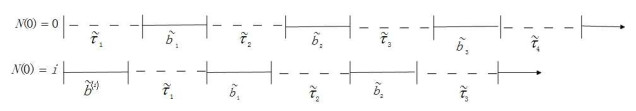
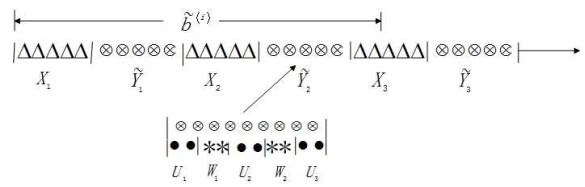
1 引言
自从1982年曹晋华和程侃[1]对
1) 顾客相继到达的间隔时间序列
2) 系统采取延迟的Min(
3) 系统中有一个服务台,服务台的寿命为
4) 在修理故障服务台的过程中,修理设备本身也可能发生失效,其使用寿命
5) 到达的间隔时间
6) 服务台和修理设备在空闲期间(没有使用的时间)内是不会发生故障,也不会影响寿命,即处于冷储备状态.
2 系统的排队指标
令
与
而且平均"广义修理时间"为
其中,
注2.1 下面类似的记号表示上面相应的含义.
令
与
而且平均"广义服务时间"为
引理2.1 如果我们把
因此本文研究的系统的排队指标可按文献[22]的讨论方法得到.为节约篇幅,本文只列出后面讨论要用到的结果.
设
推论2.1[29] 对
其中,
又令
3 系统有关可靠性指标
3.1 服务台的不可用度
首先,考虑一个经典的单部件可靠性系统[24],部件的工作寿命
引理3.1[24] 对
且有平稳结果
有了以上准备后,下面讨论服务台的不可用度.对
其中,
定理3.1 对
且平稳结果为
其中
证 1) 根据模型描述,服务台在系统闲期内不失效,而且在每个"广义忙期"的开始时刻服务台都正常,所以时刻
其中,
2) 类似文献[23]定理3.2中(3.17)式的推导,用
于是
3) 将(3.6)式代入(3.4)式,并对(3.4)-(3.6)式作拉普拉斯变换,整理即可得到(3.1)与(3.2)式.
4) 再根据
即可得证.
3.2 在时间 (0, t]
定理3.2 对
且平稳结果为
证 1) 显然,有
对
其中
2) 类似文献[23]定理3.3中(3.27)式的推导,用
于是
3) 将(3.12)式代入(3.11)式,并对(3.10)和(3.11)式作拉普拉斯-斯蒂尔切斯变换,整理即可得(3.7)-(3.8)式.
4) 再根据
4 修理设备的可靠性指标
4.1 修理设备的不可用度
修理设备的"广义忙期":是指修理设备从开始修理失效服务台的时刻起,直到服务台被修复好的这段时间,其中包括了因修理设备本身发生故障而进行更换(修理)的时间.显然,修理设备的"广义忙期"长度就是服务台的"广义修理时间"长度
为了讨论修理设备的不可用度,我们作如下准备.
首先,考虑修理设备的寿命
图 1
对
引理4.1[24] 对
而且平稳结果
证 由修理设备的寿命
其次,在修理设备的"广义忙期"期间,修理设备的寿命
图 2
其中,
其中
因此可得如下引理4.2.
引理4.2 对
其中,
又考虑
图 3
修理设备在服务员对顾客进行服务的"广义忙期"长度
对于交替更新过程
引理4.3 对
而且平稳结果
证 由图 3,可得
其中
对
同样,因为修理设备只在"广义忙期"
其中,
图 4
其中,
对
下面我们来讨论在该文系统中修理设备的不可用度.对
定理4.1 对
且平稳结果为
证 1) 由模型的假设可知,修理设备只在它修理故障服务台的期间才可能发生故障,即在修理设备的"广义忙期"中才可能发生故障,而且形成正常、失效(更换)的交替更新过程,因此,时刻
图 5
于是对
其中
2) 由于修理设备在服务台的每个忙期的开始和结束时刻都是正常的,而且在服务台的广义忙期
图 6
于是得到
3) 将(4.6)式代入(4.4)式,并对(4.4)式和(4.5)式作拉普拉斯变换,整理即可得(4.1)-(4.2)式.再根据
4.2 修理设备在(0, t]
对
定理4.2 对
且平稳结果为
证 1) 显然,有
对
其中
2) 类似文献[17]定理2中(33)式,用
于是得到
其中
3) 将(4.12)式代入(4.11)式,并对(4.10)和(4.11)式作拉普拉斯-斯蒂尔切斯变换,整理即可得(4.7)-(4.8)式.
4) 再根据
5 费用模型下的最优策略
本文建立的费用模型如下.
