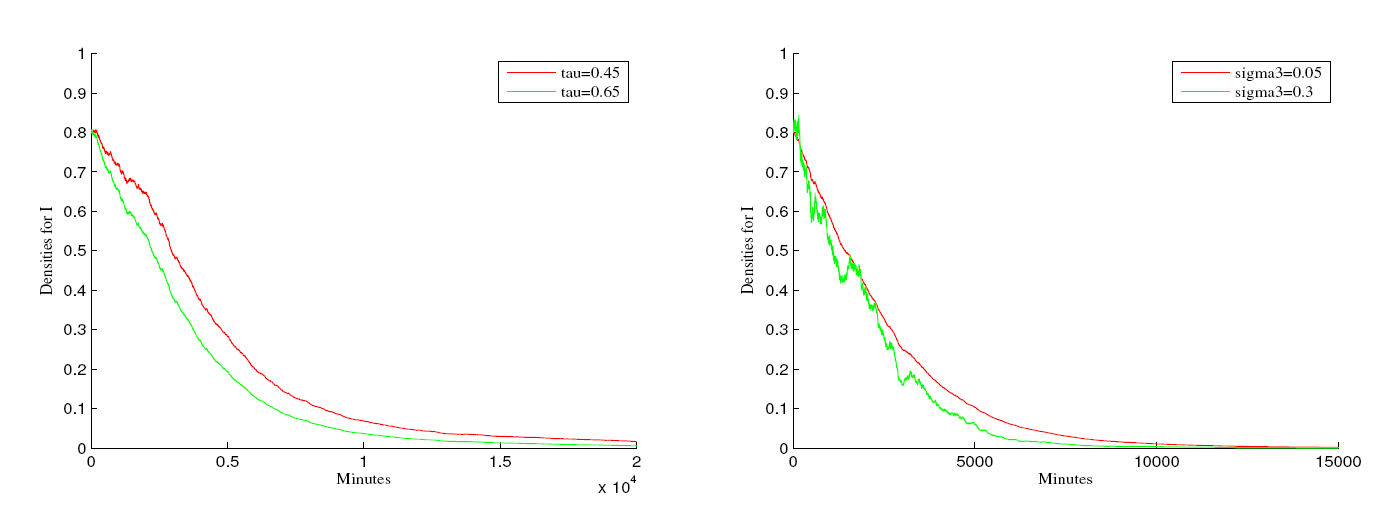
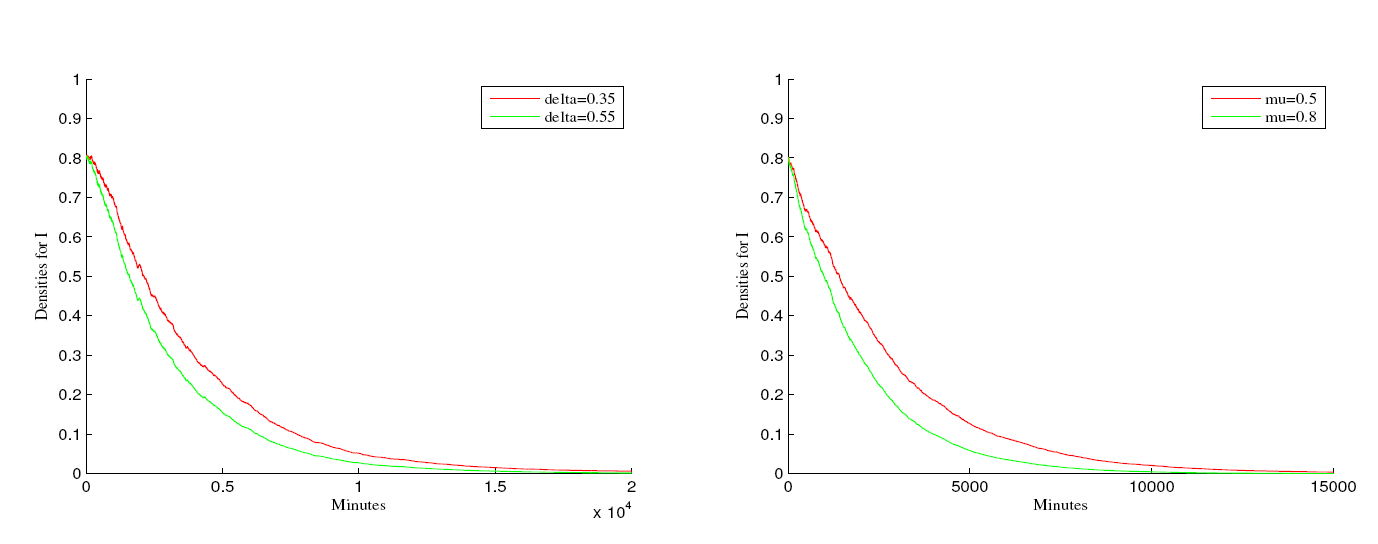
Acta mathematica scientia,Series A ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1595-1606.
