
- May. 14, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 258-266.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212967
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xian-xin QIU1,2,Xu HAN3,Yao WANG3,Wei-na DING3,Ya-wen SUN3,Yan ZHOU3,Hao LEI1,2,Fu-chun LIN1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-27
Online:2022-09-05
Published:2022-03-03
Contact:
Fu-chun LIN
E-mail:fclin@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Xian-xin QIU,Xu HAN,Yao WANG,Wei-na DING,Ya-wen SUN,Yan ZHOU,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN. The Alteration of Rich Club in Brain Functional Network in Internet Gaming Disorder[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 258-266.
Table 1
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the subjects
| IGD | HC | p值 | |
| 年龄/岁 | 20.17±1.98 | 20.60±3.38 | 0.55 |
| 性别(女性/男性) | 12/18 | 12/18 | 1.00 |
| 受教育年限/年 | 11.20±1.61 | 11.60±2.22 | 0.43 |
| CIAS得分 | 73.10±10.21 | 39.83±8.81 | <0.001 |
| SAS得分 | 49.87±9.84 | 41.17±7.21 | <0.001 |
| SDS得分 | 53.27±9.91 | 44.57±9.77 | 0.001 |
| BIS-11得分 | 61.07±8.76 | 53.40±7.67 | 0.001 |
| 认知冲动得分 | 15.03±2.76 | 12.93±2.50 | 0.003 |
| 行动冲动得分 | 20.33±4.06 | 17.97±3.12 | 0.014 |
| 非计划冲动得分 | 25.77±3.78 | 22.50±4.45 | 0.003 |
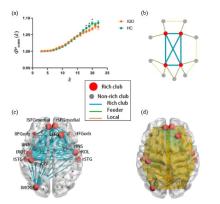
Fig.1
(a) The normalized rich club coefficients (Φωnorm (k), mean±standard error) were lager than 1 in both IGD group and HC group. The Φωnorm (k) values in IGD group were significantly lower than that in HC group when k was 18, 19 and 20(*, p=0.04, 0.03 and 0.03); (b) A simplified example of the rich club, feeder and local connections; (c) rich club regions and rich club connections in HC group. The top 13 brain regions (15%) with the highest average degree in HC group were selected as rich club regions and the corresponding degree was k>9.68 in this study. The prefix l and r represent left and right, respectively. SFGmedial (the bilateral medial part of superior frontal gyrus), IFGorb (pars orbitalis of inferior frontal gyrus), INS (insula), ROL (Rolandic operculum), STG (superior temporal gyrus), SFG (superior frontal gyrus), PoCG (postcentral gyrus); MOG (middle occipital gyrus); (d)The feeder and local connections within group-averaged HCs

Table 2
rich club, feeder and local connections and their differences among the groups
| 连接类型 | 连接 | p值 | ||||||
| 男性对照 | 男性IGD | 女性对照 | 女性IGD | IGD | 性别 | IGD*性别 | ||
| rich club连接 | 16.26±2.71 | 17.76±2.65 | 17.52±3.59 | 19.59±4.89 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 0.44 | |
| feeder连接 | 98.98±10.13 | 99.02±15.34 | 94.33±18.60 | 102.04±13.37 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 0.16 | |
| local连接 | 245.9±20.99 | 239.09±17.09 | 232.08±16.75 | 241.82±17.02 | 0.82 | 0.25 | 0.04 | |
Table 3
The relationships between rich club, feeder, local connections and behavior characteristics
| 连接类型 | CIAS 得分 | SAS 得分 | SDS 得分 | BIS-11 得分 | BIS-11 -认知冲动得分 | BIS-11 -行为冲动得分 | BIS-11 -非计划冲动得分 | |
| rich club连接 | r | ?0.08 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.28 | ?0.15 | 0.00 |
| p | 0.69 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.90 | 0.17 | 0.48 | 0.99 | |
| feeder连接 | r | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.15 | ?0.28 | ?0.05 | ?0.39 | ?0.19 |
| p | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 0.17 | 0.80 | 0.05 | 0.35 | |
| local连接 | r | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.03 | ?0.07 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| p | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.87 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.79 |
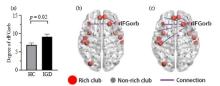
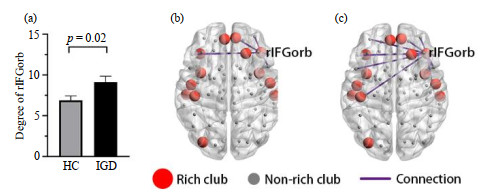
Fig.3
(a) The degree of the right pars orbitalis of inferior frontal gyrus (rIFGorb) in IGD group was significantly higher than that in HC group. Connections between rIFGorb and other brain areas in HC group (b) and IGD group (c). Each connection existed in more than 70% subjects in the corresponding group
| 1 | KUSS D JInternet gaming addiction: current perspectives[J].Psychol Res Behav Manag,2013,6,125-137. |
| 2 |
YOUNG KUnderstanding online gaming addiction and treatment issues for adolescents[J].Am J Fam Ther,2009,37(5):355-372.
