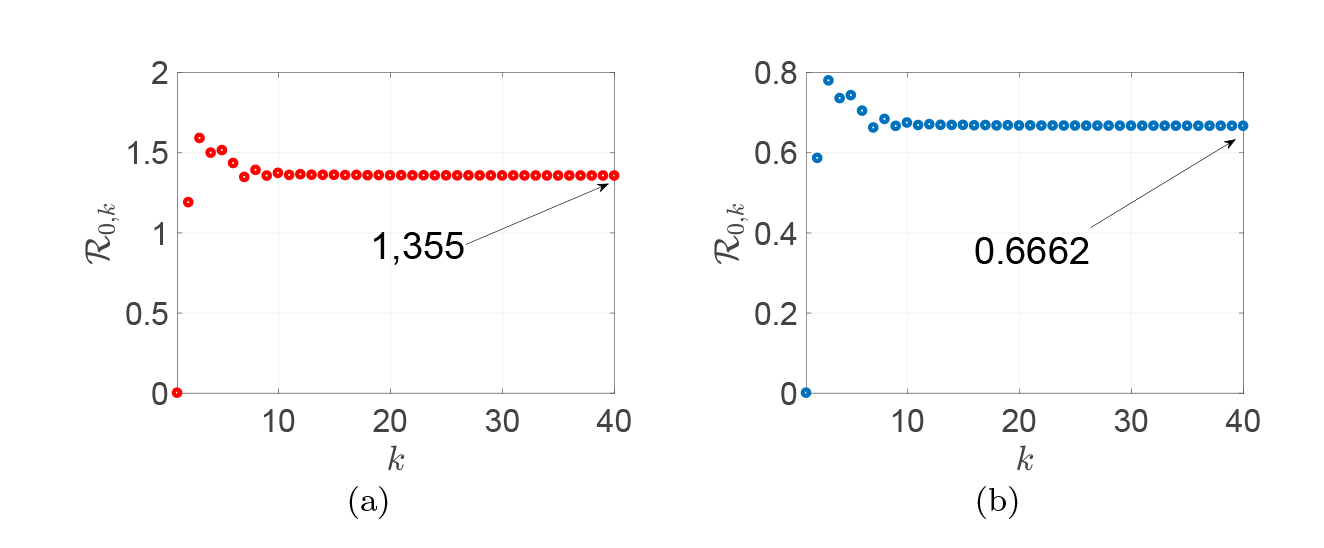
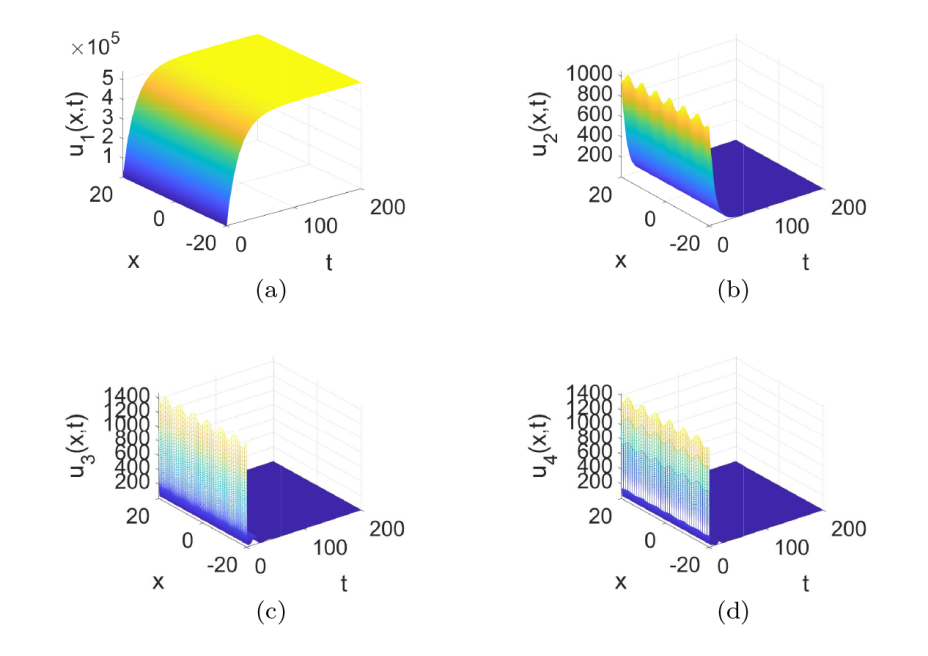
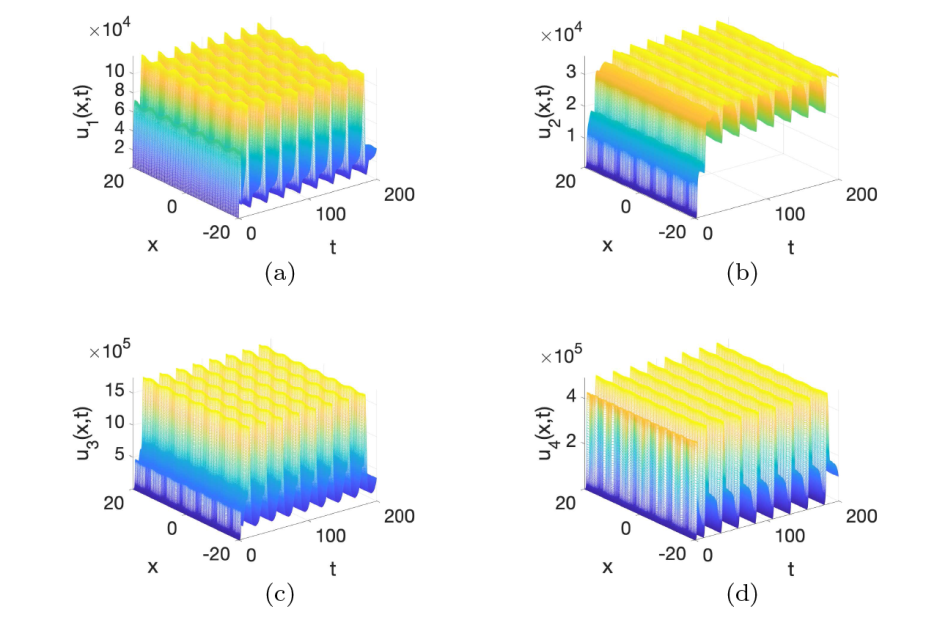
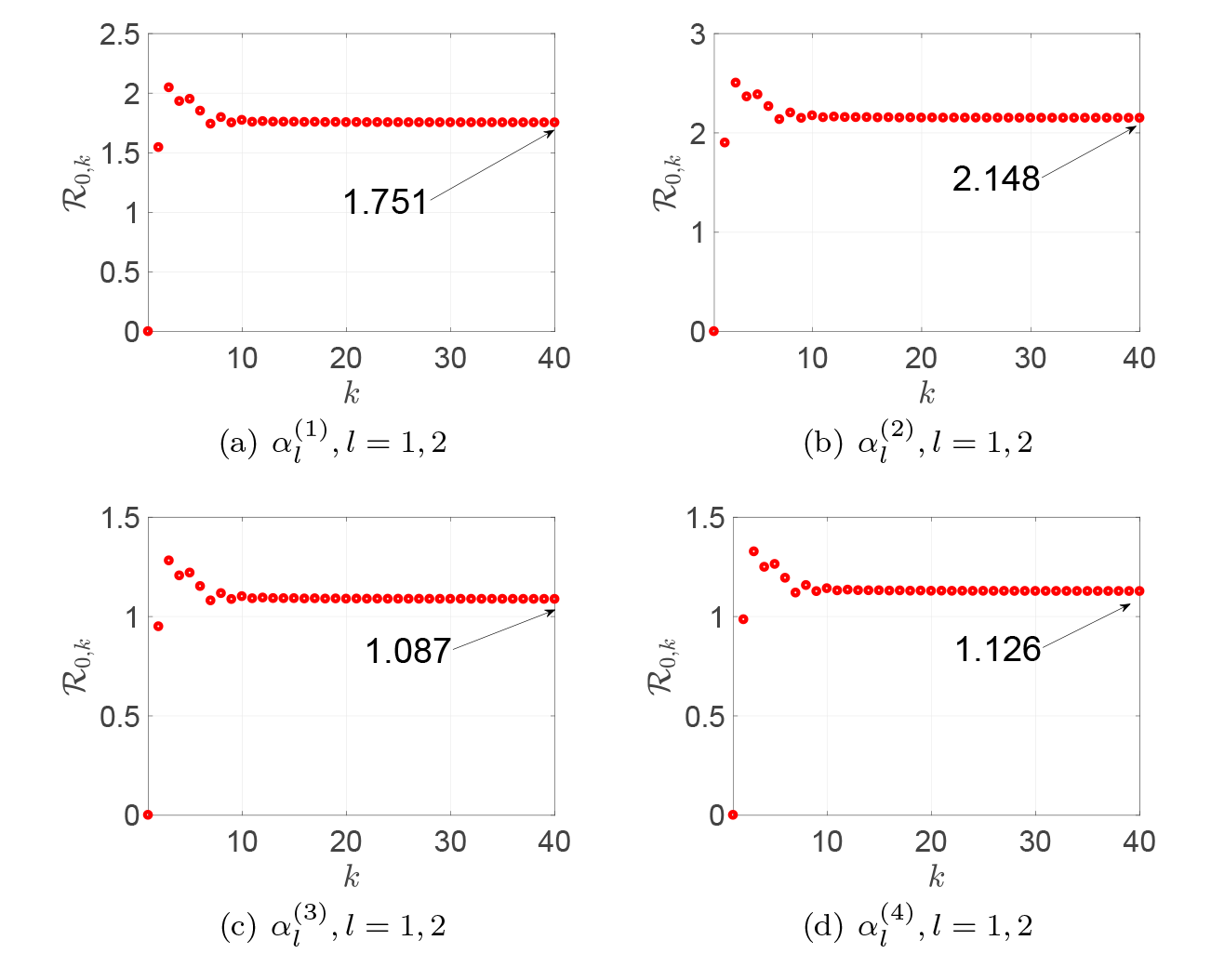
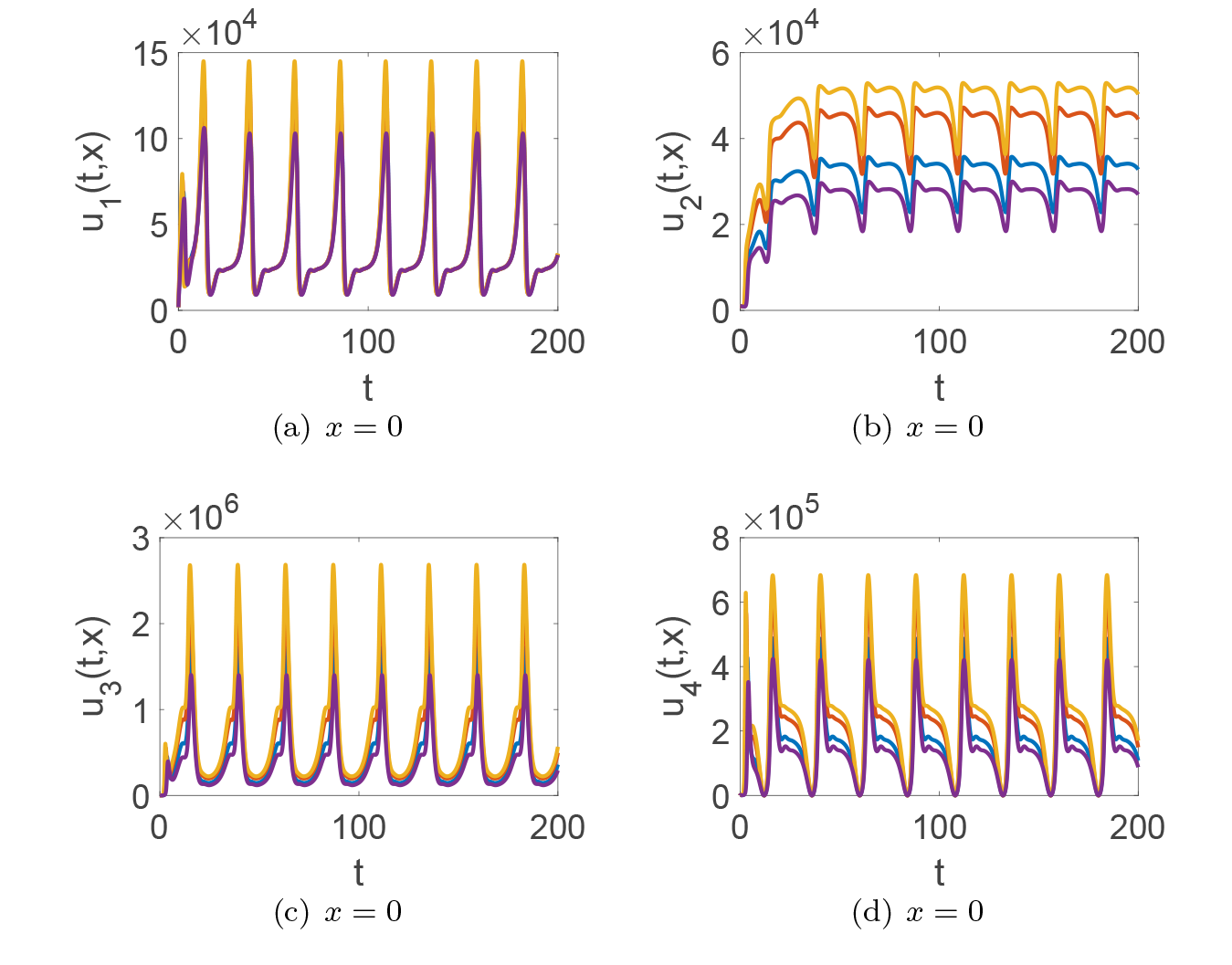
Acta mathematica scientia,Series A ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 209-226.
Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatio-temporal Dynamics of HIV Infection Model with Periodic Antiviral Therapy and Nonlocal Infection
- 1. School of Sciences, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018
2. School of Data Sciences, Zhejiang University of Finance and Economics, Hangzhou 310018
3. Institute of Operational Research and Cybernetics, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018
-
Received:2022-11-07Revised:2023-10-07Online:2024-02-26Published:2024-01-10 -
Supported by:NSFC(12201557);NSFC(12201007);NSFC(11871185);Foundation of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department(Y202249921);Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation(2108085MA10)
CLC Number:
- O175.23
Cite this article
Wu Peng, He Zerong. Spatio-temporal Dynamics of HIV Infection Model with Periodic Antiviral Therapy and Nonlocal Infection[J].Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2024, 44(1): 209-226.