Previous Articles Next Articles
Survival Analysis of an SVIR Epidemic Model with Media Coverage
Li Dan1,Wei Fengying2,*( ),Mao Xuerong3
),Mao Xuerong3
- 1School of Mathematics and Statistics, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350116
2Key Laboratory of Operations Research and Control of Universities in Fujian, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350116
3Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow G1 1XH, UK
-
Received:2022-04-22Revised:2022-10-31Online:2023-10-26Published:2023-08-09 -
Contact:Fengying Wei E-mail:weifengying@fzu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(61911530398);Special Projects of the Central Government Guiding Local Science, Technology Development(2021L3018);Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China(2021J01621);Royal Society, UK(WM160014);Royal Society, UK (Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award);Royal Society and the Newton Fund, UK(NA160317);Royal Society and the Newton Fund, UK (Royal Society-Newton Advanced Fellowship);EPSRC, the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council(EP/K503174/1)
CLC Number:
- O175.13
Cite this article
Li Dan,Wei Fengying,Mao Xuerong. Survival Analysis of an SVIR Epidemic Model with Media Coverage[J].Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2023, 43(5): 1595-1606.
share this article
| [1] |
Adimy M, Chekroun A, Kuniya T. Traveling waves of a differential-difference diffusive Kermack-McKendrick epidemic model with age-structured protection phase. J Math Anal Appl, 2022, 505(1): 125464
doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2021.125464 |
| [2] |
Cao Z W, Feng W, Wen X D. Dynamical behavior of a stochastic SEI epidemic model with saturation incidence and logistic growth. Physica A, 2019, 523: 894-907
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.04.228 |
| [3] |
Capasso V, Serio G. A generalization of the Kermack-McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math Biosci, 1978, 42: 43-61
doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(78)90006-8 |
| [4] | Caraballo T, El Fatini M, Pettersson R, et al. A stochastic SIRI epidemic model with relapse and media coverage. Discrete Cont Dyn Sys B, 2018, 23(8): 3483-3501 |
| [5] |
Chen L H, Wei F Y. Persistence and distribution of a stochastic susceptible-infected-removed epidemic model with varying population size. Physica A, 2017, 483: 386-397
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2017.04.114 |
| [6] | Chen L J, Wei F Y. Study on a susceptible-exposed-infected-recovered model with nonlinear incidence rate. Adv Differ Equ, 2020, Article number 206 |
| [7] |
Cui J G, Sun Y H, Zhu H P. The impact of media on the control of infectious diseases. J Dyn Differ Equ, 2008, 20(1): 31-53
doi: 10.1007/s10884-007-9075-0 pmid: 32214759 |
| [8] | Feng T, Meng X Z, Zhang T H, et al. Analysis of the predator-prey interactions: A stochastic model incorporating disease invasion. Qual Theory Dyn Sys, 2020, 19: Article number 55 |
| [9] | Guo Q, Liu W, Mao X R, et al. The partially truncated Euler-Maruyama method and its stability and boundedness. Appl Numer Math, 2017, 115: 235-251 |
| [10] |
Guo W J, Zhang Q M, Li X N, et al. Dynamic behavior of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with media coverage. Math Method Appl Sci 2018, 41(14): 5506-5525
doi: 10.1002/mma.v41.14 |
| [11] |
Han B T, Jiang D Q, Zhou B Q, et al. Stationary distribution and probability density function of a stochastic SIRSI epidemic model with saturation incidence rate and logistic growth. Chaos, Solitons Fractals, 2011, 142: 110519
doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110519 |
| [12] |
Higham D J. An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev, 2001, 43: 525-546
doi: 10.1137/S0036144500378302 |
| [13] |
Hou T F, Lan G J, Yuan S L, et al. Threshold dynamics of a stochastic SIHR epidemic model of COVID-19 with general population-size dependent contact rate. Math Biosci Eng, 2022, 19: 4217-4236
doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022195 pmid: 35341295 |
| [14] |
Lan G J, Yuan S L, Song B J. The impact of hospital resources and environmental perturbations to the dynamics of SIRS model. J Frankl Inst-Eng Appl Math, 2021, 358(4): 2405-2433
doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.01.015 |
| [15] |
Li J H, Teng Z D, Wang G Q, et al. Stability and bifurcation analysis of an SIR epidemic model with logistic growth and saturated treatment. Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2017, 99: 63-71
doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2017.03.047 |
| [16] |
Li Y F, Cui J G. The effect of constant and pulse vaccination on SIS epidemic models incorporating media coverage. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul, 2019, 14(5): 2353-2365
doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2008.06.024 |
| [17] | Liu J M, Chen L J, Wei F Y. The persistence and extinction of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with Logistic growth. Adv Differ Equ, 2018, Article number 68 |
| [18] |
Liu Q, Jiang D Q, Hayat T, et al. Dynamical behavior of a higher order stochastically perturbed SIRI epidemic model with relapse and media coverage. Chaos Solitons Fractals, 2020, 139: 110013
doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110013 |
| [19] |
Liu Q, Jiang D Q, Hayat T, et al. Dynamics of a stochastic predator-prey model with stage structure for predator and Holling type II functional response. J Nonlinear Sci, 2018, 28: 1151-1187
doi: 10.1007/s00332-018-9444-3 |
| [20] | Liu Q, Jiang D Q, Shi N, et al. Dynamical behavior of a stochastic HBV infection model with logistic hepatocyte growth. Acta Math Sci, 2017, 37B(4): 927-940 |
| [21] |
Lu R X, Wei F Y. Persistence and extinction for an age-structured stochastic SVIR epidemic model with generalized nonlinear incidence rate. Physica A, 2019, 513: 572-587
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.016 |
| [22] |
Mao X R, Wei F Y, Wiriyakraikul T. Positivity preserving truncated Euler-Maruyama method for stochastic Lotka-Volterra competition model. J Comput Appl Math, 2021, 394: 113566
doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2021.113566 |
| [23] | Mao X R. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications. Chichester: Horwood Publishing, 2007 |
| [24] |
Mu X J, Zhang Q M, Rong L B. Optimal vaccination strategy for an SIRS model with imprecise parameters and Lèvy noise. J Frankl Inst-Eng Appl Math, 2019, 356(18): 11385-11413
doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.03.043 |
| [25] |
Nguyen D H, Nguyen N N, Yin G. Stochastic functional Kolmogorov equations, I: Persistence. Stoch Process Appl, 2021, 142: 319-364
doi: 10.1016/j.spa.2021.09.007 |
| [26] |
Nguyen D H, Nguyen N N, Yin G. Stochastic functional Kolmogorov equations II: Extinction. J Differ Equ, 2021, 294(5): 1-39
doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2021.05.043 |
| [27] |
Nguyen D H, Yin G, Zhu C. Long-term analysis of a stochastic SIRS model with general incidence rates. SIAM J Appl Math, 2020, 80(2): 814-838
doi: 10.1137/19M1246973 |
| [28] |
Rajasekar S P, Pitchaimani M, Zhu Q X. Dynamic threshold probe of stochastic SIR model with saturated incidence rate and saturated treatment function. Physica A, 2019, 535: 122300
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.122300 |
| [29] | Rajasekar S P, Pitchaimani M. Ergodic stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with logistic growth and nonlinear incidence. Appl Math Comput, 2020, 377: 125143 |
| [30] |
Sahu G P, Dhar J. Analysis of an SVEIS epidemic model with partial temporary immunity and saturation incidence rate. Appl Math Model, 2012, 36(3): 908-923
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2011.07.044 |
| [31] |
Sun C J, Yang W, Arino J, et al. Effect of media-induced social distancing on disease transmission in a two patch setting. Math Biosci, 2011, 230(2): 87-95
doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2011.01.005 pmid: 21296092 |
| [32] | Tchuenche J M, Dube N, Bhunu C P, et al. The impact of media coverage on the transmission dynamics of human influenza. BMC Public Health, 2011, 11(1): Article number S5 |
| [33] |
Wang L W, Liu Z J, Zhang X G. Global dynamics for an age-structured epidemic model with media impact and incomplete vaccination. Nonlinear Anal: Real World Appl, 2016, 32: 136-158
doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2016.04.009 |
| [34] |
Wei F Y, Chen F X. Stochastic permanence of an SIQS epidemic model with saturated incidence and independent random perturbations. Physica A, 2016, 453: 99-107
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.01.059 |
| [35] |
Wei F Y, Chen L H. Psychological effect on single-species population models in a polluted environment. Math Biosci, 2017, 290: 22-30
doi: S0025-5564(17)30142-6 pmid: 28583848 |
| [36] |
Wei F Y, Jiang H, Zhu Q X. Dynamical behaviors of a heroin population model with standard incidence rates between distinct patches. J Frankl Inst-Eng Appl Math, 2021, 358(9): 4994-5013
doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.04.024 |
