
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2024, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 19-29.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20233064
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Zhenshun1,YUAN Xiaohan2,HUANG Ziheng1,SHAO Chengwei2,WU Jie1,#( ),BIAN Yun2,*(
),BIAN Yun2,*( )
)
Received:2023-04-19
Published:2024-03-05
Online:2023-06-08
Contact:
# Tel: 021-55271116, E-mail: CLC Number:
XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29.
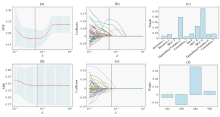
Fig. 3
(a) Mean Square Error (MSE) graphs corresponding to different λ values of radiomics features. The MSE is minimized by adjusting the λ value to determine the optimal λ value; (b) Convergence diagram of the optimal characteristic coefficient of radiomics features; (c) Weight of radiomics features screened by LASSO, Skewness.1 represents skewness, Busyness.1 represents complexity, MCC.2 represents morphological correlation coefficient, DependencyVariance.2 represents dependency difference, Idn.4 represents inverse difference moment, and Correlation.7 represents correlation; (d) Mean square error (MSE) graphs corresponding to different λ values of deep learning features; (e) Convergence diagram of the optimal characteristic coefficient of deep learning features; (f) Weight of deep learning features screened by LASSO

Table 3
Performance of the feature models in the four classifiers
| 特征模型 | 分类器 | 准确率 | 召回率 | 精确率 | AUC | F1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAD | SVM | 0.8077 | 0.5789 | 0.8462 | 0.7592 | 0.6875 | |||
| ADAboost | 0.8269 | 0.6842 | 0.8125 | 0.7967 | 0.7429 | ||||
| Random Forest | 0.7885 | 0.6742 | 0.7222 | 0.7663 | 0.6974 | ||||
| Logistic | 0.8269 | 0.6316 | 0.8571 | 0.7855 | 0.7273 | ||||
| DL | SVM | 0.6731 | 0.1176 | 0.5303 | 0.5595 | 0.1925 | |||
| ADAboost | 0.7692 | 0.9000 | 0.6429 | 0.8645 | 0.7500 | ||||
| Random Forest | 0.7115 | 0.7619 | 0.6154 | 0.8407 | 0.6809 | ||||
| Logistic | 0.7500 | 0.2857 | 0.5714 | 0.5770 | 0.3809 | ||||
| RAD_DL | SVM | 0.8462 | 0.6111 | 0.7908 | 0.8051 | 0.6894 | |||
| ADAboost | 0.8269 | 0.7727 | 0.8095 | 0.6882 | 0.7907 | ||||
| Random Forest | 0.8077 | 0.6364 | 0.8750 | 0.8051 | 0.7369 | ||||
| Logistic | 0.8462 | 0.9444 | 0.7083 | 0.8441 | 0.8095 | ||||
| Clinical_RAD_DL | SVM | 0.8846 | 0.8235 | 0.8235 | 0.8689 | 0.8235 | |||
| ADAboost | 0.8654 | 0.8823 | 0.7500 | 0.8697 | 0.8108 | ||||
| Random Forest | 0.7692 | 0.7059 | 0.6316 | 0.7529 | 0.6667 | ||||
| Logistic | 0.9231 | 0.8824 | 0.8820 | 0.9126 | 0.8822 | ||||
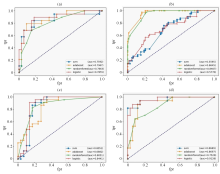
Fig. 4
ROC curve of four characteristic models. The abscissa is fpr (false positive rate) and the ordinate is tpr (true positive rate). The four classifiers are SVM, adaboost (ADAboost), randomforest (Random Forest) and logistic (Logistic). (a) ROC curve used by RAD feature model; (b) ROC curve of DL feature model; (c) ROC curve of RAD_DL feature model; (d) ROC curve of Clinical _RAD_DL feature model

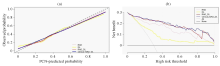
Fig. 5
Calibration curves and decision curves. (a) Calibration curves of RAD, DL, RAD_DL, and Clinical-RAD_DL feature model. The abscissa represents the PCN-predicted probability of PCN classification model, and the ordinate represents the observed probability; (b) Decision curves used by RAD, DL, RAD_DL, and Clinical-RAD_DL feature model. The abscissa represents the high risk threshold, and the ordinate represents the net benefit of the model, the All curve represents the net benefit predicted as MCN, and the None curve represents the net benefit predicted as SCN

| [1] | LI Z S, JIN Z D, LI X. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreas cystic neoplasm(2022)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39(2): 290-298. |
| 李兆申, 金震东, 李汛. 中国胰腺囊性肿瘤诊断指南(2022年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(2): 290-298. | |
| [2] |
BIAN Y, JIANG H, CAO K, et al. The relationship between microscopic tumor size and CT tumor size in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Clin Imag, 2021, 76: 30-37.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.11.039 pmid: 33548890 |
| [3] |
JAYASREE C, ABHISHEK M, LIOR G, et al. CT radiomics to predict high-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Med phys, 2018, 45(11): 5019-5029.
