
- Jul. 10, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 439-447.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20222983
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rui QIN1,2,Chao WANG2,Qiang WANG2,Min HU2,3,Jin-lin LI1,*( ),Jun XU2,*(
),Jun XU2,*( ),Feng DENG2
),Feng DENG2
Received:2022-03-15
Online:2022-12-05
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Jin-lin LI,Jun XU
E-mail:lij@mail.scuec.edu.cn;xujun@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Rui QIN,Chao WANG,Qiang WANG,Min HU,Jin-lin LI,Jun XU,Feng DENG. Formation and Reactivity of Surface Methoxy Species in Methanol Conversion over SSZ-13 Zeolite[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 439-447.
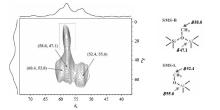
Fig.3
2D 13C-27Al HMQC NMR spectrum of trapped products obtained from reaction of 13C-methanol over SSZ-13 at 250 ℃ for 1 min. The cross-peak framed by dotted lines is originated from the quadrupole broadening of tetrahedral Al in the 27Al dimension. Schematic models of the methoxy species formed on Brønsted site (SMS-B) and Lewis site (SMS-L) are shown in the right panel

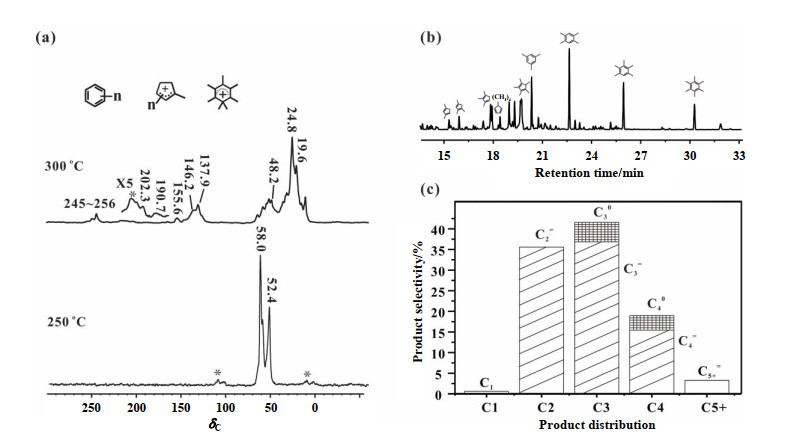
Fig.4
1H→13C CP/MAS NMR spectra of trapped products obtained from reaction of 13C-methanol over SSZ-13 at 250 ℃ and 300 ℃ for 15 min (a), GC analysis of extract of the retained species on reacted catalyst at 300 ℃ (b) and product selectivity of effluent products (c). *Asterisks denote spinning sidebands
| 1 |
CHANG C D, SILVESTRI A J The conversion of methanol and other O-compounds to hydrocarbons over zeolite catalysts[J]. J Catal, 1977, 47 (2):249-259.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(77)90172-5 |
| 2 |
CHANG C D Hydrocarbons from methanol[J]. Catal Rev, 1983, 25 (1):1-118.
doi: 10.1080/01614948308078874 |
| 3 |
HAW J F, SONG W, MARCUS D M, et al The mechanism of methanol to hydrocarbon catalysis[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2003, 36 (5):317-326.
doi: 10.1021/ar020006o |
| 4 |
OLSBYE U, SVELLE S, BJ RGEN M, et al Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons: How zeolite cavity and pore size controls product selectivity[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51 (24):5810-5831.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201103657 |
| 5 |
ILIAS S, BHAN A Mechanism of the catalytic conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons[J]. ACS Catal, 2013, 3 (1):18-31.
doi: 10.1021/cs3006583 |
| 6 |
WANG C, XU J, DENG F Mechanism of methanol-to-hydrocarbon reaction over zeolites: A solid-state NMR perspective[J]. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12 (4):965-980.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.201901937 |
| 7 |
MOLE T, BETT G, SEDDON D Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons over ZSM-5 zeolite: An examination of the role of aromatic hydrocarbons using 13carbon- and deuterium-labeled feeds[J]. J Catal, 1983, 84 (2):435-445.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(83)90014-3 |
| 8 |
HAW J F, NICHOLAS J B, SONG W, et al Roles for cyclopentenyl cations in the synthesis of hydrocarbons from methanol on zeolite catalyst HZSM-5[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2000, 122 (19):4763-4775.
doi: 10.1021/ja994103x |
| 9 |
SONG W G, HAW J F, NICHOLAS J B, et al Methylbenzenes are the organic reaction centers for methanol-to-olefin catalysis on HSAPO-34[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2000, 122 (43):10726-10727.
