
波谱学杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 381-392.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20222974
裴云山1,2,张偲1,2,刘晓黎1,成凯1,张则婷1,*( ),李从刚1
),李从刚1
收稿日期:2022-01-28
出版日期:2022-12-05
发布日期:2022-03-10
通讯作者:
张则婷
E-mail:zhangzeting@wipm.ac.cn
基金资助:
Yun-shan PEI1,2,Cai ZHANG1,2,Xiao-li LIU1,Kai CHENG1,Ze-ting ZHANG1,*( ),Cong-gang LI1
),Cong-gang LI1
Received:2022-01-28
Online:2022-12-05
Published:2022-03-10
Contact:
Ze-ting ZHANG
E-mail:zhangzeting@wipm.ac.cn
摘要:
α-突触核蛋白(α-synuclein,αsyn)的错误折叠和聚集是帕金森症的疾病特征.分子伴侣蛋白质二硫键异构酶(PDI)可在体外结合αsyn的N端并抑制其聚集,但PDI的识别机制至今仍不明确.我们通过液体核磁共振(NMR)实验,发现人源PDI b'xa'可结合αsyn的N端区域.此外,硫黄素T(ThT)荧光实验结果表明PDI b'xa'会显著抑制αsyn的聚集.我们进一步利用NMR滴定实验确定了PDI主要通过b'结构域的疏水空腔结合αsyn.最后,我们以此构建了PDI结合αsyn的对接模型,并提出了PDI抑制αsyn聚集的作用机理.这一工作为理解PDI抑制αsyn聚集提供了实验依据.
中图分类号:
裴云山, 张偲, 刘晓黎, 成凯, 张则婷, 李从刚. 蛋白质二硫键异构酶与α-突触核蛋白的相互作用及对其聚集的影响[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(4): 381-392.
Yun-shan PEI, Cai ZHANG, Xiao-li LIU, Kai CHENG, Ze-ting ZHANG, Cong-gang LI. Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by the Interaction Between Protein Disulfide Isomerase and α-Synuclein[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 381-392.

图1
