
- Nov. 6, 2025
- Home
- About Us
- Editorial Board
- Instruction
- Subscription
- Advertisement
- Contact Us
- Chinese
- RSS

Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 148-157.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20223035
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-11-14
Published:2023-06-05
Online:2022-12-20
Contact:
GONG Zhou
E-mail:gongzhou@apm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
ZHAO Chang,GONG Zhou. Investigation of Dynamic Structure of Protein Encountering Complex with Paramagnetic NMR[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 148-157.
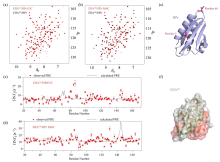
Fig. 2
1H-15N HSQC spectra of EIIAGlc/HPr solution (black) and EIIAGlc/HPr E5C (a) or EIIAGlc/HPr E66C (b) (red) were compared under 25 ℃. Experimental observations (red dots) and theoretical calculations (black solid lines) of intermolecular PRE of EIIAGlc and HPr E5C (c) or HPr E66C (d); (e) Structure diagram of HPr probe connection site; (f) Schematic diagram of EIIAGlc structure, where areas with large differences between PRE experimental values and theoretical calculated values are shown in red
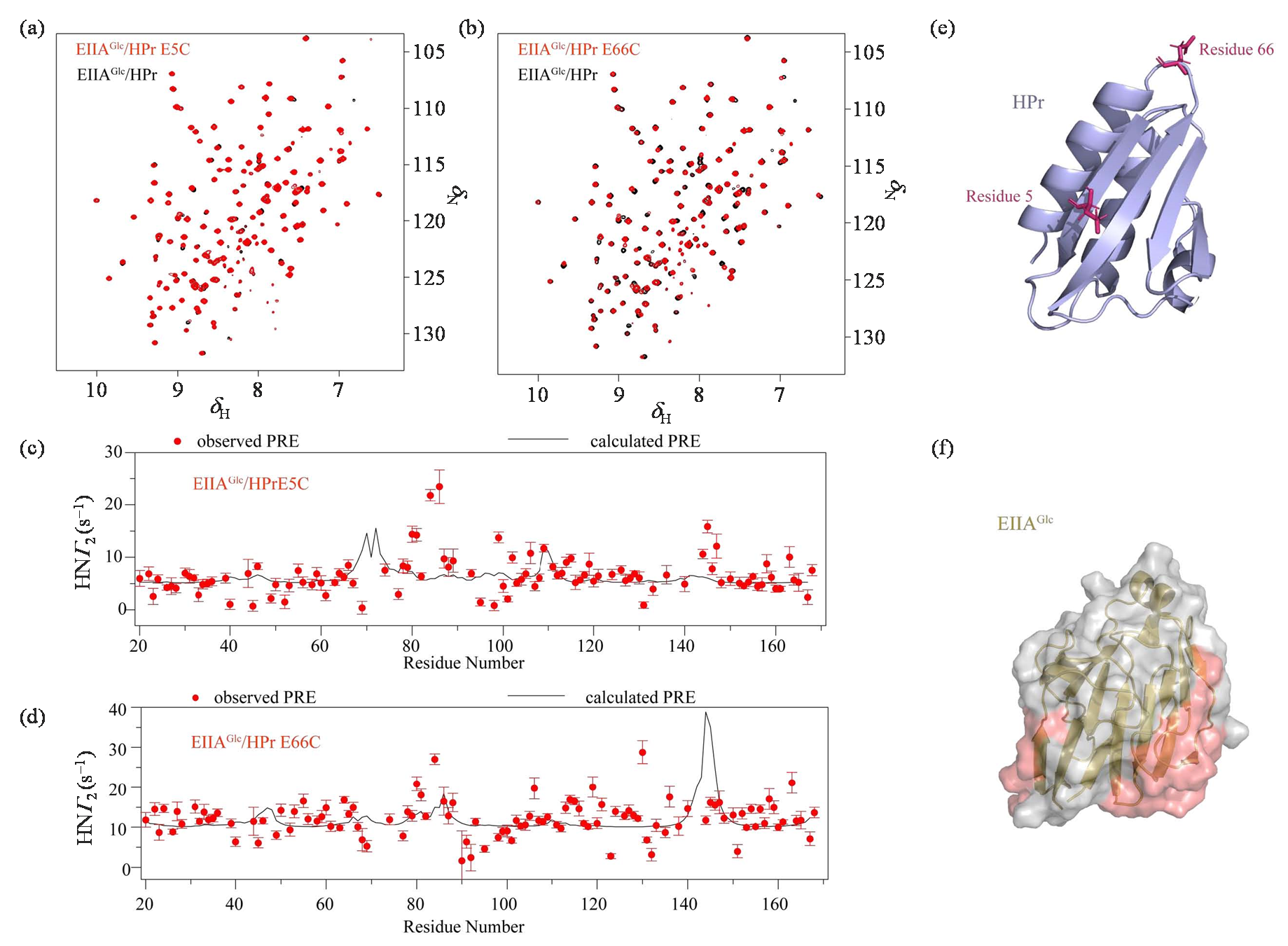

Fig. 4
Calculated ensemble structures of EIIAGlc/HPr E5C (a) and EIIAGlc/HPr E66C (b) complexes in dilute buffer. The specific complex of EIIAGlc (yellow) and HPr (blue) are shown as cartoon, and the mass center of HPr molecules of the calculated EIIAGlc/HPr E5C and EIIAGlc/HPr E66C complexes are shown as gray dots. According to the location on the EIIAGlc surface, HPr molecules are divided into three clusters marked using dashed cycles
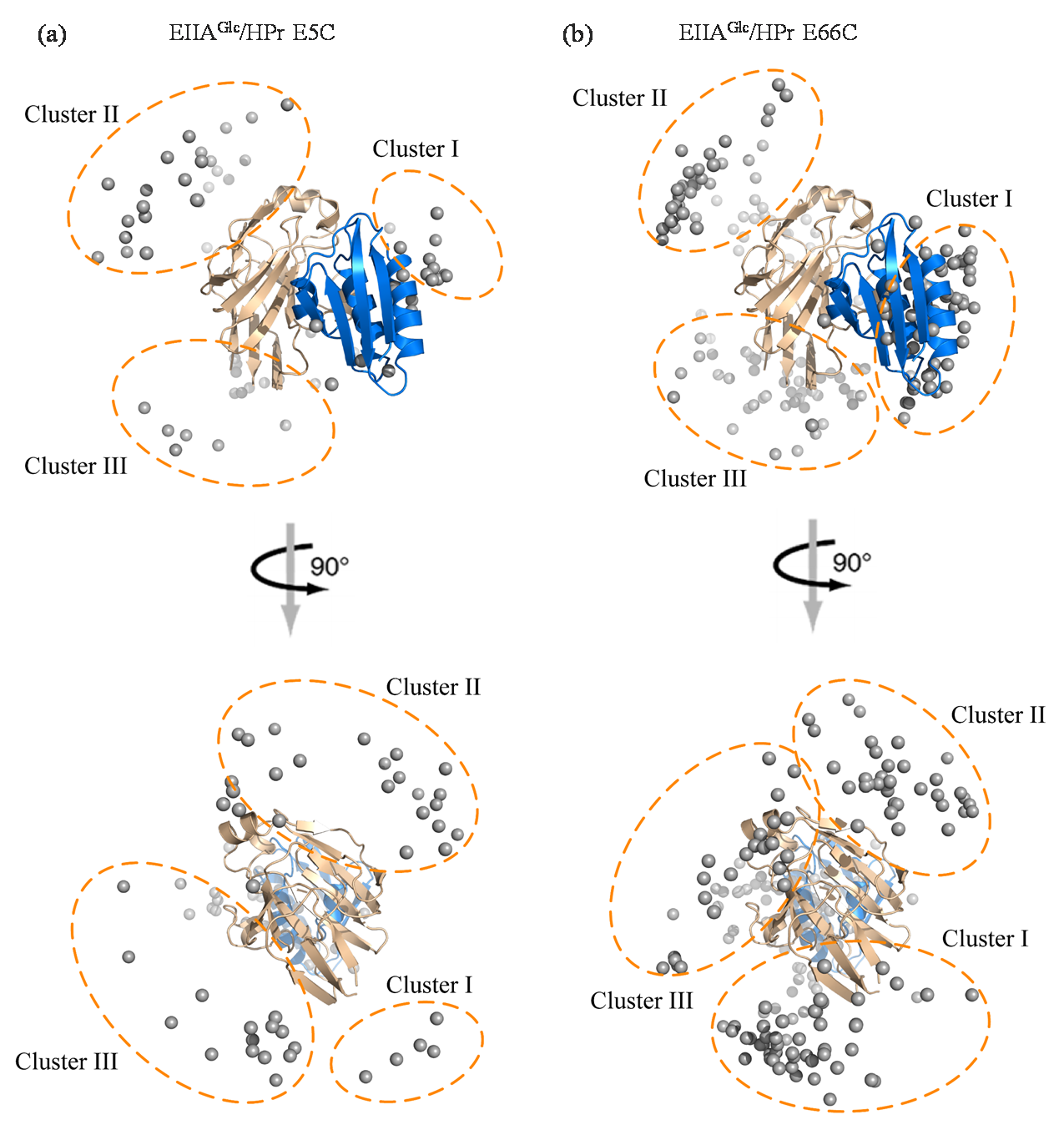
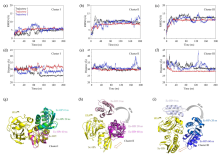
Fig. 5
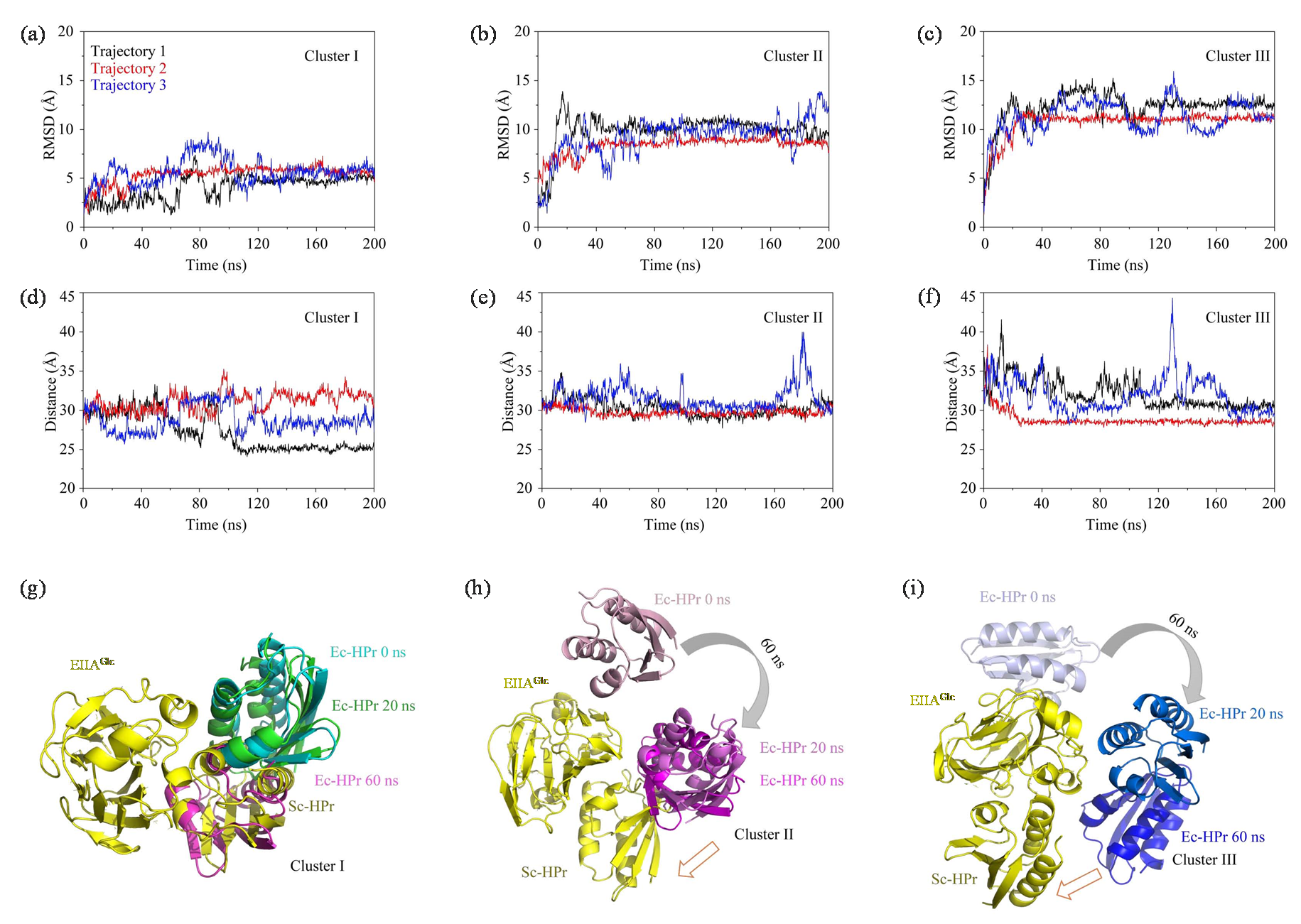
(a)~(c) The RMSD plots of three encounter complexes in three parallel trajectories; (d)~(f) The distance plots of three encounter complexes in three parallel