doi: 10.1002/mp.13159 pmid: 30176047 |
| [4] |
AVANZO M, WEI L S, STANCANELLO J, et al. Machine and deep learning methods for radiomics[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(5): 185-202.
doi: 10.1002/mp.13678 pmid: 32418336 |
| [5] | HAN B, XU J, WANG Y J, et al. Classification of BI-RADS 3-5 breast lesions based on MRI radiomics[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2023, 40(1): 52-67. |
| 韩冰, 徐晶, 王远军, 等. 基于MRI影像组学的BI-RADS 3-5类乳腺病变三分类[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2023, 40(1): 52-67. | |
| [6] |
SHBOUL Z A, ALAM M, VIDYARATNE L, et al. Feature-guided deep radiomics for glioblastoma patient survival prediction[J]. Front Neurosci, 2019, 13: 966-982.
doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00966 |
| [7] |
LI J, LIU F, FANG X, et al. CT Radiomics features in differentiation of focal-type autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a propensity score analysis[J]. Acad Radiol, 2021, 29(3): 358-366.
doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.04.014 pmid: 34108115 |
| [8] |
PREUSS K, THACH N, LIANG X, et al. Using quantitative imaging for personalized medicine in pancreatic cancer: a review of radiomics and deep learning applications[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(7): 1654.
doi: 10.3390/cancers14071654 |
| [9] | NGUON L S, SEO K, LIM J H, et al. Deep learning-based differentiation between mucinous cystic neoplasm and serous cystic neoplasm in the pancreas using endoscopic ultrasonography[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2021, 11(6): 1052. |
| [10] | YANG Y F, QI Z X, NIE S D. Differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions based on multimodal MRI and deep learning[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(4): 401-412. |
| 杨一风, 祁章璇, 聂生东. 基于多模态MRI与深度学习的乳腺病变良恶性鉴别[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(4): 401-412. | |
| [11] | ZHANG Y F, XU S S, WU J, et al. Value of CT texture analysis in differentiating pancreatic serous cystadenoma from mucinous cystadenoma[J]. Journal of Southeast University, 2022, 41(3): 308-316. |
| 张怡帆, 徐姗姗, 吴锦, 等. CT纹理分析在鉴别胰腺浆液性囊腺瘤与黏液性囊腺瘤中的价值[J]. 东南大学学报, 2022, 41(3): 308-316. | |
| [12] |
PARK H J, SHIN K, YOU M W, et al. Deep learning-based detection of solid and cystic pancreatic neoplasms at contrast-enhanced CT[J]. Radiology, 2023, 306(1): 140-149.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.220171 |
| [13] |
ISLAM W, JONES M, FAIZ R, et al. Improving performance of breast lesion classification using a ResNet50 model optimized with a novel attention mechanism[J]. Tomography, 2022, 8(5): 2411-2425.