1) 一个顾客在系统中逗留(包括等待和服务)单位时间所需要的费用为
2) 系统在一个忙循环内的固定消耗费用(如启动费用等)为
其中,
下面用
(1) 当忙期结束后,第一个顾客的到达发生在延迟期,其概率为
此时,
(2) 当忙期结束后,第一个顾客的到达发生在服务员的闲期,且在闲期到达
此时,
(3) 当忙期结束后,第一个顾客的到达发生在服务员的闲期,且在闲期到达
此时,
综合上述(1)-(3)可得
根据文献[22],系统在稳态下的平均队长为
其中,
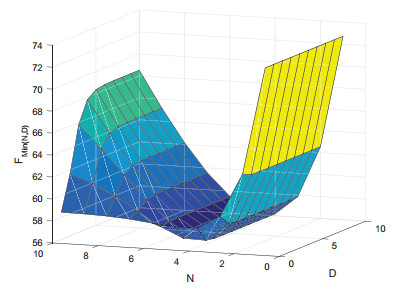
由(5.4)式看出,
例 某专科医院为了提高声誉,计划高薪聘请一个兼职资深专家医生坐诊,专家医生只需在医院需要的时间内来坐诊,在其他时间内该专家医生到其他单位去兼职或休息(这段时间可以看成服务员的休假).为了控制成本,医院采取延迟Min(
由(5.4)式可得
表 1
不同阀值
| D | |||||||||||
| N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5.1381 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 1 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 | 72.7177 |
| 2 | 62.9313 | 62.5521 | 62.5335 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 | 62.5325 |
| 3 | 58.9588 | 57.9496 | 57.8746 | 57.8695 | 57.8692 | 57.8692 | 57.8692 | 57.8692 | 57.8692 | 57.8692 | 57.8692 |
| 4 | 57.7637 | 56.3324 | 56.1923 | 56.1802 | 56.1793 | 56.1792 | 56.1792 | 56.1792 | 56.1792 | 56.1792 | |
| 5 | 57.7136 | 56.3969 | 56.2830 | 56.2739 | 56.2733 | 56.2732 | 56.2732 | 56.2732 | 56.2732 | 56.2732 | 56.2732 |
| 6 | 57.9797 | 57.3362 | 57.4734 | 57.5142 | 57.5207 | 57.5209 | 57.5215 | 57.5216 | 57.5216 | 57.5216 | 57.5216 |
| 7 | 58.2257 | 58.6056 | 59.3190 | 59.5182 | 59.5541 | 59.5556 | 59.5591 | 59.5597 | 59.5598 | 59.5598 | 59.5598 |
| 8 | 58.3738 | 59.8524 | 61.4852 | 62.0234 | 62.1400 | 62.1452 | 62.1592 | 62.1618 | 62.1621 | 62.1621 | 62.1621 |
| 9 | 58.4444 | 60.8845 | 63.7075 | 64.8239 | 65.1145 | 65.1292 | 65.1712 | 65.1801 | 65.1813 | 65.1814 | 65.1814 |
| 10 | 58.4728 | 61.6369 | 65.7848 | 67.7421 | 68.3483 | 68.3828 | 68.4877 | 68.5132 | 68.5171 | 68.5176 | 68.5177 |
图 7
参考文献
服务台可修的M/G/1排队系统分析
Analysis of M/G/1 queueing system with repairable service station
服务设备可修的机器服务模型分析
Analysis of machine service model with a repairable service equipment
Reliability analysis of a multistate system with a replaceable repair facility
Reliability analysis of a two unit cold standby system with a replaceable repair facility
服务台可修的M/G/1排队系统的进一步分析
Further analysis of M/G/1 queueing system with repairable service station
A single-server M/G/1 queuing system subject to breakdowns-some reliability and queueing problems
DOI:10.1016/S0026-2714(96)00018-2
Reliability analysis of M/G/1 queuing systems with server breakdowns and vacations
可修排队系统可靠性指标的分解特性
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6093.2004.04.010
The decomposition properties of reliability indices in repairable queueing systems
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6093.2004.04.010
多级适应性延误休假MX/G(M/G)/1可修排队系统的可靠性指标
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6093.2008.03.011
Some reliability indices in MX/G(M/G)/1 repairable queueing system with adaptive multistate delay vacation
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6093.2008.03.011
Control policies of an M/G/1 queue under the dyadic Min(N, D)-policy and its cost optimization
DOI:10.1016/j.peva.2008.04.006
多重休假中以概率p进入的M/G/1可修排队系统
M/G/1 repairable queueing system with p-entering discipline during server vacations
Reliability indices of discrete-time GeoX/G/1 queueing system with unreliable service station and multiple adaptive delayed vacations
修理设备可更换且修理延迟的两同型部件并联可修系统
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3085.2005.01.001 [本文引用: 1]
Two-unit same paralleled repairable system with a replaceable facility and delay repair
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-3085.2005.01.001 [本文引用: 1]
修理设备可更换且修理延迟的N部件串联系统分析
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2007.01.009
Analysis of N-unit series system with a replaceable facility and delay repair
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2007.01.009
修理有延迟且修理设备可更换的多状态可修系统的可靠性分析
Reliability analysis of a multi-state repairable system with a replaceable repair facility and delay repair
修理设备可更换的M/G/1可修排队系统分析
Analysis of M/G/1 repairable queueing system with a replaceable repair facility
修理设备可更换的N -策略M/G/1可修排队系统分析
Analysis of M/G/1 repairable queueing system with N-policy and a replaceable repair facility
Analysis of an M/G/1 queue with N-policy, single vacation, unreliable service station and replaceable repair facility
DOI:10.1007/s12597-015-0201-1 [本文引用: 1]
具有Bernoulli反馈和Min(N, D)策略控制的Geoλ1, λ2/G/1离散时间可修排队的可靠性分析
Reliability analysis of discrete-time Geoλ1, λ2/G/1 repairable queue with bernoulli feedback and Min(N, D)-policy
基于多重休假的Min(N, V) -策略M/G/1排队系统的队长分布
Queue length distribution of M/G/1 queueing system with Min(N, V)-policy based on multiple server vacations
基于Min(N, D) -策略的M/G/1排队系统的队长分布及最优策略
Queue length distribution and optimal policy for M/G/1 queueing system under Min(N, D)-policy
Min(N, D) -延迟Min(N, D) -策略的M/G/1排队系统的队长分布与数值计算
Queue length distribution and numerical calculation of M/G/1 queueing system with delay Min(N, D)-policy
具有Min(N, D) -策略控制的M/G/1可修排队系统及最优控制策略
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2017.02.014 [本文引用: 6]
M/G/1 Repairable Queueing System and Optimal Control Policy with Min(N, D)-policy
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2017.02.014 [本文引用: 6]