1 引言
流行性传染病的传播是医学界、生物学界、生态环境学界十分关注的对象.特别是非典病毒、埃博拉病毒、艾滋病毒等.这些病毒在人类和生物界的传播,值得人们广泛地重视.它对人类健康和生态环境带来了严重的威胁.关于病毒传播的研究,最初局限于采用一些观察和简单的数据统计来分析与推断.但它不能较有效的反映病毒传播的本质.近来,对流行性传染病病毒的传播研究和讨论,在国内、外学术界已经将它们归纳转化为数学物理动力学研究的方法[1-8].即归纳为一个能反映它的基本规律的数学物理非线性微分方程动力学系统模型,然后利用数学物理的解析方法来求出相应动力学系统的解.将求得的结果作为依据,结合医学、生态、生物、数学物理等交叉学科理论,来综合研究它们的动态规律.最后对有关生态物理量预测.本文就是以相应的一个非线性动力学的系统模型为基础,用近代数学物理中的理论工具,从生态医学的观点来讨论流行性传染病的传播规律.
2 流行性病传播动力学系统模型
考虑如下流行性病传播人群生态动力学的数学物理系统模型
其中
3 泛函分析同伦映射
为了使用泛函映射方法得到流行性病传播人群的生态动力学微分系统的模型(2.1), (2.2)的渐近解,令
其中
显然,由(3.2)-(3.3)式知,
首先选取原动力学系统(2.1), (2.2)的初始函数
的解.且由(3.6)和(3.7)式,初始值为
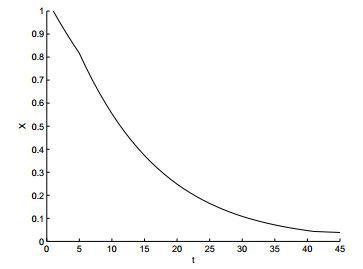
图 1
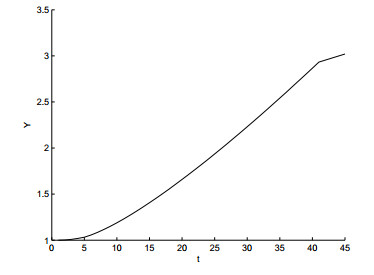
图 2
4 动力学模型渐近解
将(3.1)式代入(3.2)和(3.3)式,展开非线性项关于
显然,我们可取
由动力学模型(2.1), (2.2)解的零次近似(4.2), (4.3)及泛函分析同伦映射(3.2), (3.3)可得
其中
由(3.1), (4.2), (4.3), (4.6), (4.7)式知,令
由动力学系统模型(2.1), (2.2)解的零次近似(4.2), (4.3)及(4.6), (4.7)式和泛函分析同伦映射(3.2), (3.3)可得
其中
由(3.1), (4.2), (4.3), (4.6), (4.7), (4.12), (4, 13)式知,令
同样可得流行性病传播人群的生态动力学微分系统(2.1), (2.2)解的
在相应的条件下,关于
就是生态动力学微分系统(2.1), (2.2)的一组精确解
就是非线性微分动力学系统(2.1), (2.2)的一组第
5 动力学系统模型解的讨论
为了简单起见,设流行性病传播人群的生态动力学微分系统(2.1), (2.2)的无量刚参数为
利用泛函分析同伦映射(3.2), (3.3)和关系式(3.1),可得
其中
所以由(3.1)和(5.3)-(5.8)式,可得到生态动力学微分系统(5.1), (5.2)的零次,一次,二次渐近解
上述
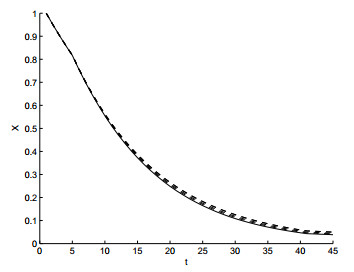
图 3
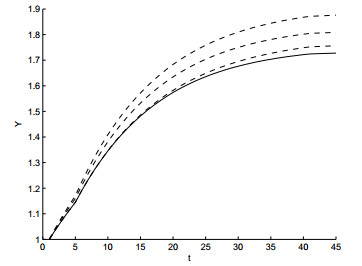
图 4
6 动力学系统模型解的意义与结论
(1)流行性病传播人群的生态系统是一个相当复杂的现象.把它简化为数学物理的动力学模型,然后用非线性近代数学物理学的处理方法来得到足够精度的渐近解.这是研究流行性病传播人群的传播问题的一个有效的途径.