trajectories; (g)~(i) The structure change schemes of three different encounter complexes during 60 ns under MD simulations, Ec represents encounter complex (Ec), Sc represents specific complex (Sc)
| [1] |
TANG C, IWAHARA J, CLORE G M. Visualization of transient encounter complexes in protein-protein association[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7117): 383-386.
doi: 10.1038/nature05201 |
| [2] |
IWAHARA J, CLORE G M. Detecting transient intermediates in macromolecular binding by paramagnetic NMR[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7088): 1227-1230.
doi: 10.1038/nature04673 |
| [3] |
XING Q, HUANG P, YANG J, et al. Visualizing an ultra-weak protein-protein interaction in phosphorylation signaling[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2014, 53(43): 11501-11505.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201405976 |
| [4] |
GABDOULLINE R R, WADE R C. Biomolecular diffusional association[J]. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 2002, 12(2): 204-213.
doi: 10.1016/S0959-440X(02)00311-1 |
| [5] |
SCHREIBER G, HARAN G, ZHOU H X. Fundamental aspects of protein-protein association kinetics[J]. Chem Rev, 2009, 109(3): 839-860.
doi: 10.1021/cr800373w pmid: 19196002 |
| [6] |
UBBINK M. The courtship of proteins: understanding the encounter complex[J]. FEBS Lett, 2009, 583(7): 1060-1066.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.02.046 pmid: 19275897 |
| [7] |
VAN SON M, SCHILDER J T, DI SAVINO A, et al. The transient complex of cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase: Insights into the encounter complex from multifrequency EPR and NMR spectroscopy[J]. Chemphyschem, 2020, 21(10): 1060-1069.
doi: 10.1002/cphc.201901160 pmid: 32301564 |
| [8] |
NORTHRUP S H, BOLES J O, REYNOLDS J C. Brownian dynamics of cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase association[J]. Science, 1988, 241(4861): 67-70.