PDI的b'xa'结构域与αsyn的N端区域相互作用. PDI(红色)的(a)一级序列模型及(b)晶体结构(PDB ID: 4EKZ)表面图,粉色和蓝色分别代表PDI ab与PDI b'xa'结构域;(c) SDS-PAGE分析各蛋白纯度,1~5泳道分别代表αsyn1-60、αsyn、PDI ab、PDI b'xa'、PDI,M代表Marker;(d)、(e) αsyn不加(黑色)与加入等量PDI(红色)或PDI b'xa'(蓝色)的谱图叠加,图中标注了明显发生信号减弱或移动的残基;(f)加入等量PDI(红色)、PDI ab(粉色)、PDI b'xa'(蓝色)后,αsyn谱峰强度变化(I/I0);(g)基于OMH法预测αsyn序列疏水性分析图,互作区域或疏水性较强的区域用灰色标出
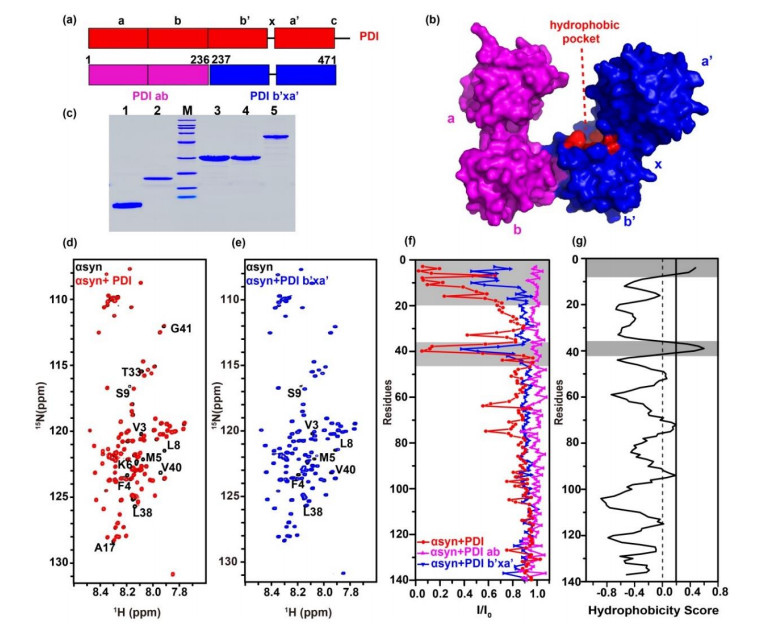
图3
PDI b'xa'与αsyn N端相互作用的NMR检测. PDI b'xa'(红色)加入(蓝色)αsyn 1-19多肽(a)、αsyn 30-42多肽(d)、αsyn 1-60蛋白(g)的1H-15N TROSY谱图,选取E239残基展示PDI b'xa'加入各底物后全局残基化学位移变化;PDI b'xa'加入αsyn 1-19多肽(b)、αsyn 30-42多肽(e)、αsyn 1-60 (h)后的CSPs柱状图,以及根据CSPs随底物αsyn 1-19多肽(c)、αsyn 30-42多肽(f)、αsyn 1-60 (i)浓度变化拟合计算解离常数. 柱状图中用CSPs的(平均值+标准差)作为阈值,高于阈值的残基标注在二维谱中,并在b'xa'的晶体结构表面用红色标记;上述高于阈值的残基通过全局拟合得到相应解离常数,离散的扰动残基通过以(平均值+2×标准差)为阈值验证并去除
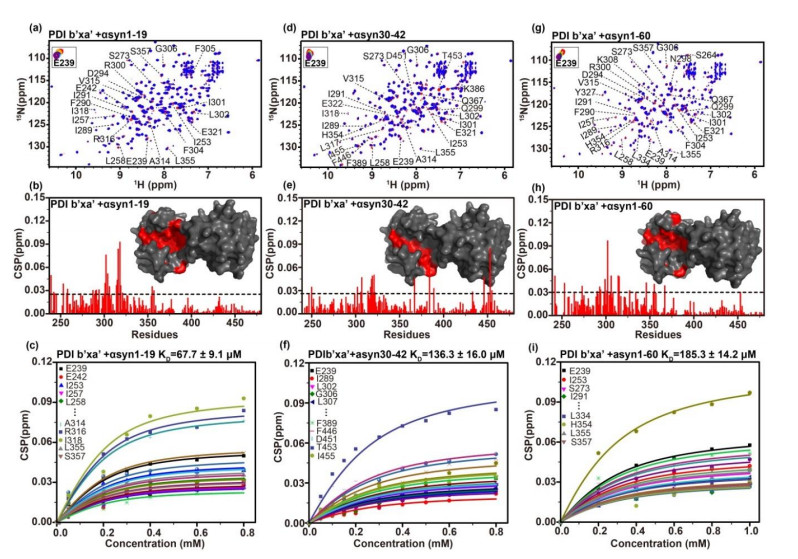
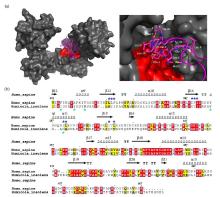
图4
PDI与αsyn N端的疏水结合模式. (a) PDI结合αsyn 1-40多肽的对接模型(左)及其结合区域的局部放大图(右),HDOCK对接实验在网站服务器(http://hdock.phys.hust.edu.cn/)上运行,上传人源PDI晶体结构,αsyn1-40序列及NMR滴定鉴定的结合位点,最佳对接结果使用PyMol软件作图,PDI表面结构呈灰色,疏水口袋以红色标出,αsyn1-40卡通结构呈品红色,右图中参与结合的αsyn残基以棒状模式显示并标出.(b)人源PDI b'xa'与HiPDI b'xa'的氨基酸序列比对.序列一致性和相似性由Clustalw[52]和ESPript 3.0[53]分析所得,相似氨基酸(黑色字母填充黄色方框)以及相同氨基酸(白色字母填充红色方框)分别被标出,顶部标注人源PDI b'xa'二级结构区域,蓝色和绿色星号分别表示αsyn结合人源PDI和HiPDI的关键疏水氨基酸残基

| 1 |
THEILLET F X, BINOLFI A, BEKEI B, et al Structural disorder of monomeric α-synuclein persists in mammalian cells[J]. Nature, 2016, 530 (7588): 45- 50.