share this article
| [1] |
Vaidya N K, Rong L. Modeling pharmacodynamics on HIV latent infection: Choice of drugs is key to successful cure via early therapy. SIAM J Appl Math, 2017, 77: 1781-1804
doi: 10.1137/16M1092003 |
| [2] |
Wu P, Zhao H. Dynamics of an HIV infection model with two infection routes and evolutionary competition between two viral strains. Appl Math Model, 2020, 84: 240-264
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.03.040 |
| [3] |
Rong L, Feng Z, Perelson A S. Mathematical analysis of age-structured HIV-1 dynamics with combination antiretroviral therapy. SIAM J Appl Math, 2007, 67: 731-756
doi: 10.1137/060663945 |
| [4] |
Wang X, Song X, Tang S, Rong L. Dynamics of an HIV model with multiple infection stages and treatment with different drugs classes. Bull Math Biol, 2016, 78: 322-349
doi: 10.1007/s11538-016-0145-5 |
| [5] | 邓萌, 徐瑞. 一类具有 CTL 免疫反应和免疫损害的 HIV 感染动力学模型的稳定性分析. 数学物理学报, 2022, 42A(5): 1592-1600 |
| Deng M, Xu R. MenStability analysis of an HIV infection dynamic model wit CTL immune response and immune impairment. Acta Math Sci, 2022, 42A(5): 1592-1600 | |
| [6] | 娄洁, 马之恩, 邵一鸣. HIV-1 的表型间变异与免疫因子相互作用的动力学模型. 数学物理学报, 2007, 27A(5): 898-906 |
| Lou J, Ma Z, Shao M. Modelling the interactions between the HIV-1 phenotypes and the cytokines. Acta Math Sci, 2007, 42A(5): 1592-1600 | |
| [7] |
Ren X, Tian Y, Liu L, Liu X. A reaction-diffusion within-host HIV model with cell-to-cell transmission. J Math Biol, 2018, 76: 1831-1872
doi: 10.1007/s00285-017-1202-x pmid: 29305736 |
| [8] |
Wu P, Zhao H. Dynamical analysis of a nonlocal delayed and diffusive HIV latent infection model with spatial heterogeneity. J Franklin Institute, 2021, 358: 5552-5587
doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.05.014 |
| [9] | 吴鹏, 赵洪涌. 基于空间异质反应扩散 HIV 感染模型的最优治疗策略. 应用数学学报, 2022, 45(5): 752-766 |
| Wu P, Zhao H. Optimal treatment strategies for a reaction-dffusion HIV infection model with spatial heterogeneity. Acta Math Appl Sinica, 2022, 45(5): 752-766 | |
| [10] | 王良平. 强一致收敛下的初值敏感性与等度连续性. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2012, 39(3): 270-272 |
| Wang L. The snsitive dependence on initial conditions and the equicontinuit under strongly uniform convergence. J Zhejiang Univ (Scicence Edition), 2012, 39(3): 270-272 | |
| [11] | Wang W, Wang X, Feng Z. Time periodic reaction-diffusion equations for modeling 2-LTR dynamics in HIV-infected patients. Nonlinear Anal RWA, 2021, 57: 103184 |
| [12] | Wu P, Zheng S, He Z. Evolution dynamics of a time-delayed reaction-diffusion HIV latent infection model with two strains and periodic therapies. Nonlinear Anal RWA, 2022, 67: 103559 |
| [13] | World Health Organization, 10 facts about HIV/AIDS fact sheet No. 204 updated July 2018. Available from: http://www.who.int/news-room/facts-in-pictures/detail/hiv-aids . [2022-11-01] |
| [14] |
Fang H, Stone E, Piacenti F. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: A nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor for the treatment of HIV infection. Clin Ther, 2002, 24: 1515-1548
pmid: 12462284 |
| [15] | Shirakawa K, Chavez L, Hakre S, et al. Reactivation of latent HIV by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Trends Microbio, 2013, 21(6): 277-285 |
| [16] |
Rasmussen T, Schmeltz S, Brinkmann C, et al. Comparison of HDAC inhibitors in clinical development: Effect on HIV production in latently infected cells and T-cell activation. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2013, 9(5): 993-1001
doi: 10.4161/hv.23800 |
| [17] | 谢强军, 张光新, 周泽魁. 一类周期反应扩散方程正周期解的存在性. 数学物理学报, 2009, 29A(2): 465-474 |
| Xie Q J, Zhang G X, Zhou Z K. The existece of positive periodic solutions for a kind of periodic reaction-diffusion equations. Acta Math Sci, 2009, 29A(2): 465-474 | |
| [18] | Levy J A. HIV and the Pathogenesis of AIDS. Washington, DC: ASM Press, 2007 |
| [19] |
