引言
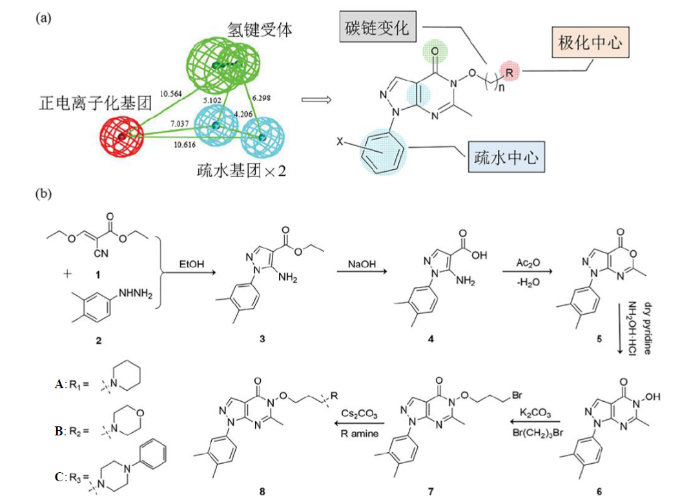
作者所在课题组曾基于配体的计算机辅助药物设计,构建了具有活性预测能力的组胺H3受体抑制剂的三维定量构效关系(3D-QSAR)药效团模型,然后通过虚拟筛选获得了具有吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮类结构的活性分子,并通过初步的药理活性评价验证了其具有中枢镇痛活性[6].为丰富吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮类化合物分子结构的多样性,并探究其中枢镇痛活性的机制,本研究基于经典的分子设计策略[图1(a)],再结合已报道的研究[7,8],以2-氰基-3-乙氧基丙烯酸乙酯与3,4-二甲基苯肼为原料,设计、合成了三种具有全新化学结构的吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮类衍生物[图1(b)].通过核磁共振(NMR,包括1H NMR、13C NMR)和液相色谱-质谱联用(LC-MS)技术对所制备的化合物1-(3,4-二甲基苯基)-6-甲基-5-[3-(哌啶-1-基)丙氧基]-1,5-二氢-4H-吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮(A)、1-(3,4-二甲基苯基)-6-甲基-5-(3-吗啉丙氧基)-1,5-二氢-4H-吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮(B)和1-(3,4-二甲基苯基)-6-甲基-5-[3-(4-苯基哌嗪-1-基)丙氧基]-1,5-二氢-4H-吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮(C)分别进行了结构表征和确证,并对它们的1H NMR信号进行了归属和解析.然后,通过小鼠脑切片质谱成像考察了化合物A的血脑屏障透过性,以及其在脑组织中的生物学分布和初步的动力学性质.最后通过小鼠福尔马林实验对化合物A进行了镇痛活性研究.本文为吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮衍生物的结构鉴定以及中枢镇痛活性研究提供了基础数据和重要依据.
图1
1 实验部分
1.1 化合物合成
实验所用起始原料2-氰基-3-乙氧基丙烯酸乙酯(1)和3,4-二甲基苯肼(2)及其他试剂均为商用分析纯试剂(国药集团化学试剂有限公司),所有试剂均未经进一步纯化,直接使用.合成路线如图1(b)所示,化合物3、4、5和6按照文献[9,10]报道的方法制备,化合物7和8参考威廉姆森醚合成反应[11]制备.具体方法如下:将化合物6(0.800 9 g,2.96 mmol)、1,3-二溴丙烷(1.208 0 g,5.98 mmol)和无水碳酸钾(0.824 2 g,5.96 mmol)混合溶于40 mL丙酮中,60 ℃恒温油浴搅拌回流8 h,经薄层色谱(TLC,V石油醚:V乙酸乙酯 = 4:1)检测反应完全后,通过柱层析(V石油醚:V乙酸乙酯 = 8:1)分离,旋蒸回收得到浅黄色固体化合物7(0.681 3 g,收率59%).将化合物7(0.402 5 g,1.03 mmol)、哌啶(C5H11N,0.112 9 g,1.33 mmol)和碳酸铯(0.669 4 g,2.05 mmol)混合溶于40 mL乙腈中,80 ℃恒温油浴搅拌回流5 h,经TLC(V二氯甲烷:V甲醇 = 10:1)检测反应完全后,通过柱层析(V乙酸乙酯:V甲醇 = 50:1)分离,旋蒸回收得到黄色固体化合物A(0.330 6 g,收率81%).同样方法分别用吗啉(C4H9NO,0.013 6 g)和1-苯基哌嗪(C10H14N2,0.026 3 g)代替哌啶,与0.050 8 g和0.052 6 g化合物7反应,对应得到黄色固体化合物B(0.037 8 g,收率73%)和黄色固体化合物C(0.034 1 g,收率54%).
