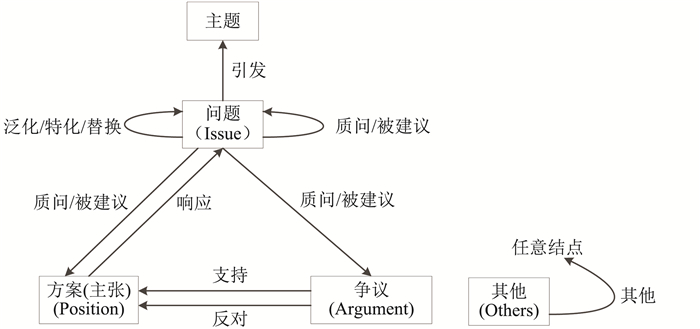
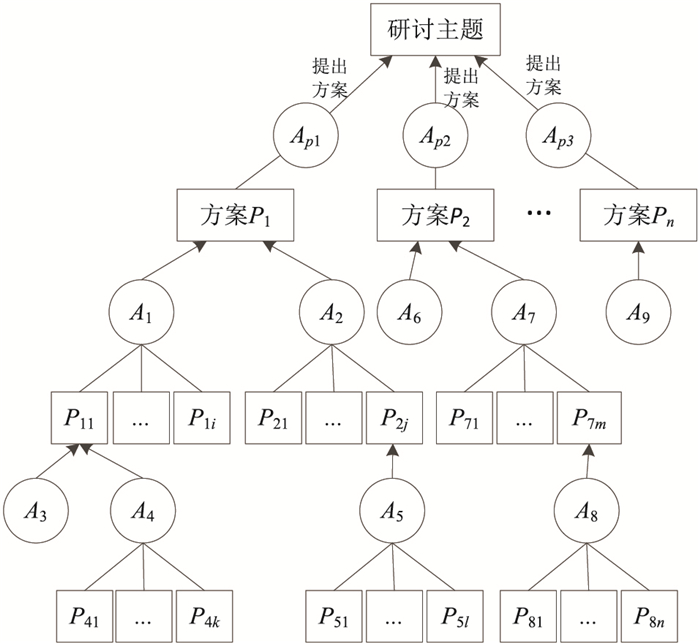
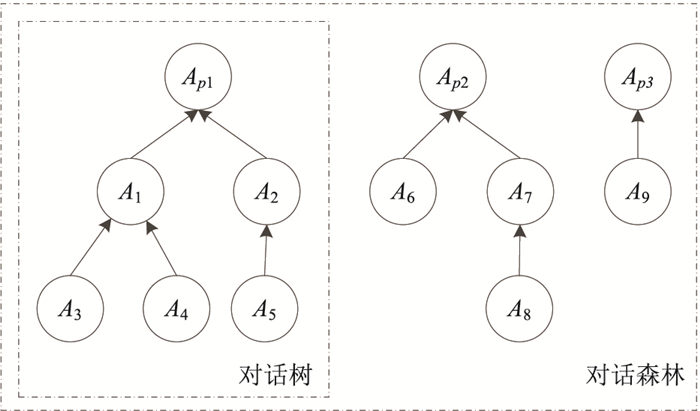
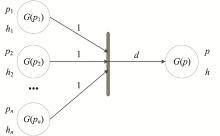
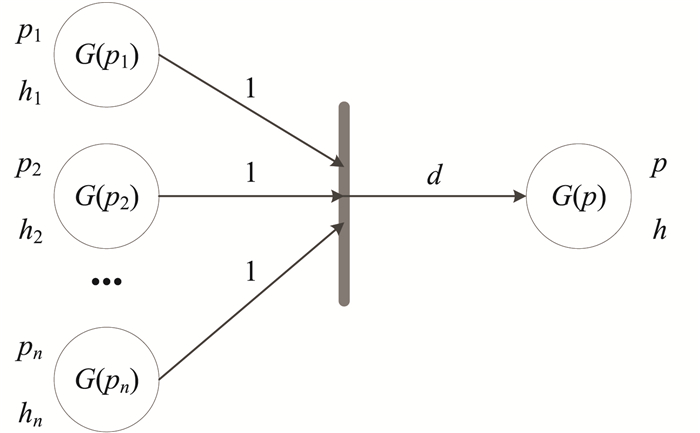
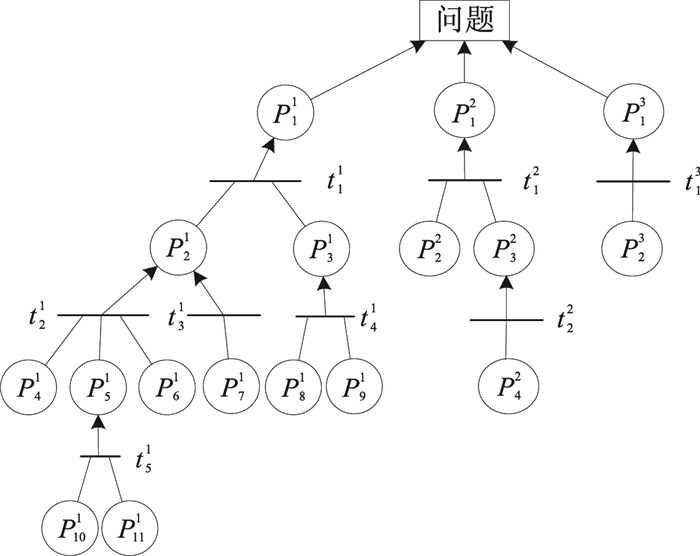
| 1 |
Modgil S, Toni F, Bex F, et al. The added value of argumentation//Ossowski S. Agreement Technologies. Dordrecht: Springer, 2013: 357-403
|
| 2 |
唐锡晋, 刘怡君. 从群体支持系统到创造力支持系统. 系统工程理论与实践, 2006, 26 (5): 63- 71
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2006.05.008
|
|
Tang X J , Liu Y J . From group support system to creativity support system. Systems Engineering-Theory and Practice, 2006, 26 (5): 63- 71
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2006.05.008
|
| 3 |
Heras S , Jordán J , Botti V , Juliàn V . Case-based strategies for argumentation dialogues in agent societies. Information Sciences, 2013, 223: 1- 30
|
| 4 |
Walton D N , Krabbe E C W . Commitment in Dialogue:Basic Concepts of Interpersonal Reasoning. New York: State University of New York Press, 1995
|
| 5 |
Hulstijn J. Dialogue Models for Inquiry and Transaction[D]. Enschede: Universiteit Twente, 2000
|
| 6 |
Governatori G , Maher M J , Antoniou G , Billington D . Argumentation semantics for defeasible logic. Journal of Logic and Computation, 2004, 14 (5): 675- 702
doi: 10.1093/logcom/14.5.675
|
| 7 |
McBurney P , Parsons S . Representing epistemic uncertainty by means of dialectical argumentation. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, 2001, 32: 125- 169
doi: 10.1023/A:1016757315265
|
| 8 |
Amgoud L, Maudet N, Parsons S. Modelling dialogues using argumentation//Werner B. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Multi-Agent Systems. Boston: IEEE Press, 2000: 7-12
|
| 9 |
Cayrol C , Lagasquie-Schiex M C . Bipolarity in argumentation graphs:Towards a better understanding. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2013, 54 (7): 876- 899
doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2013.03.001
|
| 10 |
Prakken H . Coherence and flexibility in dialogue games for argumentation. Journal of Logic and Computation, 2005, 15 (6): 1009- 1040
doi: 10.1093/logcom/exi046