doi: 10.1021/ja002195g |
| 10 | ARSTAD B, KOLBOE S Methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction over SAPO-34. Molecules confined in the catalyst cavities at short time on stream[J]. Catal Lett, 2001, 71 (3-4):209-212. |
| 11 |
SVELLE S, BJ RGEN M, KOLBOE S, et al Intermediates in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons (MTH) reaction: A gas phase study of the unimolecular reactivity of multiply methylated benzenium cations[J]. Catal Lett, 2006, 109 (1-2):25-35.
doi: 10.1007/s10562-006-0052-8 |
| 12 |
ILIAS S, BHAN A The mechanism of aromatic dealkylation in methanol-to-hydrocarbons conversion on H-ZSM-5: What are the aromatic precursors to light olefins?[J]. J Catal, 2014, 311, 6-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.11.003 |
| 13 |
SUN X Y, MUELLER S, SHI H, et al On the impact of co-feeding aromatics and olefins for the methanol-to-olefins reaction on HZSM-5[J]. J Catal, 2014, 314, 21-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.03.013 |
| 14 |
YARULINA I, DE WISPELAERE K, BAILLEUL S, et al Structure–performance descriptors and the role of Lewis acidity in the methanol-to-propylene process[J]. Nat Chem, 2018, 10 (8):804-812.
doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0081-0 |
| 15 |
ST CKER M Methanol-to-hydrocarbons: catalytic materials and their behavior[J]. Micropor Mesopor Mat, 1999, 29 (1-2):3-48.
doi: 10.1016/S1387-1811(98)00319-9 |
| 16 |
LIU Y, M LLER S, BERGER D, et al Formation mechanism of the first carbon–carbon bond and the first olefin in the methanol conversion into hydrocarbons[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55 (19):5723-5726.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201511678 |
| 17 |
CHOWDHURY A D, HOUBEN K, WHITING G T, et al Initial carbon–carbon bond formation during the early stages of the methanol-to-olefin process proven by zeolite-trapped acetate and methyl acetate[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55 (51):15840-15845.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201608643 |
| 18 |
WANG C, CHU Y Y, XU J, et al Extra-framework aluminum-assisted initial C−C bond formation in methanol-to-olefins conversion on zeolite H-ZSM-5[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57 (32):10197-10201.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201805609 |
| 19 |
LESTHAEGHE D, VAN SPEYBROECK V, MARIN G B, et al Understanding the failure of direct C-C coupling in the zeolite-catalyzed methanol-to-olefin process[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45 (11):1714-1719.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200503824 |
| 20 |
MARCUS D M, MCLACHLAN K A, WILDMAN M A, et al Experimental evidence from H/D exchange studies for the failure of direct C-C coupling mechanisms in the methanol-to-olefin process catalyzed by HSAPO-34[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45 (19):3133-3136.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200504372 |
| 21 |
SONG W g, MARCUS D M, FU H, et al An oft-studied reaction that may never have been: Direct catalytic conversion of methanol or dimethyl ether to hydrocarbons on the solid acids HZSM-5 or HSAPO-34[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124 (15):3844-3845.
doi: 10.1021/ja016499u |
| 22 |
HUTCHINGS G J, GOTTSCHALK F, HUNTER R Hydrocarbon formation from methylating agents over the zeolite catalyst ZSM-5. Comments on the mechanism of carbon?carbon bond and methane formation[J]. J Chem Soc, Farady Trans, 1987, 83 (3):571-583.
doi: 10.1039/f19878300571 |
| 23 |
WU X Q, XU S T, ZHANG W N, et al Direct mechanism of the first carbon–carbon bond formation in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons process[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2017, 56 (31):9039-9043.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201703902 |
| 24 |
DESSAU R M, LAPIERRE R B On the mechanism of methanol conversion to hydrocarbons over HZSM-5[J]. J Catal, 1982, 78 (1):136-141.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(82)90292-5 |
| 25 |
MOLE T, WHITESIDE J A, SEDDON D Aromatic co-catalysis of methanol conversion over zeolite catalysts[J]. J Catal, 1983, 82 (2):261-266.
doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(83)90192-6 |
| 26 |
DAHL I, KOLBOE S On the reaction mechanism for propene formation in the MTO reaction over SAPO-34[J]. Catal Lett, 1993, 20 (3-4):329-336.