1.2 LC-MS与NMR实验
LC-MS实验采用Agilent 1290 Infinity II/6545B Q-TOF液质联用系统,配备电喷雾离子源(ESI).化合物A~C分别溶于乙腈,配制成浓度为1 mg/L的溶液上样,其中色谱分离使用ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 (2.1 mm × 50 mm,1.8 μm粒径)分析柱.流动相由水(α)和乙腈(β)组成,流速为0.250 mL/min,梯度设置为:0.00~4.00 min,0.00% α;4.00~4.10 min,80% α;4.10~7.00 min,80% α.质谱分析采用正离子扫描模式,质荷比(m/z)扫描范围从100到1 000.
NMR实验均在Bruker AVANCE III 700 MHz谱仪上完成,分别取15 mg合成的化合物A~C溶于550 μL含有四甲基硅烷(TMS)的DMSO-d6(99.9% D,购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司),以TMS(δH 0.00, δC 0.0)为内标.1H NMR(谱宽13 888.89 Hz,中心频率3 351.18 Hz,累加次数4)和13C NMR(谱宽 35 714.29 Hz,中心频率17 607.80 Hz,累加次数1 024)的工作频率分别为700.25 MHz和176.08 MHz,实验温度为298.0 K,均采用标准脉冲程序.
1.3 质谱成像与福尔马林实验
无特定病原体(SPF)级C57BL/6小鼠(7周龄,体重17~21 g)购买自湖北省实验动物研究中心,许可证号:SCXK(鄂)2020-0018.本实验中动物实验部分由中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院动物实验伦理委员会批准(APM20014A).饲养环境温度为(23±2)℃,湿度50%~70%,12 h交替光照,自由饮水和摄食,适应性饲养两天后开始实验.实验用化合物A使用5%DMSO+5%吐温80+90%生理盐水作为载体溶剂溶解.
随机选取3只雌性小鼠同时腹腔注射20 mg/kg化合物A溶液,分别在腹腔注射20、30和60 min后颈椎脱臼处死小鼠,处死后立刻解剖取出完整脑组织用液氮急冻(不直接接触)后置于-80 ℃冰箱冷冻过夜,然后制备成10 μm厚度的冷冻切片,并放置在有氧化铟锡(ITO)镀层的载玻片上,处理后利用Bruker timsTOF fleX质谱仪对脑切片进行质谱成像数据采集.进行质谱成像前,用HTX TM-Sprayer基质喷雾仪在组织切片表面喷涂基质. 扫描质量范围设定为m/z 50~650,激光强度55%,累计次数400 shots,空间分辨率设定为30 μm.
福尔马林实验将小鼠随机分为空载组(Veh组)、对照组(C组)、标准药物组(Pregabalin组)以及三组不同浓度实验药物组,每组8只,雌雄各半,共计6组.空载组和对照组腹腔注射200 μL载体溶剂,标准药物组腹腔注射等体积40 mg/kg的标准镇痛药普瑞巴林[7],实验药物组分别腹腔注射等体积5、10和20 mg/kg浓度的化合物A. 腹腔注射30 min后在空载组小鼠的左后爪趾底注射20 μL生理盐水,其余各组注射等体积的5%福尔马林溶液(含1.85%甲醛),注射后立刻放入透明观察盒中开始录像并计时,观察记录0~5 min(I阶段)和15~45 min(II阶段)期间小鼠舔、咬和抖动被注射足的时间.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 MS谱图分析
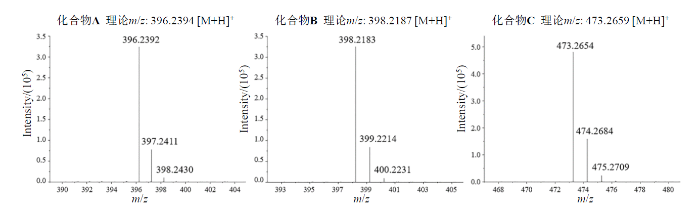
化合物A(C22H29N5O2)信号最强的是m/z为396.239 2 [M+H]+的准分子离子峰,同位素峰m/z为397.241 1和398.243 0;化合物B(C21H27N5O3)信号最强的是m/z为398.218 3 [M+H]+的准分子离子峰,同位素峰m/z为399.221 4和400.223 1;化合物C(C27H32N6O2)信号最强的是m/z为473.265 4 [M+H]+的准分子离子峰,同位素峰m/z为474.268 4和475.270 9.三种化合物的实验结果均与其[M+H]+理论值相符.