De Mottoni P, Orlandi E, Tesei A. Asymptotic behavior for a system describing epidemics with migration and spatial spread of infection. Nonlinear Anal, 1979, 3(5): 663-675
doi: 10.1016/0362-546X(79)90095-6 |
| [20] | Pazy A. Semigroups of Linear Operators and Application to Partial Differential Equations. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1983 |
| [21] | Yang J, Xu R, Sun H. Dynamics of a seasonal brucellosis diseaase model with nonlocal transmission and spatial diffusion. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numeri Simult, 2021, 94: 105551 |
| [22] | Martin R H, Smith H L. Abstract functional dierential equations and reaction-diffusion systems. Trans Amer Math Soc, 1990, 321: 1-44 |
| [23] |
Zhang L, Wang Z C, Zhao X Q. Threshold dynamics of a time periodic reaction-diffusion epidemic model with latent period. J Differ Equat, 2015, 258: 3011-3036
doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2014.12.032 |
| [24] | 《数学辞海》总编辑委员会. 《数学辞海》第3卷. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 2002 |
| Mathematical Dictionary Editoral Committe. Mathematical Dictionary Volume iii. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 2002 | |
| [25] | Krein M G, Rutman M A. Linear operators leaving invariant a cone in a Banach space. Uspehi Matem Nauk (NS), 1948, 23: 3-95 |
| [26] |
Liu Z Z, When S Z, Wang H, Jin Z. Analysis of a local diffusive model with seasonality and nonlocal incidence of infection. SIAM J Appl Math, 2019, 79: 2218-2241
doi: 10.1137/18M1231493 |
| [27] |
Peng R, Zhao X Q. A reaction-diffusion SIS epidemic model in a time-periodic environment. Nonlinearity, 2012, 25: 1451-1471
doi: 10.1088/0951-7715/25/5/1451 |
| [28] | Zhao X Q. Uniform persistence and periodic coexistence states in infnite-dimension periodic semiflows with applications. Canad Appl Math Quart, 1995, 3: 473-495 |
| [29] |
Magal P, Zhao X Q. Global attractors and steady states for uniformly persistent dynamical systems. SIAM J Math Anal, 2005, 37: 251-275
doi: 10.1137/S0036141003439173 |
| [30] | Zhao X Q. Dynamical Systems in Population Biology. Switzerland: Springer, 2003 |
| [31] |
Wu P, Wang X, Wang H. Threshold dynamics of nonlocal dispersal HIV/AIDS epidemic model with spatial heterogeneity and antiretroviral therapy. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat, 2022, 115: 106728
doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2022.106728 |
| [1] | Wu Peng,Wang Xiunan,He Zerong. Dynamical Analysis of an Age-Space Structured HIV/AIDS Model with Homogeneous Dirichlet Boundary Condition [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2023, 43(3): 970-984. |
| [2] | Zhenxiang Hu,Linfei Nie. Analysis of a Reaction-Diffusion Epidemic Model with Horizontal Transmission and Environmental Transmission [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2022, 42(6): 1849-1860. |
| [3] | Meng Deng,Rui Xu. Stability Analysis of an HIV Infection Dynamic Model with CTL Immune Response and Immune Impairment [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2022, 42(5): 1592-1600. |
| [4] | Tailei Zhang,Junli Liu,Mengjie Han. Dynamics of an Anthrax Epidemiological Model with Time Delay and Seasonality [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2022, 42(3): 851-866. |
| [5] | Yu Yang. Global Attractivity of a Nonlocal Delayed and Diffusive SVIR Model [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(6): 1864-1870. |
| [6] | Xianglin Han,Weigang Wang,Jiaqi Mo. Bionomics Dynamic System for Epidemic Virus Transmission [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2019, 39(1): 200-208. |
| [7] |
Lou J; Ma Zhien ;Shao Yiming.
Modeling the Interactions between the HIV-1 Phenotypes and the Cytokines |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 204
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 102
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|