doi: 10.1038/nature16531 |
| 2 |
WEINREB P H, ZHEN W, POON A W, et al NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer's disease and learning, is natively unfolded[J]. Biochemistry, 1996, 35 (43): 13709- 13715.
doi: 10.1021/bi961799n |
| 3 |
IADANZA M G, JACKSON M P, HEWITT E W, et al A new era for understanding amyloid structures and disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19 (12): 755- 773.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0060-8 |
| 4 |
LIU C W, GIASSON B I, LEWIS K A, et al A precipitating role for truncated alpha-synuclein and the proteasome in alpha-synuclein aggregation - Implications for pathogenesis of Parkinson disease[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280 (24): 22670- 22678.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501508200 |
| 5 |
DETTMER U, SELKOE D, BARTELS T New insights into cellular α-synuclein homeostasis in health and disease[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2016, 36, 15- 22.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2015.07.007 |
| 6 |
SPILLANTINI M G, SCHMIDT M L, LEE V M Y, et al α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies[J]. Nature, 1997, 388 (6645): 839- 840.
doi: 10.1038/42166 |
| 7 |
LAUTENSCHL GER J, KAMINSKI C F, KAMINSKI SCHIERLE G S α-synuclein – regulator of exocytosis, endocytosis, or both?[J]. Trends in Cell Biol, 2017, 27 (7): 468- 479.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.02.002 |
| 8 |
MAHUL-MELLIER A L, BURTSCHER J, MAHARJAN N, et al The process of Lewy body formation, rather than simply α-synuclein fibrillization, is one of the major drivers of neurodegeneration[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020, 117 (9): 4971- 4982.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913904117 |
| 9 |
SHAHMORADIAN S H, LEWIS A J, GENOUD C, et al Lewy pathology in Parkinson's disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2019, 22 (7): 1099- 1109.
doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0423-2 |
| 10 |
BARTELS T, AHLSTROM L S, LEFTIN A, et al The N-terminus of the intrinsically disordered protein α-synuclein triggers membrane binding and helix folding[J]. Biophys J, 2010, 99 (7): 2116- 2124.
doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.035 |
| 11 |
BURMANN B M, GEREZ J A, MATEČKO-BURMANN I, et al Regulation of α-synuclein by chaperones in mammalian cells[J]. Nature, 2020, 577 (7788): 127- 132.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1808-9 |
| 12 |
GRUSCHUS J M, YAP T L, PISTOLESI S, et al NMR structure of calmodulin complexed to an N-terminally acetylated α-synuclein peptide[J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52 (20): 3436- 3445.
doi: 10.1021/bi400199p |
| 13 |
GIASSON B I, MURRAY I V, TROJANOWSKI J Q, et al A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276 (4): 2380- 2386.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008919200 |
| 14 |
BINOLFI A, RASIA R M, BERTONCINI C W, et al Interaction of alpha-synuclein with divalent metal ions reveals key differences: A link between structure, binding specificity and fibrillation enhancement[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128 (30): 9893- 9901.
doi: 10.1021/ja0618649 |
| 15 |
NIELSEN M S, VORUM H, LINDERSSON E, et al Ca2+ binding to alpha-synuclein regulates ligand binding and oligomerization[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276 (25): 22680- 22684.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101181200 |
| 16 |
BINOLFI A, RASIA R M, BERTONCINI C W, et al Interaction of alpha-synuclein with divalent metal ions reveals key differences: a link between structure, binding specificity and fibrillation enhancement[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128 (30): 9893- 9901.