图2
2.2 NMR数据分析
图3
图3
化合物A、B和C的化学结构及原子编号
Fig. 3
Chemical structures and atomic numbers of compounds A, B
图4
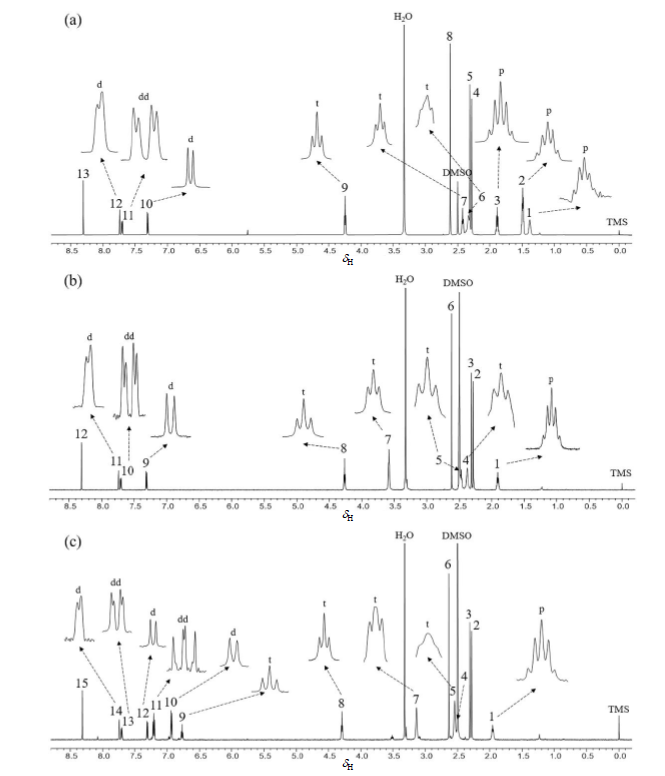
化合物A的1H NMR谱[图4(a)]显示有13组化合物质子信号.低场区(δH 7.20~8.40)为芳香环和吡唑环上的质子信号,单峰δH 8.31(s,1H)归属为H-9.H-1与H-2为J3耦合,H-1与H-5为较弱的J4耦合,因此δH 7.71(dd,J=8.1/2.3 Hz,1H)、δH 7.31(d,J=8.1 Hz,1H)和δH 7.74(d,J=2.3 Hz,1H)分别归属为H-1、H-2和H-5.H-13和H-15都有两个氢原子,且理论上均为三重裂分,H-13与氧原子直接相连,H-15与氮原子直接相连,而氧的电负性大于氮,所以H-13应比H-15更偏向低场区,因此三重峰δH 4.25(t,J=6.2 Hz,2H)归属为H-13,另一个三重峰δH 2.43(t,J=7.0 Hz,2H)归属为H-15.化合物A上共有三个甲基峰δH 2.62(s,3H)、δH 2.31(s,3H)与δH 2.28(s,3H),从中间体化合物3和4的1H NMR谱[图S1(a),S2(a)]可以看出苯环上两个甲基峰的化学位移相近,中间体化合物5的 1H NMR谱[图S3(a)]开始出现第三个甲基峰,且随着中间体化合物6和7结构(即化合物A上H-12附近基团)的改变,它们的1H NMR谱[图S4(a),S5(a)]中位置处于相对低场的甲基峰的化学位移改变较大,因此化合物A中的甲基峰δH 2.62(s,3H)归属为H-12.苯环上C-6与氮原子直接相连,对位的电子云密度比间位的电子云密度高,故推测处于间位甲基上的H-17核会比对位甲基上的H-16核更“裸露”,因此将甲基峰δH 2.31(s,3H)归属为H-17,另一个甲基峰δH 2.28(s,3H)归属为H-16.氢原子数为4的三重峰δH 2.33(t,J=6.8 Hz,4H)归属为H-18和H-22.氢原子数为4的五重峰δH 1.49(p,J=5.5 Hz,4H)归属为H-19和H-21.H-14和H-20均为氢原子数为2的五重峰,从1H NMR谱上看,化合物A变成化合物B和C时,H-14的五重峰不变而H-20的五重峰会消失,且R基上基团变化位置离H-14较远,理论上对H-14的化学位移影响较小,因此化合物A的五重峰δH 1.89(p,J=6.6 Hz,2H)归属为H-14.δH 1.39(p,J=5.9 Hz,2H)归属为H-20. 至此化合物A的所有质子信号得到归属.A的13C NMR谱[图S6(a)]显示有20个信号峰,与化合物A结构相符.化合物A的所有1H NMR数据如表1所示.
表1 化合物A的1H NMR实验数据(溶剂:DMSO-d6)
Table 1
| 编号 | δH | 氢原子个数 | 谱峰裂分(J/Hz) | 归属 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.39 | 2 | p (5.9) | H-20 |
| 2 | 1.49 | 4 | p (5.5) | H-19, H-21 |