pmid: 2838904 |
| [9] |
SCHREIBER G, FERSHT AR. Rapid, electrostatically assisted association of proteins[J]. Nat Struct Biol, 1996, 3(5): 427-431.
pmid: 8612072 |
| [10] |
VIJAYAKUMAR M, WONG KY, SCHREIBER G, et al. Electrostatic enhancement of diffusion-controlled protein-protein association: comparison of theory and experiment on barnase and barstar[J]. J Mol Biol, 1998, 278(5): 1015-1024.
pmid: 9600858 |
| [11] |
SELZER T, ALBECK S, SCHREIBER G. Rational design of faster associating and tighter binding protein complexes[J]. Nat Struct Biol, 2000, 7(7): 537-541.
pmid: 10876236 |
| [12] |
ZHOU H X, SZABO A. Enhancement of association rates by nonspecific binding to DNA and cell membranes[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 93(17): 178101.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.178101 |
| [13] |
HAREL M, COHEN M, SCHREIBER G. On the dynamic nature of the transition state for protein-protein association as determined by double-mutant cycle analysis and simulation[J]. J Mol Biol, 2007, 371(1): 180-196.
pmid: 17561113 |
| [14] |
GENET J P. Asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation. Design of new Ru catalysts and chiral ligands: from laboratory to industrial applications[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2003, 36(12): 908-918.
doi: 10.1021/ar020152u |
| [15] |
WORRALL J A, LIU Y, CROWLEY P B, et al. Myoglobin and cytochrome b5: a nuclear magnetic resonance study of a highly dynamic protein complex[J]. Biochemistry, 2002, 41(39): 11721-11730.
pmid: 12269814 |
| [16] |
UBBINK M, BENDALL D S. Complex of plastocyanin and cytochrome c characterized by NMR chemical shift analysis[J]. Biochemistry, 1997, 36(21): 6326-6335.
pmid: 9174347 |
| [17] |
WORRALL J A, REINLE W, BERNHARDT R, et al. Transient protein interactions studied by NMR spectroscopy: the case of cytochrome C and adrenodoxin[J]. Biochemistry, 2003, 42(23): 7068-7076.
pmid: 12795602 |
| [18] |
BASHIR Q, SCANU S, UBBINK M. Dynamics in electron transfer protein complexes[J]. FEBS J, 2011, 278(9): 1391-1400.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08062.x pmid: 21352493 |
| [19] |
HU Y F, LI C G, HE L C, et al. Mechanisms of chaperones as active assistant/protector for proteins: Insights from NMR studies[J]. Chinese J Chem, 2019, 38(4): 406-413.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v38.4 |
| [20] |
TOLMAN J R, FLANAGAN J M, KENNEDY M A, et al. NMR evidence for slow collective motions in cyanometmyoglobin[J]. Nat Struct Biol, 1997, 4(4): 292-297.
pmid: 9095197 |
| [21] | WANG J N, LIN Y L, ZHU Q J, et al. NMR assignments and characterization of the DNA-binding domain of Arabidopsis transcription factor WRKY11[J]. Magn Reson Lett, 2021, 1(2): 112-120. |
| [22] |
BRUCE N J, GANOTRA G K, KOKH D B, et al. New approaches for computing ligand-receptor binding kinetics[J]. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 2018, 49: 1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.10.001 |
| [23] |
DICKSON A, TIWARY P, VASHISTH H. Kinetics of ligand binding through advanced computational approaches: A review[J]. Curr Top Med Chem, 2017, 17(23): 2626-2641.
doi: 10.2174/1568026617666170414142908 pmid: 28413946 |
| [24] |
DE VIVO M, MASETTI M, BOTTEGONI G, et al. Role of molecular dynamics and related methods in drug discovery[J]. J Med Chem, 2016, 59(9): 4035-4061.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01684 pmid: 26807648 |
| [25] |
BERNETTI M, CAVALLI A, MOLLICA L. Protein-ligand (un)binding kinetics as a new paradigm for drug discovery at the crossroad between experiments and modelling[J]. Medchemcomm, 2017, 8(3): 534-550.