doi: 10.1021/ja0618649 |
| 17 |
SERRANO A, QIAO X, MATOS J O, et al Reversal of alpha-synuclein fibrillization by protein disulfide isomerase[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8, 726.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00726 |
| 18 |
DEDMON M M, CHRISTODOULOU J, WILSON M R, et al Heat shock protein 70 inhibits alpha-synuclein fibril formation via preferential binding to prefibrillar species[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280 (15): 14733- 14740.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413024200 |
| 19 |
DIMANT H, EBRAHIMI-FAKHARI D, MCLEAN P J Molecular chaperones and co-chaperones in Parkinson disease[J]. Neuroscientist, 2012, 18 (6): 589- 601.
doi: 10.1177/1073858412441372 |
| 20 |
GAO X, CARRONI M, NUSSBAUM-KRAMMER C, et al Human Hsp70 disaggregase reverses Parkinson's-linked α-synuclein amyloid fibrils[J]. Mol Cell, 2015, 59 (5): 781- 793.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.012 |
| 21 |
PEMBERTON S, MADIONA K, PIERI L, et al Hsc70 protein interaction with soluble and fibrillar alpha-synuclein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286 (40): 34690- 34699.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.261321 |
| 22 |
RANJAN P, KUMAR A The involvement of His50 during protein disulfide isomerase binding is essential for inhibiting α-Syn fibril formation[J]. Biochemistry, 2016, 55 (19): 2677- 2680.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00280 |
| 23 |
UEHARA T, NAKAMURA T, YAO D, et al S-nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration[J]. Nature, 2006, 441 (7092): 513- 517.
doi: 10.1038/nature04782 |
| 24 |
WANG C, LI W, REN J, et al Structural insights into the redox-regulated dynamic conformations of human protein disulfide isomerase[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2013, 19 (1): 36- 45.
doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4630 |
| 25 |
DARBY N J, CREIGHTON T E Functional properties of the individual thioredoxin-like domains of protein disulfide isomerase[J]. Biochemistry, 1995, 34 (37): 11725- 11735.
doi: 10.1021/bi00037a009 |
| 26 |
KLAPPA P, RUDDOCK L W, DARBY N J, et al The b' domain provides the principal peptide-binding site of protein disulfide isomerase but all domains contribute to binding of misfolded proteins[J]. EMBO J, 1998, 17 (4): 927- 935.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.4.927 |
| 27 |
YAO Y, ZHOU Y, WANG C Both the isomerase and chaperone activities of protein disulfide isomerase are required for the reactivation of reduced and denatured acidic phospholipase A2[J]. EMBO J, 1997, 16 (3): 651- 658.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.3.651 |
| 28 |
ELLGAARD L, RUDDOCK L W The human protein disulphide isomerase family: substrate interactions and functional properties[J]. EMBO Rep, 2005, 6 (1): 28- 32.
doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400311 |
| 29 |
PAPP E, NARDAI G, STI C, et al Molecular chaperones, stress proteins and redox homeostasis[J]. Biofactors, 2003, 17 (1-4): 249- 257.
doi: 10.1002/biof.5520170124 |
| 30 |
CHEN X, ZHANG X, LI C, et al S-nitrosylated protein disulfide isomerase contributes to mutant SOD1 aggregates in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. J Neurochem, 2013, 124 (1): 45- 58.
doi: 10.1111/jnc.12046 |
| 31 |
CHENG H, WANG L, WANG C C Domain a' of protein disulfide isomerase plays key role in inhibiting alpha-synuclein fibril formation[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2010, 15 (4): 415- 421.
doi: 10.1007/s12192-009-0157-2 |
| 32 |
YAGI-UTSUMI M, SATOH T, KATO K Structural basis of redox-dependent substrate binding of protein disulfide isomerase[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5, 13909.