| 3 | 1.89 | 2 | p (6.6) | H-14 |
| 4 | 2.28 | 3 | s | H-16 |
| 5 | 2.31 | 3 | s | H-17 |
| 6 | 2.33 | 4 | t (6.8) | H-18, H-22 |
| 7 | 2.43 | 2 | t (7.0) | H-15 |
| 8 | 2.62 | 3 | s | H-12 |
| 9 | 4.25 | 2 | t (6.2) | H-13 |
| 10 | 7.31 | 1 | d (8.1) | H-2 |
| 11 | 7.71 | 1 | dd (8.1/2.3) | H-1 |
| 12 | 7.74 | 1 | d (2.3) | H-5 |
| 13 | 8.31 | 1 | s | H-9 |
注:表中编号对应
表2 化合物B的1H NMR实验数据(溶剂:DMSO-d6)
Table 2
| 编号 | δH | 氢原子个数 | 谱峰裂分(J/Hz) | 归属 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.91 | 2 | p (6.5) | H-14 |
| 2 | 2.28 | 3 | s | H-16 |
| 3 | 2.31 | 3 | s | H-17 |
| 4 | 2.38 | 4 | t (6.8) | H-18, H-21 |
| 5 | 2.48 | 2 | t (7.0) | H-15 |
| 6 | 2.62 | 3 | s | H-12 |
| 7 | 3.58 | 4 | t (4.5) | H-19, H-20 |
| 8 | 4.27 | 2 | t (6.3) | H-13 |
| 9 | 7.31 | 1 | d (8.1) | H-2 |
| 10 | 7.71 | 1 | dd (8.1/2.3) | H-1 |
| 11 | 7.75 | 1 | d (2.3) | H-5 |
| 12 | 8.31 | 1 | s | H-9 |
注:表中编号对应
表3 化合物C的1H NMR实验数据(溶剂:DMSO-d6)
Table 3
| 编号 | δH | 氢原子个数 | 谱峰裂分(J/Hz) | 归属 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.95 | 2 | p (6.6) | H-14 |
| 2 | 2.28 | 3 | s | H-16 |
| 3 | 2.31 | 3 | s | H-17 |
| 4 | 2.52 | 2 | t (7.0) | H-15 |
| 5 | 2.55 | 4 | t (6.8) | H-18, H-21 |
| 6 | 2.64 | 3 | s | H-12 |
| 7 | 3.13 | 4 | t (5.5) | H-19, H-20 |
| 8 | 4.29 | 2 | t (6.2) | H-13 |
| 9 | 6.77 | 1 | t (7.3) | H-25 |
| 10 | 6.93 | 2 | d (8.1) | H-23, H-27 |
| 11 | 7.21 | 2 | dd (8.7/7.2) | H-24, H-26 |