doi: 10.3390/tomography8050200 pmid: 36287799 |
| [14] | LU J, WU Y, XIONG Y, et al. Breast tumor computer-aided detection system based on magnetic resonance imaging using convolutional neural network[J]. Comput Model Eng Sci, 2022, 130(1): 365-377. |
| [15] | 中国人民解放军海军军医大学第一附属医院. 胰腺外分泌功能评价模型的训练方法、系统、电子设备及介质: 中国, CN2022107020513[P], 2022-08-09. |
| [16] |
LIANG W, TIAN W, WANG Y, et al. Classification prediction of pancreatic cystic neoplasms based on radiomics deep learning models[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 1237-1246.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10273-4 pmid: 36447168 |
| [17] | WANG D, HU Y, ZHAN C, et al. A nomogram based on radiomics signature and deep-learning signature for preoperative prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12(20): 940-950. |
| [18] |
XIE T, WANG X, ZHANG Z, et al. CT-based radiomics analysis for preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm and atypical serous cystadenomas[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11(6): 621520.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.621520 |
| [19] | SHAO C, FENG X, YU J, et al. A nomogram for predicting pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm and serous cystic neoplasm[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2021, 46(8): 3963-3973. |
| [20] | CHEN S. Application of CT radiomics in differential diagnosis of pancreatic serous and mucinous cystic neoplasm[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2022, 20(10): 92-105. |
| 陈帅. 基于CT影像组学对胰腺浆液及黏液性囊性肿瘤鉴别诊断[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(10): 92-105. |
| [1] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [2] | LAI Jiawen, WANG Yuling, CAI Xiaoyu, ZHOU Lihua. Multidimensional Information Fusion Method for Meniscal Tear Classification Based on CNN-SVM [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 423-434. |
| [3] | WANG Hui, WANG Tiantian, WANG Lijia. Squeeze-and-excitation Residual U-shaped Network for Left Myocardium Segmentation Based on Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 435-447. |
| [4] | Li Yijie, YANG Xinyu, YANG Xiaomei. Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction of Multi-scale Residual Unet Fused with Attention Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 307-319. |
| [5] | LU Qiqi, LIAN Zifeng, LI Jialong, SI Wenbin, MAI Zhaohua, FENG Yanqiu. Magnetic Resonance R2* Parameter Mapping of Liver Based on Self-supervised Deep Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 258-269. |
| [6] | ZHANG Jiajun, LU Yucheng, BAO Yifang, LI Yuxin, GENG Chen, HU Fuyuan, DAI Yakang. An Automatic Segmentation Method of Cerebral Arterial Tree in TOF-MRA Based on DBCNet [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 320-331. |
| [7] | TIAN Hui, WU Jie, BIAN Yun, ZHANG Zhiwei, SHAO Chengwei. Classification of Pancreatic Cystic Tumors Based on DenseNet and Transfer Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 270-279. |
| [8] | QIAN Chengyi,WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Imaging Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 220-238. |
| [9] | HUANG Min,LI Siyi,CHEN Junbo,ZHOU Dao. Progress of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting Technology and Its Clinical Application [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 207-219. |
| [10] | HAN Bing,XU Jing,WANG Yuanjun,WANG Zhongling. Classification of BI-RADS 3-5 Breast Lesions Based on MRI Radiomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 52-67. |
| [11] | SHI Weicheng,JIN Zhaoyang,YE Zheng. Fast Multi-channel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based on PCAU-Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 39-51. |
| [12] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [13] | Di LI, Lei HUO, Meng-yun WAN, Ning-yang JIA, Li-jia WANG. Application of Radiomics Based on New Support Vector Machine in the Classification of Hepatic Nodules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 278-290. |
| [14] | Qin ZHOU, Yuan-jun WANG. Groupwise Registration for Magnetic Resonance Image Based on Variational Inference [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 291-302. |
| [15] | Xiao CHANG,Xin CAI,Guang YANG,Sheng-dong NIE. Applications of Generative Adversarial Networks in Medical Image Translation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 366-380. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||