doi: 10.1080/01926180902942191 |
| 3 | ASSOCIATION A PDiagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed. )[M]. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013. |
| 4 |
LEUNG LNet-generation attributes and seductive properties of the internet as predictors of online activities and internet addiction[J].Cyberpsychol Behav,2004,7(3):333-348.
doi: 10.1089/1094931041291303 |
| 5 |
KUHN S, ROMANOWSKI A, SCHILLING C, et alThe neural basis of video gaming[J].Transl Psychiatry,2011,1(11):e53.
doi: 10.1038/tp.2011.53 |
| 6 |
YUAN K, QIN W, WANG G H, et alMicrostructure abnormalities in adolescents with internet addiction disorder[J].PLoS One,2011,6(6):e20708.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020708 |
| 7 |
ZHOU Y, LIN F C, DU Y S, et alGray matter abnormalities in Internet addiction: a voxel-based morphometry study[J].Eur J Radiol,2011,79(1):92-95.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.10.025 |
| 8 |
HONG S B, KIM J W, CHOI E J, et alReduced orbitofrontal cortical thickness in male adolescents with internet addiction[J].Behav Brain Funct,2013,9,11.
doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-9-11 |
| 9 |
LIN F C, ZHOU Y, DU Y S, et alAbnormal white matter integrity in adolescents with internet addiction disorder: a tract-based spatial statistics study[J].PLoS One,2012,7(1):e30253.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030253 |
| 10 |
KO C H, LIU G C, HSIAO S, et alBrain activities associated with gaming urge of online gaming addiction[J].J Psychiatr Res,2009,43(7):739-747.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.09.012 |
| 11 | LIU J, GAO X P, OSUNDE I, et alIncreased regional homogeneity in internet addiction disorder: a resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging study[J].Chin Med J (Engl),2010,123(14):1904-1908. |
| 12 |
DONG G S, HUANG J, DU X XAlterations in regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in internet gaming addicts[J].Behav Brain Funct,2012,8,41.
doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-8-41 |
| 13 |
ZHANG J T, YAO Y W, LI C S, et alAltered resting-state functional connectivity of the insula in young adults with Internet gaming disorder[J].Addict Biol,2016,21(3):743-751.
doi: 10.1111/adb.12247 |
| 14 |
PARK H S, KIM S H, BANG S A, et alAltered regional cerebral glucose metabolism in internet game overusers: a 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography study[J].CNS Spectr,2010,15(3):159-166.
doi: 10.1017/S1092852900027437 |
| 15 |
ZHAI J Q, LUO L, QIU L J, et alThe topological organization of white matter network in internet gaming disorder individuals[J].Brain Imaging Behav,2017,11(6):1769-1778.
doi: 10.1007/s11682-016-9652-0 |
| 16 |
CHEN S Y, LI H, WANG L X, et alA preliminary study of disrupted functional network in individuals with Internet gaming disorder: Evidence from the comparison with recreational game users[J].Addict Behav,2020,102,106202.
doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106202 |
| 17 |
WANG L X, WU L D, LIN X, et alAltered brain functional networks in people with Internet gaming disorder: Evidence from resting-state fMRI[J].Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging,2016,254,156-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.07.001 |
| 18 |
VAN DEN HEUVEL M P, SPORNS O, COLLIN G, et alAbnormal rich club organization and functional brain dynamics in schizophrenia[J].JAMA Psychiatry,2013,70(8):783-792.
doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1328 |
| 19 |
YAN T Y, WANG W H, YANG L, et alRich club disturbances of the human connectome from subjective cognitive decline to Alzheimer's disease[J].Theranostics,2018,8(12):3237-3255.
doi: 10.7150/thno.23772 |
| 20 | SHEEHAN D V, LECRUBIER Y, SHEEHAN K H, et alThe mini-international neuropsychiatric interview (M. I. N. I. ): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10[J].J Clin Psychiatry,1998,59,22-33. |
| 21 |
BEARD K W, WOLF E MModification in the proposed diagnostic criteria for Internet addiction[J].Cyberpsychol Behav,2001,4(3):377-383.
doi: 10.1089/109493101300210286 |
| 22 |
KO, YEN J Y, YEN C F, et alScreening for internet addiction: an empirical study on cut-off points for the Chen internet addiction scale[J].Kaohsiung J Med Sci,2005,21(12):545-551.
doi: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70206-2 |
| 23 |
YAN C G, WANG X D, ZUO X N, et alDPABI: Data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging[J].Neuroinform.,2016,14(3):339-351.
doi: 10.1007/s12021-016-9299-4 |
| 24 |
FRISTON K J, WILLIAMS S, HOWARD R, et alMovement-related effects in fMRI time-series[J].Magn Reson Med,1996,35(3):346-355.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910350312 |
| 25 | 辛红涛, 吴光耀, 文之, 等抗逆转录病毒治疗对艾滋病患者脑灰质体积的影响[J].波谱学杂志,2021,38(1):69-79. |
| XIN H T, WU G Y, WEN Z, et alEffects of antiretroviral therapy on brain gray matter volumes in AIDS patients[J].Chinese J Magn Reson,2021,38(1):69-79. | |
| 26 |
TZOURIO-MAZOYER N, LANDEAU B, PAPATHANASSIOU D, et alAutomated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain[J].Neuroimage,2002,15(1):273-289.
doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0978 |
| 27 | 蔡文琴, 王远军基于磁共振成像的人脑图谱构建方法研究进展[J].波谱学杂志,2020,37(2):241-253. |
| CAI W Q, WANG Y JAdvances in construction of human brain atlases from magnetic resonance images[J].Chinese J Magn Reson,2020,37(2):241-253. | |
| 28 | WANG J H, WANG X D, XIA M R, et alGRETNA: a graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics[J].Front Hum Neurosci,2015,9,386. |
| 29 |
VAN DEN HEUVEL M P, SPORNS ORich-club organization of the human connectome[J].J Neurosci,2011,31(44):15775-15786.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3539-11.2011 |
| 30 |
WANG Y, DENG F, JIA Y, et alDisrupted rich club organization and structural brain connectome in unmedicated bipolar disorder[J].Psychol Med,2019,49(3):510-518.
doi: 10.1017/S0033291718001150 |
| 31 |
ZHOU C, PING L L, CHEN W, et alAltered white matter structural networks in drug-naïve patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder[J].Brain Imaging Behav,2021,15(2):700-710.
doi: 10.1007/s11682-020-00278-7 |
| 32 |
CROSSLEY N A, MECHELLI A, V RTES P E, et alCognitive relevance of the community structure of the human brain functional coactivation network[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2013,110(28):11583-11588.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220826110 |
| 33 |
ZSIDO A N, DARNAI G, INHOF O, et alDifferentiation between young adult Internet addicts, smokers, and healthy controls by the interaction between impulsivity and temporal lobe thickness[J].J Behav Addict,2019,8(1):35-47.
doi: 10.1556/2006.8.2019.03 |
| 34 | ZHANG R, SHAO R, XU G, et alAberrant brain structural-functional connectivity coupling in euthymic bipolar disorder[J].Hum Brain Mapp,2019,40(12):3452-3463. |
| 35 | CROSSLEY N A, MECHELLI A, SCOTT J, et alThe hubs of the human connectome are generally implicated in the anatomy of brain disorders[J]. Brain, 2014, 137 (Pt 8): 2382- 2395. |
| 36 |
KANG K D, JUNG T W, PARK I H, et alEffects of equine-assisted activities and therapies on the affective network of adolescents with internet gaming disorder[J].J Altern Complement Med,2018,24(8):841-849.
doi: 10.1089/acm.2017.0416 |
| 37 |
WANG Y, YIN Y, SUN Y W, et alDecreased prefrontal lobe interhemispheric functional connectivity in adolescents with internet gaming disorder: a primary study using resting-state FMRI[J].PLoS One,2015,10(3):e0118733.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118733 |
| 38 |
HESTER R, GARAVAN HExecutive dysfunction in cocaine addiction: evidence for discordant frontal, cingulate, and cerebellar activity[J].J Neurosci,2004,24(49):11017-11022.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3321-04.2004 |
| 39 |
TREMBLAY L, SCHULTZ WRelative reward preference in primate orbitofrontal cortex[J].Nature,1999,398(6729):704-708.
doi: 10.1038/19525 |
| 40 |
VOLKOW N D, WANG G J, TOMASI D, et alUnbalanced neuronal circuits in addiction[J].Curr Opin Neurobiol,2013,23(4):639-648.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.002 |
| 41 |
WANG J, WANG L, ZANG Y, et alParcellation-dependent small-world brain functional networks: a resting-state fMRI study[J].Hum Brain Mapp,2009,30(5):1511-1523.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.20623 |
| [1] | Yang-yang CUI,Huai-bin LIANG,Qian ZHU,Wei TANG,Ting-ting GAO,Jian-ren LIU,Xiao-xia DU. A Study on the Alteration of Spontaneous Brain Activity in Somatic Symptoms Disorder Combining Regional Homogeneity and Amplitude of Low-frequency Fluctuation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 64-71. |
| [2] | JIA Jia-ying, KUANG Li-qun, XIONG Feng-guang, HAN Xie. Analysis of Dynamic Evolution of Complex Brain Networks Based on Persistent Homology [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(1): 80-91. |
| [3] | CHENG Li-wei, WANG Lu-lu, ZHONG Kai. Application of fMRI in Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Researches [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2020, 37(4): 533-546. |
| [4] | . THE APPLICATION OF FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC REGSONANCE IMAGING IN PSYCHIATRIC DISEASES [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2001, 18(1): 91-98. |
| [5] | Pu Yonglin, Luo Dexin, Zhang Siqin, Gao Jian, Li Qingfeng, Hong Nan, Wang Yongheng, Feng Yilian, Ye Anpei, Li Jinqi. FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF CEREBELLAR DENTATE NUCLEI [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 1997, 14(1): 19-24. |
| [6] | Menq Qingan. MRI SIGNAL CHANGES IN HUMANBRAIN DURING FINGER MOVEMENT [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 1995, 12(2): 113-118. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 170
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 200
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||