
- May. 31, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 1-12.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20243107cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20243107
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHAO Zhengze, WANG Xingle, YANG Xue, XIN Jiaxiang, WEI Daxiu*( ), YAO Yefeng#(
), YAO Yefeng#( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Published:2025-03-05
Online:2024-04-28
Contact:
*Tel: 021-62233281, E-mail: dxwei@phy.ecnu.edu.cn;# Tel: 021-62234328, E-mail: yfyao@phy.ecnu.edu.cn.
CLC Number:
SHAO Zhengze, WANG Xingle, YANG Xue, XIN Jiaxiang, WEI Daxiu, YAO Yefeng. A Spectral Editing Technique Based on Optimized Control of Nuclear Spin to Realize Lactate Signal Selection[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 1-12.
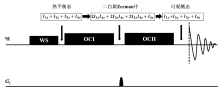
Fig. 1
The pulse sequence based on spectral editing method to selectively detect lactate, which is called OC-spectral editing method. The black rectangles represent water suppression pulse (WS), pulses of OC I and OC II, respectively. The black bell denotes the gradient field used to coherence diphase
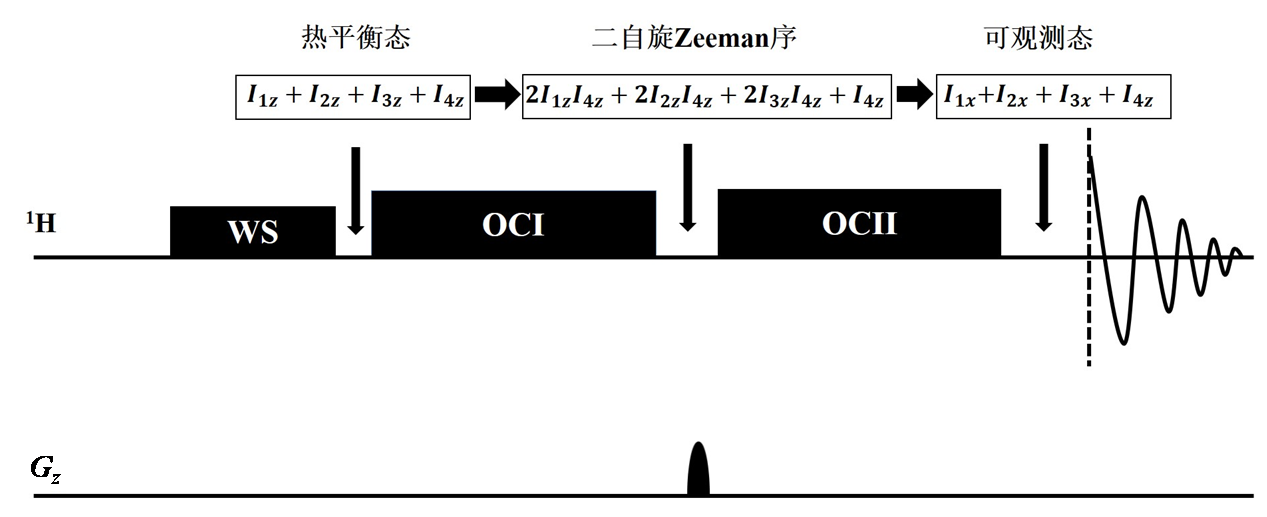
Fig. 4
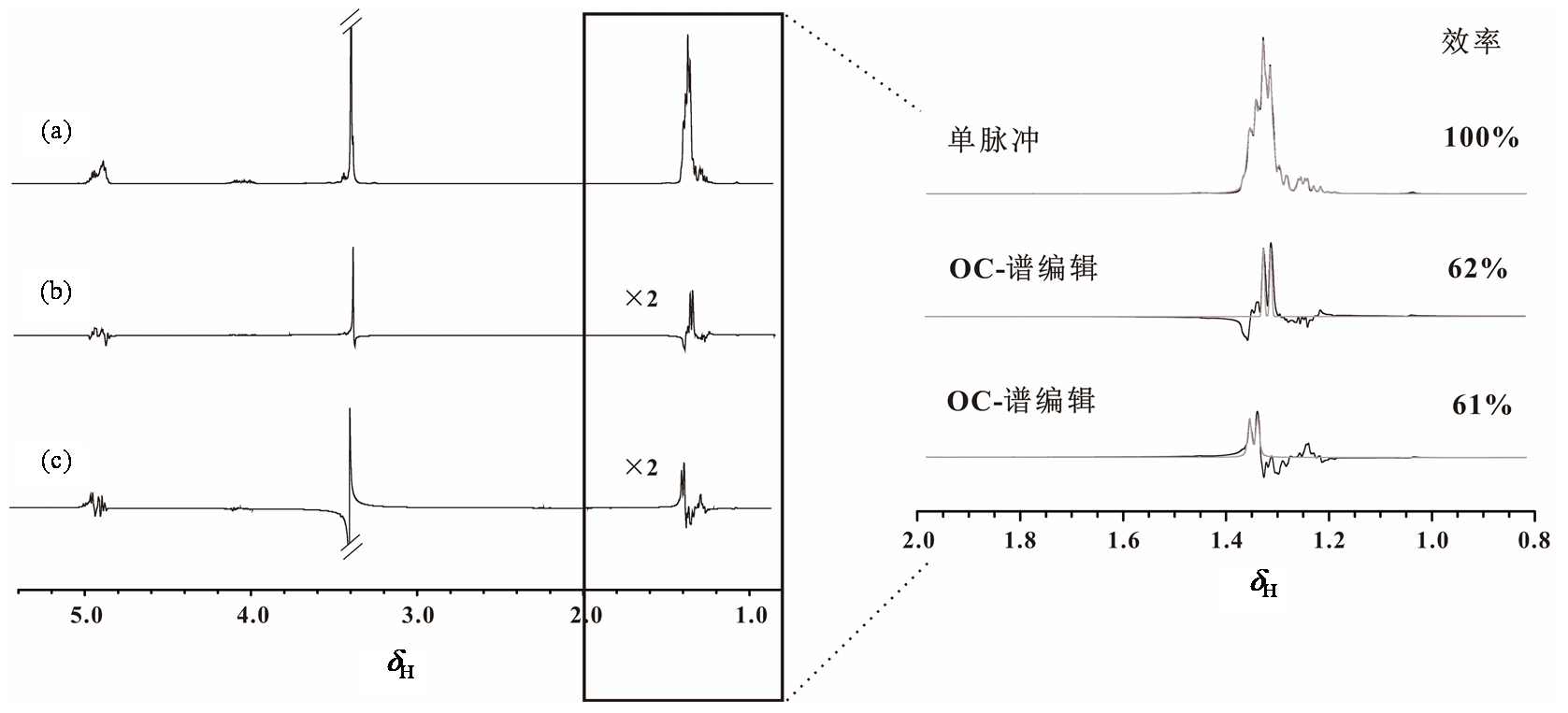
Simulated 1H NMR spectra obtained by (a) single-pulse sequence, (b) OC-spectral editing pulse sequence, (c) the CPMG pulse sequence, and (d) the OC singlet-state pulse sequence to selectively detect the signal of methyl in lactate. The inset on the right provides a magnified view of the signal within the box
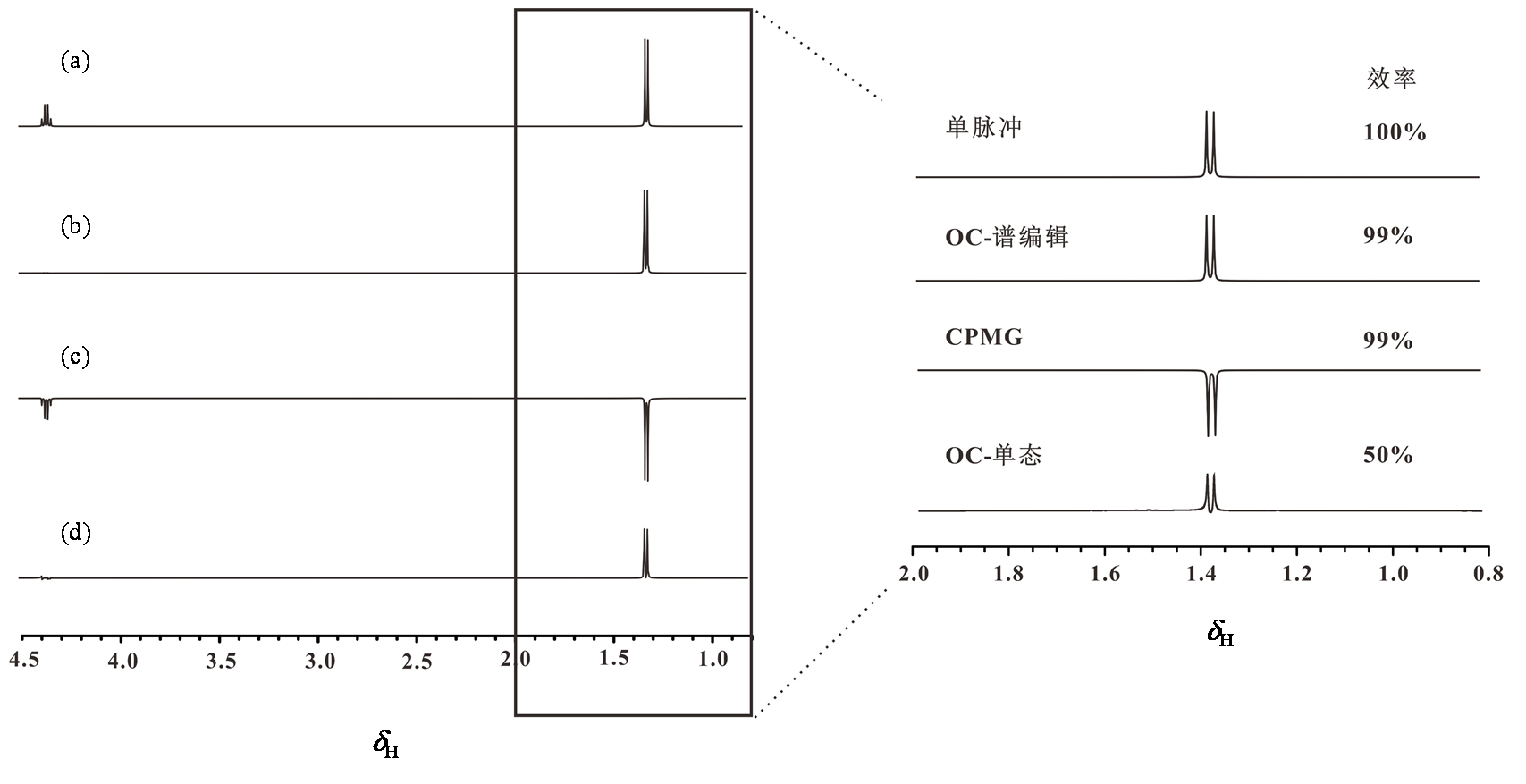

Fig. 12
1H NMR spectra obtained by applying a single pulse (a), OC-spectral editing pulse sequence to δ1.33 (b) and δ1.35 (c) of sample 4, respectively. Signal intensity of OC-spectral editing filtered spectrum has been magnified twofold. The inset on the right provides a magnified view of the signal within the box
| [1] | KARAGIANNIS A, GALLOPIN T, LACROIX A, et al. Lactate is an energy substrate for rodent cortical neurons and enhances their firing activity[J]. Elife, 2021, 10: e71424. |
| [2] |
MAGISTRETTI P J, ALLAMAN I. Lactate in the brain: from metabolic end-product to signalling molecule[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2018, 19(4): 235-249.
doi: 10.1038/nrn.2018.19 pmid: 29515192 |
| [3] |
MA C, XU P, QIU J, et al. An enzymatic route to produce pyruvate from lactate[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2004, 66: 34-39.
pmid: 15252696 |
| [4] | BROOKS G A. Lactate as a fulcrum of metabolism[J]. Redox Biol, 2020, 35: 101454. |
| [5] |
HUGHES D, ROZANSKI E R, SHOFER F S, et al. Effect of sampling site, repeated sampling, pH, and PCO2 on plasma lactate concentration in healthy dogs[J]. Am J Vet Res, 1999, 60(4): 521-524.