doi: 10.1039/c6md00581k pmid: 30108770 |
| [26] |
SHAN Y, KIM E T, EASTWOOD M P, et al. How does a drug molecule find its target binding site?[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133(24): 9181-9183.
doi: 10.1021/ja202726y pmid: 21545110 |
| [27] |
DROR R O, PAN A C, ARLOW D H, et al. Pathway and mechanism of drug binding to G-protein-coupled receptors[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108(32): 13118-13123.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104614108 |
| [28] |
TRAN D P, KITAO A. Dissociation process of a MDM2/p53 complex investigated by parallel cascade selection molecular dynamics and the markov state model[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2019, 123(11): 2469-2478.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b10309 |
| [29] |
DICKSON A. Mapping the ligand binding landscape[J]. Biophys J, 2018, 115(9): 1707-1719.
doi: S0006-3495(18)31102-0 pmid: 30327139 |
| [30] |
PLATTNER N, NOÉ F. Protein conformational plasticity and complex ligand-binding kinetics explored by atomistic simulations and Markov models[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 7653.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8653 pmid: 26134632 |
| [31] |
SILVA D A, BOWMAN G R, SOSA-PEINADO A, et al. A role for both conformational selection and induced fit in ligand binding by the LAO protein[J]. PLoS Comput Biol, 2011, 7(5): e1002054.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002054 |
| [32] |
REIZER J, SAIER JR M H, DEUTSCHER J, et al. The phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in gram-positive bacteria: properties, mechanism, and regulation[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 1988, 15(4): 297-338.
pmid: 3060316 |
| [33] |
HERZBERG O, KLEVIT R. Unraveling a bacterial hexose transport pathway[J]. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 1994, 4(6): 814-822.
doi: 10.1016/0959-440X(94)90262-3 |
| [34] |
WANG G, LOUIS J M, SONDEJ M, et al. Solution structure of the phosphoryl transfer complex between the signal transducing proteins HPr and IIA(glucose) of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system[J]. EMBO J, 2000, 19(21): 5635-5649.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.21.5635 |
| [35] |
GONG Z, DING Y H, DONG X, et al. Visualizing the ensemble structures of protein complexes using chemical cross-linking coupled with mass spectrometry[J]. Biophys Rep, 2015, 1: 127-138.
doi: 10.1007/s41048-015-0015-y |
| [36] |
FAWZI N L, DOUCLEFF M, SUH J Y, et al. Mechanistic details of a protein-protein association pathway revealed by paramagnetic relaxation enhancement titration measurements[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107(4): 1379-1384.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909370107 |
| [37] |
DING Y H, GONG Z, DONG X, et al. Modeling protein excited-state structures from “over-length” chemical cross-links[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(4): 1187-1196.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.761841 |
| [38] |
WANG G, LOUIS J M, SONDEJ M, et al. Solution structure of the phosphoryl transfer complex between the signal transducing proteins HPr and IIA(glucose) of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system[J]. EMBO J, 2000, 19(21): 5635-5649.
pmid: 11060015 |
| [39] |
AN Y, CHEN L, SUN S, et al. QuikChange shuffling: a convenient and robust method for site-directed mutagenesis and random recombination of homologous genes[J]. N Biotechnol, 2011, 28(4): 320-325.
doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2011.03.001 |
| [40] |
SCHWIETERS C D, KUSZEWSKI J J, TJANDRA N, et al. The Xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package[J]. J Magn Reson, 2003, 160(1): 65-73.