doi: 10.1007/BF00769305 |
| 27 |
XU S T, ZHENG A M, WEI Y X, et al Direct observation of cyclic carbenium ions and their role in the catalytic cycle of the methanol-to-olefin reaction over chabazite zeolites[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2013, 52 (44):11564-11568.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201303586 |
| 28 |
SVELLE S, JOENSEN F, NERLOV J, et al Conversion of methanol into hydrocarbons over zeolite H-ZSM-5: Ethene formation is mechanistically separated from the formation of higher alkenes[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128 (46):14770-14771.
doi: 10.1021/ja065810a |
| 29 |
BJORGEN M, SVELLE S, JOENSEN F, et al Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons over zeolite H-ZSM-5: On the origin of the olefinic species[J]. J Catal, 2007, 249 (2):195-207.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.04.006 |
| 30 |
YU B W, LOU C Y, ZHANG W N, et al Insight into the dual cycle mechanism of methanol-to-olefins reaction over SAPO-34 molecular sieve by isotopic tracer studies[J]. Chem Res Chinese U, 2020, 36 (6):1203-1208.
doi: 10.1007/s40242-020-0216-x |
| 31 |
MCCANN D M, LESTHAEGHE D, KLETNIEKS P W, et al A complete catalytic cycle for supramolecular methanol-to-olefins conversion by linking theory with experiment[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47 (28):5179-5182.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200705453 |
| 32 |
WANG C, XU J, QI G D, et al Methylbenzene hydrocarbon pool in methanol-to-olefins conversion over zeolite H-ZSM-5[J]. J Catal, 2015, 332, 127-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.10.001 |
| 33 |
WANG C, CHU Y Y, ZHENG A M, et al New insight into the hydrocarbon-pool chemistry of the methanol-to-olefins conversion over zeolite H-ZSM-5 from GC-MS, solid-state NMR spectroscopy, and DFT calculations[J]. Chem Eur J, 2014, 20 (39):12432-12443.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201403972 |
| 34 |
WANG W, SEILER M, HUNGER M Role of surface methoxy species in the conversion of methanol to dimethyl ether on acidic zeolites investigated by in situ stopped-flow MAS NMR spectroscopy[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2001, 105 (50):12553-12558.
doi: 10.1021/jp0129784 |
| 35 |
WANG W, BUCHHOLZ A, SEILER M, et al Evidence for an initiation of the methanol-to-olefin process by reactive surface methoxy groups on acidic zeolite catalysts[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125 (49):15260-15267.
doi: 10.1021/ja0304244 |
| 36 |
COMAS-VIVES A, VALLA M, COP RET C, et al Cooperativity between Al sites promotes hydrogen transfer and carbon–carbon bond formation upon dimethyl ether activation on alumina[J]. ACS Cent Sci, 2015, 1 (6):313-319.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.5b00226 |
| 37 |
DEIMUND M A, HARRISON L, LUNN J D, et al Effect of heteroatom concentration in SSZ-13 on the methanol-to-olefins reaction[J]. ACS Catal, 2016, 6 (2):542-550.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b01450 |
| 38 | 赵星岭, 齐国栋, 王强, 等 Ga改性Ga/ZSM-5分子筛的结构、性质及其催化丙烷芳构化的固体核磁共振波谱研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41 (12):2681-2689. |
| ZHAO X L, QI G D, WANG Q, et al Structure, nature and activity of ga species for propane aromatization in Ga/ZSM-5 revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Chem J Chinese U, 2020, 41 (12):2681-2689. | |
| 39 |
ZHOU X, WANG C, CHU Y Y, et al Mechanistic insight into ethanol dehydration over sapo-34 zeolite by solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Chem Res Chinese U, 2022, 38 (1):155-160.
doi: 10.1007/s40242-022-1450-1 |
| 40 | 齐国栋, 叶晓栋, 徐君, 等 分子筛上糖类催化转化的核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42 (1):148-164. |
| QI G D, YE X D, XU J, et al Progress in NMR studies of carbohydrates conversion on zeolites[J]. Chem J Chinese U, 2021, 42 (1):148-164. | |
| 41 |
WANG W, HUNGER M Reactivity of surface alkoxy species on acidic zeolite catalysts[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2008, 41 (8):895-904.
doi: 10.1021/ar700210f |
| 42 |
LI S H, LAFON O, WANG W Y, et al Recent advances of solid-state nmr spectroscopy for microporous materials[J]. Adv Mater, 2020, 32 (44):2002879.