pmid: 10211699 |
| [6] |
WILLIAMS D L, DOIG A R, KOROSI A. Electrochemical-enzymatic analysis of blood glucose and lactate[J]. Anal Chem, 1970, 42(1): 118-121.
pmid: 5409504 |
| [7] |
NAKAMURA H, DOI M, SUZUKI T, et al. The significance of lactate and lipid peaks for predicting primary neuroepithelial tumor grade with proton MR spectroscopy[J]. Magn Reson Med Sci, 2018, 17(3): 238-243.
doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2017-0042 pmid: 28819084 |
| [8] | KOZIĆ D, BJELAN M, BOBAN J, et al. A prominent lactate peak as a potential key magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) feature of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML): Spectrum pattern observed in three patients[J]. Bosnian J Basic Med, 2017, 17(4): 349. |
| [9] | KOBUS T, WRIGHT A J, VAN ASTEN J J, et al. In vivo 1H MR spectroscopic imaging of aggressive prostate cancer: Can we detect lactate?[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 71(1): 26-34. |
| [10] |
BREDELLA M A, GHOMI R H, THOMAS B J, et al. Comparison of 3.0 T proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy short and long echo-time measures of intramyocellular lipids in obese and normal-weight women[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2010, 32(2): 388-393.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.22226 pmid: 20677267 |
| [11] | NIESS F, ROAT S, BOGNER W, et al. 3D localized lactate detection in muscle tissue using double-quantum filtered 1H MRS with adiabatic refocusing pulses at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 87(3): 1174-1183. |
| [12] | VAN DIJK J, BOSMAN D, CHAMULEAU R, et al. A localized in vivo detection method for lactate using zero quantum coherence techniques[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1991, 22(2): 493-498. |
| [13] |
PAYNE G S, DESOUZA N M, MESSIOU C, et al. Single-shot single-voxel lactate measurements using FOCI-LASER and a multiple-quantum filter[J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28(4): 496-504.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3276 pmid: 25802214 |
| [14] | PAYNE G, HARRIS L, CAIRNS G, et al. Validating a robust double-quantum-filtered 1H MRS lactate measurement method in high-grade brain tumours[J]. NMR Biomed, 2016, 29(10): 1420-1426. |
| [15] |
KEHLET C T, SIVERTSEN A C, BJERRING M, et al. Improving solid-state NMR dipolar recoupling by optimal control[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(33): 10202-10203.
pmid: 15315406 |
| [16] |
KHANEJA N, REISS T, KEHLET C, et al. Optimal control of coupled spin dynamics: design of NMR pulse sequences by gradient ascent algorithms[J]. J Magn Reson, 2005, 172(2): 296-305.
pmid: 15649756 |
| [17] | XIN J X, WEI D X, REN Y, et al. Distinguishing glutamate and glutamine in in vivo 1H MRS based on nuclear spin singlet order filtering[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(5): 1728-1740. |
| [18] | YANG X, LIU Y, FU C X, et al. Selectively probing the magnetic resonance signals of γ-aminobutyric acid in human brains in vivo[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2024, 59(3): 954-963. |
| [19] | REGENOLD W T, PHATAK P, MARANO C M, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid lactate concentrations in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: implications for the mitochondrial dysfunction hypothesis[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2009, 65(6): 489-494. |
| [20] |
TOŠNER Z, VOSEGAARD T, KEHLET C, et al. Optimal control in NMR spectroscopy: Numerical implementation in SIMPSON[J]. J Magn Reson, 2009, 197(2): 120-134.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2008.11.020 pmid: 19119034 |
| [21] | UNTIDT T S, NIELSEN N C. Analytical unitary bounds on quantum dynamics: Design of optimum NMR experiments in two-spin-1/2 systems[J]. J Chem Phys, 2000, 113(19): 8464-8471. |
| [22] | HU K R, YANG X, HUANG Z M, et al. Preparing nuclear spin singlet state in a three-spin system and its application in 2D spectrum[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(1): 96-107. |
|