pmid: 12565051 |
| [41] |
CHEN R, LI L, WENG Z. ZDOCK: an initial-stage protein-docking algorithm[J]. Proteins, 2003, 52(1): 80-87.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0134 |
| [42] |
IWAHARA J, SCHWIETERS C D, CLORE G M. Ensemble approach for NMR structure refinement against (1)H paramagnetic relaxation enhancement data arising from a flexible paramagnetic group attached to a macromolecule[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(18): 5879-5896.
pmid: 15125681 |
| [1] | KOU Xinhui, ZHANG Yubing. Study on the Enantiomeric Recognition of Chiral Ureas Containing Amino Acid Units [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 221-230. |
| [2] | DU Qunjie. Experimental Study on Accurate Determination of Shale Porosity by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 275-284. |
| [3] | SHEN Zhiqiang, DENG Yabo, YANG Peiju, HU Xiaoxue, HUANG Xiaojuan, XU Chuanzhi, SONG Huanling. Design and Application of an in situ NMR Device for Light-Induced Reaction Systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 22-33. |
| [4] | XU Xiaojie, CHEN Yan’an, LI Xufei, ZHANG Yuncai, ZHANG Yong, ZHAN Dongkai, PAN Ting. Structural Elucidation of Hybutimibe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 43-55. |
| [5] | WANG Feng, LIU Tingwei, XU Yajie, YU Peng, WANG Ya, PENG Bowen, YANG Xiaodong. A Miniaturised NMR RF Probe Design with External Field-locking Channel [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 332-340. |
| [6] | WANG Yuanfang,WANG Xiaohua,SHU Chang,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili,ZENG Danyun. The Aggregation of ATAD2 Bromodomain in Solution [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 169-178. |
| [7] | ZHAN Jianhua,HU Qin,ZHU Qinjun,JIANG Bin,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili. Track the Conformational Change of Unlabeled Yeast Cytochrome c in Cell Homogenate Using NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 22-29. |
| [8] | CI Jie,YANG Xue,XIN Jiaxiang,WEI Daxiu,YAO Yefeng. Preparation and Lifetime Studies of the Singlet State of Five Spins in Hexene Molecules Used to Guide the Preservation of the Parahydrogen-induced Nuclear Polarization State [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 30-38. |
| [9] | Yun-shan PEI, Cai ZHANG, Xiao-li LIU, Kai CHENG, Ze-ting ZHANG, Cong-gang LI. Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by the Interaction Between Protein Disulfide Isomerase and α-Synuclein [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 381-392. |
| [10] | Xiao-yang ZHANG, Shou-quan YAO, Jun-cheng XU, Yu JIANG. Magnetic Field Locking System Based on Fluxgate and Time Domain Digital Frequency Discrimination [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 448-458. |
| [11] | Han HU,Wei-yu WANG,Jun XU,Feng DENG. 1, 3-Butadienen Hydrogenation on Supported Pd-Sn Bimetallic Catalysts Investigated by Parahydrogen-induced Polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 133-143. |
| [12] | Qian XU,Lang CHEN,Xiang-ying HU,Cong-gang LI,Yi-xiang LIU,Ling JIANG. The Effect of T69E-mimicked Phosphorylation on the Interaction Between Bcl-2 and Nur77 [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 87-95. |
| [13] | Xiao-qing LIN,Shi-jia DU,Hao-lin ZHAN,Yu-qing HUANG,Zhong CHEN. Two-Dimensional Homonuclear Orthogonal-Pattern Phase-Sensitive J-Resolved NMR Spectroscopy Based on Pure Shifts [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 448-459. |
| [14] | Yao XIAO,Chang-jiu XIA,Xian-feng YI,Feng-qing LIU,Shang-bin LIU,An-min ZHENG. Progress in the Studies on Sn-Zeolites by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 571-584. |
| [15] | Xiao-dong HU,Wen-xian LAN,Chun-xi WANG,Chun-yang CAO. Research Advance and NMR Studies of Anti-Cancer Small Molecules Targeting c-MYC G4-DNA [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 503-513. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