doi: 10.1038/srep13909 |
| 33 | 余锦波, 张偲, 张则婷, 等 Alpha-突触核蛋白与完整线粒体相互作用的NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38 (2): 164- 172. |
| YU J B, ZHANG C, ZHANG Z T, et al Interactions between α-synuclein and intact mitochondria studied by NMR[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38 (2): 164- 172. | |
| 34 | 寇新慧, 刘乙祥, 刘兴弘, 等 探测应答调控蛋白PhoBNF20D自由态中存在的Pre-Active构象[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2019, 36 (2): 164- 171. |
| KOU X H, LIU Y X, LIU X H, et al Visualizing the pre-active conformation of response regulator PhoBNF20D in its apo state[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2019, 36 (2): 164- 171. | |
| 35 |
JAO C C, DER-SARKISSIAN A, CHEN J, et al Structure of membrane-bound alpha-synuclein studied by site-directed spin labeling[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101 (22): 8331- 8336.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400553101 |
| 36 |
HOYER W, ANTONY T, CHERNY D, et al Dependence of alpha-synuclein aggregate morphology on solution conditions[J]. J Mol Biol, 2002, 322 (2): 383- 393.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00775-1 |
| 37 | 戴晨晔, 刘买利, 李从刚 低盐和高盐环境下α-synuclein构象的19F NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2015, 32 (1): 33- 44. |
| DAI C Y, LIU M L, LI C G Salt content-dependent conformational changes of alpha-synuclein studied by 19F NMR[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2015, 32 (1): 33- 44. | |
| 38 |
PEI Y, LIU X, CHENG K, et al Backbone resonance assignment of PDI b'xa' domain construct[J]. Biomol NMR Assign, 2021, 15 (2): 409- 413.
doi: 10.1007/s12104-021-10038-3 |
| 39 | DELAGLIO F, GRZESIEK S, VUISTER G W, et al NMRPipe: A multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes[J]. J Biomol NMR, 1995, 6 (3): 277- 293. |
| 40 |
LEE W, TONELLI M, MARKLEY J L NMRFAM-SPARKY: enhanced software for biomolecular NMR spectroscopy[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31 (8): 1325- 1327.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu830 |
| 41 |
WILLIAMSON, MIKE P Using chemical shift perturbation to characterise ligand binding[J]. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc, 2013, 73, 1- 16.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2013.02.001 |
| 42 |
ARAI M, FERREON J C, WRIGHT P E Quantitative analysis of multisite protein-ligand interactions by NMR: binding of intrinsically disordered p53 transactivation subdomains with the TAZ2 domain of CBP[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134 (8): 3792- 3803.
doi: 10.1021/ja209936u |
| 43 |
DE OLIVEIRA G A P, SILVA J L Alpha-synuclein stepwise aggregation reveals features of an early onset mutation in Parkinson's disease[J]. Commun Biol, 2019, 2, 374.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0598-9 |
| 44 |
CAMPIONI S, CARRET G, JORDENS S, et al The presence of an air-water interface affects formation and elongation of α-synuclein fibrils[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136 (7): 2866- 2875.
doi: 10.1021/ja412105t |
| 45 |
CROKE R, PATIL S, QUEVREAUX J, et al NMR determination of pK(a) values in α-synuclein[J]. Protein sci, 2011, 20 (2): 256- 269.
doi: 10.1002/pro.556 |
| 46 |
SWEET R M, EISENBERG D Correlation of sequence hydrophobicities measures similarity in three-dimensional protein structure[J]. J Mol Biol, 1983, 171 (4): 479- 488.
doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90041-4 |
| 47 |
BIANCALANA M, KOIDE S Molecular mechanism of thioflavin-T binding to amyloid fibrils[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2010, 1804 (7): 1405- 1412.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.04.001 |
| 48 |
KHURANA R, COLEMAN C, IONESCU-ZANETTI C, et al Mechanism of thioflavin T binding to amyloid fibrils[J]. J Struct Biol, 2005, 151 (3): 229- 238.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.06.006 |
| 49 | 陈艳华, 张则婷, 白佳, 等 PDI抑制α-synuclein纤维化聚集作用机制研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2017, 34 (2): 131- 136. |
| CHEN Y H, ZHANG Z T, BAI J, et al Inhibition mechanisms of protein disulfide isomerase on α-synuclein fibril aggregation[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2017, 34 (2): 131- 136. | |
| 50 |
BYRNE LEE J, SIDHU A, WALLIS A K, et al Mapping of the ligand-binding site on the b′ domain of human PDI: interaction with peptide ligands and the x-linker region[J]. Biochem J, 2009, 423 (2): 209- 217.