(2)从数学理论来看,泛函分析同伦映射方法是一个数学物理的解析方法.它不同于通常的数值求解,更不是一个简单的模拟方法.由本方法得到解的解析表示式,还能继续进行解析运算.我们还能对得到的渐近解析表示式进一步进行定性和定量的研究.例如,可用微分的方法算出感染者和易感染者数量的变化速度、画出上述两者的变化曲线,从中发现其变化规律,并预报出感染者和易感染者在一定时期内的数量和发展趋向等规律.又譬如,我们还可以从足够精度的渐近表示式出发,分别对模型参数
参考文献
Will a large complex system be stable
DOI:10.1038/238413a0 [本文引用: 1]
Biological populations with nonoverlapping generations:stable point, stable cycles and chaos
DOI:10.1126/science.186.4164.645
Energetics, patterns of interaction strengths and stability in real ecosystems
DOI:10.1126/science.269.5228.1257
An age-structured model for the AIDS epidemic
DOI:10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00288-X
The differential infectivity and staged progression models for the transmission of HIV
An age-structured model for the AIDS epidemic
The summary of dynamic models for HIV transmission
Singular perturbation of N-front traveling waves in the Fitzhugh-Nagumo equations
Kinetic decomposition for singularly perturbed higher order partial differential equations
Coexistence of a pulse and multiple spikes and transition layers in the standing waves of a reaction-diffusion system
Global behavior of solutions of a reactio n-diffusion equation with gradient bsorption in unbounded domains
Regularization of discontinuous vector fields on R3 via singular perturbation
Periodic traveling waves for diffusion equations with time delayed and non-local responding reaction
Fast reaction limit and large time behavior of solutions to a nonlinear model of sulphation phenomena
On a singular perturbation problem for a class of variational inequalities
The corner layer solution of Robin problem for semilinear equation
Homotopic mapping method of solitary wave solutions for generalized complex Burgers equation
A class of nonlinear singularly perturbed problems for reaction diffusion equations with boundary perturbation
The singularly perturbed nonlocal reaction diffusion system
A class of singularly perturbed differential-difference reaction diffusion equation
Homotopiv mapping solving method for gain fluency of a laser pulse amplifier
Approximate solution of homotopic mapping to solitary wave for generalized nomlinear KdV system
DOI:10.1088/0256-307X/26/1/010204
Singularly perturbed reaction diffusion problem for nonlinear boundary condition with two parameters
DOI:10.1088/1674-1056/19/1/010203
一类广义非线性扰动色散方程孤立波的近似解
Approximate analytic solution of solitary wave for a class of nonlinear disturbed Nizhnik-Novikov-Veselov system
双参数非线性非局部奇摄动问题的广义解
Generalized solution of nonlinear nonloacl singularly perturbed problems with two parameters
分数阶双参数奇摄动非线性微分方程的渐近解
Asymptotic solution for the fractional order singularly perturbed nonlinear differential equation with two parameters
一类海-气振子模型的微扰解
Small perturbed solution for a class of the sea-air oscillator
一类量子等离子体类孤波的近似解析解
Approximate analytic solution of solitary-like waves in a class of quantum plasma
An elementary introduction to recently developed asymptotic methodsand nanomechanics in textile engineering
DOI:10.1142/S0217979208048668 [本文引用: 1]