|
| 11 |
Cayrol C, Lagasquie-Schiex M C. On the acceptability of arguments in bipolar argumentation frameworks//Godo L. Symbolic and Quantitative Approaches to Reasoning with Uncertainty. Berlin: Springer, 2005: 378-389
|
| 12 |
Fox J , Glasspool D , Grecu D , et al. Argumentation-based inference and decision making -A medical perspective. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2007, 22 (6): 34- 41
doi: 10.1109/MIS.2007.102
|
| 13 |
Tolchinsky P , Modgil S , Atkinson K , et al. Deliberation dialogues for reasoning about safety critical actions. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2012, 25 (2): 209- 259
doi: 10.1007/s10458-011-9174-5
|
| 14 |
Kok E M, Meyer J, Prakken H, Vreeswijk G. A formal argumentation framework for deliberation dialogues//McBurney P, Rahwan I, Parsons S. Argumentation in Multi-Agent Systems: 7th International Workshop, ArgMAS 2010 Revised, Selected and Invited Papers. Berlin: Springer, 2011: 31-48
|
| 15 |
McBurney P , Hitchcock D , Parsons S . The eightfold way of deliberation dialogue. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2007, 22 (1): 95- 132
|
| 16 |
Toulmin S E . The Uses of Argument. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1958
|
| 17 |
Kunz W , Rittel H . Issues as Elements of Information Systems. Berkeley: University of California, 1970
|
| 18 |
Dung P M . On the acceptability of arguments and its fundamental role in nonmonotonic reasoning, logic programming and n-person games. Artificial Intelligence, 1995, 77 (2): 321- 357
|
| 19 |
Gordon T F , Prakken H , Walton D . The Carneades model of argument and burden of proof. Artificial Intelligence, 2007, 171 (10): 875- 896
|
| 20 |
Gordon T F, Karacapilidis N. The Zeno argumentation framework//Zeleznikow J, Hunter D, Branting K. Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law. New York: ACM, 1997: 10-18
|
| 21 |
Karacapilidis N , Papadias D . Computer supported argumentation and collaborative decision making:the HERMES system. Information Systems, 2001, 26 (4): 259- 277
|
| 22 |
Baroni P , Romano M , Toni F , et al. Automatic evaluation of design alternatives with quantitative argumentation. Argument & Computation, 2015, 6 (1): 24- 49