doi: 10.1042/BJ20090565 |
| 51 |
YAN Y, ZHANG D, ZHOU P, et al HDOCK: a web server for protein-protein and protein-DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45 (W1): W365- W373.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx407 |
| 52 |
LARKIN M A, BLACKSHIELDS G, BROWN NP, et al Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23 (21): 2947- 2948.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404 |
| 53 |
ROBERT X, GOUET P Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42 (W1): W320- W324.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gku316 |
| 54 |
DOHERTY C P A, ULAMEC S M, MAYA-MARTINEZ R, et al A short motif in the N-terminal region of α-synuclein is critical for both aggregation and function[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2020, 27 (3): 249- 259.
doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-0384-x |
| [1] | 胡涵,王伟宇,徐君,邓风. Pd-Sn双金属催化剂催化1, 3-丁二烯加氢反应的仲氢诱导极化研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(2): 133-143. |
| [2] | 徐倩,陈朗,胡翔颖,李从刚,刘乙祥,姜凌. T69E模拟磷酸化修饰对Bcl-2与Nur77相互作用的影响[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(1): 87-95. |
| [3] | 胡晓东,蓝文贤,王春喜,曹春阳. 靶向肿瘤因子c-MYC基因启动区G4-DNA的小分子药物设计及核磁共振研究进展[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(4): 503-513. |
| [4] | 王子豪,徐赫,汪涛,杨善中,丁运生,魏海兵. 外型和内型C-2位单取代降冰片烯衍生物的核磁共振波谱研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(3): 323-335. |
| [5] | 王崇武,黄曦,石磊,陈世桢,周欣. 组织蛋白酶B响应的超极化129Xe MRI探针对肺癌细胞的超灵敏探测[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(3): 336-344. |
| [6] | 吴嘉敏,贺玉成,徐征,朱延河,姜文正. 用于土壤水分测量的磁共振射频线圈宽频匹配方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(3): 414-423. |
| [7] | 赵心怡,韩冬,罗红军,沈文斌,杨功俊. 德拉沙星葡甲胺波谱学数据解析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(2): 268-276. |
| [8] | 余锦波,张偲,张则婷,徐国华,李从刚. Alpha-突触核蛋白与完整线粒体相互作用的NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(2): 164-172. |
| [9] | 廖怀玉, 韩红园, 陈飞, 张海艳, 杨静, 赵天增. 苦皮藤中两个新的 β-二氢沉香呋喃型化合物的 NMR 数据解析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 101-109. |
| [10] | 李玉江, 赵伟, 郭晓河, 陶乐, 张祥, 张海艳, 赵天增. 盐酸马尼地平的核磁共振数据解析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 110-117. |
| [11] | 王睿迪, 徐贝贝, 宋艳红, 王雪璐, 姚叶锋. 原位核磁共振技术研究光催化甲醇重整过程中甲醇与水的相互作用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38(1): 43-57. |
| [12] | 柯汉平, 蔡宏浩. 基于哈德曼编码的新型高分辨定域谱[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 524-532. |
| [13] | 刘思, 安艳捧, 唐惠儒. 冷冻干燥对人类体液代谢组影响的NMR研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 484-489. |
| [14] | 李英俊, 杨鸿境, 刘季红, 靳焜, 林乐弟, 刘雪洁. 基于咔唑-三嗪并吲哚的N-酰腙衍生物的NMR数据归属[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 496-504. |
| [15] | 刘欢, 徐锦绣, 郑炀, 熊镭. 渤海J油田储层核磁共振测井孔隙度影响因素分析及校正[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(3): 370-380. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||