胡凯瑞, 杨雪, 黄志明, 等. 三自旋体系核自旋单重态的制备与单重态二维谱的实现[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(1): 96-107.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212910 |
|
| [23] | WANG Z W, XIN J X, WEI D X, et al. Preparation efficiency of singlet states in multi-spin systems with different coupling configurations[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2024, 41(1): 67-76. |
|
王子文, 辛家祥, 魏达秀, 等. 不同耦合构型多自旋体系单重态制备效率研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2024, 41(1): 67-76.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20233063 |
|
| [24] | TESSEM M B, SWANSON M G, KESHARI K R, et al. Evaluation of lactate and alanine as metabolic biomarkers of prostate cancer using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of biopsy tissues[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2008, 60(3): 510-516. |
| [1] | ZHU Xiangwei, YANG Xue, WEI Daxiu, YAO Yefeng. In Vivo Glutathione Molecular MRS Signal Selection Based on Nuclear Spin Singlet States [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 373-381. |
| [2] | LI Ren, CHANG Xiao, ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Xiaoyong. Progress of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in the Study of the Effects of Smoking on the Brain [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 471-480. |
| [3] | CI Jie,YANG Xue,XIN Jiaxiang,WEI Daxiu,YAO Yefeng. Preparation and Lifetime Studies of the Singlet State of Five Spins in Hexene Molecules Used to Guide the Preservation of the Parahydrogen-induced Nuclear Polarization State [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 30-38. |
| [4] | Kai-rui HU,Xue YANG,Zhi-ming HUANG,Jia-xiang XIN,Da-xiu WEI,Ye-feng YAO. Preparing Nuclear Spin Singlet State in a Three-spin System and Its Application in 2D Spectrum [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 96-107. |
| [5] | Xi-feng XIA,Wen-jing ZHANG,Zhi-ye LIN,Xiao-kang KE,Yu-jie WEN,Fang WANG,Jun-chao CHEN,Lu-ming PENG. Solid-State NMR Studies on the Surface Structure and Properties of Oxide Nanomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 533-542. |
| [6] | LIU Tao-tao, WANG Jie, GUO Xiang-yang. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Brain Science Researches [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(2): 232-240. |
| [7] | YANG Yi-ning, WANG Xue-lu, YAO Ye-feng. The Effects of Reaction Environment on Photocatalytic Methanol Reforming Studied by Operando Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(1): 104-113. |
| [8] | WANG Hong-zhi, WANG Shen-lin, HU Bin-wen, YU Yi-hua, SONG Yi-qiao, YAO Ye-feng. A Virtual NMR Spectrometer Based on Numerical Computational Simulations [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2019, 36(3): 288-297. |
| [9] | ZHANG Miao, ZHAI Guo-qiang, LI Gai-ying, WANG Yi, FAN Ming-xia, LI Jian-qi. An Auto-Processing Algorithm for Liver Fat Quantification [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2018, 35(4): 427-439. |
| [10] | HUA Rui, SUN Yu, WEN Lin-fei, LIU Hui, WAN Sui-ren. Optimization of the MEGA-PRESS Sequence for Detection of γ-Aminobutyric Acid in Vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2018, 35(2): 188-197. |
| [11] | MA Lin-ge, LONG Yin-hua. Determination of Aromatic Carbon Mole Ratio in Oil Samples by Quantitative 13C NMR Spectroscopy with DFSS Methodology [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2017, 34(1): 8-15. |
| [12] | WANG Lu-lu, ZHU Yong, ZHONG Kai. Progresses in MRI and MRS Studies on Obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2016, 33(1): 168-178. |
| [13] |
ZHANG Zhu-wei1, CHEN Lu-guang2, PEI Meng-chao3, LI Jian-qi1*.
Retrospective Motion Correction in GABA-Editing Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Using the Residual Water Signals [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2015, 32(4): 596-605. |
| [14] | JIN Ya-ying,CHEN Zhi-wei. A New DEPT Spectral Editing Method [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2015, 32(1): 59-66. |
| [15] | CHEN Lu-guang,LI Jian-qi*,WANG Qian-feng. Detection of GABA in Human Brain on Clinical 3 T MRI Scanner [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2013, 30(3): 345-353. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||