doi: 10.1002/adma.202002879 |
| 43 |
QI G D, WANG Q, XU J, et al Solid-state NMR studies of internuclear correlations for characterizing catalytic materials[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2021, 50 (15):8382-8399.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS01130D |
| 44 |
RAVI M, SUSHKEVICH V L, VAN BOKHOVEN J A Towards a better understanding of Lewis acidic aluminium in zeolites[J]. Nat Mater, 2020, 19 (10):1047-1056.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-0751-3 |
| 45 |
PHUNG T K, BUSCA G On the Lewis acidity of protonic zeolites[J]. App Catal A: Gen, 2015, 504, 151-157.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.11.031 |
| 46 |
LESTHAEGHE D, VANDER MYNSBRUGGE J, VANDICHEL M, et al Full theoretical cycle for both ethene and propene formation during methanol-to-olefin conversion in H-ZSM-5[J]. ChemCatChem, 2011, 3 (1):208-212.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.201000286 |
| 47 |
LIU Y, KIRCHBERGER F M, M LLER S, et al Critical role of formaldehyde during methanol conversion to hydrocarbons[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10 (1):1462.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09449-7 |
| 48 |
ARORA S S, NIESKENS D L S, MALEK A, et al Lifetime improvement in methanol-to-olefins catalysis over chabazite materials by high-pressure H2 co-feeds[J]. Nat Catal, 2018, 1 (9):666-672.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-018-0125-2 |
| [1] | Shu ZENG, Shu-tao XU, Ying-xu WEI, Zhong-min LIU. Investigation of the Ethanol Dehydration to Ethene Reaction on H-SSZ-13 Molecular Sieve by in situ Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 123-132. |
| [2] | Han-di CHEN,Hai-yu KONG,Zhen-chao ZHAO,Wei-ping ZHANG. Exploring the Na+ Locations and Al Distributions in SSZ-39 Zeolite by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy and DFT Calculations [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 543-551. |
| [3] | Wen-jie YANG,Jun HUANG. Analysis of Local Structure, Acidic Property and Activity of Solid Acids by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 460-473. |
| [4] | Xi-feng XIA,Wen-jing ZHANG,Zhi-ye LIN,Xiao-kang KE,Yu-jie WEN,Fang WANG,Jun-chao CHEN,Lu-ming PENG. Solid-State NMR Studies on the Surface Structure and Properties of Oxide Nanomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 533-542. |
| [5] | Yong-xiang WANG,Qiang WANG,Jun XU,Qing-hua XIA,Feng DENG. The Effects of Ammonium Hexafluorosilicate Post-Treatment on the Acidity of H-ZSM-5 Zeolite Studied by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 514-522. |
| [6] | Zi-chun WANG,Jun HUANG,Yi-jiao JIANG. Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy Studies of Enhanced Acidity of Silica-Aluminas Based on Penta-Coordinated Aluminum Species [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 552-570. |
| [7] | Yao XIAO,Chang-jiu XIA,Xian-feng YI,Feng-qing LIU,Shang-bin LIU,An-min ZHENG. Progress in the Studies on Sn-Zeolites by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 571-584. |
| [8] | Shu-shu GAO,Shu-tao XU,Ying-xu WEI,Zhong-min LIU. Applications of Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Methanol-to-Olefins Reaction [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 433-447. |
| [9] | Xin CHEN,Ying-yi FU,Bin YUE,He-yong HE. Acidity and Basicity of Solid Acid Catalysts Studied by Solid-State NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 491-502. |
| [10] | LEI Zhen-yu, LIANG Xin-miao, LEI You-yi, YANG Li, FENG Ji-wen. Progresses in Solid-State NMR Studies on Carbon Anode Materials for Lithium/Sodium-Ion Batteries [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 28-39. |
| [11] | WEI Ling, ZHANG Shan-min. Suppressing Background 13C NMR Signal From the Probe Head by Phase Incremented Pulses [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 123-130. |
| [12] | LIN Ze-yu, HUO Hua, WANG Qi-hang. Progress in Solid-State NMR Studies of Monoclinic Lithium Vanadium Phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 16-27. |
| [13] | WANG Jia-xin, FENG Ji-wen, CHEN Jun-fei, WANG Li-ying, LIU Chao-yang. Design and Fabrication of a Magic-Angle Spinning Rotor for Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Probe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2019, 36(4): 446-455. |
| [14] | YAN Xiao-jing, HU Bing-wen. Probing 15N-15N Correlations in g-C3N4 Samples with Solid-State NMR SHA+ Pulse Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2016, 33(3): 361-367. |
| [15] | LI Bo-jie,XU Jun*,WANG Qiang,WANG Xiu-mei,QI Guo-dong,DENG Feng*. Carbonylation of Methanol on Cu-H-MOR Zeolites: Insights from Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2014, 31(3): 331-340. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||