|
| 23 |
Baroni P, Romano M, Toni F, et al. An argumentation-based approach for automatic evaluation of design debates//Leite J, Son T. Proceedings of the 14th International Workshop on Computational Logic in Multi-Agent Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2013: 340-356
|
| 24 |
Chanda N, Liu X F. Intelligent analysis of software architecture rationale for collaborative software design//2015 International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems. Atlanta:IEEE, 2015:287-294
|
| 25 |
Sigman S , Liu X F . A computational argumentation methodology for capturing and analyzing design rationale arising from multiple perspectives. Information and Software Technology, 2003, 45 (3): 113- 122
|
| 26 |
谭俊峰, 张朋柱, 黄丽宁. 综合集成研讨厅中的研讨信息组织模型. 系统工程理论与实践, 2005, 25 (1): 86- 92
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2005.01.013
|
|
Tan J F , Zhang P Z , Huang L N . A group argumentation information-structuring model in hall for workshop of metasynthetic engineering. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2005, 25 (1): 86- 92
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2005.01.013
|
| 27 |
陈俊良, 陈超, 姜鑫, 张震. 基于IBIS和Toulmin辩论形式的群体研讨模型. 计算机应用, 2011, 31 (9): 2526- 2529
|
|
Chen J l , Chen C , Jiang X , Zhang Z . Group argumentation model based on IBIS and Toulmin's argument schema. Journal of Computer Applications, 2011, 31 (9): 2526- 2529
|
| 28 |
Kunz W , Rittel H W J . Issues as Elements of Information Systems. Berkeley: University of California, 1970
|
| 29 |
Murata T . Petri nets:Properties, analysis and applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1989, 77 (4): 541- 580
doi: 10.1109/5.24143
|
| 30 |
Wang W M , Peng X , Zhu G N , et al. Dynamic representation of fuzzy knowledge based on fuzzy petri net and genetic-particle swarm optimization. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41 (4): 1369- 1376
|
| 31 |
Shortliffe E H , Buchanan B G . A model of inexact reasoning in medicine. Mathematical Biosciences, 1975, 23 (3/4): 351- 379
|
 ),Xuan Li2,Na Deng1,Dahai Xia1
),Xuan Li2,Na Deng1,Dahai Xia1