| [37] |
Wei F Y, Wang C J. Survival analysis of a single-species population model with fluctuations and migrations between patches. Appl Math Model, 2020, 81: 113-127
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.12.023 |
| [38] |
Wei F Y, Xue R. Stability and extinction of SEIR epidemic models with generalized nonlinear incidence. Math Comput Simul, 2020, 170: 1-15
doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2018.09.029 |
| [39] |
Zhang Y, Fan K G, Guo S J, et al. Ergodic stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model incorporating media coverage and saturated incidence rate. Physica A, 2019, 514: 671-685
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.124 |
| [40] | Zhao Y N, Jiang D Q. Dynamics of stochastically perturbed SIS epidemic model with vaccination. Abstr Appl Anal, 2013, Article number 517439 |
| [41] | Zhao Y N, Jiang D Q. The threshold of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination. Appl Math Comput, 2014, 243: 718-727 |
| [42] |
Zhao Y, Zhang Y P, Yuan S L. The effect of media coverage on threshold dynamics for a stochastic SIS epidemic model. Physica A, 2018, 512: 248-260
doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.08.113 pmid: 32288106 |
| [1] | Yanjun Zhao,Xiaohui Sun,Li Su,Wenxuan Li. Qualitative Analysis of Stochastic SIRS Epidemic Model with Logistic Growth and Beddington-DeAngelis Incidence Rate [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2022, 42(6): 1861-1872. |
| [2] | Jiang Li,Guijie Lan,Shuwen Zhang,Chunjin Wei. Dynamics Analysis of a Stochastic Glucose-Insulin Model [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(6): 1937-1949. |
| [3] | Liya Liu,Daqing Jiang. Global Dynamics of a Stochastic Chemostat Model with General Response Function and Wall Growth [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(6): 1912-1924. |
| [4] | Tengfei Wang,Tao Feng,Xinzhu Meng. Complex Dynamics and Stochastic Sensitivity Analysis of a Predator-Prey Model with Crowley-Martin Type Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(4): 1192-1203. |
| [5] | Zhonghua Zhang,Qian Zhang. Qualitative Analysis of a Stochastic SIVS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Perturbations Under Regime Switching [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(4): 1218-1234. |
| [6] | Lixiang Feng,Defen Wang. Global Stability of an Epidemic Model with Quarantine and Incomplete Treatment [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2021, 41(4): 1235-1248. |
| [7] | Xinxin Cheng,Yaqing Rao,Gang Huang. COVID-19 Transmission Model in an Enclosed Space: A Case Study of Japan Diamond Princess Cruises [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2020, 40(2): 540-544. |
| [8] | Zhongwei Cao,Xiangdan Wen,Wei Feng,Li Zu. Dynamics of a Nonautonomous SIRI Epidemic Model with Random Perturbations [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2020, 40(1): 221-233. |
| [9] | Xinzhe Zhang,Guofeng He,Gang Huang. Dynamical Properties of a Delayed Epidemic Model with Vaccination and Saturation Incidence [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2019, 39(5): 1247-1259. |
| [10] | Guijie Lan,Yingjie Fu,Chunjin Wei,Shuwen Zhang. Stationary Distribution and Periodic Solution for Stochastic Predator-Prey Systems with Holling-Type Ⅲ Functional Response [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2018, 38(5): 984-1000. |
| [11] | Hua Li,Sanhong Liu,Yile Fang,Xingan Zhang. Mathematical Modeling and Computer Simulation on Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in Children [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2018, 38(5): 1032-1040. |
| [12] | Zhang Liping, Zhao Yu, Yuan Sanling. Threshold Dynamical Behaviors of a Stochastic SIS Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2018, 38(1): 197-208. |
| [13] | Wei Fengying, Lin Qingteng. Extinction and Distribution for an SIQS Epidemic Model with Quarantined-Adjusted Incidence [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2017, 37(6): 1148-1161. |
| [14] | Meng Xiaoying. Analysis of a Stochastic Delayed Epidemic Model with a Non-Monotonic Incidence Rate [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2017, 37(6): 1162-1175. |
| [15] | Xu Yanli. Exponential Convergence of An Epidemic Model with Delays and Oscillating Recovery Rates [J]. Acta mathematica scientia,Series A, 2015, 35(5): 987-994. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 363
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 146
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|