| 12 | 7.30 | 1 | d (8.2) | H-2 |
| 13 | 7.71 | 1 | dd (8.2/2.3) | H-1 |
| 14 | 7.75 | 1 | d (2.3) | H-5 |
| 15 | 8.31 | 1 | s | H-9 |
注:表中编号对应
2.3 质谱成像与镇痛活性分析
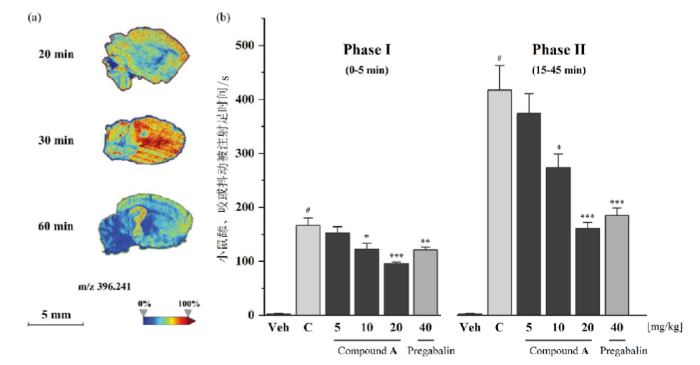
小分子化合物能否穿透血脑屏障可用logP来预测,通过chemdraw对三个化合物的logP值进行计算,化合物A、B、C的logP值分别为3.07、1.87、4.11,因此优选logP适中的化合物A进行质谱成像和镇痛活性研究.给药后不同时间点处死的小鼠的脑切片质谱成像数据如图5(a)所示,颜色代表化合物A浓度高低分布:蓝色代表低浓度,红色代表高浓度.实验结果表明腹腔注射的化合物A能通过吸收进入血液循环,并有效透过血脑屏障到达小鼠脑部.
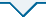
图5
图5
(a)小鼠脑切片质谱成像;(b)福尔马林实验中化合物A的镇痛活性
Fig. 5
(a) Mass spectrometry imaging of mouse brain slices; (b) Analgesic activity of compound A
福尔马林模型能较好地模拟临床的病理性疼痛,其中0~5 min为I阶段(急性神经源性痛),15~45 min为II阶段(炎性痛)[14].普瑞巴林(Pregabalin)和化合物A在小鼠福尔马林实验两个阶段的镇痛效果如图5(b)所示,每列值代表8只小鼠舔、咬或抖动被注射足的平均时间±标准误差(SEM).从Veh组和C组可以看出注射枪头插入和载体溶液注射对小鼠刺激很小,而福尔马林注射会引起明显伤害性反应.药物注射组结果表明普瑞巴林(40 mg/kg)在两个阶段均显示出镇痛作用,化合物A也在两个阶段均展现出显著的剂量依赖性的镇痛效果.实验数据使用单因素方差分析,事后Dunnett检验.统计学显著性:C组与Veh组相比#p<0.001;普瑞巴林组和实验药物组与C组相比*p < 0.05,**p < 0.01,***p < 0.001.
3 结论
本文通过多步反应成功合成了三种未见文献报道的1-(3,4-二甲基苯基)-6-甲基-5-丙氧基-1,5-二氢-4H-吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮类衍生物,通过1H NMR、13C NMR和LC-MS确证了其结构,并完整归属了这三种化合物的1H NMR信号.此外,通过小鼠脑切片质谱成像实验证明了1-(3,4-二甲基苯基)-6-甲基-5-[3-(哌啶-1-基)丙氧基]-1,5-二氢-4H-吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮(A)能够有效透过血脑屏障;福尔马林急性疼痛模型显示出化合物A具有显著的镇痛活性.这些结果为以吡唑并[3,4-d]嘧啶-4-酮为骨架的镇痛药物研发提供了科学参考.
致谢
感谢布鲁克(北京)科技有限公司影像应用部主管李鹏飞工程师提供质谱成像上机测试帮助.
