.1)满足
则系统(1.1)的边界周期解
证 由系统(1.1)的第三个式子可知
因此考虑如下脉冲微分方程
由脉冲微分方程比较定理得
即,对任意小的
成立.
构造比较系统
利用伊藤公式,沿着系统(3.14)对
两边从
由于
当
因此当
由于
所以当
则对任意的
构造比较系统
利用伊藤公式,沿着系统(3.17)对
两边从
由于
由于
又因为
同理可证,当
因此,当
定理3.4 当
则种群
证 结合系统(3.15)和脉冲微分方程比较定理可得:
将上式代入
有
其中
由(3.20)和(3.21)式可知
令
上式两端同时从
整理得
上式两端同时取对数有
两端同时除以
由洛必达法则可得
其中
则当
同理,沿着系统的解对
两端同时从
由
则
定理3.5 当
其中
证 考虑系统
根据文献[17]及任意小的
由微分方程的比较定理,可知
根据系统(1.1)的第一个等式和(3.23)式,对
由(3.25)式可得
即
结合(3.26)式对系统(1.1)的第二个式子运用伊藤公式可得
由(3.24)式可知,对任意的
则对任意的
其中
由引理2.3和
证毕.
4 数值模拟与结论
令周期数
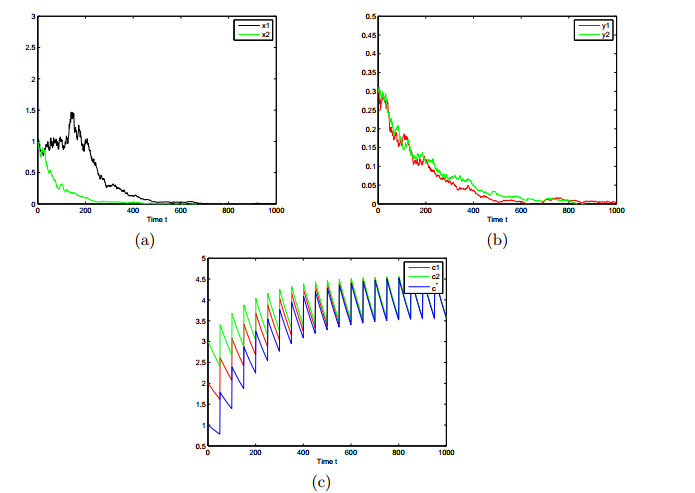
(1)令脉冲值
图 1
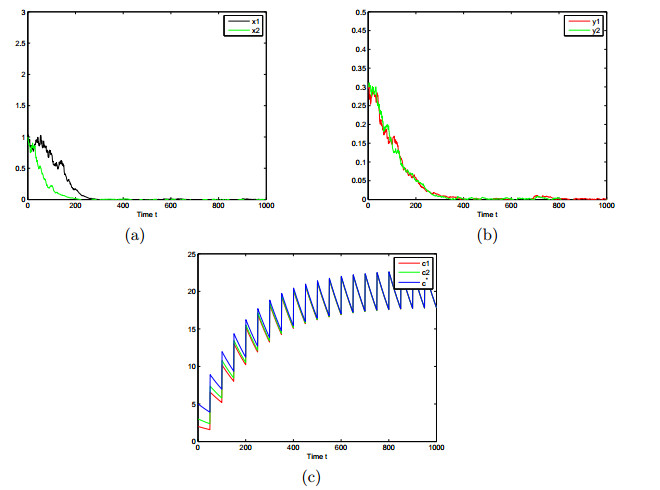
(2)令脉冲值
图 2
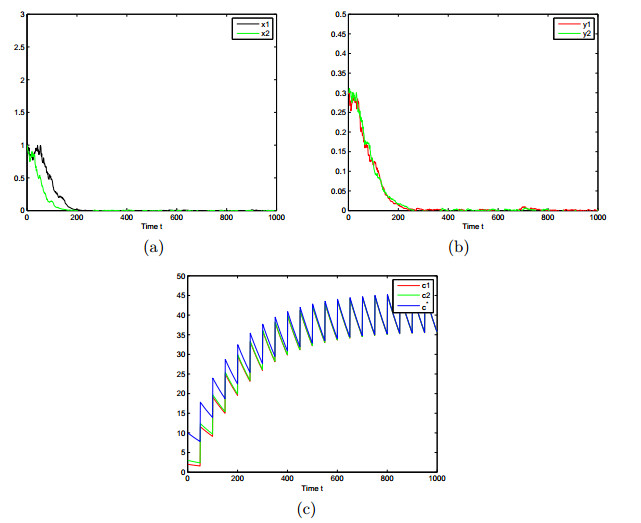
(3)令脉冲值
图 3
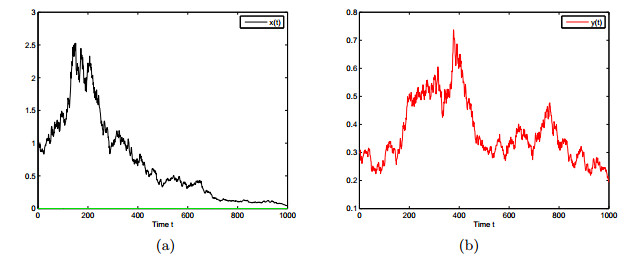
(4)令脉冲值
图 4
5 小结
本文通过研究周期脉冲毒素输入的随机捕食-食饵系统,证明了系统的均值有界性,全局正解的存在唯一性,并得到种群灭绝与持续生存的阈值
(1)当
(2)当
(3)当
由理论结果和数值模拟可知,当脉冲毒素输入超过一定阈值
参考文献
The effect of Lévy noise on the survival of a stochastic competitive model in an impulsive polluted environment
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2016.01.056 [本文引用: 1]
Dynamic of a delayed predator-prey model with birth pulse and impulsive harvesting in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2014.12.003
Psychological effect on single-species population models in a polluted environment
Optimal harvesting policy of a stochastic two-species competitive model with Lévy noise in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2017.02.019
Persistence and extinction of an n-species mutualism model with random perturbations in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2017.08.083
Periodic solution for a stochastic non-autonomous competitive Lotka-Volterra model in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2016.12.008 [本文引用: 1]
Dynamics of the stochastic Leslie-Gower predator-prey system with randomized intrinsic growth rate
Stationary distribution and periodic solutions for stochastic Holling-Leslie predator-prey systems
Dynamics of stochastic predator-prey models with Holling Ⅱ functional response
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2016.01.005
Stochastic persistence and stationary distribution in an SIS epidemic model with media coverage
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2017.11.137
Survival analysis of a stochastic cooperation system in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1142/S0218339011003877 [本文引用: 2]
具脉冲输入毒素的单种群随机干扰模型
A single population model in a polluted environment with pulse toxicant input and random perturbations
Study of chemostat model with impulsive input and nutrient recycling in a polluted environment
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2010.09.030 [本文引用: 1]
Global stability and stochastic permanence of nonautonomous lodistic equation with random perturbation
DOI:10.1016/j.jmaa.2007.08.014 [本文引用: 1]
Qualitative analysis of a stochastic ratio-dependent predator-prey system
DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2010.08.021 [本文引用: 1]
Stationary distribution and periodic solution for stochastic predator-prey systems with nonlinear predator harvesting
DOI:10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.11.014 [本文引用: 1]