利益冲突
无
附件材料
图S1 中间体化合物3的(a) 1H NMR和(b) 13C NMR谱图.
图S2 中间体化合物4的(a) 1H NMR和(b) 13C NMR谱图.
图S3 中间体化合物5的(a) 1H NMR和(b) 13C NMR谱图.
图S4 中间体化合物6的(a) 1H NMR和(b) 13C NMR谱图.
图S5 中间体化合物7的(a) 1H NMR和(b) 13C NMR谱图.
图S6 化合物A、B和C的13C NMR谱图以及化学位移数据.
可在论文网页版获取.
参考文献
Novel pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives targeting COXs and iNOS enzymes; design, synthesis and biological evaluation as potential anti-inflammatory agents
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.ejps.2014.05.025
PMID:24907682
[本文引用: 1]

A novel set of 4-substituted-1-phenyl-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine and 5-substituted-1-phenyl-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one derivatives were synthesized and evaluated as potential anti-inflammatory agents. The newly prepared compounds were assessed through the examination of their in vitro inhibition of four targets; cyclooxygenases subtypes (COX-1 and COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). Compounds 8a, 10c and 13c were the most potent and selective ligands against COX-2 with inhibition percentages of 79.6%, 78.7% and 78.9% at a concentration of 2 μM respectively, while compound 13c significantly inhibited both COX subtypes. On the other hand, fourteen compounds showed high iNOS inhibitory activities with IC50 values in the range of 0.22-8.5μM where the urea derivative 11 was the most active compound with IC50 value of 0.22 μM. Most of the tested compounds were found to be devoid of inhibitory activity against NF-kB. Moreover, almost all compounds were not cytotoxic, (up to 25 μg/ml), against a panel of normal and cancer cell lines. The in silico docking results were in agreement with the in vitro inhibitory activities against COXs and iNOS enzymes. The results of in vivo anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive studies were consistent with that of in vitro studies which confirmed that compounds 8a, 10c and 13c have significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities comparable to that of the control, ketorolac. Taken together, dual inhibition of COXs and iNOS with novel pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives is a valid strategy for the development of anti-inflammatory/analgesic agents with the probability of fewer side effects.Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Design, synthesis and evaluation of some pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives bearing thiazolidinone moiety as anti-inflammatory agents
[J].
DOI:S0045-2068(18)30400-0
PMID:29929077
[本文引用: 1]

Two new series of pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine bearing thiazolidinone moiety were designed and synthesized. The newly synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro (COX-1 and COX-2) inhibitory assay. Compounds that showed promising COX-2 selectivity were further subjected to in vivo anti-inflammatory screening applying formalin induced paw edema (acute model) and cotton-pellet induced granuloma (chronic model) assays using celecoxib and diclofenac sodium as reference drugs. The histopathological and ulcerogenic potential were also determined. In vivo anti-inflammatory data showed that compounds 2, 6, 7d displayed anti-inflammatory activity higher than both references in the formalin induced paw edema model. On the other hand, compounds 2, 3d, 3e, 7b and 7d displayed anti-inflammatory activity greater than or nearly equivalent to diclofenac sodium in the cotton pellet-induced granuloma assay. Moreover, most of the tested compounds revealed good gastrointestinal safety profile. Collectively, compounds 2 and 7d were considered as promising candidates in managing both acute and chronic inflammation with safe gastrointestinal margin.Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Development and validation of hplc determination of related substances in a novel anticonvulsant agent epimidin
[J].
Synthesis and biological activity of novel Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one derivatives as potent antifungal agent
[J].
DOI:10.1002/ps.6406
PMID:33837653
[本文引用: 1]

To promote the discovery and development of new fungicide with novel scaffolds or modes of action, a series of novel 5-(2-chloroethyl)-1-phenyl-6-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one derivatives were synthesized, and evaluated for their antifungal activities.The bioassay data showed that compound 8IIId (EC = 1.93 mg/L) is superior to boscalid (EC = 6.71 mg/L) against Valsa mali. We introduced chiral groups on the structure of 8IIId, and two chiral configurations were respectively synthesized, which are 8Vc and 8Vd. Surprisingly, 8Vc showed significant antifungal activities against Valsa mali and Physalospora piricola with EC values of 0.22 and 0.55 mg/L. Physiological and biochemical studies showed that the primary action mechanism of compound 8Vc on Valsa mali may involve changing mycelial morphology and increasing cell membrane permeability.These results demonstrated that 8Vc could be further modified as fungicide and provided a valuable reference for antifungal agents with pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one skeleton.This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Synthesis and pharmacological properties of pyrazolotriazolopyrimidine derivatives
[J].DOI:10.1016/0223-5234(92)90064-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Synthesis and evaluation of histamine H3 receptor ligand based on lactam scaffold as agents for treating neuropathic pain
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.04.015 URL [本文引用: 2]
Rational design of new multitarget histamine H3 receptor ligands as potential candidates for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112743 URL [本文引用: 1]
Synthesis of new 1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,5-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin- 4-one derivatives
[J].DOI:10.1134/S1070428017040157 URL [本文引用: 2]
Synthesis and anticancer activity of some new pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one derivatives
[J].
DOI:10.3390/molecules19033297
PMID:24647032
[本文引用: 2]

3,6-Dimethyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one (3) was prepared by hydrolysis of ethyl 5-amino-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate (1) to afford the corresponding carboxylic acid 2, which was reacted with acetic anhydride to give 3. The pyrazolo[3,4-d][1,3]oxazin-4-one 3 was reacted with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, urea, thiourea, thiosemicarbazide, phenylhydrazine and aromatic amines to afford the corresponding pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-ones 4, 5a,b, 6, 7, 8a-e, respectively. Condensation of pyrazoloxazine derivative 3 with 99% hydrazine hydrate afforded the 5-aminopyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidine derivative 9. Coupling of 9 with aromatic aldehydes yielded a series of 3,6-dimethyl-5-(4-substitutedbenzylideneamino)-1-phenyl-1,5-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin- 4-ones 10a-e. The new compounds were tested for their antitumor activity on the MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cell line. Almost all the tested compounds revealed antitumor activity, especially 3,6-dimethyl-5-(4-nitrobenzylideneamino)-1-phenyl-1,5-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one (10e) which displayed the most potent inhibitory activity with a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC₅₀) of 11 µM.
Metallic salts of alcohols and alcohol analogs
[J].DOI:10.1021/cr60049a002 URL [本文引用: 2]
NMR spectroscopic studies on C-2 monosubstituted norbornene derivatives
[J].
外型和内型C-2位单取代降冰片烯衍生物的核磁共振波谱研究
[J].
Structural elucidation and quantitative analysis of hydrogenation products of anthracene by NMR spectroscopy
[J].
蒽加氢产物的结构指认和定量核磁共振分析
[J].
Modified formalin test: characteristic biphasic pain response
[J].
DOI:10.1016/0304-3959(89)90222-4
PMID:2478947
[本文引用: 1]

A modified formalin test in mice was investigated. The pain response curve induced by 0.5% formalin was biphasic, having 2 peaks, from 0 to 5 min (first phase) and from 15 to 20 min (second phase). A low concentration of formalin was used, allowing the effects of weak analgesics to be detected. Centrally acting drugs such as narcotics inhibited both phases equally. Peripherally acting drugs such as aspirin, oxyphenbutazone, hydrocortisone and dexamethasone only inhibited the second phase. Aminopyrine and mefenamic acid which acted on both central and peripheral sites inhibited both phases, but the second phase was inhibited by lower doses. Thus, this method enables one to easily distinguish the site of action of analgesics. Furthermore, pain response in the first phase was inhibited by capsaicin-treated desensitization and Des-Arg9-(Leu8)-bradykinin (bradykinin inhibitor). The second phase was inhibited by compound 48/80 pretreatment, indomethacin and bradykinin inhibitor. Therefore, it is suggested that substance P and bradykinin participate in the manifestation of the first phase response, and histamine, serotonin, prostaglandin and bradykinin are involved in the second phase. These results indicate that the first and second phase responses induced by formalin have distinct characteristic properties, and it is a very useful method for examining pain, nociception and its modulation by pharmacological or other means.